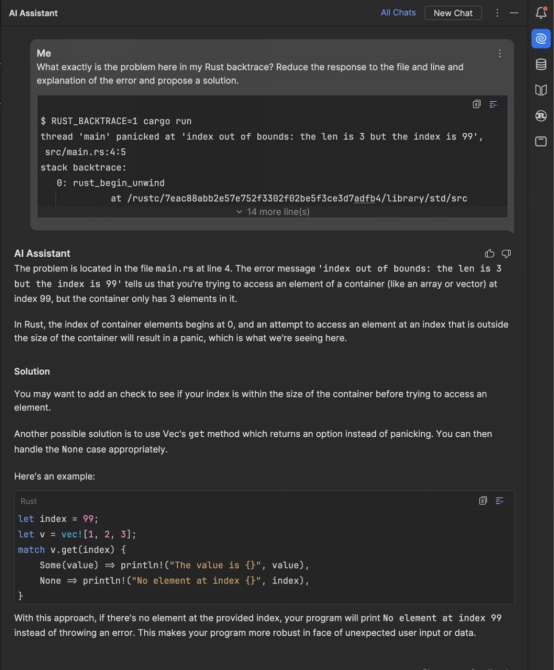
2.2主要内容
比较快速排序,归并排序以及堆排序算法的时间效率。了解影响算法执行时间的 主要因素以及如何降低算法的执行时间。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include"string.h"
#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
typedef struct RedType {
int key;
}RedType;
typedef struct SqList {
RedType* r;
int Length;
}SqList;
SqList* CreateRandomSqList(int sqListLen) {
SqList* sq;
int i;
sq = (SqList*)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
//输入序列长度
sq->Length = sqListLen;
sq->r = (RedType*)malloc(sizeof(RedType) * (sq->Length + 1)); //给序列的每个元素分配空间
srand((unsigned)(time(NULL)));
for (i = 1; i <= sq->Length; i++) {
sq->r[i].key = int(rand());
}
return sq; //返回序列起始地址
}
//创建一个与csp一样的存储空间
SqList* CopyRandomSqList(SqList* csp) {
SqList* sq;
int i;
sq = (SqList*)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
//输入序列长度
sq->Length = csp->Length;
sq->r = (RedType*)malloc(sizeof(RedType) * (sq->Length + 1)); //给序列的每个元素分配空间
for (i = 1; i <= sq->Length; i++) {
sq->r[i].key = csp->r[i].key;
}
return sq; //返回序列起始地址
}
void WritetoFile(int num, int sortTime[], FILE* fp) {
char ch[20];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
_itoa_s(sortTime[i], ch, 10);
strcat_s(ch, ",");
fwrite(ch, sizeof(char), strlen(ch), fp);
}
fwrite("\n", sizeof(char), 1, fp);
}
//快速排序
void QuickSort(RedType q[], int l, int r) {
if (l >= r)return;
int i = l - 1, j = r + 1, x = q[l + r >> 1].key;
while (i < j) {
do i++; while (q[i].key < x);
do j--; while (q[j].key > x);
if (i < j)swap(q[i].key, q[j].key);
}
QuickSort(q, l, j);
QuickSort(q, j + 1, r);
}
//堆排序
void HeapAdjust(RedType* SR, int s, int m)//一次筛选的过程
{
int rc, j;
rc = SR[s].key;
for (j = 2 * s; j <= m; j = j * 2)//通过循环沿较大的孩子结点向下筛选
{
if (j < m&& SR[j].key < SR[j + 1].key) j++;//j为较大的记录的下标
if (rc > SR[j].key) break;
SR[s] = SR[j]; s = j;
}
SR[s].key = rc;//插入
}
void HeapSort(RedType* SR, int n)
{
int temp, i, j;
for (i = n / 2; i > 0; i--)//通过循环初始化顶堆
{
HeapAdjust(SR, i, n);
}
for (i = n; i > 0; i--)
{
temp = SR[1].key;
SR[1].key = SR[i].key;
SR[i].key = temp;//将堆顶记录与未排序的最后一个记录交换
HeapAdjust(SR, 1, i - 1);//重新调整为顶堆
}
}
//归并排序
void aMerge(RedType* SR, int i, int m, int n) {
int j, k;
for (j = m + 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (SR[j].key <= SR[j - 1].key) {
int temp = SR[i].key;
for (k = j - 1; temp < SR[k].key && k >= i; --k)
SR[k + 1].key = SR[k].key;
SR[k + 1].key = temp;
}
}
return;
}
void aMSort(RedType* SR, int s, int t)
{
if (s < t) {
int mid = (s + t) / 2;
aMSort(SR, s, mid);
aMSort(SR, mid + 1, t);
aMerge(SR, s, mid, t);
}
return;
}
void MergeSort(SqList* L) {
aMSort(L->r, 1, L->Length);
return;
}
int main() {
SqList* L, * L1, * L2;
struct __timeb64 stime, etime;
long int rmtime, rstime;
char ch[20];
int quickSortTime[105], mergeSortTime[105], heapSortTime[105];
FILE* fp;
fp = fopen("Curv.csv", "w");
for (int i = 10000; i <= 1000000; i = i + 10000) {
_itoa_s(i, ch, 10);
strcat_s(ch, ",");
fwrite(ch, sizeof(char), strlen(ch), fp);
}
fwrite("\n", sizeof(char), 1, fp);
int k = 0;
for (int i = 10000; i <= 1000000; i = i + 10000) {
L = CreateRandomSqList(i);
L1 = CopyRandomSqList(L);
L2 = CopyRandomSqList(L);
//归并排序
_ftime64_s(&stime);
MergeSort(L);
_ftime64_s(&etime);
free(L->r);
free(L);
rstime = etime.time - stime.time;
rmtime = rstime * 1000;
rmtime += etime.millitm - stime.millitm;
mergeSortTime[k] = rmtime;
//快速排序
_ftime64_s(&stime);
QuickSort(L1->r, 0, L1->Length - 1);
_ftime64_s(&etime);
free(L1->r);
free(L1);
rstime = etime.time - stime.time;
rmtime = rstime * 1000;
rmtime += etime.millitm - stime.millitm;
quickSortTime[k] = rmtime;
//堆排序
_ftime64_s(&stime);
HeapSort(L2->r, L2->Length - 1);
_ftime64_s(&etime);
free(L2->r);
free(L2);
rstime = etime.time - stime.time;
rmtime = rstime * 1000;
rmtime += etime.millitm - stime.millitm;
heapSortTime[k] = rmtime;
k++;
}
WritetoFile(100, mergeSortTime, fp);
WritetoFile(100, quickSortTime, fp);
WritetoFile(100, heapSortTime, fp);
fclose(fp);
return 1;
}
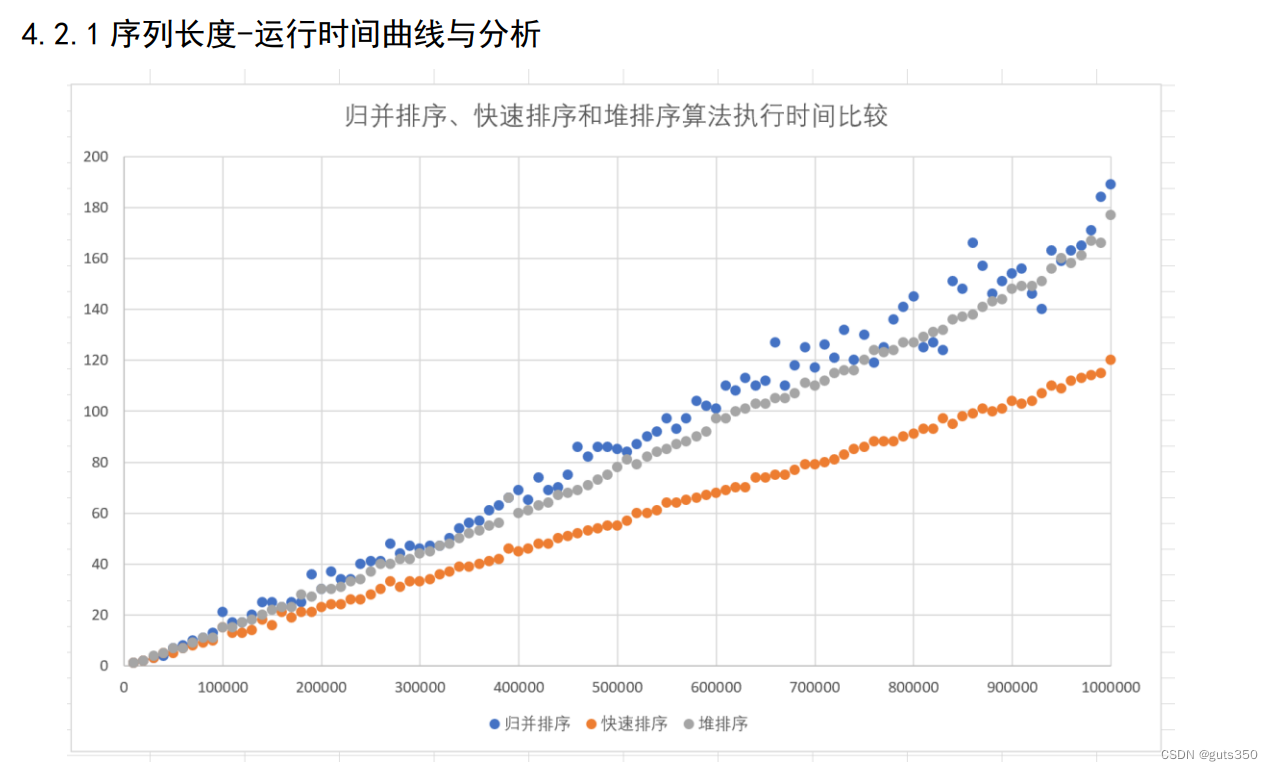
2.3主要内容
学习分析递归程序结构的时间复杂度和影响算法运行时间的因素。
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include"string.h"
#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
#define M 4
#define N 15
using namespace std;
class Color {
friend int mColoring(int, int, int**);
public:
bool Ok(int k);
void Backtrack(int k);
int n, m, ** a, * x;
long sum;
};
long long cifang(int n,int m)
{
int count = 0;long long c = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
c = c*(m/2);//防止时间复杂度太大了,进行缩小
count++;
}
return c;
}
void WritetoFile(int num, int sortTime[], FILE* fp) {
char ch[20];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
_itoa_s(sortTime[i], ch, 10);
strcat_s(ch, ",");
fwrite(ch, sizeof(char), strlen(ch), fp);
}
fwrite("\n", sizeof(char), 1, fp);
}
int mColoring(int, int, int**);
int main() {
int n, m, ** a, sum; long long timecom{ 0 };
//cout << "Please input the number of colors:";
//cin >> m;
struct __timeb64 stime, etime;
long int rmtime, rstime;
char ch[20];
int paintTime[105]{0};
FILE* fp;
fp = fopen("Curv.csv", "w");
for (int i = 5; i <= N; i = i + 1) {
_itoa_s(i, ch, 10);
strcat_s(ch, ",");
fwrite(ch, sizeof(char), strlen(ch), fp);
}
fwrite("\n", sizeof(char), 1, fp);
int k{ 0 };
/*for (int i = 5; i <= N; i = i + 1) {
//cout << "Please input the number of nodes:";
n=i;
a = new int* [n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = new int[n + 1];
}
//cout << "Please input the ralation of nodes:1-->Connected,0-->Not connected";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
//cout << "please input the ralation of" << i << "and" << j << ":";
//cin >> a[i][j];
//a[i][j] = 1;//完全图,最外面的i循环换成 i <= M,注意要改四处
a[i][j] = 0;//一条边都没有,最外面的i循环换成 i <= N
a[j][i] = a[i][j];
}
}
_ftime64_s(&stime);
sum = mColoring(n, M, a);
_ftime64_s(&etime);
rstime = etime.time - stime.time;
rmtime = rstime * 1000;
rmtime += etime.millitm - stime.millitm;
paintTime[k] = rmtime;
k++;
delete[]a;
}
WritetoFile(11, paintTime, fp);
for (int i = 5; i <= N; i = i + 1)
{
timecom = i * cifang(i,M);
_itoa_s(timecom, ch, 10);
strcat_s(ch, ",");
fwrite(ch, sizeof(char), strlen(ch), fp);
}
fwrite("\n", sizeof(char), 1, fp);*/
k = 0;
n = 10;
for (int j = 5; j <= N; j = j + 1) {
//cout << "Please input the number of nodes:";
m = j;
a = new int* [n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = new int[n + 1];
}
//cout << "Please input the ralation of nodes:1-->Connected,0-->Not connected";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
//cout << "please input the ralation of" << i << "and" << j << ":";
//cin >> a[i][j];
//a[i][j] = 1;//完全图,注意要改四处
a[i][j] = 0;//一条边都没有
a[j][i] = a[i][j];
}
}
_ftime64_s(&stime);
sum = mColoring(n, m, a);
_ftime64_s(&etime);
rstime = etime.time - stime.time;
rmtime = rstime * 1000;
rmtime += etime.millitm - stime.millitm;
paintTime[k] = rmtime;
k++;
delete[]a;
}
WritetoFile(11, paintTime, fp);
for (int i = 5; i <= N; i = i + 1)
{
timecom = n * cifang(n,i);
_itoa_s(timecom, ch, 10);
strcat_s(ch, ",");
fwrite(ch, sizeof(char), strlen(ch), fp);
}
fwrite("\n", sizeof(char), 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
//cout << sum << endl;
return 1;
}
bool Color::Ok(int k)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if ((a[k][j] == 1 && x[j] == x[k]))
return false;
return true;
}
void Color::Backtrack(int t) {
if (t > n) {
sum++;
/*for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << x[i] << " ";
cout << endl;*/
}
else {
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
x[t] = i;
if (Ok(t))Backtrack(t + 1);
x[t] = 0;
}
}
}
int mColoring(int n, int m, int** a) {
Color X;
X.n = n;
X.m = m;
X.a = a;
X.sum = 0;
int* p = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)p[i] = 0;
X.x = p;
X.Backtrack(1);
delete[]p;
return X.sum;
}
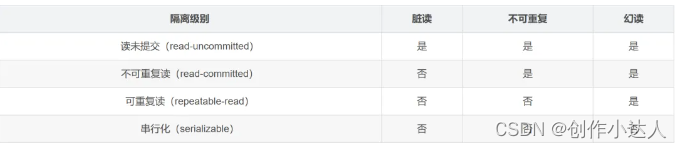
时间复杂度分析:





![SpringBoot学习06-[SpringBoot与AOP、SpringBoot自定义starter]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2bb9a6af1b574a31aeef3b766cae26f5.png)