文章目录
- 大整数GMP
- 概述
- GMP
- 安装 [cygwin](https://cygwin.com/install.html)
- 安装 gmp
- example
- Eigen
- 基本属性和运算
大整数GMP
概述
GMP
GMP是一个用于任意精度算术的免费库,可对有符号整数、有理数和浮点数进行操作。除了运行GMP的机器的可用内存所暗示的精度外,没有实际的限制。GMP具有丰富的功能集,各功能具有规则的接口。
GMP的主要目标应用是密码学应用与研究、互联网安全应用、代数系统、计算代数研究等。
GMP被精心设计为尽可能快,无论是小操作数还是大操作数。速度是通过使用全字作为基本算术类型,通过使用快速算法,为许多cpu最常见的内循环使用高度优化的汇编代码,以及对速度的总体强调来实现的。
第一个GMP版本于1991年发布。它被不断地开发和维护,大约每年发布一次新版本。
安装 cygwin
下面系列必须安装
1.gcc-core,gcc-g++,mingw-w64-gcc-core,mingw-w64-gcc-c++
2.m4,make
安装 gmp
$ ./configure --enable-cxx
make
make install
- gmp编译选项
–prefix and --exec-prefix
The --prefix option can be used in the normal way to direct GMP to install under a particular tree. The default is ‘/usr/local’. --exec-prefix can be used to direct architecture-dependent files like libgmp.a to a different location. This can be used to sharearchitecture-independent parts like the documentation, but separate
the dependent parts. Note however that gmp.h is architecture-dependent
since it encodes certain aspects of libgmp, so it will be necessary to
ensure both $prefix/include and $exec_prefix/include are available to
the compiler.
–disable-shared, --disable-staticBy default both shared and static libraries are built (where possible), but one or other can be disabled. Shared libraries resultin smaller executables and permit code sharing between separate
running processes, but on some CPUs are slightly slower, having a
small cost on each function call. Native Compilation,
–build=CPU-VENDOR-OSFor normal native compilation, the system can be specified with ‘--build’. By default ‘./configure’ uses the output from running‘./config.guess’. On some systems ‘./config.guess’ can determine the
exact CPU type, on others it will be necessary to give it explicitly.
For example,./configure --build=ultrasparc-sun-solaris2.7 In all cases the ‘OS’ part is important, since it controls how libtool generates shared libraries. Running ‘./config.guess’ is thesimplest way to see what it should be, if you don’t know already.
Cross Compilation, --host=CPU-VENDOR-OSWhen cross-compiling, the system used for compiling is given by ‘--build’ and the system where the library will run is given by‘–host’. For example when using a FreeBSD Athlon system to build
GNU/Linux m68k binaries,./configure --build=athlon-pc-freebsd3.5 --host=m68k-mac-linux-gnu Compiler tools are sought first with the host system type as a prefix. For example m68k-mac-linux-gnu-ranlib is tried, then plainranlib. This makes it possible for a set of cross-compiling tools to
co-exist with native tools. The prefix is the argument to ‘–host’,
and this can be an alias, such as ‘m68k-linux’. But note that tools
don’t have to be set up this way, it’s enough to just have a PATH with
a suitable cross-compiling cc etc.Compiling for a different CPU in the same family as the build system is a form of cross-compilation, though very possibly this wouldmerely be special options on a native compiler. In any case
‘./configure’ avoids depending on being able to run code on the build
system, which is important when creating binaries for a newer CPU
since they very possibly won’t run on the build system.In all cases the compiler must be able to produce an executable (of whatever format) from a standard C main. Although only objectfiles will go to make up libgmp, ‘./configure’ uses linking tests for
various purposes, such as determining what functions are available on
the host system.Currently a warning is given unless an explicit ‘--build’ is used when cross-compiling, because it may not be possible to correctlyguess the build system type if the PATH has only a cross-compiling cc.
Note that the ‘--target’ option is not appropriate for GMP. It’s for use when building compiler tools, with ‘--host’ being where theywill run, and ‘–target’ what they’ll produce code for. Ordinary
programs or libraries like GMP are only interested in the ‘–host’
part, being where they’ll run. (Some past versions of GMP used
‘–target’ incorrectly.) CPU typesIn general, if you want a library that runs as fast as possible, you should configure GMP for the exact CPU type your system uses.However, this may mean the binaries won’t run on older members of the
family, and might run slower on other members, older or newer. The
best idea is always to build GMP for the exact machine type you intend
to run it on.The following CPUs have specific support. See configure.ac for details of what code and compiler options they select. Alpha: ‘alpha’, ‘alphaev5’, ‘alphaev56’, ‘alphapca56’, ‘alphapca57’, ‘alphaev6’, ‘alphaev67’, ‘alphaev68’, ‘alphaev7’ Cray: ‘c90’, ‘j90’, ‘t90’, ‘sv1’ HPPA: ‘hppa1.0’, ‘hppa1.1’, ‘hppa2.0’, ‘hppa2.0n’, ‘hppa2.0w’, ‘hppa64’ IA-64: ‘ia64’, ‘itanium’, ‘itanium2’ MIPS: ‘mips’, ‘mips3’, ‘mips64’ Motorola: ‘m68k’, ‘m68000’, ‘m68010’, ‘m68020’, ‘m68030’, ‘m68040’, ‘m68060’, ‘m68302’, ‘m68360’, ‘m88k’, ‘m88110’ POWER: ‘power’, ‘power1’, ‘power2’, ‘power2sc’ PowerPC: ‘powerpc’, ‘powerpc64’, ‘powerpc401’, ‘powerpc403’, ‘powerpc405’, ‘powerpc505’, ‘powerpc601’, ‘powerpc602’, ‘powerpc603’,‘powerpc603e’, ‘powerpc604’, ‘powerpc604e’, ‘powerpc620’,
‘powerpc630’, ‘powerpc740’, ‘powerpc7400’, ‘powerpc7450’,
‘powerpc750’, ‘powerpc801’, ‘powerpc821’, ‘powerpc823’, ‘powerpc860’,
‘powerpc970’
SPARC: ‘sparc’, ‘sparcv8’, ‘microsparc’, ‘supersparc’, ‘sparcv9’, ‘ultrasparc’, ‘ultrasparc2’, ‘ultrasparc2i’, ‘ultrasparc3’,
‘sparc64’
x86 family: ‘i386’, ‘i486’, ‘i586’, ‘pentium’, ‘pentiummmx’, ‘pentiumpro’, ‘pentium2’, ‘pentium3’, ‘pentium4’, ‘k6’, ‘k62’, ‘k63’,
‘athlon’, ‘amd64’, ‘viac3’, ‘viac32’
Other: ‘arm’, ‘sh’, ‘sh2’, ‘vax’,CPUs not listed will use generic C code. Generic C Build If some of the assembly code causes problems, or if otherwise desired, the generic C code can be selected with the configure–disable-assembly.
Note that this will run quite slowly, but it should be portable and should at least make it possible to get something running if allelse fails. Fat binary, --enable-fat
Using --enable-fat selects a “fat binary” build on x86, where optimized low level subroutines are chosen at runtime according to theCPU detected. This means more code, but gives good performance on all
x86 chips. (This option might become available for more architectures
in the future.) ABIOn some systems GMP supports multiple ABIs (application binary interfaces), meaning data type sizes and calling conventions. Bydefault GMP chooses the best ABI available, but a particular ABI can
be selected. For example./configure --host=mips64-sgi-irix6 ABI=n32 See ABI and ISA, for the available choices on relevant CPUs, and what applications need to do. CC, CFLAGS By default the C compiler used is chosen from among some likely candidates, with gcc normally preferred if it’s present. The usual‘CC=whatever’ can be passed to ‘./configure’ to choose something
different.For various systems, default compiler flags are set based on the CPU and compiler. The usual ‘CFLAGS="-whatever"’ can be passed to‘./configure’ to use something different or to set good flags for
systems GMP doesn’t otherwise know.The ‘CC’ and ‘CFLAGS’ used are printed during ‘./configure’, and can be found in each generated Makefile. This is the easiest way tocheck the defaults when considering changing or adding something.
Note that when ‘CC’ and ‘CFLAGS’ are specified on a system supporting multiple ABIs it’s important to give an explicit‘ABI=whatever’, since GMP can’t determine the ABI just from the flags
and won’t be able to select the correct assembly code.If just ‘CC’ is selected then normal default ‘CFLAGS’ for that compiler will be used (if GMP recognises it). For example ‘CC=gcc’ canbe used to force the use of GCC, with default flags (and default ABI).
CPPFLAGSAny flags like ‘-D’ defines or ‘-I’ includes required by the preprocessor should be set in ‘CPPFLAGS’ rather than ‘CFLAGS’.Compiling is done with both ‘CPPFLAGS’ and ‘CFLAGS’, but preprocessing
uses just ‘CPPFLAGS’. This distinction is because most preprocessors
won’t accept all the flags the compiler does. Preprocessing is done
separately in some configure tests. CC_FOR_BUILDSome build-time programs are compiled and run to generate host-specific data tables. ‘CC_FOR_BUILD’ is the compiler used forthis. It doesn’t need to be in any particular ABI or mode, it merely
needs to generate executables that can run. The default is to try the
selected ‘CC’ and some likely candidates such as ‘cc’ and ‘gcc’,
looking for something that works.No flags are used with ‘CC_FOR_BUILD’ because a simple invocation like ‘cc foo.c’ should be enough. If some particular options arerequired they can be included as for instance ‘CC_FOR_BUILD=“cc
-whatever”’. C++ Support, --enable-cxxC++ support in GMP can be enabled with ‘--enable-cxx’, in which case a C++ compiler will be required. As a convenience‘–enable-cxx=detect’ can be used to enable C++ support only if a
compiler can be found. The C++ support consists of a library
libgmpxx.la and header file gmpxx.h (see Headers and Libraries).A separate libgmpxx.la has been adopted rather than having C++ objects within libgmp.la in order to ensure dynamic linked C programsaren’t bloated by a dependency on the C++ standard library, and to
avoid any chance that the C++ compiler could be required when linking
plain C programs.libgmpxx.la will use certain internals from libgmp.la and can only be expected to work with libgmp.la from the same GMP version. Futurechanges to the relevant internals will be accompanied by renaming, so
a mismatch will cause unresolved symbols rather than perhaps
mysterious misbehaviour.In general libgmpxx.la will be usable only with the C++ compiler that built it, since name mangling and runtime support are usuallyincompatible between different compilers. CXX, CXXFLAGS
When C++ support is enabled, the C++ compiler and its flags can be set with variables ‘CXX’ and ‘CXXFLAGS’ in the usual way. The defaultfor ‘CXX’ is the first compiler that works from a list of likely
candidates, with g++ normally preferred when available. The default
for ‘CXXFLAGS’ is to try ‘CFLAGS’, ‘CFLAGS’ without ‘-g’, then for g++
either ‘-g -O2’ or ‘-O2’, or for other compilers ‘-g’ or nothing.
Trying ‘CFLAGS’ this way is convenient when using ‘gcc’ and ‘g++’
together, since the flags for ‘gcc’ will usually suit ‘g++’.It’s important that the C and C++ compilers match, meaning their startup and runtime support routines are compatible and that theygenerate code in the same ABI (if there’s a choice of ABIs on the
system). ‘./configure’ isn’t currently able to check these things very
well itself, so for that reason ‘–disable-cxx’ is the default, to
avoid a build failure due to a compiler mismatch. Perhaps this will
change in the future.Incidentally, it’s normally not good enough to set ‘CXX’ to the same as ‘CC’. Although gcc for instance recognises foo.cc as C++ code,only g++ will invoke the linker the right way when building an
executable or shared library from C++ object files. Temporary Memory,
–enable-alloca=GMP allocates temporary workspace using one of the following three methods, which can be selected with for instance‘–enable-alloca=malloc-reentrant’.
‘alloca’ - C library or compiler builtin. ‘malloc-reentrant’ - the heap, in a re-entrant fashion. ‘malloc-notreentrant’ - the heap, with global variables. For convenience, the following choices are also available. ‘--disable-alloca’ is the same as ‘no’. ‘yes’ - a synonym for ‘alloca’. ‘no’ - a synonym for ‘malloc-reentrant’. ‘reentrant’ - alloca if available, otherwise ‘malloc-reentrant’. This is the default. ‘notreentrant’ - alloca if available, otherwise ‘malloc-notreentrant’. alloca is reentrant and fast, and is recommended. It actually allocates just small blocks on the stack; larger ones usemalloc-reentrant.
‘malloc-reentrant’ is, as the name suggests, reentrant and thread safe, but ‘malloc-notreentrant’ is faster and should be used ifreentrancy is not required.
The two malloc methods in fact use the memory allocation functions selected by mp_set_memory_functions, these being malloc and friends bydefault. See Custom Allocation.
An additional choice ‘--enable-alloca=debug’ is available, to help when debugging memory related problems (see Debugging). FFTMultiplication, --disable-fft
By default multiplications are done using Karatsuba, 3-way Toom, higher degree Toom, and Fermat FFT. The FFT is only used on large tovery large operands and can be disabled to save code size if desired.
Assertion Checking, --enable-assertThis option enables some consistency checking within the library. This can be of use while debugging, see Debugging. ExecutionProfiling, --enable-profiling=prof/gprof/instrument
Enable profiling support, in one of various styles, see Profiling. MPN_PATH Various assembly versions of each mpn subroutines are provided. For a given CPU, a search is made through a path to choose a versionof each. For example ‘sparcv8’ has
MPN_PATH="sparc32/v8 sparc32 generic" which means look first for v8 code, then plain sparc32 (which is v7), and finally fall back on generic C. Knowledgeable users withspecial requirements can specify a different path. Normally this is
completely unnecessary.
example
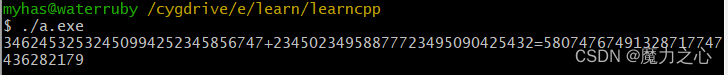
$ g++ main.cpp -lgmpxx -lgmp -I/cygdrive/d/gmp-6.3.0 -L/cygdrive/d/gmp-6.3.0/.libs
#include <iostream>
#include "gmp.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
mpz_t a, b, c;
mpz_init(a);
mpz_init(b);
mpz_init(c);
mpz_set_str(a, "34624532532450994252345856747", 10);
mpz_set_str(b, "23450234958877723495090425432", 10);
mpz_add(c, a, b);
gmp_printf("%Zd+%Zd=%Zd\n", a,b,c);
mpz_clear(a);
mpz_clear(b);
mpz_clear(c);
return 0;
}
Eigen
基本属性和运算
- 代码
#include <iostream>
#include "e:/eigen/Eigen/Dense"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Eigen::Matrix2d mat;
mat << 10, 20,
30, 40;
cout << "Here is mat.sum(): " << mat.sum() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.prod(): " << mat.prod() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.mean(): " << mat.mean() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.minCoeff(): " << mat.minCoeff() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.maxCoeff(): " << mat.maxCoeff() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.trace(): " << mat.trace() << endl;
}
- 函数功能
sum():求元素之和
prod() :求元素之积
prod() :求元素平均值
minCoeff() :最小元素
maxCoeff() :最大元素
trace() : the sum of the coefficients on the main diagonal.主对角线之和 - 运行结果
Here is mat.sum(): 100
Here is mat.prod(): 240000
Here is mat.mean(): 25
Here is mat.minCoeff(): 10
Here is mat.maxCoeff(): 40
Here is mat.trace(): 50
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.323 s
Press any key to continue.








![【2024最新华为OD-C/D卷试题汇总】[支持在线评测] 数字排列游戏(200分) - 三语言AC题解(Python/Java/Cpp)](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/32042c370ca64534b8347252bf707ac2.png)