【List】判断集合相等、集合拷贝
- 【一】判断集合是否相等
- 【1】☆使用list中的containAll
- 【2】使用for循环遍历+contains方法
- 【3】将list先排序再转为String进行比较
- 【4】使用list.retainAll()方法
- 【5】使用MD5加密方式
- 【6】转换为Java8中的新特性steam流再进行排序来进行比较
- 【二】准备一个判断集合是否相等的工具类
- 【三】List的深拷贝和浅拷贝
- 【1】什么是浅拷贝(Shallow Copy)和深拷贝(Deep Copy)?
- 【2】浅拷贝
- 【3】深拷贝
- 【4】对象如何实现深拷贝?
- 【四】List如何实现复制
- 【1】浅拷贝
- 【1】循环遍历复制(含测试方法)
- 【2】使用 List 实现类的构造方法
- 【3】使用 list.addAll() 方法
- 【4】使用 java.util.Collections.copy() 方法
- 【5】使用 Java 8 Stream API 将 List 复制到另一个 List 中
- 【6】在 JDK 10 中的使用方式
- 【2】深拷贝
【一】判断集合是否相等
【1】☆使用list中的containAll
此方法是判断list2是否是list的子集,即list2包含于list
//方法一:使用list中的containsAll方法,此方法是判断list2是否是list的子集,即list2包含于list
public static void compareByContainsAll(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size()==list2.size()){
if (list.containsAll(list2)){
flag = true;
}
}
System.out.println("方法一:"+flag);
}
【2】使用for循环遍历+contains方法
//方法二:使用for循环遍历+contains方法
public static void compareByFor(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size()==list2.size()){
for (String str :list){
if (!list2.contains(str)){
System.out.println(flag);
return;
}
}
flag = true;
}
System.out.println("方法二:"+flag);
}
【3】将list先排序再转为String进行比较
(此方法由于涉及同集合内的排序,因此需要该集合内数据类型一致)
//方法三:将list先排序再转为String进行比较(此方法由于涉及同集合内的排序,因此需要该集合内数据类型一致)
public static void compareByString(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size()==list2.size()){
//使用外部比较器Comparator进行排序,并利用Java8中新添加的特性方法引用来简化代码
list.sort(Comparator.comparing(String::hashCode));
//使用集合的sort方法对集合进行排序,本质是将集合转数组,再使用比较器进行排序
Collections.sort(list2);
if (list.toString().equals(list2.toString())){
flag = true;
}
}
System.out.println("方法三:"+flag);
}
如果涉及到引用数据的排序比如里面的一个个对象数据,则需要实现Comparable接口,并重写CompareTo方法,在此方法中指定排序原则
package com.example.demo.utils;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author zhangqianwei
* @date 2021/9/7 17:25
*/
@Data
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name, int age, String sex) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//按照年龄排序
int result=this.getAge()-o.getAge();
return result;
}
}
//如果涉及到引用数据的排序比如里面的一个个对象数据,则需要实现Comparable接口,并重写CompareTo方法,在此方法中指定排序原则
public static void compareBySort(){
ArrayList<Student> stus=new ArrayList<Student>();
Student stu1=new Student(1,"张三",23,"男");
Student stu2=new Student(2,"李四",21,"女");
Student stu3=new Student(3,"王五",22,"女");
Student stu4=new Student(4,"赵六",22,"女");
stus.add(0,stu1);
stus.add(1,stu2);
stus.add(2,stu3);
stus.add(3,stu4);
System.out.println("原始顺序:"+stus);
Collections.sort(stus);
System.out.println("排序后:"+stus);
}
【4】使用list.retainAll()方法
如果集合list2中的元素都在集合list中则list2中的元素不做移除操作,反之如果只要有一个不在list中则会进行移除操作。即:list进行移除操作返回值为:true反之返回值则为false。
//方法四:使用list.retainAll()方法,此方法本质上是判断list是否有移除操作,如果list2是list的子集则不进行移除返回false,否则返回true
//如果集合list2中的元素都在集合list中则list2中的元素不做移除操作,反之如果只要有一个不在list中则会进行移除操作。即:list进行移除操作返回值为:true反之返回值则为false。
public static void compareByRetainAll(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size()==list2.size()){
if (!list.retainAll(list2)){
flag = true;
}
System.out.println("方法四:"+flag);
}
}
【5】使用MD5加密方式
使用MD5加密方式判断是否相同,这也算是list转String的一个变化,将元素根据加密规则转换为String加密字符串具有唯一性故可以进行判断;
根据唯一性可以想到map中的key也是具有唯一性的,将list中的元素逐个添加进map中作为key然后遍历比较list2中的元素是否都存在其中,不过这个要求list中的元素不重复
【6】转换为Java8中的新特性steam流再进行排序来进行比较
public static void compareBySteam(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size() == list2.size()){
String steam = list.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.joining());
String steam2 = (String) list2.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.joining());
if (steam.equals(steam2)){
flag = true;
}
}
System.out.println("方法六:"+flag);
}
【二】准备一个判断集合是否相等的工具类
静态方法,全局调用
package com.example.demo.utils;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @author zhangqianwei
* @date 2021/10/8 11:46
*/
public class compareList {
//比较两个集合是否相同
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("南京");
list.add("苏州");
list.add("常州");
List list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add("常州");
list2.add("苏州");
list2.add("南京");
compareByContainsAll(list,list2);
compareByFor(list,list2);
compareByString(list,list2);
compareBySort();
compareByRetainAll(list,list2);
compareBySteam(list,list2);
}
//方法一:使用list中的containsAll方法,此方法是判断list2是否是list的子集,即list2包含于list
public static void compareByContainsAll(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size()==list2.size()){
if (list.containsAll(list2)){
flag = true;
}
}
System.out.println("方法一:"+flag);
}
//方法二:使用for循环遍历+contains方法
public static void compareByFor(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size()==list2.size()){
for (String str :list){
if (!list2.contains(str)){
System.out.println(flag);
return;
}
}
flag = true;
}
System.out.println("方法二:"+flag);
}
//方法三:将list先排序再转为String进行比较(此方法由于涉及同集合内的排序,因此需要该集合内数据类型一致)
public static void compareByString(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size()==list2.size()){
//使用外部比较器Comparator进行排序,并利用Java8中新添加的特性方法引用来简化代码
list.sort(Comparator.comparing(String::hashCode));
//使用集合的sort方法对集合进行排序,本质是将集合转数组,再使用比较器进行排序
Collections.sort(list2);
if (list.toString().equals(list2.toString())){
flag = true;
}
}
System.out.println("方法三:"+flag);
}
//如果涉及到引用数据的排序比如里面的一个个对象数据,则需要实现Comparable接口,并重写CompareTo方法,在此方法中指定排序原则
public static void compareBySort(){
ArrayList<Student> stus=new ArrayList<Student>();
Student stu1=new Student(1,"张三",23,"男");
Student stu2=new Student(2,"李四",21,"女");
Student stu3=new Student(3,"王五",22,"女");
Student stu4=new Student(4,"赵六",22,"女");
stus.add(0,stu1);
stus.add(1,stu2);
stus.add(2,stu3);
stus.add(3,stu4);
System.out.println("原始顺序:"+stus);
Collections.sort(stus);
System.out.println("排序后:"+stus);
}
//方法四:使用list.retainAll()方法,此方法本质上是判断list是否有移除操作,如果list2是list的子集则不进行移除返回false,否则返回true
//如果集合list2中的元素都在集合list中则list2中的元素不做移除操作,反之如果只要有一个不在list中则会进行移除操作。即:list进行移除操作返回值为:true反之返回值则为false。
public static void compareByRetainAll(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size()==list2.size()){
if (!list.retainAll(list2)){
flag = true;
}
System.out.println("方法四:"+flag);
}
}
//方法五:使用MD5加密方式判断是否相同,这也算是list转String的一个变化,将元素根据加密规则转换为String加密字符串具有唯一性故可以进行判断
//根据唯一性可以想到map中的key也是具有唯一性的,将list中的元素逐个添加进map中作为key然后遍历比较list2中的元素是否都存在其中,不过这个要求list中的元素不重复
//方法六:转换为Java8中的新特性steam流再进行排序来进行比较
public static void compareBySteam(List<String> list,List list2){
boolean flag = false;
if (list.size() == list2.size()){
String steam = list.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.joining());
String steam2 = (String) list2.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.joining());
if (steam.equals(steam2)){
flag = true;
}
}
System.out.println("方法六:"+flag);
}
}
【三】List的深拷贝和浅拷贝
【1】什么是浅拷贝(Shallow Copy)和深拷贝(Deep Copy)?
浅拷贝只复制某个对象的引用,而不复制对象本身,新旧对象还是共享同一块内存。深拷贝会创造一个一模一样的对象,新对象和原对象不共享内存,修改新对象不会改变原对象。
假设 B 复制了 A,当修改 A 时,看 B 是否会发生变化。如果 B 也跟着变了,说明这是浅拷贝,如果 B 没变,那就是深拷贝。
【2】浅拷贝
对于数据类型是基本数据类型(整型:byte、short、int、long;字符型:char;浮点型:float、double;布尔型:boolean)的成员变量,浅拷贝会直接进行值传递,也就是将该属性值复制一份给新的对象。因为是两份不同的数据,所以对其中一个对象的该成员变量值进行修改,不会影响另一个对象拷贝得到的数据。
对于数据类型是引用数据类型(比如说成员变量是某个数组、某个类的对象等)的成员变量,浅拷贝会进行引用传递,也就是只是将该成员变量的引用值(内存地址)复制一份给新的对象。因为实际上两个对象的该成员变量都指向同一个实例,在这种情况下,在一个对象中修改该成员变量会影响到另一个对象的该成员变量值。
【3】深拷贝
相对于浅拷贝而言,深拷贝对于引用类型的修改,并不会影响到对应的拷贝对象的值。
备注:一般在讨论深拷贝和浅拷贝时,通常是针对引用数据类型而言的。因为基本数据类型在进行赋值操作时(也就是拷贝)是直接将值赋给了新的变量,也就是该变量是原变量的一个副本,这个时候你修改两者中的任何一个的值都不会影响另一个。而对于引用数据类型来说,在进行浅拷贝时,只是将对象的引用复制了一份,也就是内存地址,即两个不同的变量指向了同一个内存地址,那么改变任一个变量的值,都是改变这个内存地址所存储的值,所以两个变量的值都会改变。
Java 对对象和基本数据类型的处理是不一样的。在 Java 中,用对象作为入口参数传递时,缺省为 “引用传递”,也就是说仅仅传递了对象的一个”引用”。当方法体对输入变量修改时,实质上就是直接操作这个对象。 除了在函数传值的时候是”引用传递”,在任何用 ”=” 向对象变量赋值的时候都是”引用传递”。
将对象序列化为字节序列后,再通过反序列化即可完美地实现深拷贝。
【4】对象如何实现深拷贝?
Object 对象声明了 clone() 方法,如下代码所示。
/**
* Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning
* of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general
* intent is that, for any object {@code x}, the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone() != x</pre></blockquote>
* will be true, and that the expression:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, but these are not absolute requirements.
* While it is typically the case that:
* <blockquote>
* <pre>
* x.clone().equals(x)</pre></blockquote>
* will be {@code true}, this is not an absolute requirement.
* <p>
* By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling
* {@code super.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except
* {@code Object}) obey this convention, it will be the case that
* {@code x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}.
* <p>
* By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent
* of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence,
* it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned
* by {@code super.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means
* copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure"
* of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these
* objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only
* primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually
* the case that no fields in the object returned by {@code super.clone}
* need to be modified.
* <p>
* The method {@code clone} for class {@code Object} performs a
* specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does
* not implement the interface {@code Cloneable}, then a
* {@code CloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays
* are considered to implement the interface {@code Cloneable} and that
* the return type of the {@code clone} method of an array type {@code T[]}
* is {@code T[]} where T is any reference or primitive type.
* Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this
* object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of
* the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the
* contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method
* performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.
* <p>
* The class {@code Object} does not itself implement the interface
* {@code Cloneable}, so calling the {@code clone} method on an object
* whose class is {@code Object} will result in throwing an
* exception at run time.
*
* @return a clone of this instance.
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not
* support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses
* that override the {@code clone} method can also
* throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot
* be cloned.
* @see java.lang.Cloneable
*/
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
Object 的 clone() 方法本身是一个浅拷贝的方法,但是我们可以通过实现 Cloneable 接口,重写该方法来实现深拷贝,除了调用父类中的 clone() 方法得到新的对象, 还要将该类中的引用变量也 clone 出来。如果只是用 Object 中默认的 clone() 方法,是浅拷贝的。
如下代码所示,我们创建一个测试类 TestClone,实现深拷贝。
package com.example.test;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
@Data
public class TestClone implements Cloneable {
private String a;
// 构造函数
TestClone(String str) {
this.a = str;
}
@Override
protected TestClone clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
TestClone newTestClone = (TestClone) super.clone();
newTestClone.setA(this.a);
return newTestClone;
}
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestClone clone1 = new TestClone("a");
TestClone clone2 = clone1.clone();
System.out.println(clone2.a); // a
clone2.setA("b");
System.out.println(clone1.a); // a
System.out.println(clone2.a); // b
}
}
【四】List如何实现复制
List 复制时有深拷贝和浅拷贝两类方式,分述如下。
【1】浅拷贝
List 其本质就是数组,而其存储的形式是地址,如下图所示。

将 listA 列表浅拷贝为 listB 时,listA 与 listB 指向同一地址,造成的后果就是,改变 listB 的同时也会改变 listA,因为改变listB 就是改变 listB 所指向的地址的内容,由于 listA 也指向同一地址,所以 listA 与 listB 一起改变。其常见的实现方式有如下几种(以上述代码中的 TestClone 为测试类)。
【1】循环遍历复制(含测试方法)
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<TestClone> listA = new ArrayList<>();
TestClone testClone = new TestClone("a");
listA.add(testClone);
System.out.println(listA); // [TestClone(a=a)]
List<TestClone> listB = new ArrayList<>(listA.size());
for (TestClone clone : listA) {
listB.add(clone);
}
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone(a=a)]
listA.get(0).setA("b");
System.out.println(listA); // [TestClone(a=b)]
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone(a=b)]
}
【2】使用 List 实现类的构造方法
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<TestClone> listA = new ArrayList<>();
TestClone testClone = new TestClone("a");
listA.add(testClone);
List<TestClone> listB = new ArrayList<>(listA);
}
【3】使用 list.addAll() 方法
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<TestClone> listA = new ArrayList<>();
TestClone testClone = new TestClone("a");
listA.add(testClone);
List<TestClone> listB = new ArrayList<>();
listB.addAll(listA);
}
【4】使用 java.util.Collections.copy() 方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<TestClone> listA = new ArrayList<>();
TestClone clone = new TestClone("a");
listA.add(clone);
List<TestClone> listB = new ArrayList<>();
listB.add(new TestClone("c"));
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone(a=c)]
Collections.copy(listB, listA);
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone(a=a)]
listA.get(0).setA("b");
System.out.println(listA); // [TestClone(a=b)]
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone(a=b)]
}
【5】使用 Java 8 Stream API 将 List 复制到另一个 List 中
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<TestClone> listA = new ArrayList<>();
TestClone clone = new TestClone("a");
listA.add(clone);
List<TestClone> listB = listA.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone(a=a)]
listA.get(0).setA("b");
System.out.println(listA); // [TestClone(a=b)]
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone(a=b)]
}
【6】在 JDK 10 中的使用方式
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<TestClone> listA = new ArrayList<>();
TestClone clone = new TestClone("a");
listA.add(clone);
List<TestClone> listB = List.copyOf(listA);
listA.get(0).setA("b");
System.out.println(listA); // [TestClone@76ed5528]
System.out.println(listA.get(0).getA()); // b
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone@76ed5528]
System.out.println(listB.get(0).getA()); // b
}
【2】深拷贝
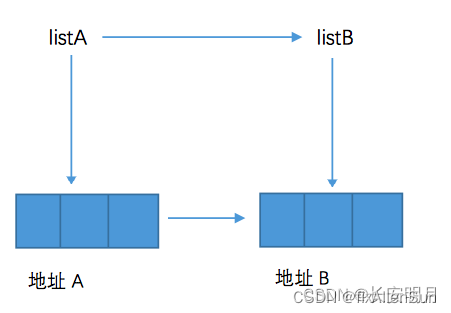
如图,深拷贝就是将 listA 复制给 listB 的同时,给 listB 创建新的地址,再将地址 A 的内容传递到地址 B。listA 与 listB 内容一致,但是由于所指向的地址不同,所以各自改变内容不会影响对方。深拷贝时,向新列表添加的是原列表中的元素执行 clone() 方法后的新对象。
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<TestClone> listA = new ArrayList<>();
TestClone testClone = new TestClone("a");
listA.add(testClone);
List<TestClone> listB = new ArrayList<>();
listB.add(listA.get(0).clone());
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone(a=a)]
listA.get(0).setA("b");
System.out.println(listA); // [TestClone(a=b)]
System.out.println(listB); // [TestClone(a=a)]
}