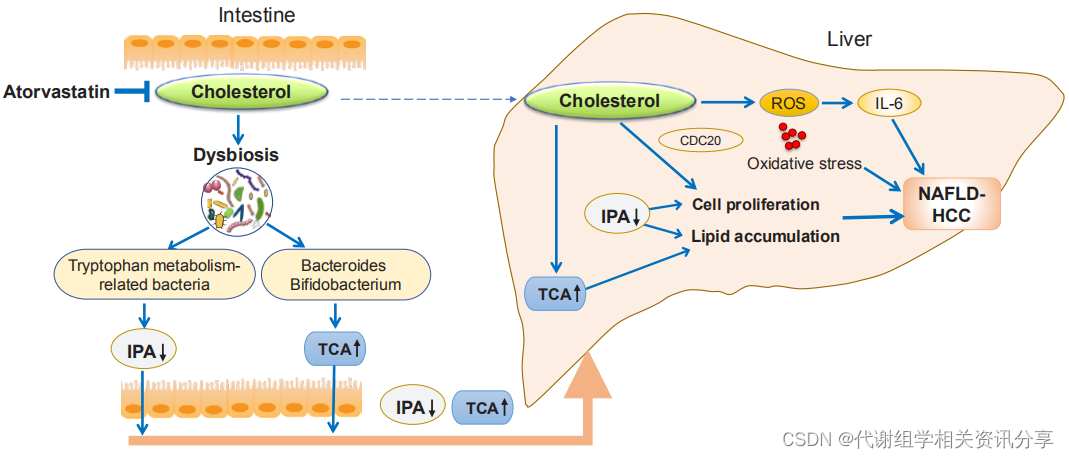
2022年8月,58同城TEG-AI Lab语音技术团队完成了WeNet端到端语音识别的大规模落地,替换了此前基于Kaldi的系统,并针对业务需求对识别效果和推理速度展开优化,取得了优异的效果,当前录音文件识别引擎处理语音时长达1000万小时/年,流式语音识别引擎支持语音对话量超过5000万次/年,详细工作可以参考《58同城:WeNet端到端语音识别大规模落地方案[1]》。
在优化工作中,我们复现了Efficient Conformer[2]模型,在实际场景数据上,与Kaldi最优模型相比,识别效果上CER绝对降低3%,解码性能提升61%。与Conformer相比,识别效果上CER从10.01%降低至9.30%,解码性能提升10%,结合int8量化,解码性能可提升60%。我们也在AISHELL-1公开数据集上进行了评测,CER为4.56%(No LM)。模型代码已开源至WeNet[3]。
本文主要介绍我们对Efficient Conformer的复现工作,包含:模型介绍、模型实现、流式推理支持以及相关实验结果。
01模型介绍
Conformer结构在语音识别领域取得了非常好的效果,已经被广泛应用于各种模型架构中。为了降低Conformer的计算复杂度、加快推理速度、减少所需的计算资源,Efficient Conformer对Conformer做出改进,提出了几种高效模型结构。实验结果证明,Efficient Conformer相比Conformer模型取得了更好的识别效果,以及更快的训练和解码速度。
Efficient Conformer的主要改进点如下:
-
Progressive Downsampling:Efficient Conformer Block在卷积模块中增加了下采样操作,降低时间维度,从而减小下采样后的(Efficient) Conformer Block的计算复杂度;
-
Grouped Attention:Efficient Conformer Block改进了Multi-Head Self Attention,增加grouped操作将自注意力模块的计算复杂度从O(n2d)降低为O(n2d/g),n为时间维度,d为隐层维度,g为group_size。
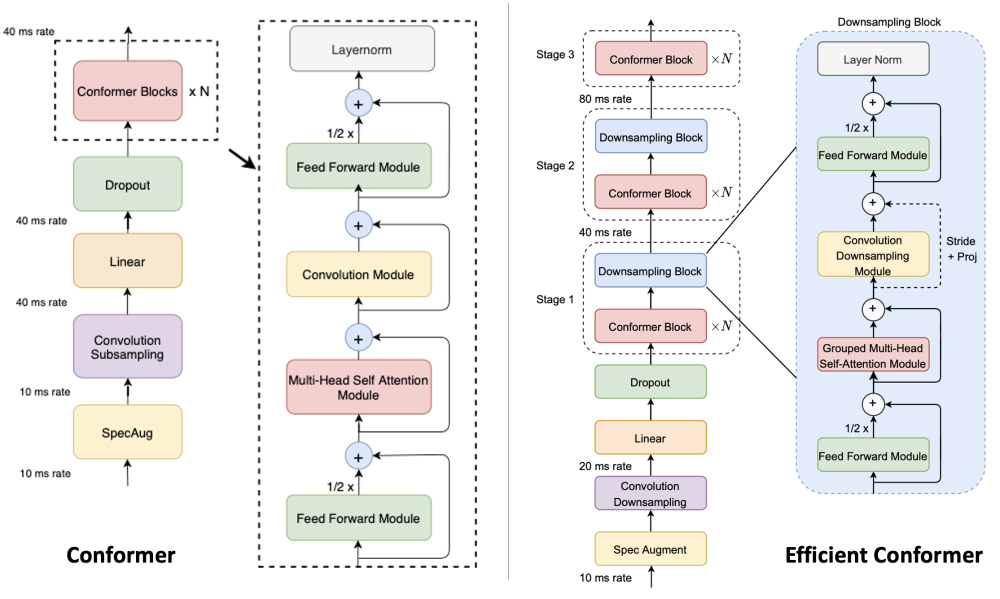
1.1 Progressive Downsampling
Efficient Conformer Encoder不同于典型Conformer,Conformer Block之前的下采样层使用1/2 subsampling(conv2d2)替换原始Conformer的1/4 subsampling(conv2d),其后一共包含三个stage,如上图右侧所示。前两个stage在N个Conformer Block之后叠加Downsampling Block,沿着时间维度进行下采样;最后一个stage叠加N个Conformer Block,不再叠加Downsampling Block。
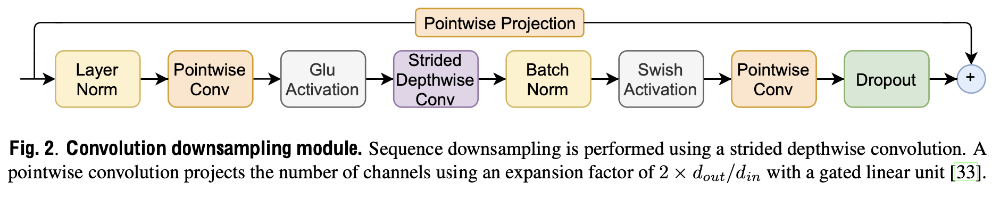
Downsampling Block结构如下图所示,实现方式为将Conformer Block中的DepthwiseConv对应的stride设置为大于1的值,从而实现时间维度下采样。因为下采样后输出的shape比输入的shape小,因此残差模块需要增加Pointwise Projection模块将输入和输出映射到相同的维度。
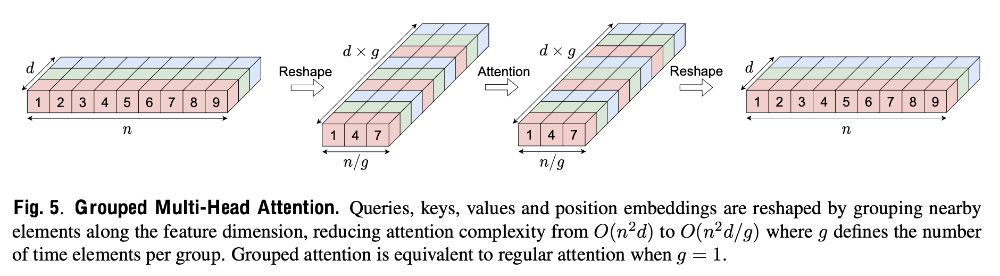
1.2 Grouped Multi-head Self-Attention(Grouped MHSA)
传统Multi-head Self-Attention模块中Q、K、V大小为(n, d),该模块的计算复杂度为O(n2d);Grouped MHSA 首先将Q、K、V的维度变换为(n/g, d*g),其中g为group_size,再进行attention计算,最后将维度变换为原始的(n, d)。变换后,注意力模块的计算复杂度可降低为O(n2d/g)。
此外,作者还提出了Stride Multi-Head Self-Attention、
Relative Multi-Head Self-Attention 和 Local Multi-Head Self-Attention 等高效MHSA结构,感兴趣的朋友可以查阅原论文和代码。
02 模型实现
我们参考Efficient Conformer的代码[4]在WeNet开源项目上进行了复现,即在wenet文件夹下增加了efficient_conformer模块。
2022年12月26日我们向WeNet开源项目提交PR,贡献代码1426行,2023年1月4日被WeNet正式合并,主要开发者:周维、王亚如、李咏泽。
主要模块的实现细节如下:
2.1 Strided Convolution
(1)在depthwise_conv模块初始化定义时传入下采样步长stride参数,实现沿时间维度的下采样(convolution.py)。
self.depthwise_conv = nn.Conv1d(channels,channels,kernel_size,stride=stride, # for depthwise_conv in StrideConvpadding=padding,groups=channels,bias=bias,)
(2)mask同步下采样(convolution.py):卷积模块增加下采样后,用于返回的输出数据的shape减小,对应返回的mask也应进行相同stride的下采样,以保持输出数据和mask的匹配。
# mask batch paddingif mask_pad.size(2) > 0: # time > 0if mask_pad.size(2) != x.size(2):mask_pad = mask_pad[:, :, ::self.stride]x.masked_fill_(~mask_pad, 0.0)
(3)带pointwise projection layer的残差结构(encoder_layer.py):由于卷积模块增加了下采样,导致输出维度小于输入维度,因此卷积模块对应的残差模块需要增加下采样操作。
# add pointwise_conv for efficient conformerif self.pointwise_conv_layer is not None:residual = residual.transpose(1, 2)residual = self.pointwise_conv_layer(residual)residual = residual.transpose(1, 2)assert residual.size(0) == x.size(0)assert residual.size(1) == x.size(1)assert residual.size(2) == x.size(2)
2.2 Grouped Multi-Head Self-Attention
(1)初始化中传入group_size参数,并重新定义位置编码偏置矩阵大小(attention.py)。
class GroupedRelPositionMultiHeadedAttention(MultiHeadedAttention):def __init__(self, n_head, n_feat, dropout_rate, group_size=3):"""Construct an RelPositionMultiHeadedAttention object."""super().__init__(n_head, n_feat, dropout_rate)# linear transformation for positional encodingself.linear_pos = nn.Linear(n_feat, n_feat, bias=False)self.group_size = group_sizeself.d_k = n_feat // n_head # for GroupedAttentionself.n_feat = n_feat# these two learnable bias are used in matrix c and matrix d# as described in https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860 Section 3.3self.pos_bias_u = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(self.h, self.d_k * self.group_size))self.pos_bias_v = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(self.h, self.d_k * self.group_size))torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.pos_bias_u)torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.pos_bias_v)
(2)增加padding和reshape函数pad4group(attention.py):对Q、K、V、P在时间维度上根据group_size进行padding,保证可被group_size整除;padding会进行补0操作,不丢弃原始数据;padding之后即可按照group_size对Q、K、V、P进行维度变换;由于维度变换之后时间维度降低,同步地mask也需要降维,此处直接对mask下采样即可。
def pad4group(self, Q, K, V, P, mask, group_size: int = 3):# Compute Overflowsoverflow_Q = Q.size(2) % group_sizeoverflow_KV = K.size(2) % group_sizepadding_Q = (group_size - overflow_Q) * int(overflow_Q // (overflow_Q + 0.00000000000000001))padding_KV = (group_size - overflow_KV) * int(overflow_KV // (overflow_KV + 0.00000000000000001))batch_size, _, seq_len_KV, _ = K.size()# Input Padding (B, T, D) -> (B, T + P, D)Q = F.pad(Q, (0, 0, 0, padding_Q), value=0.0)K = F.pad(K, (0, 0, 0, padding_KV), value=0.0)V = F.pad(V, (0, 0, 0, padding_KV), value=0.0)if mask is not None and mask.size(2) > 0 : # time2 > 0:mask = mask[:, ::group_size, ::group_size]Q = Q.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, self.h, self.d_k * group_size).transpose(1, 2)K = K.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, self.h, self.d_k * group_size).transpose(1, 2)V = V.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, self.h, self.d_k * group_size).transpose(1, 2)# process pos_embP_batch_size = P.size(0)overflow_P = P.size(1) % group_sizepadding_P = group_size - overflow_P if overflow_P else 0P = F.pad(P, (0, 0, 0, padding_P), value=0.0)P = P.view(P_batch_size, -1, self.h, self.d_k * group_size).transpose(1, 2)return Q, K, V, P, mask, padding_Q
(3)forward_attention函数中(attention.py),在attention计算完毕后,输出数据需要变换为padding之后的维度,再去掉padding部分,截取有效输出。
# n_feat!=h*d_k may be happened in GroupAttentionx = (x.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(n_batch, -1, self.n_feat)) # (batch, time1, d_model)if padding_q is not None:# for GroupedAttention in efficent conformerx = x[:, :x.size(1) - padding_q]
2.3 其它细节实现
(1)pointwise projection(encoder.py)
由于卷积模块进行了下采样,导致输入和输出维度不匹配,残差模块需要增加pointwise projection layer或下采样层将输入和输出维度进行统一。该模块在实现上有多种选择,比如可以使用卷积下采样或Pooling下采样。
我们在实验中对比了卷积下采样(kernel=3, stride=2, causal=true)和Pooling下采样(AvgPool1d)两种实现方式。实验结果显示,卷积下采样效果不如Pooling;且考虑到卷积的流式实现需要设置causal为true、并开辟和维护cache,而Pooling没有参数、不需要cache,简单适配即可直接用于流式训练和解码,最终我们采用AvgPool1d实现卷积模块的残差下采样。
# conformer module definitionif i in self.stride_layer_idx:# conformer block with downsamplingconvolution_layer_args_stride = (output_size, self.cnn_module_kernels[index], activation,cnn_module_norm, causal, True, self.stride[index])layers.append(StrideConformerEncoderLayer(output_size,encoder_selfattn_layer(*encoder_selfattn_layer_args),positionwise_layer(*positionwise_layer_args),positionwise_layer(*positionwise_layer_args) if macaron_style else None,convolution_layer(*convolution_layer_args_stride) if use_cnn_module else None,torch.nn.AvgPool1d(kernel_size=self.stride[index], stride=self.stride[index],padding=0, ceil_mode=True,count_include_pad=False), # pointwise_conv_layerdropout_rate,normalize_before,concat_after,))
(2)不同encoder layer attention维度不变(encoder.py)
原始论文中,为了平衡下采样前后不同层的计算量,不同stage的Attention维度不同,且逐渐增大;我们的实现中为了简单方便灵活、节约计算资源、减小计算量,所有layer的Attention维度均保持一致;仅使用Grouped MHSA对不同layer的计算复杂度进行平衡,可以灵活设计添加Grouped MHSA模块的位置及group_size。通常选择连续对Downsampling Block之前的N层增加grouped操作。
03流式推理
WeNet框架在流式推理时调用encoder中的forward_chunk接口,音频被划分为chunk_size大小输入到模型,在Conformer架构下实现流式需要记录Attention的K和V作为下一个chunk模型推理的att_cache。另外,流式场景下depthwize_conv通常使用因果卷积(Casual Convolution),因此需要记录隐变量的后 kernel_size-1 维向量作为cnn_cache,以便在下一个chunk卷积计算时使用,如下图所示。
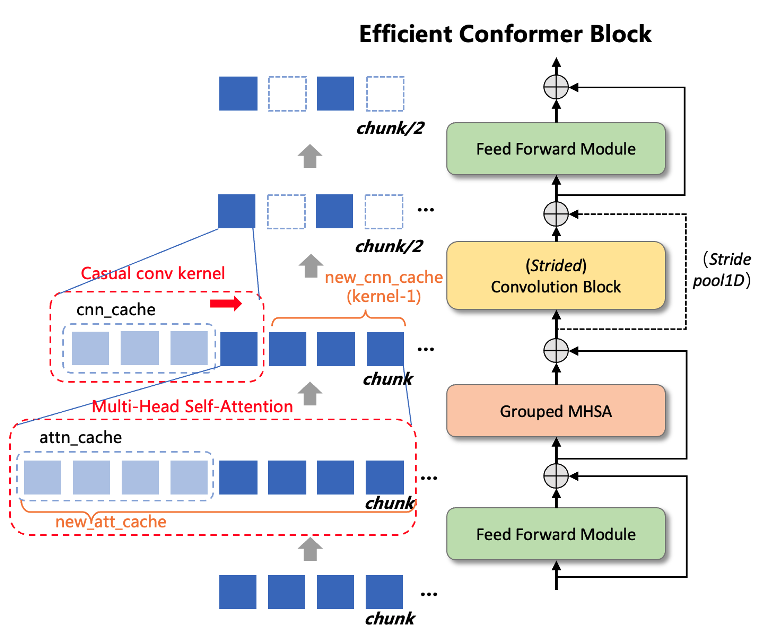
而Efficient Conformer在Strided Convolution层会对输入向量在时间维度做下采样操作,导致cache在时间维度缩短,为了保证接口不变,需要在forward_chunk中对每层的cache做适当的“填充”。
我们首先参考Squeezeformer的实现方式,用以下函数计算每层的下采样倍数(encoder.py)。
def calculate_downsampling_factor(self, i: int) -> int:factor = 1for idx, stride_idx in enumerate(self.stride_layer_idx):if i > stride_idx:factor *= self.stride[idx]return factor
对于att_cache,我们在时间维度重复factor倍数,并在使用att_cache时按照对应的factor进行下采样(encoder.py)。
for i, layer in enumerate(self.encoders):factor = self.calculate_downsampling_factor(i)xs, _, new_att_cache, new_cnn_cache = layer(xs, att_mask, pos_emb,mask_pad=mask_pad,att_cache=att_cache[i:i + 1, :, ::factor, :],cnn_cache=cnn_cache[i, :, :, :]if cnn_cache.size(0) > 0 else cnn_cache)# shape(new_att_cache) = [batch, head, time2, outdim]new_att_cache = new_att_cache[:, :, next_cache_start // factor:, :]# use repeat_interleave to new_att_cachenew_att_cache = new_att_cache.repeat_interleave(repeats=factor, dim=2)
对于cnn_cache,则直接padding到 kernel_size-1 即可(encoder.py)。
# shape(new_cnn_cache) = [1, batch, outdim, cache_t2]new_cnn_cache = new_cnn_cache.unsqueeze(0)# padding new_cnn_cache to cnn.lorder for casual convolutionnew_cnn_cache = F.pad(new_cnn_cache,(self.cnn_module_kernel - 1 - new_cnn_cache.size(3), 0))
由于Grouped MHSA实际为reshape操作,所以new_att_cache的记录需要在reshape操作之前进行,这样可以保证cache的维度与常规MHSA一致(attention.py)。
if cache.size(0) > 0:# use attention cachekey_cache, value_cache = torch.split(cache, cache.size(-1) // 2, dim=-1)k = torch.cat([key_cache, k], dim=2)v = torch.cat([value_cache, v], dim=2)new_cache = torch.cat((k, v), dim=-1)# May be k and p does not match. eg. time2=18+18/2=27 > mask=36/2=18if mask is not None and mask.size(2) > 0:time2 = mask.size(2)k = k[:, :, -time2:, :]v = v[:, :, -time2:, :]# q k v p: (batch, head, time1, d_k)q, k, v, p, mask, padding_q = self.pad4group(q, k, v, p, mask, self.group_size)
forward_chunk接口会输入offset用于计算流式模式下的相对位置编码,由于Efficient Conformer会对时间维度下采样,导致输出与输入维度不匹配,因此通过y.size(1)计算的offset为下采样后的值,需要在使用时按照模型整体下采样倍数恢复(encoder.py)。
# using downsampling factor to recover offsetoffset *= self.calculate_downsampling_factor(self.num_blocks + 1)
04实验结果
使用Efficient Conformer,只需要在配置文件中配置encoder参数即可。
encoder: efficientConformer在自有场景下测试,Efficient Conformer获得了好于Conformer的效果,具体可参考文章[1]。
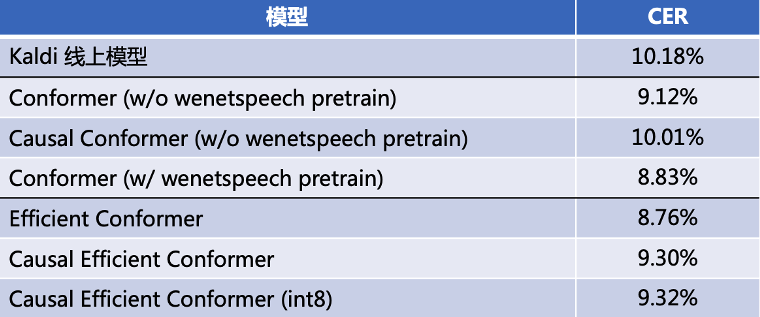
同时我们在AISHELL-1上进行了两版模型实验。V1为我们线上使用的结构,即在Encoder的前1/3处使用Strided Convolution下采样(共12层),前4层均为Grouped MHSA结构,同时cnn_module_kernel会在Strided Convolution之后缩减同样倍数(如15->7),前置下采样使用1/4 subsampling的conv2d。V1 large将output维度从256增加至512,同时cnn_module_kernel从15增加至31。
efficient_conf:stride_layer_idx: [3] # layer id with StrideConvstride: [2] # stride size of each StrideConvgroup_layer_idx: [0, 1, 2, 3] # layer id with GroupedAttentiongroup_size: 3 # group size of every GroupedAttention layerstride_kernel: true # true: recompute cnn kernels with stride
V2符合原始Efficient Conformer论文结构,前置下采样为1/2 subsampling的conv2d2,在Encoder的1/3和2/3处做两次下采样,cnn_module_kernel固定不变。
efficient_conf:stride_layer_idx: [3, 7] # layer id with StrideConvstride: [2, 2] # stride size of each StrideConvgroup_layer_idx: [3, 7] # layer id with GroupedAttentiongroup_size: 3 # group size of every GroupedAttention layerstride_kernel: false # true: recompute cnn kernels with stride
在不使用语言模型的情况下效果如下:
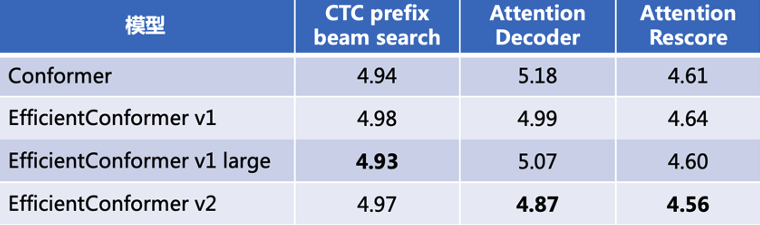
可见,在WeNet项目当前已合并的模型中(截止2023-1-9),Efficient Conformer在AISHELL-1公开数据集上目前最优的CER为4.56%,超过Conformer效果4.61%。
后续计划:
-
进一步完善开源数据上的测试效果;
-
支持Efficient Conformer的ONNX导出,和GPU流式部署。
参考文献
[1] 58同城:WeNet端到端语音识别大规模落地方案
[2] Efficient Conformer: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2109.01163.pdf
[3] WeNet Efficient Conformer PR:https://github.com/wenet-e2e/wenet/pull/1636
[4] Efficient Conformer Code: https://github.com/burchim/EfficientConformer
作者介绍:
-
周维,58同城TEG-AI Lab算法架构师,语音算法部负责人,负责语音识别、语音合成算法研发。
-
王亚如,58同城TEG-AI Lab语音算法部算法高级工程师,主要负责端到端语音识别算法研发。
58同城AI Lab部门简介
58同城AI Lab隶属TEG技术工程平台群,旨在推动AI技术在58同城的落地,打造AI中台能力,以提高前台业务人效、收入和用户体验。