文章目录
- String类
- 字符串的遍历
- 字符串的比较
- 字符串的替换
- 字符串的转换
- 字符串的切割
- 字符串的切片
- 字符串的查找
- 总结
String类
在C语言中已经涉及到字符串了,但是在C语言中要表示字符串只能使用字符数组或者字符指针,可以使用标准库提
供的字符串系列函数完成大部分操作,但是这种将数据和操作数据方法分离开的方式不符合面向对象的思想,而字
符串应用又非常广泛,因此Java语言专门提供了String类。
String是一种不可变对象
在java.lang包里,不需要import手动导包,系统自动导好了
package java.lang;
字符串常量池:
字符串内容不可修改的原因
误区1:认为final修饰了String,被final修饰意味着不能被继承,并不是不能修改
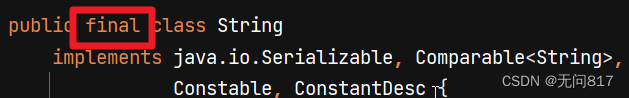
误区2:以为final修饰了value
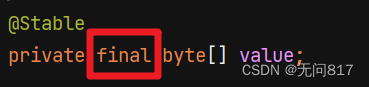
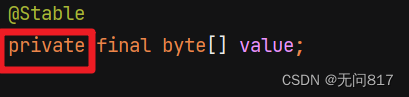
正确的答案是:
是因为value是由private修饰的,只能在本类中使用,所以不能修改value的值,只能创建新的字符串对象
字符串的创建
推荐使用直接赋值
new字符串对象需要在堆上开辟空间
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="hello world";
String str1=new String("hello world");
String str2=str1;
System.out.println(str+" "+str1);
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
内存图
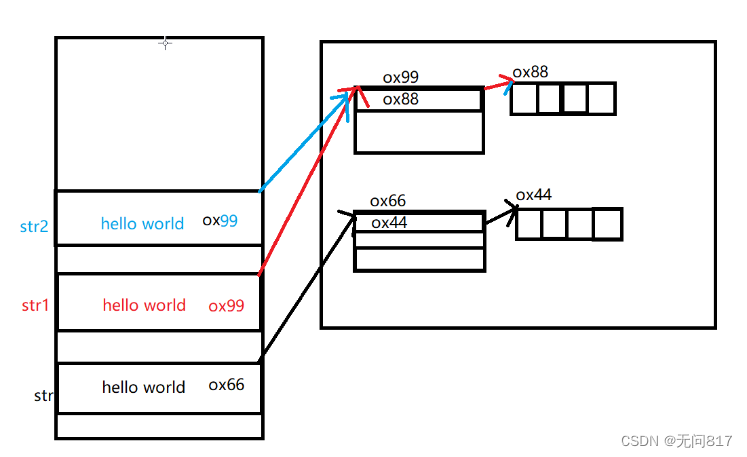
由于字符串不可修改,使用方法都是创建了新的对象,所以使用了方法需要用变量接收
字符串的遍历
通过length()方法
和charAt()获取字符串中的元素
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
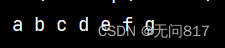
String s="abcdefg";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
System.out.print(s.charAt(i)+" ");
}
}
字符串的比较
==比较的是地址
通过.equals比较的是字符串的内容是否一致,返回的是boolean类型
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a="haha";
String b=new String("haha");
System.out.println(a==b);
System.out.println(a.equals(b));
}
输出结果是

a的地址是在堆中的字符串池里的,而b是new出来的在堆里的另一块地址,地址不一样,==比较的是地址故输出false;而equal是比较内容是否相同
引用类型不能直接比较大小
字符串的替换
替换单个字符
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abcdefg";
String replace = s.replace('a', 'v');
System.out.println(replace);
}
}


替换所有内容
public class demo1 {
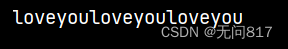
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1= "ayouayouayou";
String s2 = s1.replaceAll("a", "love");
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
替换出现的第一个内容
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1= "ayouayouayou";
String s2 = s1.replaceFirst("a", "love");
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
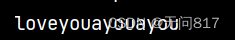
字符串的转换
- 大小写的转换
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1= "Sbfabfcsf";
String s = s1.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(s);
String s2 = s1.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s2);
}
}

- 字符串和数组的转换
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="ahfkfIH";
//字符串转数组
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
System.out.print(chars[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//数组转字符串
String str2=new String(chars);
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
- 数值和字符串的转换
数值转字符串
各种类型都可以转换成字符串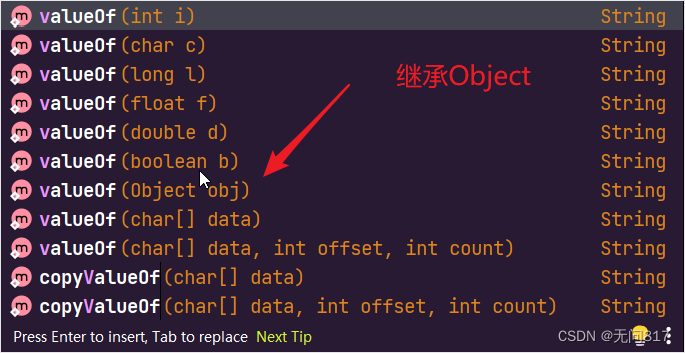
valueOf是于Object类的,在调用时需要用类名去调用
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str=String.valueOf(113);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
字符串转数字
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "123";
int i = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "123.21";
double i = Double.parseDouble(str);
System.out.println(i);
}
}


字符串的切割
一个是从起始位置截到末尾
一个是在指定范围内切割

示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="ahhfbg";
String str1 = str.substring(2);
System.out.println(str1);
String str2 = str.substring(2, 4);
System.out.println(str2);
}

字符串的切片
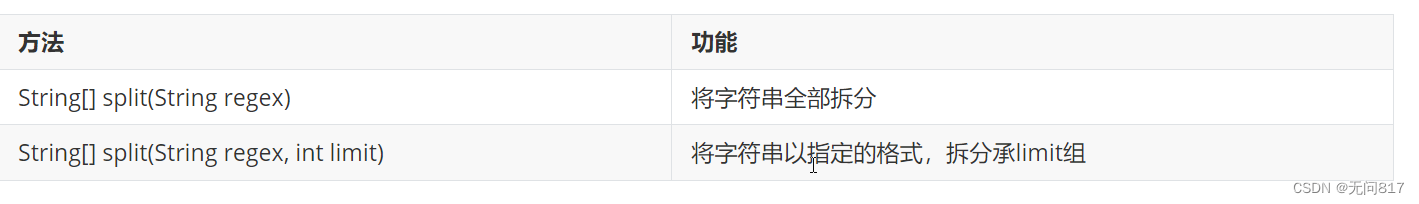
演示:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/manage/article?spm=1011.2266.3001.5448" ;
String[] result = str.split("/") ;
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
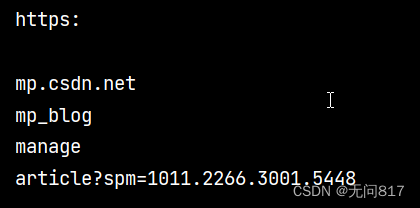
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "https:/hhhh/mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/manage/article?spm=1011.2266.3001.5448" ;
String[] result = str.split("/",3) ;
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
注意:
- 字符"|" ,“*”,“+“都得加上转义字符,前面加上”\\”.
- 而如果是"\“,那么就得写成”\\\\".
- 如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用"|"作为连字符.
字符串的查找
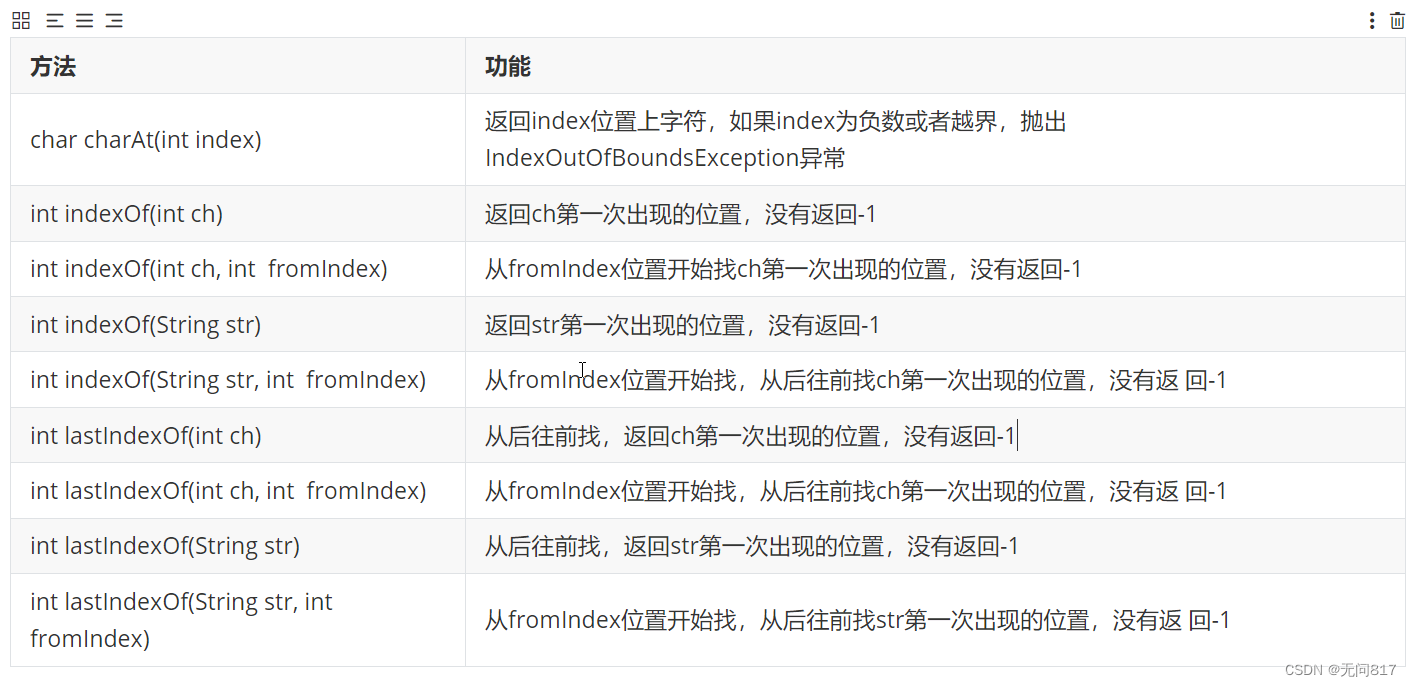
重点掌握charAt()
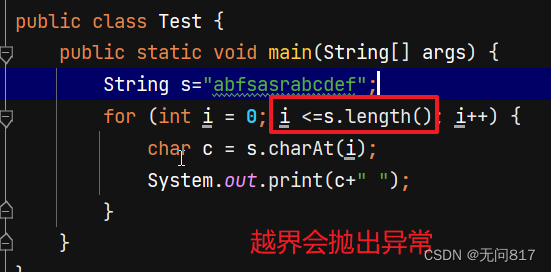

如何处理异常我们下篇博客介绍!
方法演示:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="abfsasrabcdef";
System.out.println(s.charAt(5));//s
System.out.println(s.indexOf('a'));//0
System.out.println(s.indexOf('a',3));//4
System.out.println(s.indexOf("sa"));//3
System.out.println(s.indexOf("sa",4));//-1
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('a'));//7
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('a',5));//4
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("ab"));//7
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("b",8));//8
}
}
总结
相信你看完已经对String类有了一定的理解,继续学习下去吧!