Meta-Prompt 实现
摘要:
本文介绍了 Noah Goodman 提出的 Meta-Prompt 方法的 LangChain 实现,该方法用于构建能够自我反思和改进的智能代理。
核心思想:
Meta-Prompt 的核心思想是促使代理反思自己的性能,并修改自己的指令。
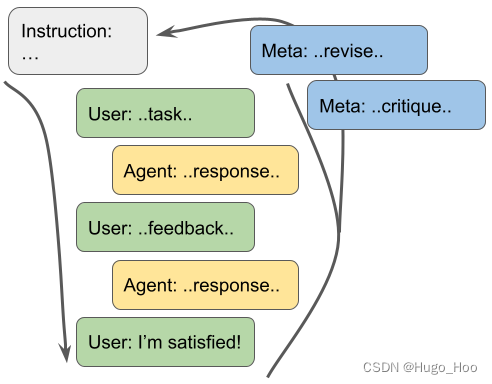
原始博客文章描述:
代理是一个简单的循环,开始时没有任何指令,并遵循以下步骤:
- 与用户进行对话,用户可能提供请求、指令或反馈。
- 在每个对话周期结束时,使用 Meta-Prompt 生成自我批评和新的指令。
该系统唯一的固定指令(我称之为元提示)是管理代理指令修订的元提示。除了每次为自己修改的指令外,智能体在情节之间没有任何记忆。尽管它很简单,但该代理可以随着时间的推移进行学习,并通过将有用的细节纳入其指令来自我改进。
以下是 Meta-Prompt 的具体实现:
我们定义了两条链。一个充当 Assistant ,另一个是批评 Assistant 性能并修改 Assistant 指令的“元链”。
# 导入必要的 LangChain 和 OpenAI 库
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferWindowMemory
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import OpenAI
def initialize_chain(instructions, memory=None):
if memory is None:
memory = ConversationBufferWindowMemory()
memory.ai_prefix = "Assistant"
template = f"""
Instructions: {instructions}
{{{memory.memory_key}}}
Human: {{human_input}}
Assistant:"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["history", "human_input"], template=template
)
chain = LLMChain(
llm=OpenAI(temperature=0),
prompt=prompt,
verbose=True,
memory=ConversationBufferWindowMemory(),
)
return chain
def initialize_meta_chain():
meta_template = """
Assistant has just had the below interactions with a User. Assistant followed their "Instructions" closely. Your job is to critique the Assistant's performance and then revise the Instructions so that Assistant would quickly and correctly respond in the future.
####
{chat_history}
####
Please reflect on these interactions.
You should first critique Assistant's performance. What could Assistant have done better? What should the Assistant remember about this user? Are there things this user always wants? Indicate this with "Critique: ...".
You should next revise the Instructions so that Assistant would quickly and correctly respond in the future. Assistant's goal is to satisfy the user in as few interactions as possible. Assistant will only see the new Instructions, not the interaction history, so anything important must be summarized in the Instructions. Don't forget any important details in the current Instructions! Indicate the new Instructions by "Instructions: ...".
"""
meta_prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["chat_history"], template=meta_template
)
meta_chain = LLMChain(
llm=OpenAI(temperature=0),
prompt=meta_prompt,
verbose=True,
)
return meta_chain
def get_chat_history(chain_memory):
memory_key = chain_memory.memory_key
chat_history = chain_memory.load_memory_variables(memory_key)[memory_key]
return chat_history
def get_new_instructions(meta_output):
delimiter = "Instructions: "
new_instructions = meta_output[meta_output.find(delimiter) + len(delimiter) :]
return new_instructions
def main(task, max_iters=3, max_meta_iters=5):
failed_phrase = "task failed"
success_phrase = "task succeeded"
key_phrases = [success_phrase, failed_phrase]
instructions = "None"
for i in range(max_meta_iters):
print(f"[Episode {i+1}/{max_meta_iters}]")
chain = initialize_chain(instructions, memory=None)
output = chain.predict(human_input=task)
for j in range(max_iters):
print(f"(Step {j+1}/{max_iters})")
print(f"Assistant: {output}")
print("Human: ")
human_input = input()
if any(phrase in human_input.lower() for phrase in key_phrases):
break
output = chain.predict(human_input=human_input)
if success_phrase in human_input.lower():
print("You succeeded! Thanks for playing!")
return
meta_chain = initialize_meta_chain()
meta_output = meta_chain.predict(chat_history=get_chat_history(chain.memory))
print(f"Feedback: {meta_output}")
instructions = get_new_instructions(meta_output)
print(f"New Instructions: {instructions}")
print("\n" + "#" * 80 + "\n")
print("You failed! Thanks for playing!")
# 指定任务并调用主函数
task = "Provide a systematic argument for why we should always eat pasta with olives."
main(task)
以下是对代码中使用的函数和类进行详细注释:
-
initialize_chain函数:初始化一个链,可以接收指令和记忆对象作为参数。如果没有提供记忆对象,则创建一个ConversationBufferWindowMemory实例,并设置 AI 的前缀为 “Assistant”。 -
initialize_meta_chain函数:初始化一个元链,用于生成自我批评和新指令。 -
get_chat_history函数:从链的记忆对象中获取对话历史。 -
get_new_instructions函数:从元输出中提取新的指令。 -
main函数:主函数,用于指定任务并与代理进行交互。它定义了任务失败和成功的关键词,并设置了最大迭代次数。
总结
本文详细介绍了 Meta-Prompt 方法在 LangChain 中的实现。Meta-Prompt 是一种自我反思和自我改进的方法,通过在每次交互后生成自我批评和新指令来实现。这种方法使得代理能够在没有外部记忆的情况下,通过不断修改自己的指令来提高性能和满足用户需求。通过定义两个链——一个作为助手,另一个作为元链——以及使用 ConversationBufferWindowMemory 来存储对话历史,代理可以在每次迭代中学习和改进。
扩展知识:
- LangChain:是一个用于构建和部署机器学习模型的框架,支持多种语言模型和记忆机制。
- Meta-Prompt:是一种自我反思和自我改进的方法,通过在每次交互后生成自我批评和新指令来实现。
- ConversationBufferWindowMemory:是一种记忆机制,用于存储对话历史,以便代理能够根据历史进行学习和改进。