文章目录
- LeetCode 491.递增子序列
- 题目详解
- 注意难点
- 示意图
- LeetCode 46.全排列
- 题目讲解
- 难点
- LeetCode47.全排列 II
- 题目讲解
- 示图
- 难点
- 总结
LeetCode 491.递增子序列
题目详解
注意难点
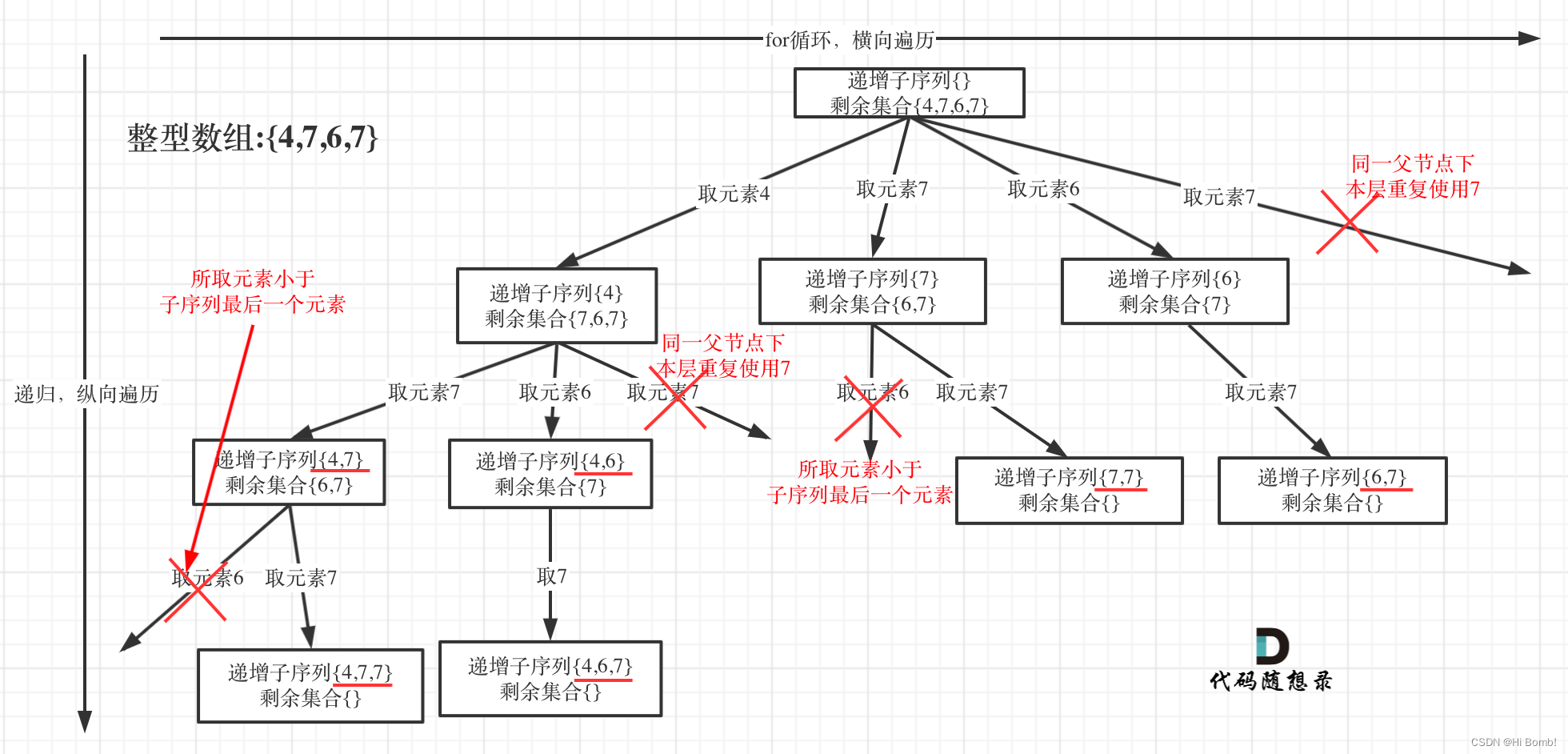
在题目中有涉及到 子集序列中至少有两个元素 可以用来进行判断
在单层遍历之前需要声明一个数组 used用来记录是否用过的记录 如果使用过就是1 生命空间 为201 因为 题目中涉及到 子集的选择范围会从-100 到正100 来看 所以生命201
示意图
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList();
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
backtrack( nums,0);
return result;
}
public void backtrack(int nums[],int startIndex)
{
if( path.size()>1)
{
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
int [] used = new int[ 201];
for(int i= startIndex;i<nums.length;i++)
{
if(!path.isEmpty()&& nums[i]< path.get(path.size()-1)|| used[nums[i]+100]==1)
continue;
used[nums[i]+100]=1;
path.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums,i+1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
LeetCode 46.全排列
题目讲解
难点
排列问题和组合问题大同小异 最大的不同体现在单层遍历上面,因为 组合上避免元素重复使用 所以需要startIndex 来不停记录走到哪了 而排列问题需要设置used数组 来记录是否该元素已经调用即可
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();// 存放符合条件结果的集合
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();// 用来存放符
boolean [] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
used= new boolean[ nums.length];
if(nums.length==0) return result;
backtrack(nums);
return result;
}
public void backtrack( int[] nums)
{
if(path.size()== nums.length)
{
result.add( new ArrayList<>( path));
return;
}
for( int i=0;i<nums.length;i++)
{
if(used[i]) continue;
used[i]=true;
path.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums);
path.removeLast();
used[i]= false;
}
}
}
LeetCode47.全排列 II
题目讲解
示图
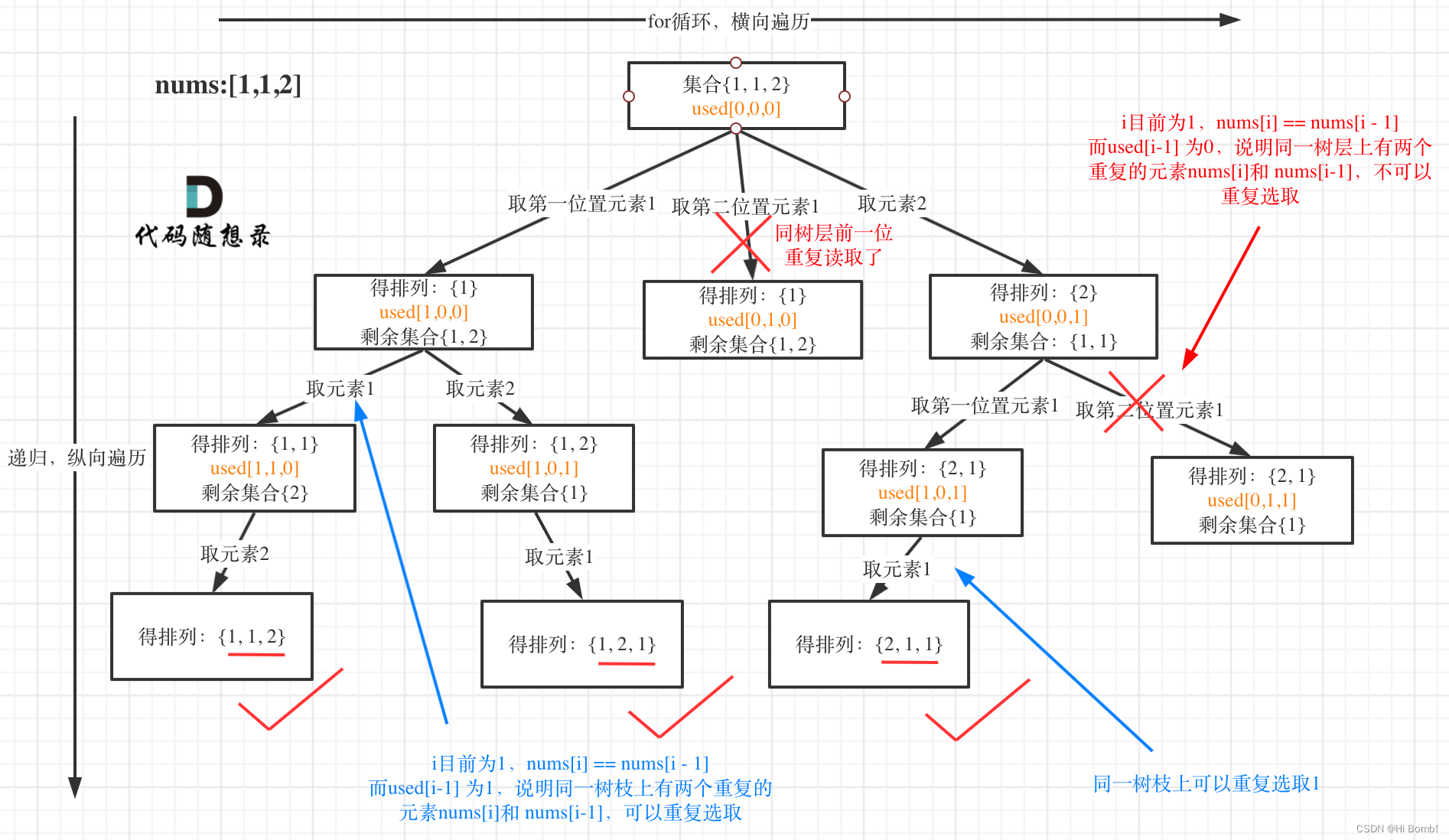
难点
在于如何进行去重 因为 给定的nums[ ]元素中有重复的所以在进行单层遍历的时候要进行剪枝操作
这里涉及到 树枝去重 和树层去重 如果是树层去重,前面用过的,后面就不能用了。而树枝去重不必在意。因为数值去重会使用到相同的元素但是其实只是值相同而已。
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result =new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
Boolean[] used= new Boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(used,false);
Arrays.sort( nums);
backtrack( nums,used);
return result;
}
public void backtrack(int[]nums, Boolean [] used)
{
if(path.size()== nums.length)
{
result.add(new ArrayList<>( path));
return;
}
for(int i= 0;i< nums.length;i++)
{
if(i>0&& nums[i-1]==nums[i]&& used[i-1]== false)
{continue;}
if( used[i]==false)
{
used[i]= true;
path.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums,used);
path.removeLast();
used[i]= false;
}
}
}
}
总结
把自律刻进DNA