暑期选择了java减轻下学期的课量,在本科期间就已经学过Java了,现在写一些笔记作为复习。
The Goal
• To understand the Java runtime environment.
• To know Java’s terminologies, advantages and characteristics.
• To recognize the form of identifiers.
• To learn Java primitive data types and object types.
• To become familiar with Java programming style and naming conventions.
• To create, compile, and run a simple Java program.
• To understand method overloading.
• To determine the scope of local variables.
• To understand Array of Java.
• To recognize the multidimensional form of arrays.
• To learn common String operations in Java.
• To use the Character class to process a single character.
• To use the StringBuffer class to process flexible strings.
• To learn how to pass strings to the main method from the command line.
Why Java
- Simple and Object-oriented
- Distributed
- Interpreted,portable and architecture-neutral
- Robust and secure
- Dynamic
Java is OO Language
OO encourages the use of object to model or represent program
At here,class(definition of objects),is a blueprint for building objects or a construct which you can specify the features.
Data field and method defined in a class.

Modifier and method
- A modifier is used to specify the properties of the data,
methods, and classes. - Some common modifiers are public, protected, private, final,
static and abstract.
Identifiers
letters, digits,_ and $
1:cannot be start with digits
2:cannot be reserved word
3:cannot be true/false/or null
The process
1:Declaration(int x;)
2:Assignment(x=1;)
3:combine 1 and 2 ->Initialization(int x=1;)
Constants
We can use final to decorate the variable
对于一个final变量,如果是基本数据类型的变量,则其数值一旦在初始化之后便不能更改;如果是引用类型的变量,则在对其初始化之后便不能再让其指向另一个对象。
Comments
- // single line
- /* multiple
lines
*/ - /** multiple
line
*/
Naming Conventions
- variable and method names:aaaBbb
- class names:AaaBbb
- constants: AB(all Upper letter)
Passing Arguments(传参)
here parameters:形式参数
arguments:实际参数
There are two ways to pass an grgument
1:passed by value(all primitive data belongs this type)
2:passed by reference(objects are passed by reference)
Overloading methods
Here,you should know firstly:
Method signature=method name+parameter lists
So,the Overloading method means:Two methods can be declared with different signatures, hence using same name but different parameter lists is allowed(test)
Scope of Variables
- Data field(of class):inside a class and outside a method
- local variable(of method):inside a method
Arrays
- This is a data structure
- Java Array is an object which is a reference type, no matter what type of elements it contains
- An array’s size is fixed once created
-> arrayRefVar.length - Default value on creation
-> 0 for the numeric primitive data types,
-> ‘\u0000’ for char types, and
-> false for boolean types. - Array’s elements accessed through index
-> array indices are 0-based - Cannot same with int creation and assignment

should:

For the two-dimensional arrays:

array.length:->row
array[0].length:->col
The string class

- construct a string:
- String message =“welcome to Java”
- String message=new String(“welcom……”)
- String s=new String();
(String object is immutable )
- Finding length:
- message.length()(returns 7)
- Concatenating Strings:
- concat()/or is same

- Extracting Substrings
- substring(start, end)returns a string from start to (end-1)
- Comparing Strings
- Using equals()/**==**operator to compare two strings
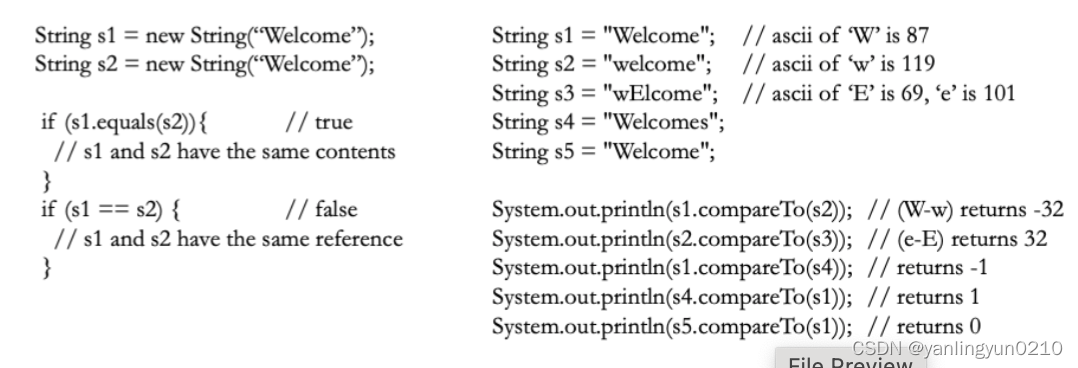
- Converting Strings
- The contents of a string cannot be changed once the string is created.But you can convert a string to a new string using the following methods

- Searching a character or a substring
- To search forward, use indexOf();
- To search backward, use lastIndexOf();

- Converting Other Types to Strings
- use valueOf()
The character class
- To construct a Character object: Character charObject=new Character(‘b’);
- To compare two characters:

The StringBuffer Class(Thread Safe)
- The StringBuffer class is an alternative to the String class. In general, a StringBuffer can be used wherever a string is used (drop-in replacement)
- StringBuffer is mutable, hence more flexible than String
public class StringBufferDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Hello");
sb.append(" World");
sb.insert(5, ",");
sb.delete(5, 6);
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
Input:Hello, World
Appending Contents to StringBuffer

Passing Parameters to Main Method
- Method1:

类A的main方法:
首先,定义了一个字符串数组strings,其中包含三个城市名称:“New York”、“Boston"和"Atlanta”。
然后,调用类B的main方法,并将strings数组作为参数传递给它。
类B的main方法:
接受一个字符串数组args作为参数。
使用一个for循环遍历args数组,并将每个元素打印到控制台。
执行流程
当你运行类A的main方法时,执行流程如下:
类A的main方法被调用。
创建一个字符串数组strings,内容为{“New York”, “Boston”, “Atlanta”}。
调用类B的main方法,并将strings数组传递给它。
类B的main方法开始执行,接收传递过来的strings数组作为参数args。
类B的main方法遍历args数组,并逐个打印数组中的元素。
输出结果
运行类A的main方法时,控制台将输出:
New York
Boston
Atlanta
总结
类A的main方法创建并初始化了一个字符串数组,然后将其传递给类B的main方法。
类B的main方法接收这个数组并打印其内容。
这种调用方式展示了如何在Java中从一个类的main方法调用另一个类的main方法,并传递参数。
Static and non-static Object context
在 Java 中,static 和 non-static 是两个关键字,用于定义类成员变量和方法。它们之间的主要区别如下:
- 内存分配:
static成员变量和方法是在类加载时分配内存,而non-static成员变量和方法是在实例化对象时分配内存。 - 访问方式:
static成员变量和方法可以通过类名直接访问,而non-static成员变量和方法只能通过实例化对象访问。 - 初始化:
static成员变量和方法只会被初始化一次,而non-static成员变量和方法每次实例化对象时都会被初始化。 - 作用域:
static成员变量和方法的作用域是整个类,而non-static成员变量和方法的作用域是实例化对象。 - 用途:
static成员变量和方法通常用于表示类级别的属性和方法,如常量、工具方法等,而non-static成员变量和方法通常用于表示对象级别的属性和方法,如实例变量、实例方法等。
下面是一个示例代码,演示了 static 和 non-static 成员变量和方法的用法:
public class MyClass {
// static 成员变量
static int staticVar = 0;
// non-static 成员变量
int nonStaticVar = 0;
// static 方法
static void staticMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a static method.");
}
// non-static 方法
void nonStaticMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a non-static method.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 直接访问 static 成员变量和方法
System.out.println(MyClass.staticVar);
MyClass.staticMethod();
// 实例化对象后访问 non-static 成员变量和方法
MyClass obj = new MyClass();
System.out.println(obj.nonStaticVar);
obj.nonStaticMethod();
}
}
输出结果为:
0
This is a static method.
0
This is a non-static method.
总之,static 和 non-static 是 Java 中两个重要的关键字,它们分别用于定义类级别和对象级别的属性和方法。根据具体的需求,我们可以选择使用它们中的一个或多个来实现我们的程序逻辑。