1.vision mamba结构与原理
Mamba成功的关键在于S6模型,该模型为NLP任务设计,通过选择性扫描空间状态序列模型,将二次复杂度降低至线性。但由于视觉信号(如图像)的无序性,Mamba的S6模型不能直接应用,
设计了 2D-selective-scan(SS2D)模块。
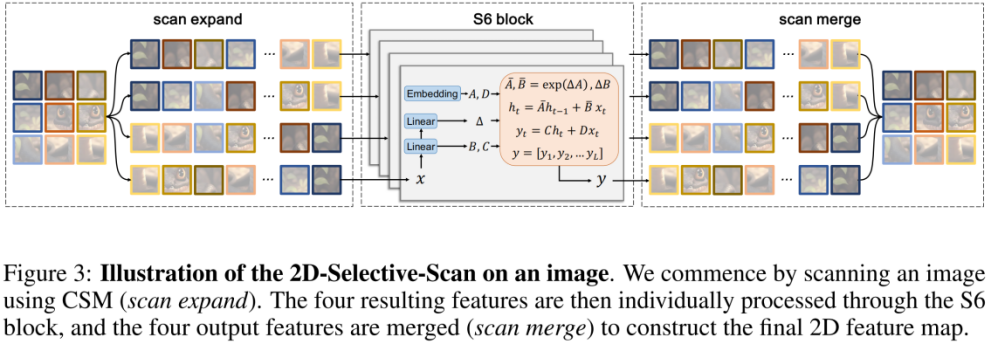
如上图所示,SS2D由三个部分组成:扫描expanding操作、S6块操作和扫描merging操作。如图2(a)所示,扫描expanding操作沿着四个不同的方向(左上到右下、左下到右上、右下到左上、右上到左下)将输入图像展开成序列。然后通过S6块对这些序列进行特征提取,确保各个方向的信息被彻底扫描,从而捕获不同的特征。随后,如图2(b)所示,扫描merging操作将来自四个方向的序列相加并合并,将输出图像恢复为与输入相同的大小。源自Mamba[16]的S6块在S4[17]之上引入了一种选择机制,通过根据输入调整SSM的参数。这使模型能够区分并保留相关信息,同时过滤掉不相关的信息。
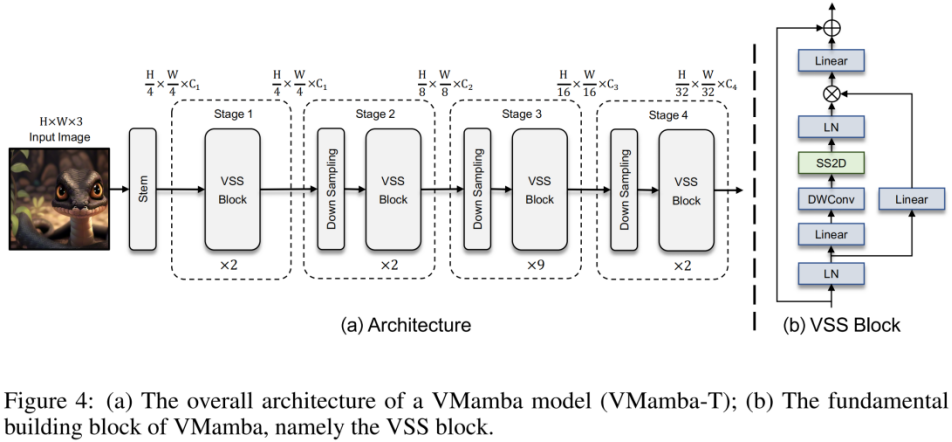
上图为本文提出的 VMamba 结构图。VMamba 的整体框架与主流的视觉模型类似,如上图 (b)所示。经过Layer Normalization后,输入被分成两个分支。在第一个分支中,输入经过一个线性层,然后是一个激活函数。在第二个分支中,输入通过线性层、深度可分离卷积和激活函数进行处理,然后输入到2D选择性扫描(SS2D)模块中进行进一步的特征提取。随后,使用Layer Normalization对特征进行归一化,然后使用第一个分支的输出执行逐元素的生成,以合并两条路径。最后,使用线性层混合特征,并将此结果与残差连接相结合,形成VSS块的输出。本文默认采用SiLU作为激活函数。
2.Vmamba(vision mamba)模块代码实现
import math
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.cuda.amp import custom_bwd, custom_fwd
from einops import rearrange, repeat
from causal_conv1d import causal_conv1d_fn
import causal_conv1d_cuda
import selective_scan_cuda
class SelectiveScanFn(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, u, delta, A, B, C, D=None, z=None, delta_bias=None, delta_softplus=False,
return_last_state=False):
if u.stride(-1) != 1:
u = u.contiguous()
if delta.stride(-1) != 1:
delta = delta.contiguous()
if D is not None:
D = D.contiguous()
if B.stride(-1) != 1:
B = B.contiguous()
if C.stride(-1) != 1:
C = C.contiguous()
if z is not None and z.stride(-1) != 1:
z = z.contiguous()
if B.dim() == 3:
B = rearrange(B, "b dstate l -> b 1 dstate l")
ctx.squeeze_B = True
if C.dim() == 3:
C = rearrange(C, "b dstate l -> b 1 dstate l")
ctx.squeeze_C = True
out, x, *rest = selective_scan_cuda.fwd(u, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, delta_softplus)
ctx.delta_softplus = delta_softplus
ctx.has_z = z is not None
last_state = x[:, :, -1, 1::2] # (batch, dim, dstate)
if not ctx.has_z:
ctx.save_for_backward(u, delta, A, B, C, D, delta_bias, x)
return out if not return_last_state else (out, last_state)
else:
ctx.save_for_backward(u, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, x, out)
out_z = rest[0]
return out_z if not return_last_state else (out_z, last_state)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, dout, *args):
if not ctx.has_z:
u, delta, A, B, C, D, delta_bias, x = ctx.saved_tensors
z = None
out = None
else:
u, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, x, out = ctx.saved_tensors
if dout.stride(-1) != 1:
dout = dout.contiguous()
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dz (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
# backward of selective_scan_cuda with the backward of chunk).
# Here we just pass in None and dz will be allocated in the C++ code.
du, ddelta, dA, dB, dC, dD, ddelta_bias, *rest = selective_scan_cuda.bwd(
u, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, dout, x, out, None, ctx.delta_softplus,
False # option to recompute out_z, not used here
)
dz = rest[0] if ctx.has_z else None
dB = dB.squeeze(1) if getattr(ctx, "squeeze_B", False) else dB
dC = dC.squeeze(1) if getattr(ctx, "squeeze_C", False) else dC
return (du, ddelta, dA, dB, dC,
dD if D is not None else None,
dz,
ddelta_bias if delta_bias is not None else None,
None,
None)
def selective_scan_fn(u, delta, A, B, C, D=None, z=None, delta_bias=None, delta_softplus=False,
return_last_state=False):
"""if return_last_state is True, returns (out, last_state)
last_state has shape (batch, dim, dstate). Note that the gradient of the last state is
not considered in the backward pass.
"""
return SelectiveScanFn.apply(u, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, delta_softplus, return_last_state)
def selective_scan_ref(u, delta, A, B, C, D=None, z=None, delta_bias=None, delta_softplus=False,
return_last_state=False):
"""
u: r(B D L)
delta: r(B D L)
A: c(D N) or r(D N)
B: c(D N) or r(B N L) or r(B N 2L) or r(B G N L) or (B G N L)
C: c(D N) or r(B N L) or r(B N 2L) or r(B G N L) or (B G N L)
D: r(D)
z: r(B D L)
delta_bias: r(D), fp32
out: r(B D L)
last_state (optional): r(B D dstate) or c(B D dstate)
"""
dtype_in = u.dtype
u = u.float()
delta = delta.float()
if delta_bias is not None:
delta = delta + delta_bias[..., None].float()
if delta_softplus:
delta = F.softplus(delta)
batch, dim, dstate = u.shape[0], A.shape[0], A.shape[1]
is_variable_B = B.dim() >= 3
is_variable_C = C.dim() >= 3
if A.is_complex():
if is_variable_B:
B = torch.view_as_complex(rearrange(B.float(), "... (L two) -> ... L two", two=2))
if is_variable_C:
C = torch.view_as_complex(rearrange(C.float(), "... (L two) -> ... L two", two=2))
else:
B = B.float()
C = C.float()
x = A.new_zeros((batch, dim, dstate))
ys = []
deltaA = torch.exp(torch.einsum('bdl,dn->bdln', delta, A))
if not is_variable_B:
deltaB_u = torch.einsum('bdl,dn,bdl->bdln', delta, B, u)
else:
if B.dim() == 3:
deltaB_u = torch.einsum('bdl,bnl,bdl->bdln', delta, B, u)
else:
B = repeat(B, "B G N L -> B (G H) N L", H=dim // B.shape[1])
deltaB_u = torch.einsum('bdl,bdnl,bdl->bdln', delta, B, u)
if is_variable_C and C.dim() == 4:
C = repeat(C, "B G N L -> B (G H) N L", H=dim // C.shape[1])
last_state = None
for i in range(u.shape[2]):
x = deltaA[:, :, i] * x + deltaB_u[:, :, i]
if not is_variable_C:
y = torch.einsum('bdn,dn->bd', x, C)
else:
if C.dim() == 3:
y = torch.einsum('bdn,bn->bd', x, C[:, :, i])
else:
y = torch.einsum('bdn,bdn->bd', x, C[:, :, :, i])
if i == u.shape[2] - 1:
last_state = x
if y.is_complex():
y = y.real * 2
ys.append(y)
y = torch.stack(ys, dim=2) # (batch dim L)
out = y if D is None else y + u * rearrange(D, "d -> d 1")
if z is not None:
out = out * F.silu(z)
out = out.to(dtype=dtype_in)
return out if not return_last_state else (out, last_state)
class MambaInnerFnNoOutProj(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
@custom_fwd
def forward(ctx, xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
A, B=None, C=None, D=None, delta_bias=None, B_proj_bias=None,
C_proj_bias=None, delta_softplus=True, checkpoint_lvl=1):
"""
xz: (batch, dim, seqlen)
"""
assert checkpoint_lvl in [0, 1]
L = xz.shape[-1]
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
x_proj_weight = x_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
delta_proj_weight = delta_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
if xz.stride(-1) != 1:
xz = xz.contiguous()
conv1d_weight = rearrange(conv1d_weight, "d 1 w -> d w")
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
conv1d_bias = conv1d_bias.contiguous() if conv1d_bias is not None else None
conv1d_out = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_fwd(x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, True)
# We're being very careful here about the layout, to avoid extra transposes.
# We want delta to have d as the slowest moving dimension
# and L as the fastest moving dimension, since those are what the ssm_scan kernel expects.
x_dbl = F.linear(rearrange(conv1d_out, 'b d l -> (b l) d'), x_proj_weight) # (bl d)
delta = rearrange(delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t(), "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
ctx.is_variable_B = B is None
ctx.is_variable_C = C is None
ctx.B_proj_bias_is_None = B_proj_bias is None
ctx.C_proj_bias_is_None = C_proj_bias is None
if B is None: # variable B
B = x_dbl[:, delta_rank:delta_rank + d_state] # (bl dstate)
if B_proj_bias is not None:
B = B + B_proj_bias.to(dtype=B.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
# B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b 1 dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
else:
if B.stride(-1) != 1:
B = B.contiguous()
if C is None: # variable C
C = x_dbl[:, -d_state:] # (bl dstate)
if C_proj_bias is not None:
C = C + C_proj_bias.to(dtype=C.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
# C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b 1 dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
else:
if C.stride(-1) != 1:
C = C.contiguous()
if D is not None:
D = D.contiguous()
out, scan_intermediates, out_z = selective_scan_cuda.fwd(
conv1d_out, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, delta_softplus
)
ctx.delta_softplus = delta_softplus
ctx.checkpoint_lvl = checkpoint_lvl
if checkpoint_lvl >= 1: # Will recompute conv1d_out and delta in the backward pass
conv1d_out, delta = None, None
ctx.save_for_backward(xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_dbl, x_proj_weight,
delta_proj_weight, conv1d_out, delta,
A, B, C, D, delta_bias, scan_intermediates, out)
# return rearrange(out_z, "b d l -> b l d")
return out_z
@staticmethod
@custom_bwd
def backward(ctx, dout):
# dout: (batch, seqlen, dim)
(xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_dbl, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
conv1d_out, delta, A, B, C, D, delta_bias, scan_intermediates, out) = ctx.saved_tensors
L = xz.shape[-1]
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
if dout.stride(-1) != 1:
dout = dout.contiguous()
if ctx.checkpoint_lvl == 1:
conv1d_out = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_fwd(x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, True)
delta = rearrange(delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t(),
"d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dz (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
# backward of selective_scan_cuda with the backward of chunk).
dxz = torch.empty_like(xz) # (batch, dim, seqlen)
dx, dz = dxz.chunk(2, dim=1)
# dout_y = rearrange(dout, "b l d -> b d l") # because no arrange at end of forward, so dout shape is b d l
dconv1d_out, ddelta, dA, dB, dC, dD, ddelta_bias, dz, out_z = selective_scan_cuda.bwd(
conv1d_out, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, dout, scan_intermediates, out, dz,
ctx.delta_softplus,
True # option to recompute out_z
)
dD = dD if D is not None else None
dx_dbl = torch.empty_like(x_dbl)
dB_proj_bias = None
if ctx.is_variable_B:
if not A.is_complex():
dB = rearrange(dB, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate").contiguous()
else:
dB = rearrange(dB, "b 1 dstate (l two) -> (b l) (dstate two)", two=2).contiguous()
dB_proj_bias = dB.sum(0) if not ctx.B_proj_bias_is_None else None
dx_dbl[:, delta_rank:delta_rank + d_state] = dB # (bl d)
dB = None
dC_proj_bias = None
if ctx.is_variable_C:
if not A.is_complex():
dC = rearrange(dC, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate").contiguous()
else:
dC = rearrange(dC, "b 1 dstate (l two) -> (b l) (dstate two)", two=2).contiguous()
dC_proj_bias = dC.sum(0) if not ctx.C_proj_bias_is_None else None
dx_dbl[:, -d_state:] = dC # (bl d)
dC = None
ddelta = rearrange(ddelta, "b d l -> d (b l)")
ddelta_proj_weight = torch.einsum("dB,Br->dr", ddelta, x_dbl[:, :delta_rank])
dx_dbl[:, :delta_rank] = torch.einsum("dB,dr->Br", ddelta, delta_proj_weight)
dconv1d_out = rearrange(dconv1d_out, "b d l -> d (b l)")
dx_proj_weight = torch.einsum("Br,Bd->rd", dx_dbl, rearrange(conv1d_out, "b d l -> (b l) d"))
dconv1d_out = torch.addmm(dconv1d_out, x_proj_weight.t(), dx_dbl.t(), out=dconv1d_out)
dconv1d_out = rearrange(dconv1d_out, "d (b l) -> b d l", b=x.shape[0], l=x.shape[-1])
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dx (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
# backward of conv1d with the backward of chunk).
dx, dconv1d_weight, dconv1d_bias = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_bwd(
x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, dconv1d_out, dx, True
)
dconv1d_bias = dconv1d_bias if conv1d_bias is not None else None
dconv1d_weight = rearrange(dconv1d_weight, "d w -> d 1 w")
return (dxz, dconv1d_weight, dconv1d_bias, dx_proj_weight, ddelta_proj_weight,
dA, dB, dC, dD,
ddelta_bias if delta_bias is not None else None,
dB_proj_bias, dC_proj_bias, None)
class MambaInnerFn(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
@custom_fwd
def forward(ctx, xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias,
A, B=None, C=None, D=None, delta_bias=None, B_proj_bias=None,
C_proj_bias=None, delta_softplus=True, checkpoint_lvl=1):
"""
xz: (batch, dim, seqlen)
"""
assert checkpoint_lvl in [0, 1]
L = xz.shape[-1]
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
x_proj_weight = x_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
delta_proj_weight = delta_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
out_proj_weight = out_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
out_proj_bias = (out_proj_bias.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
if out_proj_bias is not None else None)
if xz.stride(-1) != 1:
xz = xz.contiguous()
conv1d_weight = rearrange(conv1d_weight, "d 1 w -> d w")
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
conv1d_bias = conv1d_bias.contiguous() if conv1d_bias is not None else None
conv1d_out = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_fwd(x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, True)
# We're being very careful here about the layout, to avoid extra transposes.
# We want delta to have d as the slowest moving dimension
# and L as the fastest moving dimension, since those are what the ssm_scan kernel expects.
x_dbl = F.linear(rearrange(conv1d_out, 'b d l -> (b l) d'), x_proj_weight) # (bl d)
delta = rearrange(delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t(), "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
ctx.is_variable_B = B is None
ctx.is_variable_C = C is None
ctx.B_proj_bias_is_None = B_proj_bias is None
ctx.C_proj_bias_is_None = C_proj_bias is None
if B is None: # variable B
B = x_dbl[:, delta_rank:delta_rank + d_state] # (bl dstate)
if B_proj_bias is not None:
B = B + B_proj_bias.to(dtype=B.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
# B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b 1 dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
else:
if B.stride(-1) != 1:
B = B.contiguous()
if C is None: # variable C
C = x_dbl[:, -d_state:] # (bl dstate)
if C_proj_bias is not None:
C = C + C_proj_bias.to(dtype=C.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
# C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b 1 dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
else:
if C.stride(-1) != 1:
C = C.contiguous()
if D is not None:
D = D.contiguous()
out, scan_intermediates, out_z = selective_scan_cuda.fwd(
conv1d_out, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, delta_softplus
)
ctx.delta_softplus = delta_softplus
ctx.out_proj_bias_is_None = out_proj_bias is None
ctx.checkpoint_lvl = checkpoint_lvl
if checkpoint_lvl >= 1: # Will recompute conv1d_out and delta in the backward pass
conv1d_out, delta = None, None
ctx.save_for_backward(xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_dbl, x_proj_weight,
delta_proj_weight, out_proj_weight, conv1d_out, delta,
A, B, C, D, delta_bias, scan_intermediates, out)
return F.linear(rearrange(out_z, "b d l -> b l d"), out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias)
@staticmethod
@custom_bwd
def backward(ctx, dout):
# dout: (batch, seqlen, dim)
(xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_dbl, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight, out_proj_weight,
conv1d_out, delta, A, B, C, D, delta_bias, scan_intermediates, out) = ctx.saved_tensors
L = xz.shape[-1]
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
if dout.stride(-1) != 1:
dout = dout.contiguous()
if ctx.checkpoint_lvl == 1:
conv1d_out = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_fwd(x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, True)
delta = rearrange(delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t(),
"d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dz (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
# backward of selective_scan_cuda with the backward of chunk).
dxz = torch.empty_like(xz) # (batch, dim, seqlen)
dx, dz = dxz.chunk(2, dim=1)
dout = rearrange(dout, "b l e -> e (b l)")
dout_y = rearrange(out_proj_weight.t() @ dout, "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
dconv1d_out, ddelta, dA, dB, dC, dD, ddelta_bias, dz, out_z = selective_scan_cuda.bwd(
conv1d_out, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, dout_y, scan_intermediates, out, dz,
ctx.delta_softplus,
True # option to recompute out_z
)
dout_proj_weight = torch.einsum("eB,dB->ed", dout, rearrange(out_z, "b d l -> d (b l)"))
dout_proj_bias = dout.sum(dim=(0, 1)) if not ctx.out_proj_bias_is_None else None
dD = dD if D is not None else None
dx_dbl = torch.empty_like(x_dbl)
dB_proj_bias = None
if ctx.is_variable_B:
if not A.is_complex():
dB = rearrange(dB, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate").contiguous()
else:
dB = rearrange(dB, "b 1 dstate (l two) -> (b l) (dstate two)", two=2).contiguous()
dB_proj_bias = dB.sum(0) if not ctx.B_proj_bias_is_None else None
dx_dbl[:, delta_rank:delta_rank + d_state] = dB # (bl d)
dB = None
dC_proj_bias = None
if ctx.is_variable_C:
if not A.is_complex():
dC = rearrange(dC, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate").contiguous()
else:
dC = rearrange(dC, "b 1 dstate (l two) -> (b l) (dstate two)", two=2).contiguous()
dC_proj_bias = dC.sum(0) if not ctx.C_proj_bias_is_None else None
dx_dbl[:, -d_state:] = dC # (bl d)
dC = None
ddelta = rearrange(ddelta, "b d l -> d (b l)")
ddelta_proj_weight = torch.einsum("dB,Br->dr", ddelta, x_dbl[:, :delta_rank])
dx_dbl[:, :delta_rank] = torch.einsum("dB,dr->Br", ddelta, delta_proj_weight)
dconv1d_out = rearrange(dconv1d_out, "b d l -> d (b l)")
dx_proj_weight = torch.einsum("Br,Bd->rd", dx_dbl, rearrange(conv1d_out, "b d l -> (b l) d"))
dconv1d_out = torch.addmm(dconv1d_out, x_proj_weight.t(), dx_dbl.t(), out=dconv1d_out)
dconv1d_out = rearrange(dconv1d_out, "d (b l) -> b d l", b=x.shape[0], l=x.shape[-1])
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dx (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
# backward of conv1d with the backward of chunk).
dx, dconv1d_weight, dconv1d_bias = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_bwd(
x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, dconv1d_out, dx, True
)
dconv1d_bias = dconv1d_bias if conv1d_bias is not None else None
dconv1d_weight = rearrange(dconv1d_weight, "d w -> d 1 w")
return (dxz, dconv1d_weight, dconv1d_bias, dx_proj_weight, ddelta_proj_weight,
dout_proj_weight, dout_proj_bias,
dA, dB, dC, dD,
ddelta_bias if delta_bias is not None else None,
dB_proj_bias, dC_proj_bias, None)
class BiMambaInnerFn(torch.autograd.Function):
@staticmethod
@custom_fwd
def forward(ctx, xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias,
A, A_b, B=None, C=None, D=None, delta_bias=None, B_proj_bias=None,
C_proj_bias=None, delta_softplus=True, checkpoint_lvl=1):
"""
xz: (batch, dim, seqlen)
"""
assert checkpoint_lvl in [0, 1]
L = xz.shape[-1]
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
x_proj_weight = x_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
delta_proj_weight = delta_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
out_proj_weight = out_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
out_proj_bias = (out_proj_bias.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
if out_proj_bias is not None else None)
if xz.stride(-1) != 1:
xz = xz.contiguous()
conv1d_weight = rearrange(conv1d_weight, "d 1 w -> d w")
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
conv1d_bias = conv1d_bias.contiguous() if conv1d_bias is not None else None
conv1d_out = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_fwd(x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, True)
# We're being very careful here about the layout, to avoid extra transposes.
# We want delta to have d as the slowest moving dimension
# and L as the fastest moving dimension, since those are what the ssm_scan kernel expects.
x_dbl = F.linear(rearrange(conv1d_out, 'b d l -> (b l) d'), x_proj_weight) # (bl d)
delta = rearrange(delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t(), "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
ctx.is_variable_B = B is None
ctx.is_variable_C = C is None
ctx.B_proj_bias_is_None = B_proj_bias is None
ctx.C_proj_bias_is_None = C_proj_bias is None
if B is None: # variable B
B = x_dbl[:, delta_rank:delta_rank + d_state] # (bl dstate)
if B_proj_bias is not None:
B = B + B_proj_bias.to(dtype=B.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
# B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b 1 dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
else:
if B.stride(-1) != 1:
B = B.contiguous()
if C is None: # variable C
C = x_dbl[:, -d_state:] # (bl dstate)
if C_proj_bias is not None:
C = C + C_proj_bias.to(dtype=C.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
# C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b 1 dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
else:
if C.stride(-1) != 1:
C = C.contiguous()
if D is not None:
D = D.contiguous()
out_f, scan_intermediates_f, out_z_f = selective_scan_cuda.fwd(
conv1d_out, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, delta_softplus
)
assert not A_b.is_complex(), "A should not be complex!!"
out_b, scan_intermediates_b, out_z_b = selective_scan_cuda.fwd(
conv1d_out.flip([-1]), delta.flip([-1]), A_b, B.flip([-1]), C.flip([-1]), D, z.flip([-1]), delta_bias,
delta_softplus,
)
out_z = out_z_f + out_z_b.flip([-1])
ctx.delta_softplus = delta_softplus
ctx.out_proj_bias_is_None = out_proj_bias is None
ctx.checkpoint_lvl = checkpoint_lvl
if checkpoint_lvl >= 1: # Will recompute conv1d_out and delta in the backward pass
conv1d_out, delta = None, None
ctx.save_for_backward(xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_dbl, x_proj_weight,
delta_proj_weight, out_proj_weight, conv1d_out, delta,
A, A_b, B, C, D, delta_bias, scan_intermediates_f, scan_intermediates_b, out_f, out_b)
return F.linear(rearrange(out_z, "b d l -> b l d"), out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias)
@staticmethod
@custom_bwd
def backward(ctx, dout):
# dout: (batch, seqlen, dim)
(xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_dbl, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight, out_proj_weight,
conv1d_out, delta, A, A_b, B, C, D, delta_bias, scan_intermediates_f, scan_intermediates_b, out_f,
out_b) = ctx.saved_tensors
L = xz.shape[-1]
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
if dout.stride(-1) != 1:
dout = dout.contiguous()
if ctx.checkpoint_lvl == 1:
conv1d_out = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_fwd(x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, True)
delta = rearrange(delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t(),
"d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dz (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
# backward of selective_scan_cuda with the backward of chunk).
dxz = torch.empty_like(xz) # (batch, dim, seqlen)
dx, dz = dxz.chunk(2, dim=1)
dout = rearrange(dout, "b l e -> e (b l)")
dout_y = rearrange(out_proj_weight.t() @ dout, "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
dconv1d_out, ddelta, dA, dB, dC, dD, ddelta_bias, dz, out_z_f = selective_scan_cuda.bwd(
conv1d_out, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, dout_y, scan_intermediates_f, out_f, dz,
ctx.delta_softplus,
True # option to recompute out_z
)
# flip one
dz_b = torch.empty_like(dz)
dconv1d_out_f_b, ddelta_f_b, dA_b, dB_f_b, dC_f_b, dD_b, ddelta_bias_b, dz_b, out_z_b = selective_scan_cuda.bwd(
conv1d_out.flip([-1]), delta.flip([-1]), A_b, B.flip([-1]), C.flip([-1]), D, z.flip([-1]), delta_bias,
dout_y.flip([-1]), scan_intermediates_b, out_b, dz_b,
ctx.delta_softplus,
True # option to recompute out_z
)
dconv1d_out = dconv1d_out + dconv1d_out_f_b.flip([-1])
ddelta = ddelta + ddelta_f_b.flip([-1])
dB = dB + dB_f_b.flip([-1])
dC = dC + dC_f_b.flip([-1])
dD = dD + dD_b
ddelta_bias = ddelta_bias + ddelta_bias_b
dz = dz + dz_b.flip([-1])
out_z = out_z_f + out_z_b.flip([-1])
dout_proj_weight = torch.einsum("eB,dB->ed", dout, rearrange(out_z, "b d l -> d (b l)"))
dout_proj_bias = dout.sum(dim=(0, 1)) if not ctx.out_proj_bias_is_None else None
dD = dD if D is not None else None
dx_dbl = torch.empty_like(x_dbl)
dB_proj_bias = None
if ctx.is_variable_B:
if not A.is_complex():
dB = rearrange(dB, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate").contiguous()
else:
dB = rearrange(dB, "b 1 dstate (l two) -> (b l) (dstate two)", two=2).contiguous()
dB_proj_bias = dB.sum(0) if not ctx.B_proj_bias_is_None else None
dx_dbl[:, delta_rank:delta_rank + d_state] = dB # (bl d)
dB = None
dC_proj_bias = None
if ctx.is_variable_C:
if not A.is_complex():
dC = rearrange(dC, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate").contiguous()
else:
dC = rearrange(dC, "b 1 dstate (l two) -> (b l) (dstate two)", two=2).contiguous()
dC_proj_bias = dC.sum(0) if not ctx.C_proj_bias_is_None else None
dx_dbl[:, -d_state:] = dC # (bl d)
dC = None
ddelta = rearrange(ddelta, "b d l -> d (b l)")
ddelta_proj_weight = torch.einsum("dB,Br->dr", ddelta, x_dbl[:, :delta_rank])
dx_dbl[:, :delta_rank] = torch.einsum("dB,dr->Br", ddelta, delta_proj_weight)
dconv1d_out = rearrange(dconv1d_out, "b d l -> d (b l)")
dx_proj_weight = torch.einsum("Br,Bd->rd", dx_dbl, rearrange(conv1d_out, "b d l -> (b l) d"))
dconv1d_out = torch.addmm(dconv1d_out, x_proj_weight.t(), dx_dbl.t(), out=dconv1d_out)
dconv1d_out = rearrange(dconv1d_out, "d (b l) -> b d l", b=x.shape[0], l=x.shape[-1])
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dx (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
# backward of conv1d with the backward of chunk).
dx, dconv1d_weight, dconv1d_bias = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_bwd(
x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, dconv1d_out, dx, True
)
dconv1d_bias = dconv1d_bias if conv1d_bias is not None else None
dconv1d_weight = rearrange(dconv1d_weight, "d w -> d 1 w")
return (dxz, dconv1d_weight, dconv1d_bias, dx_proj_weight, ddelta_proj_weight,
dout_proj_weight, dout_proj_bias,
dA, dA_b, dB, dC, dD,
ddelta_bias if delta_bias is not None else None,
dB_proj_bias, dC_proj_bias, None)
def mamba_inner_fn(
xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias,
A, B=None, C=None, D=None, delta_bias=None, B_proj_bias=None,
C_proj_bias=None, delta_softplus=True
):
return MambaInnerFn.apply(xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias,
A, B, C, D, delta_bias, B_proj_bias, C_proj_bias, delta_softplus)
def bimamba_inner_fn(
xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias,
A, A_b, B=None, C=None, D=None, delta_bias=None, B_proj_bias=None,
C_proj_bias=None, delta_softplus=True
):
return BiMambaInnerFn.apply(xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias,
A, A_b, B, C, D, delta_bias, B_proj_bias, C_proj_bias, delta_softplus)
def mamba_inner_fn_no_out_proj(
xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
A, B=None, C=None, D=None, delta_bias=None, B_proj_bias=None,
C_proj_bias=None, delta_softplus=True
):
return MambaInnerFnNoOutProj.apply(xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
A, B, C, D, delta_bias, B_proj_bias, C_proj_bias, delta_softplus)
def mamba_inner_ref(
xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias,
A, B=None, C=None, D=None, delta_bias=None, B_proj_bias=None,
C_proj_bias=None, delta_softplus=True
):
L = xz.shape[-1]
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
x = causal_conv1d_fn(x, rearrange(conv1d_weight, "d 1 w -> d w"), conv1d_bias, "silu")
# We're being very careful here about the layout, to avoid extra transposes.
# We want delta to have d as the slowest moving dimension
# and L as the fastest moving dimension, since those are what the ssm_scan kernel expects.
x_dbl = F.linear(rearrange(x, 'b d l -> (b l) d'), x_proj_weight) # (bl d)
delta = delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t()
delta = rearrange(delta, "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
if B is None: # variable B
B = x_dbl[:, delta_rank:delta_rank + d_state] # (bl d)
if B_proj_bias is not None:
B = B + B_proj_bias.to(dtype=B.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
if C is None: # variable B
C = x_dbl[:, -d_state:] # (bl d)
if C_proj_bias is not None:
C = C + C_proj_bias.to(dtype=C.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
y = selective_scan_fn(x, delta, A, B, C, D, z=z, delta_bias=delta_bias, delta_softplus=True)
return F.linear(rearrange(y, "b d l -> b l d"), out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias)
def bimamba_inner_ref(
xz, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, x_proj_weight, delta_proj_weight,
out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias,
A, A_b, B=None, C=None, D=None, delta_bias=None, B_proj_bias=None,
C_proj_bias=None, delta_softplus=True
):
L = xz.shape[-1]
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
x = causal_conv1d_fn(x, rearrange(conv1d_weight, "d 1 w -> d w"), conv1d_bias, "silu")
# We're being very careful here about the layout, to avoid extra transposes.
# We want delta to have d as the slowest moving dimension
# and L as the fastest moving dimension, since those are what the ssm_scan kernel expects.
x_dbl = F.linear(rearrange(x, 'b d l -> (b l) d'), x_proj_weight) # (bl d)
delta = delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t()
delta = rearrange(delta, "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
if B is None: # variable B
B = x_dbl[:, delta_rank:delta_rank + d_state] # (bl d)
if B_proj_bias is not None:
B = B + B_proj_bias.to(dtype=B.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
if C is None: # variable B
C = x_dbl[:, -d_state:] # (bl d)
if C_proj_bias is not None:
C = C + C_proj_bias.to(dtype=C.dtype)
if not A.is_complex():
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
else:
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
y = selective_scan_fn(x, delta, A, B, C, D, z=z, delta_bias=delta_bias, delta_softplus=True)
y_b = selective_scan_fn(x.flip([-1]), delta.flip([-1]), A_b, B.flip([-1]), C.flip([-1]), D, z.flip([-1]),
delta_bias, delta_softplus=True)
y = y + y_b.flip([-1])
return F.linear(rearrange(y, "b d l -> b l d"), out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias)
#------------------------------------------
class Mamba(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
d_model,
d_state=16,
d_conv=4,
expand=2,
dt_rank="auto",
dt_min=0.001,
dt_max=0.1,
dt_init="random",
dt_scale=1.0,
dt_init_floor=1e-4,
conv_bias=True,
bias=False,
use_fast_path=True, # Fused kernel options
layer_idx=None,
device=None,
dtype=None,
bimamba_type="none"
):
factory_kwargs = {"device": device, "dtype": dtype}
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.d_state = d_state
self.d_conv = d_conv
self.expand = expand
self.d_inner = int(self.expand * self.d_model)
self.dt_rank = math.ceil(self.d_model / 16) if dt_rank == "auto" else dt_rank
self.use_fast_path = use_fast_path
self.layer_idx = layer_idx
self.bimamba_type = bimamba_type
self.in_proj = nn.Linear(self.d_model, self.d_inner * 2, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
self.conv1d = nn.Conv1d(
in_channels=self.d_inner,
out_channels=self.d_inner,
bias=conv_bias,
kernel_size=d_conv,
groups=self.d_inner,
padding=d_conv - 1,
**factory_kwargs,
)
self.activation = "silu"
self.act = nn.SiLU()
self.x_proj = nn.Linear(
self.d_inner, self.dt_rank + self.d_state * 2, bias=False, **factory_kwargs
)
self.dt_proj = nn.Linear(self.dt_rank, self.d_inner, bias=True, **factory_kwargs)
# Initialize special dt projection to preserve variance at initialization
dt_init_std = self.dt_rank**-0.5 * dt_scale
if dt_init == "constant":
nn.init.constant_(self.dt_proj.weight, dt_init_std)
elif dt_init == "random":
nn.init.uniform_(self.dt_proj.weight, -dt_init_std, dt_init_std)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
# Initialize dt bias so that F.softplus(dt_bias) is between dt_min and dt_max
dt = torch.exp(
torch.rand(self.d_inner, **factory_kwargs) * (math.log(dt_max) - math.log(dt_min))
+ math.log(dt_min)
).clamp(min=dt_init_floor)
# Inverse of softplus: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/72759
inv_dt = dt + torch.log(-torch.expm1(-dt))
with torch.no_grad():
self.dt_proj.bias.copy_(inv_dt)
# Our initialization would set all Linear.bias to zero, need to mark this one as _no_reinit
self.dt_proj.bias._no_reinit = True
# S4D real initialization
A = repeat(
torch.arange(1, self.d_state + 1, dtype=torch.float32, device=device),
"n -> d n",
d=self.d_inner,
).contiguous()
A_log = torch.log(A) # Keep A_log in fp32
self.A_log = nn.Parameter(A_log)
self.A_log._no_weight_decay = True
# D "skip" parameter
self.D = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(self.d_inner, device=device)) # Keep in fp32
self.D._no_weight_decay = True
# bidirectional
assert bimamba_type == "v2"
A_b = repeat(
torch.arange(1, self.d_state + 1, dtype=torch.float32, device=device),
"n -> d n",
d=self.d_inner,
).contiguous()
A_b_log = torch.log(A_b) # Keep A_b_log in fp32
self.A_b_log = nn.Parameter(A_b_log)
self.A_b_log._no_weight_decay = True
self.conv1d_b = nn.Conv1d(
in_channels=self.d_inner,
out_channels=self.d_inner,
bias=conv_bias,
kernel_size=d_conv,
groups=self.d_inner,
padding=d_conv - 1,
**factory_kwargs,
)
self.x_proj_b = nn.Linear(
self.d_inner, self.dt_rank + self.d_state * 2, bias=False, **factory_kwargs
)
self.dt_proj_b = nn.Linear(self.dt_rank, self.d_inner, bias=True, **factory_kwargs)
self.D_b = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(self.d_inner, device=device)) # Keep in fp32
self.D_b._no_weight_decay = True
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(self.d_inner, self.d_model, bias=bias, **factory_kwargs)
def forward(self, hidden_states, inference_params=None):
"""
hidden_states: (B, L, D)
Returns: same shape as hidden_states
"""
batch, seqlen, dim = hidden_states.shape
conv_state, ssm_state = None, None
if inference_params is not None:
conv_state, ssm_state = self._get_states_from_cache(inference_params, batch)
if inference_params.seqlen_offset > 0:
# The states are updated inplace
out, _, _ = self.step(hidden_states, conv_state, ssm_state)
return out
# We do matmul and transpose BLH -> HBL at the same time
xz = rearrange(
self.in_proj.weight @ rearrange(hidden_states, "b l d -> d (b l)"),
"d (b l) -> b d l",
l=seqlen,
)
if self.in_proj.bias is not None:
xz = xz + rearrange(self.in_proj.bias.to(dtype=xz.dtype), "d -> d 1")
A = -torch.exp(self.A_log.float()) # (d_inner, d_state)
# In the backward pass we write dx and dz next to each other to avoid torch.cat
if self.use_fast_path and inference_params is None: # Doesn't support outputting the states
if self.bimamba_type == "v2":
A_b = -torch.exp(self.A_b_log.float())
out = mamba_inner_fn_no_out_proj(
xz,
self.conv1d.weight,
self.conv1d.bias,
self.x_proj.weight,
self.dt_proj.weight,
A,
None, # input-dependent B
None, # input-dependent C
self.D.float(),
delta_bias=self.dt_proj.bias.float(),
delta_softplus=True,
)
out_b = mamba_inner_fn_no_out_proj(
xz.flip([-1]),
self.conv1d_b.weight,
self.conv1d_b.bias,
self.x_proj_b.weight,
self.dt_proj_b.weight,
A_b,
None,
None,
self.D_b.float(),
delta_bias=self.dt_proj_b.bias.float(),
delta_softplus=True,
)
# F.linear(rearrange(out_z, "b d l -> b l d"), out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias)
out = F.linear(rearrange(out + out_b.flip([-1]), "b d l -> b l d"), self.out_proj.weight, self.out_proj.bias)
else:
out = mamba_inner_fn(
xz,
self.conv1d.weight,
self.conv1d.bias,
self.x_proj.weight,
self.dt_proj.weight,
self.out_proj.weight,
self.out_proj.bias,
A,
None, # input-dependent B
None, # input-dependent C
self.D.float(),
delta_bias=self.dt_proj.bias.float(),
delta_softplus=True,
)
else:
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
# Compute short convolution
if conv_state is not None:
conv_state.copy_(x[:, :, -self.d_conv :]) # Update state (B D W)
if causal_conv1d_fn is None:
x = self.act(self.conv1d(x)[..., :seqlen])
else:
assert self.activation in ["silu", "swish"]
x = causal_conv1d_fn(
x,
rearrange(self.conv1d.weight, "d 1 w -> d w"),
self.conv1d.bias,
self.activation,
)
# We're careful here about the layout, to avoid extra transposes.
# We want dt to have d as the slowest moving dimension
# and L as the fastest moving dimension, since those are what the ssm_scan kernel expects.
x_dbl = self.x_proj(rearrange(x, "b d l -> (b l) d")) # (bl d)
dt, B, C = torch.split(x_dbl, [self.dt_rank, self.d_state, self.d_state], dim=-1)
dt = self.dt_proj.weight @ dt.t()
dt = rearrange(dt, "d (b l) -> b d l", l=seqlen)
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=seqlen).contiguous()
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=seqlen).contiguous()
assert self.activation in ["silu", "swish"]
y = selective_scan_fn(
x,
dt,
A,
B,
C,
self.D.float(),
z=z,
delta_bias=self.dt_proj.bias.float(),
delta_softplus=True,
return_last_state=ssm_state is not None,
)
if ssm_state is not None:
y, last_state = y
ssm_state.copy_(last_state)
y = rearrange(y, "b d l -> b l d")
out = self.out_proj(y)
return out
class MambaLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, d_state=16, d_conv=4, expand=2):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dim)
self.mamba = Mamba(
d_model=dim, # Model dimension d_model
d_state=d_state, # SSM state expansion factor
d_conv=d_conv, # Local convolution width
expand=expand, # Block expansion factor
bimamba_type="v2",
)
def forward(self, x):
B, C = x.shape[:2]
assert C == self.dim
n_tokens = x.shape[2:].numel()
img_dims = x.shape[2:]
x_flat = x.reshape(B, C, n_tokens).transpose(-1, -2)
x_norm = self.norm(x_flat)
# x_norm = x_norm.to('cuda')
x_mamba = self.mamba(x_norm)
out = x_mamba.transpose(-1, -2).reshape(B, C, *img_dims)
#out = out.to(x.device)
return out3. vision mamba-yolov8 环境检测与安装
1)代码运行环境验证与安装
应代码需要用到cuda的一些库函数,因此需要安装显卡的驱动以及cuda、以及支持gpu的pytorch版本
验证方式:
命令行输入 nvidia-smi ,若有输出表示驱动已经安装
命令行输入 nvcc -V,若有输出,表示cuda已经安装
命令行分别输入
python
import torch
print(torch.cuda.is_available()),若有输出,支持gpu的pytorch已经安装
若以上均正常输出,则进行4,否则需要进行对应的安装
2)代码运行环境安装
可参考以下博客进行安装
- 关于ubuntu 的显卡的驱动以及cuda安装可参考
- 深度学习项目GPU开发环境安装-CSDN博客
- 关于Windows下安装显卡的驱动以及cuda安装可参考Windows下安装CUDA并配置cuDNN教程_windows安装cudnn-CSDN博客g
- 关于支持gpu的pytorch安装,可参考
- Mamba项目实战-Ubuntu-CSDN博客
4. vision mamba-yolov8 代码安装与改进
1) 克隆yolov8源码
命令行运行
# Clone the ultralytics repository
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics或 百度网盘
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1H9VlKlbRxW5W3wrZGYDPQw
提取码:dbfa
2) 安装yolov8
进入pyproject.toml的同级目录命令行
# Navigate to the cloned directory
cd ultralytics-main运行命令安装 yolov8全部所需要的库
# Install the package in editable mode for development
pip install -e .3)安装 causal-conv1d-main 、mamba-ssm-1.0.1
下载causal-conv1d-main,至ultralytics的同级目录下,进入causal-conv1d-main文件夹,进行安装
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1W4mTvjzMJhf-uT_vryT5Kg
提取码:egfj
cd causal-conv1d-main/安装causal-conv1d-main
python setup.py install安装mamba-ssm-1.0.1
pip install mamba-ssm==1.0.14)添加Vmamba模块
在ultralytics/nn目录下新建Addmoudules目录,并在该目录中新建VMamba.py,以及__init__.py文件。

并将“2.Vmamba(vision mamba)模块代码实现”中代码复制到Vmamba.py里面。
__init__.py填入
from .VMamba import *5)更改task.py文件
打开ultralytics/nn/tasks.py
在第七行处,导入模块

from .Addmodules import *
第300行进行替换

替换为
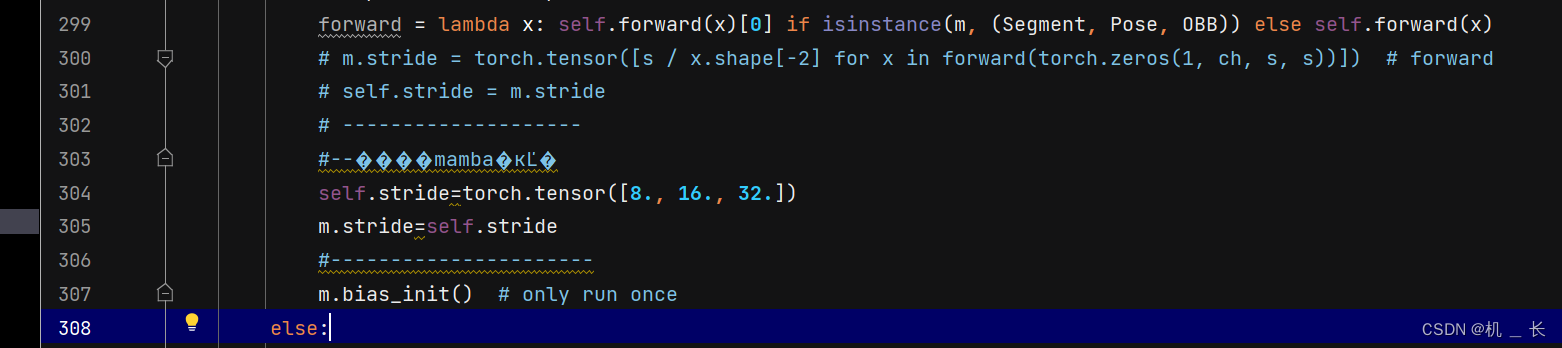
替换代码
# m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))]) # forward
# self.stride = m.stride
# --------------------
#--����mamba�ĸĽ�
self.stride=torch.tensor([8., 16., 32.])
m.stride=self.stride
#----------------------895行增加 MambaLayer


6)添加VMamba-yolov8.yaml
在ultralytics/cfg/models/v8,新建VMamba-yolov8.yaml文件
在里面写入
# Ultralytics YOLO ??, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 2 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
d: [0.67, 0.50, 768] #YOLOv8s summary: 295 layers, 11716214 parameters, 11716189 gradients, 36.2 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2 # 0. 320
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4 # 1. 160
- [-1, 3, MambaLayer, [128]] # 2. 160
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8 # 3. 80
- [-1, 6, MambaLayer, [256]] # 4. 80
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16 # 5. 40
- [-1, 6, MambaLayer, [512]] # 6. 40
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32 # 7. 20
- [-1, 3, MambaLayer, [1024]] # 8. 20
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9 # 9. 20
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
7) 运行训练
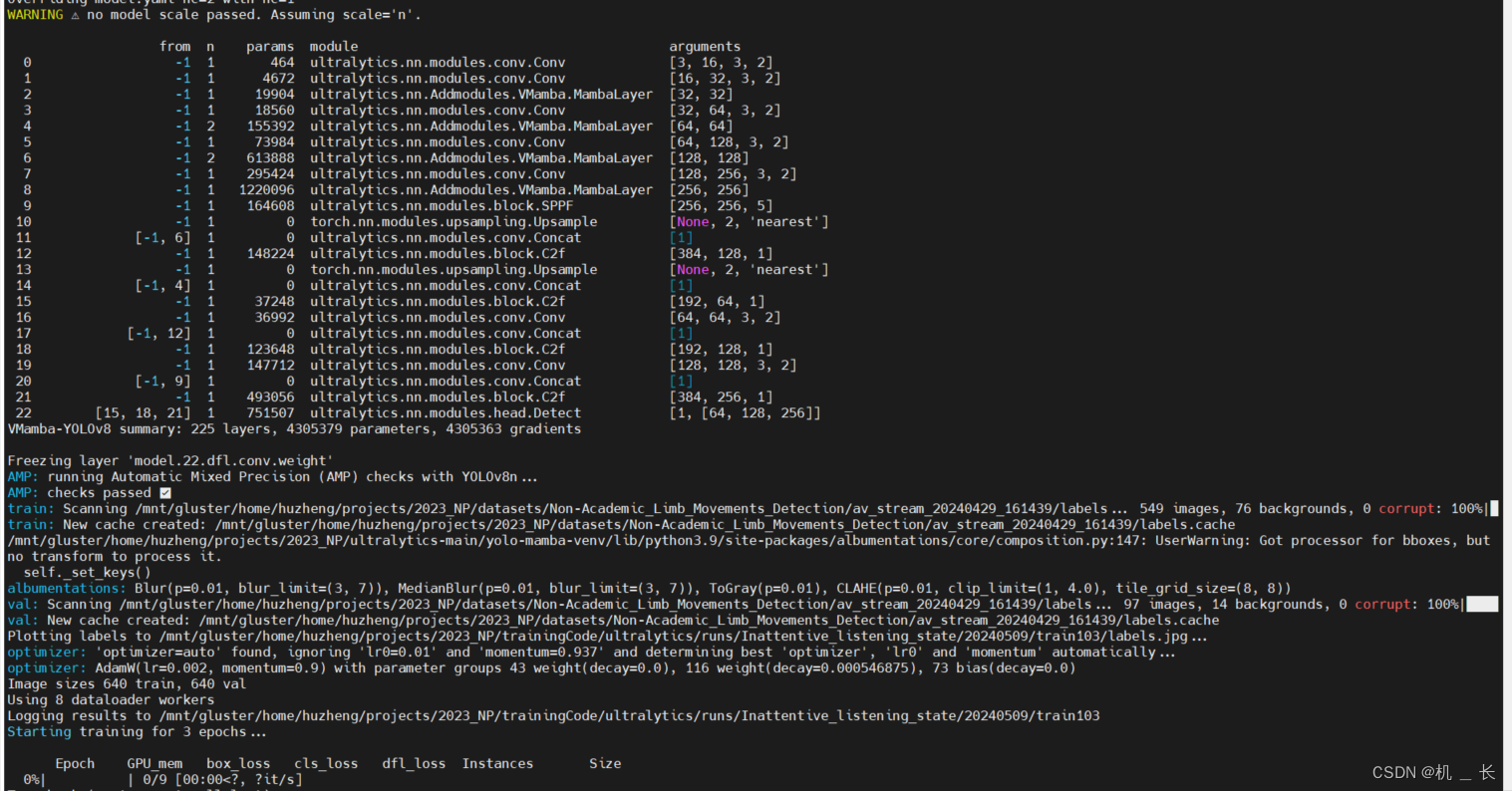
在ultralytics-main目录下新建train.py,
在里面写入
from ultralytics import YOLO
model = YOLO('./ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/VMamba-yolov8.yaml')
model.train(data='数据集配置文件路径',device="0",epochs=300,amp=False ,project="训练结果保存路径",batch=70,imgsz=640)
5.vision mamba-yolov8 训练展示