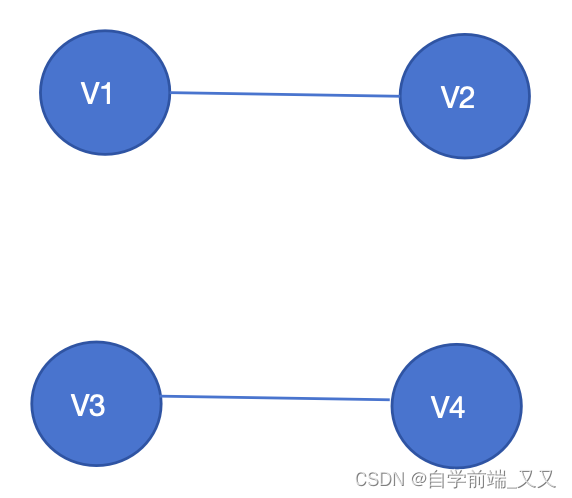
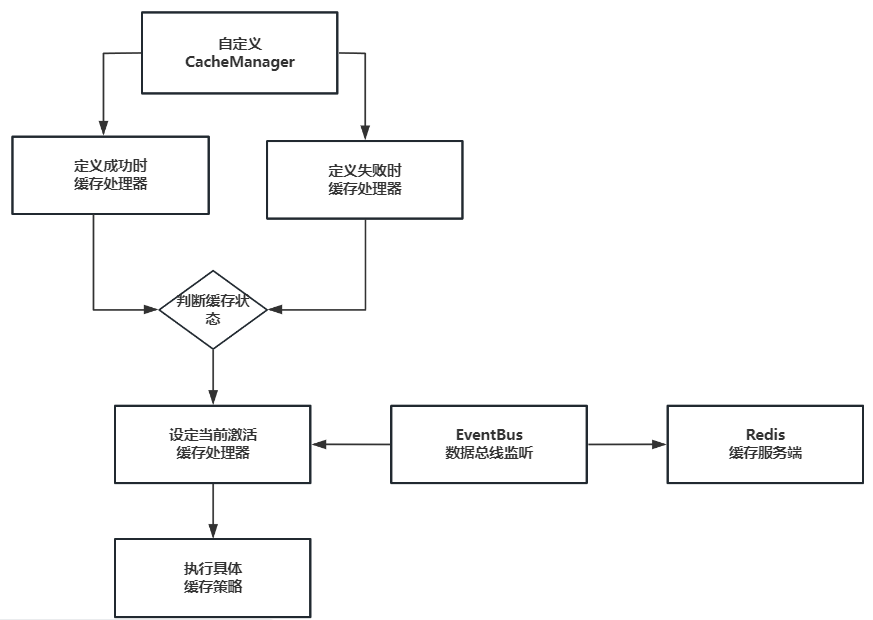
2的信号量集就是semaphore


这个图很重要!!!

无名管道:
练习一:读操作
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipefd[2]={0};
int ret = pipe(pipefd);
if(-1 == ret)
{
perror("pipe");
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)
{
char buf[]="hello,world";
close(pipefd[0]);
sleep(3);
write(pipefd[1],buf,strlen(buf));
}
else if(0 == pid)
{
close(pipefd[1]);
char buf[100]={0};
read(pipefd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("pipe %s\n",buf);
}
else
{
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
结果为:

练习:写操作
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipefd[2]={0};
int ret = pipe(pipefd);
if(-1 == ret)
{
perror("pipe");
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)
{
char buf[1024]={0};
close(pipefd[0]);
memset(buf,'a',1024);
int i = 0 ;
for(i=0;i<65;i++)
{
write(pipefd[1],buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("i is %d\n",i);
}
}
else if(0 == pid)
{
close(pipefd[1]);
char buf[100]={0};
// read(pipefd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));
// printf("pipe %s\n",buf);
while(1)sleep(1);
}
else
{
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}结果为:

练习3:broken操作(管道破裂)
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipefd[2]={0};
int ret = pipe(pipefd);
if(-1 == ret)
{
perror("pipe");
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)
{
char buf[]="hello,world";
close(pipefd[0]);
sleep(3);
// 管道破裂 gdb 跟踪
write(pipefd[1],buf,strlen(buf));
printf("aaaa\n");
}
else if(0 == pid)
{
close(pipefd[1]);
close(pipefd[0]);
}
else
{
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}结果如下:

练习4:end操作
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipefd[2]={0};
int ret = pipe(pipefd);
if(-1 == ret)
{
perror("pipe");
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)
{
char buf[]="hello,world";
close(pipefd[0]);
write(pipefd[1],buf,strlen(buf));
write(pipefd[1],buf,strlen(buf));
close(pipefd[1]);
}
else if(0 == pid)
{
close(pipefd[1]);
char buf[5]={0};
while(1)
{
//memset(buf,0,5);
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));
int rd_ret = read(pipefd[0],buf,sizeof(buf)-1);
if(rd_ret<=0)
{
break;
}
printf("pipe %s\n",buf);
}
}
else
{
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}结果为:

练习5:cp操作,父进程与子进程,把父进程的内容cp到子进程里面

代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipefd[2]={0};
int ret = pipe(pipefd);
if(-1 == ret)
{
perror("pipe");
exit(1);
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid>0)
{
close(pipefd[0]);
int fd = open("/home/linux/1.png",O_RDONLY);
if(-1 == fd)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
while(1)
{
char buf[4096]={0};
int rd_ret = read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(rd_ret<=0)
{
break;
}
write(pipefd[1],buf,rd_ret);
}
close(fd);
close(pipefd[1]);
}
else if(0 == pid)
{
close(pipefd[1]);
int fd = open("2.png",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666);
if(-1==fd)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
while(1)
{
char buf[1024]={0};
int rd_ret = read(pipefd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));
if(rd_ret<=0)
{
break;
}
write(fd,buf,rd_ret);
}
close(fd);
close(pipefd[0]);
}
else
{
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}结果就是把1.png复制出了一个新的2.png(图片里面包含的是一些二进制的数字,所以要用文件IO,而且为了避免遇到0,不要使用strlen,因为strlen遇到0就不继续往后读了,所以要用sizeof)


有名管道:
练习1:写操作
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret = mkfifo("myfifo",0666);
if(-1 == ret)
{
//如果是管道文件已存在错误,让程序继续运行
if(EEXIST== errno)
{
}else
{
perror("mkfifo");
exit(1);
}
}
//open 会阻塞,等到另一端读段打开,解除阻塞
int fd = open("myfifo",O_WRONLY);
if(-1 == fd)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
char buf[256]="hello,fifo,test";
write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));
close(fd);
return 0;
}
练习2:读操作
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret = mkfifo("myfifo",0666);
if(-1 == ret)
{
//如果是管道文件已存在错误,让程序继续运行
if(EEXIST== errno)
{
}else
{
perror("mkfifo");
exit(1);
}
}
int fd = open("myfifo",O_RDONLY);
if(-1 == fd)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
char buf[256]={0};
read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("fifo %s\n",buf);
close(fd);
//remove("myfifo");
return 0;
}