官方定义:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#spring-core
Using the @ImportAnnotation
Much as the <import/> element is used within Spring XML files to aid in modularizing
configurations, the @Import annotation allows for loading @Bean definitions from another
configuration class, as the following example shows:
@Import注解的作用与Spring的XML配置文件中的<import/>元素一样:都是用于帮助建立模块化配置,@Import可以从其他配置类中加载 @Bean的定义,如下所示:
@Configuration
public class ConfigA {
@Bean
public A a() {
return new A();
}
}
@Configuration
@Import(ConfigA.class)
public class ConfigB {
@Bean
public B b() {
return new B();
}
}
Now, rather than needing to specify both ConfigA.class and ConfigB.class when instantiating the
context, only ConfigB needs to be supplied explicitly, as the following example shows:
如上代码,在类ConfigB中添加了注解 @Import(ConfigA.class) ,那么,在初始化上下文(如下所示)时就不需要同时指定类 ConfigA.class 和 类ConfigB.class 了,只需要显示的指定类 ConfigB即可,下面是例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigB.class);
// now both beans A and B will be available...
A a = ctx.getBean(A.class);
B b = ctx.getBean(B.class);
}
如上,初始化上下文ctx时只需要使用ConfigB,同样可以通过 ctx.getBean(A.class)获取在ConfigA中配置的A实例(bean)
This approach simplifies container instantiation, as only one class
needs to be dealt with, rather than requiring you to remember a
potentially large number of @Configuration classes during construction.
这种方法简化了容器的初始化,在初始化构造时,只需要处理一个类,而不必记住潜在的大量的@Configuration配置类。
小结: 以上是针对通过:
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConfigB.class);
这种方式获取bean实例时
A a = ctx.getBean(A.class);
B b = ctx.getBean(B.class);
通过@Import注解时,可以简化容器的初始化!
但是,如果直接通过@Autowired注入的方式获取容器中的bean,@Import还有用武之地吗?
因为只要容器中有对应的bean存在,@Autowired就会将其注入过来!既然这样,那@Import似乎没有什么作用了!, 如下示例:
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
public class Pen {
private String name = "this is apple!";
public Pen () {
System.out.println("+++constructing pen object+++");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class Eraser {
@Bean
public Pen genPenBean() {
return new Pen();
}
}
以上代码,在容器启动时会初始化一个Pen对象/实例/bean
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
public class Apple {
private String name = "this is apple!";
public Apple() {
System.out.println("***constructing Apple object***");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class Tree {
@Bean
public Apple genAppleBean() {
return new Apple();
}
}
以上代码,在容器启动时会初始化一个Apple对象/实例/bean
编写测试类:
通过@Autowired直接获取想要的bean
package com.xl.test.logtest.controller;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Apple;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Pen;
@RestController
public class LogTestController {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogTestController.class);
@Autowired
Pen pen;
@Autowired
Apple apple;
@GetMapping("/log")
public String log() {
Assert.notNull(pen, "对象为空!");
Assert.notNull(apple, "对象为空!");
return "pen : "+ pen.getName()+ " ; apple: "+apple.getName();
}
}
启动项目:完成bean的创建
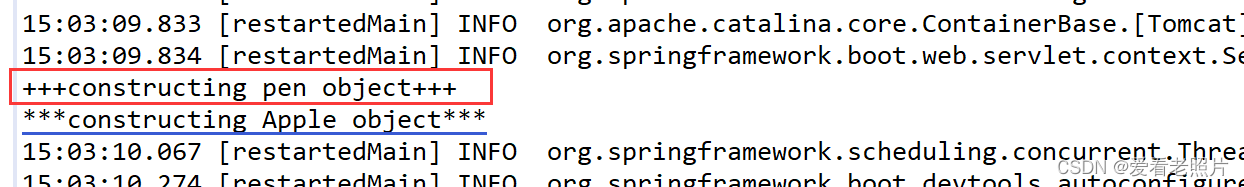
浏览器访问,验证:
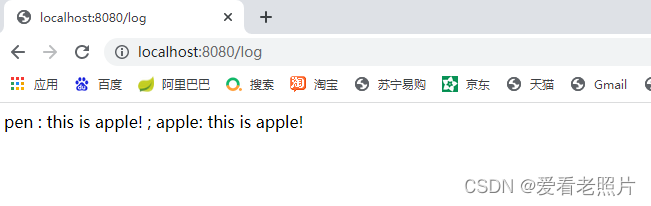
断言Assert 并没有抛出异常信息,说明pen和apple对象都不为null,同时浏览器也输出了pen和apple的名字。
给类Eraser加上@Import(Tree.class)或者给类Tree加上@Import(Eraser.class),项目运行情况和测试结果没有任何变化!@Import注解没有起作用!验证略。
实际上,针对@Autowired注解的场景不是没有用,而是@Import是有它特定的使用场景的:@Import可以引入外部的bean。
何为外部的bean??
外部bean指的是:Spring容器启动时不会自动扫描的类并生成的bean。
Spring容器启动时会去扫描哪些类? : 主启动类所在包及子包下面的带有@Component注解的类!
而@Import注解就是用于引入外部的bean的, 示例如下:
在外部新建一个类Paper,如下:
package com.other.pkg;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Color;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Picture;
@Configuration
public class Paper {
@Bean
public Color getColorBean() {
System.out.println("********************color bean init********************");
return new Color();
}
@Bean
public Picture getPictureBean() {
System.out.println("********************picture bean init********************");
return new Picture();
}
}
在不使用@Import注解时,在测试类中注入外部类Paper中的bean :
package com.xl.test.logtest.controller;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.other.pkg.Paper;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Apple;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Color;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Pen;
import com.xl.test.logtest.utils.Picture;
@RestController
public class LogTestController {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogTestController.class);
@Autowired
Paper paper;
@Autowired
Color color;
@Autowired
Picture picture;
@GetMapping("/log")
public String log() {
return "paper : "+ paper+ " ; color: "+color.getName()+" ; picture: "+picture.getSize();
}
}
启动项目,观察:
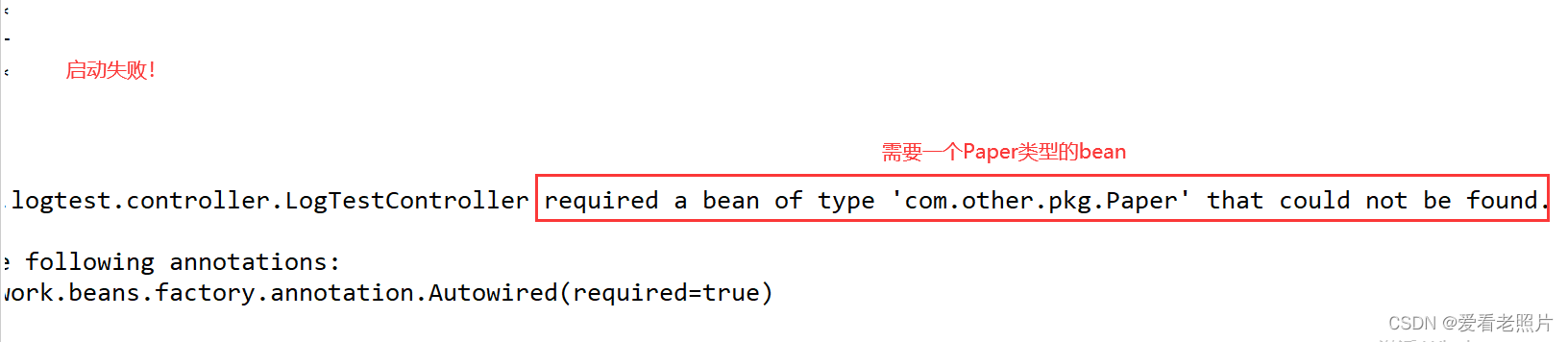
在主启动类的包或子包下新建一个带@Component的类,同时,加上@Import注解:
package com.xl.test.logtest.utils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.other.pkg.Paper;
@Import(Paper.class)
@Component
public class ForImport {
}
启动项目,测试:
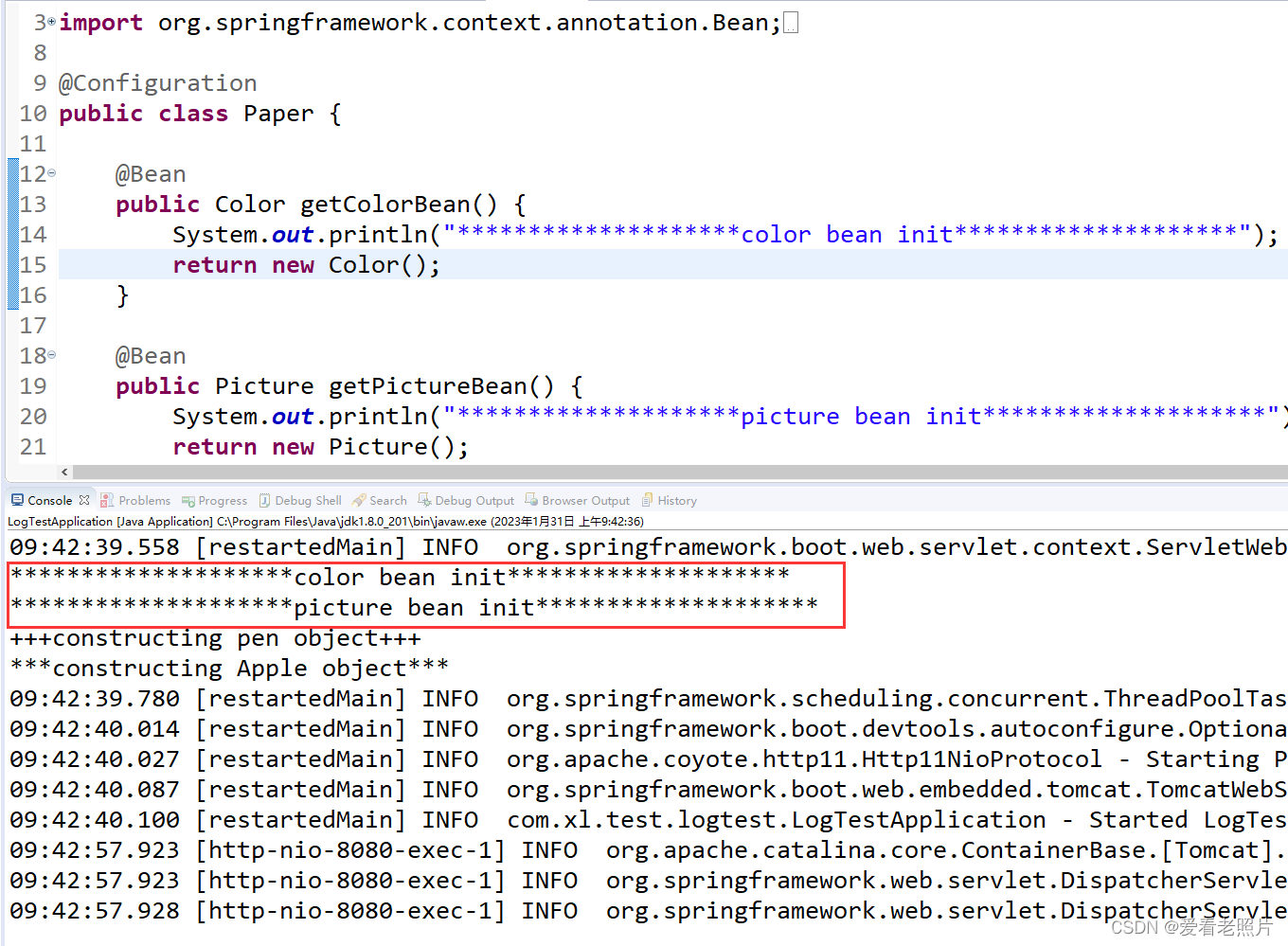
如上所示,项目启动成功,并完成外部类中相关bean的初始化; 访问项目再次测试:
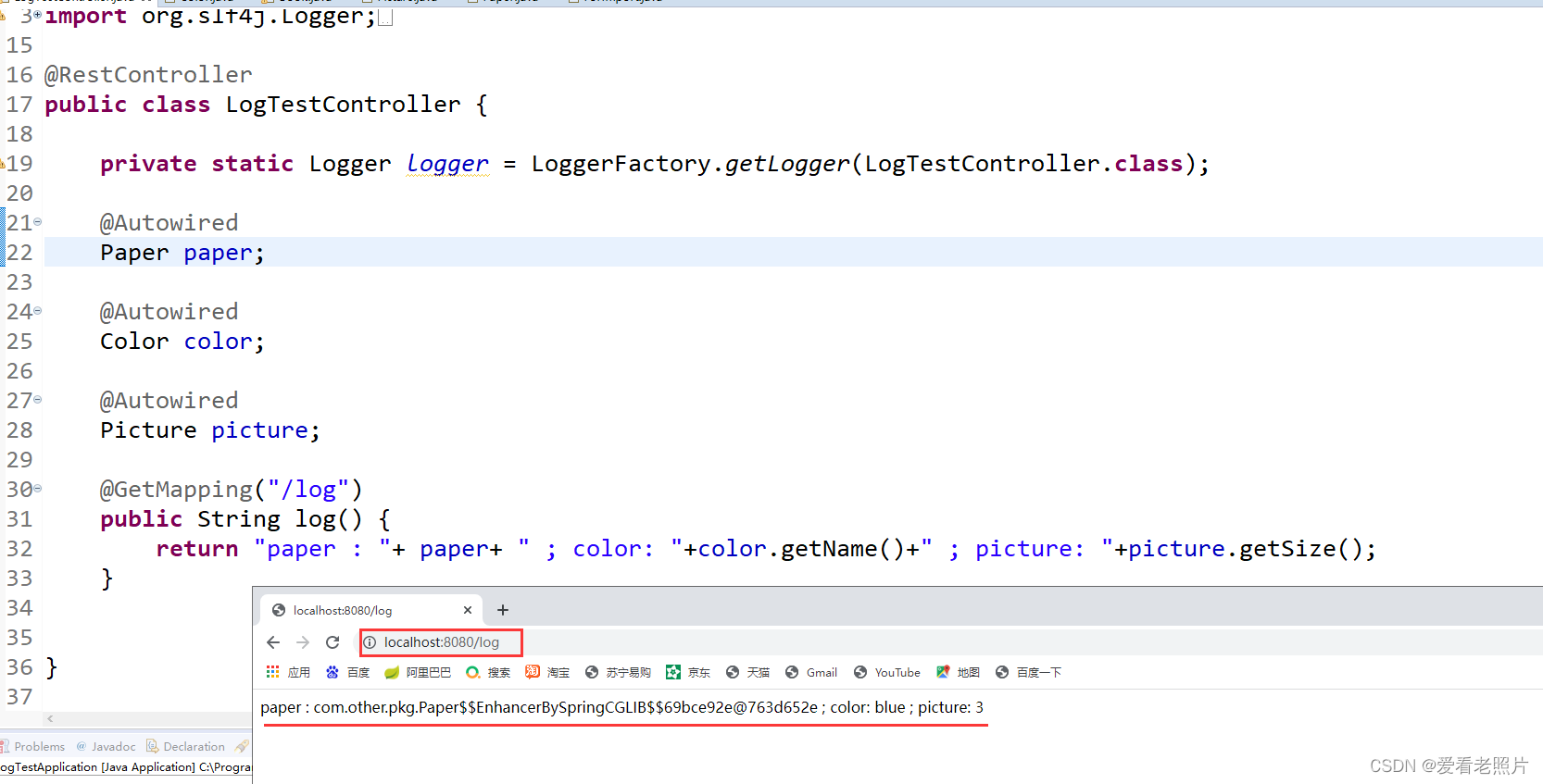
同样,获取到了外部类中的bean。