Title
题目
Prior Knowledge-guided Triple-Domain Transformer-GAN for Direct PET Reconstruction from Low-Count Sinograms
基于先验知识引导的三域Transformer-GAN,用于直接从低计数正电子发射断层扫描图像重建
01
文献速递介绍
正电子发射断层扫描(PET)作为一种超灵敏且非侵入性的核医学成像技术,能够可视化和量化代谢过程,在疾病诊断和干预中得到广泛应用 。在临床实践中,医生倾向于选择标准计数PET扫描,因其诊断质量较高。然而,在扫描过程中注入人体的放射性示踪剂固有地带来潜在的辐射危害。另一方面,降低示踪剂剂量不可避免地会引入意外噪音和伪影,从而损害图像质量并限制提供的诊断信息。为了解决这一临床困境,一个可行的解决方案是从相应的低计数PET(LPET)重建标准计数PET(SPET)图像,从而在获得临床可接受的PET图像的同时减少辐射暴露。
特别地,PET的原始层析数据通常以称为正电子发射断层扫描图(sinogram)的投影直方图形式存储,这对观察者来说是不可理解的,但可以转换为医学可解释的图像。然而,由于原始sinogram数据中存在随机噪声,PET图像重建是一个逆问题。已经提出了一系列研究来解决这个问题。传统的重建方法包括解析方法 和迭代方法 ,已经展示了它们在从sinogram重建高质量图像方面的潜力。然而,依赖于手工设计的假设统计模型来近似真实数据分布,这些方法通常在近似和目标分布之间存在不一致,导致重建图像中出现伪影 。为了消除假设模型可能带来的误导,并减轻人为干预,
Abstract
摘要
为了在最小化辐射暴露的同时获得高质量的正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像,已经有许多方法致力于从低计数PET(LPET)中获取标准计数PET(SPET)。然而,当前的方法未能充分利用来自多个域的不同强调信息,即正电子发射断层扫描图、图像和频率域,导致关键细节的丢失。同时,它们忽视了正电子发射断层扫描图的独特内部结构,因此未能完全捕捉其结构特征和关系。为了解决这些问题,在本文中,我们提出了一种基于先验知识引导的三域Transformer-GAN,即PK-TriDo,用于直接从LPET正电子发射断层扫描图重建SPET图像。我们的PK-TriDo包括以下组成部分:基于正电子发射断层扫描图内部结构的去噪Transformer(SISD-Former),用于去噪输入的LPET正电子发射断层扫描图;频率适应的图像重建Transformer(FaIR-Former),通过图像域先验知识引导,从去噪后的正电子发射断层扫描图重建高质量的SPET图像;以及通过对抗训练进一步增强重建质量的对抗网络(AdvNet)。针对PET成像机制,我们引入了正电子发射断层扫描图嵌入模块,通过行和列分割正电子发射断层扫描图,获得角度和距离的1D序列,以忠实地保留正电子发射断层扫描图的内部结构。此外,为了减轻高频率失真并增强重建细节,我们在FaIR-Former中集成了全局-局部频率解析器(GLFPs),用于校准不同频率带的分布和比例,从而迫使网络保留高频率细节。在三个不同剂量水平和成像场景的数据集上的评估结果表明,我们的PK-TriDo优于现有的最先进方法。
Method
方法
The architecture of our proposed PK-TriDoFig. is illustrated in 2, which consists of three sub-networks: (1) SISD-Formerto retain sinogram inner-structure while filtering the noise, (2) FaIR-Former to achieve sinogram-tohigh-frequency details preserved, and (3) image reconstruction with AdvNet to further enhance the image quality via adversarial training. Particularly, taking the LPET sinogram as input, the SISD-Former and FaIRFormer jointly act as the generator to predict fake PET images. Then, the AdvNet which serves as the discriminator tries todistinguish the fake image from the corresponding real one. Our model components are elaborated as follows.
我们提出的PK-TriDo的架构如图2所示,包括三个子网络:(1) SISD-Former,用于保留正电子发射断层扫描图的内部结构并滤除噪声,(2) FaIR-Former,用于保留正电子发射断层扫描图到高频细节的转换,以及 (3) 带有AdvNet的图像重建,通过对抗训练进一步增强图像质量。特别地,以LPET正电子发射断层扫描图作为输入,SISD-Former和FaIR-Former共同作为生成器预测假PET图像。然后,作为鉴别器的AdvNet尝试区分假图像和相应的真实图像。我们的模型组件详述如下。
Conclusion
结论
In this paper, we innovatively proposed a prior knowledgeguided triple-domain transformer-GAN (PK-TriDo) that unites sinogram, image, and frequency domains to directly reconstruct high-quality SPET images from LPET sinograms. To effectively suppress noise in Lessential structural details, we design PET sinograms while preserving ed the SISD-Former with sinogram embeddings to denoise LPET sinograms, which is tailored for the PET imaging mechanism. Then, we proposed a FaIR-Former for reconstructing SPET-like images from the denoised sinograms generated by SISD-Former. Specifically, to compensate for the loss of high-frequency details in the reconstructed images, the GLFPfrequency information and restor , which is able to calibratee high-frequency details, is injected into the FaIR-Former. In addition, prior knowledge from the image domain is progressively integrated into the reconstruction to further guide and constrain the training. Experimental results have demonstrated the feasibility and superiority of our method.
本文创新性地提出了一种基于先验知识引导的三重领域变压器生成对抗网络(PK-TriDo),将正电子发射断层扫描图(sinogram)、图像和频率领域结合,直接从LPET正电子发射断层扫描图重建高质量的标准计数PET(SPET)图像。为了有效抑制噪声并保留PET正电子发射断层扫描图中的重要结构细节,我们设计了SISD-Former,利用扫描图嵌入对LPET正电子发射断层扫描图进行去噪,该方法专为PET成像机制量身定制。随后,我们提出了FaIR-Former,用于从SISD-Former生成的去噪扫描图中重建类似SPET的图像。具体来说,为了补偿重建图像中高频细节的损失,我们将全局-局部频率解析器(GLFP)的频率信息注入FaIR-Former,用于校准和恢复高频细节。此外,从图像领域获取的先验知识逐步集成到重建过程中,进一步指导和约束训练。实验结果表明了我们方法的可行性和优越性。
Figure
图
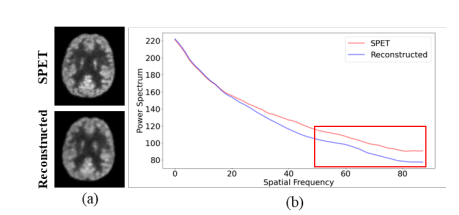
Fig. 1. (a) Visualization and (b) 1D power spectrum of the SPET image (denoted as SPET) and the image reconstructed by current leading method Transformer-GAN [16] (denoted as Reconstructed).
图1. (a) 标准计数PET图像(标记为SPET)的可视化和 (b) 1D功率谱,以及当前领先方法Transformer-GAN [16] 重建的图像(标记为重建)。
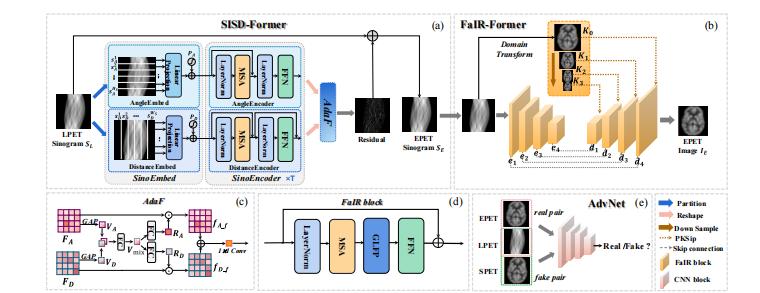
Fig. 2. An Overview of the proposed PK-TriDo architecture. (a) Sketch of the Sinogram Inner-Structure-based Denoising Transformer (SISDFormer); (b) Sketch of the Frequency-adapted Image Reconstruction Transformer (FaIR-Former); (c) Details of the Adaptive Fusion (AdaF) module in the SISD-Former; (d) Details of a FaIR block that constitutes the FaIR-Former; (e) Sketch of the Adversarial Network (AdvNet). In our PK-TriDo, the SISD-Former and the FaIR-Former jointly function as the generator to predict SPET-like images, whereas the AdvNet is the discriminator to determine the authenticity of the images.
图2. PK-TriDo架构概述。(a) 正电子发射断层扫描图内部结构基础去噪Transformer(SISD-Former)的草图;(b) 频率适应的图像重建Transformer(FaIR-Former)的草图;(c) SISD-Former中自适应融合(AdaF)模块的详细信息;(d) 构成FaIR-Former的FaIR块的详细信息;(e) 对抗网络(AdvNet)的草图。在我们的PK-TriDo中,SISD-Former和FaIR-Former共同作为生成器预测类似于标准计数PET图像的图像,而AdvNet作为鉴别器确定图像的真实性。
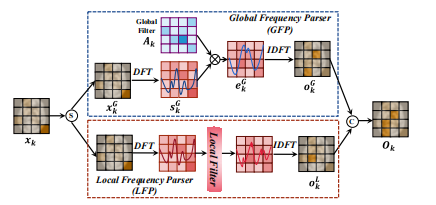
Fig. 3. Illustration of the Global-Local Frequency Parser (GLFP).
图3. 全局-局部频率解析器(GLFP)的示意图。
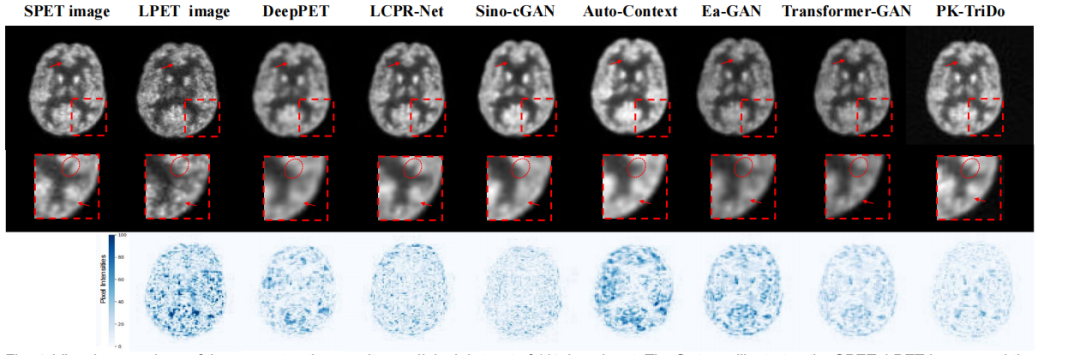
Fig. 4. Visual comparison of the reconstruction results on clinical dataset of 1/4 dose input. The first row illustrates the SPET, LPET image, and the reconstructed images, the second row presents the zoom-in areas of the images for closer inspection, and the third row is the absolute error mapsbetween the reconstructed and the SPET images (darker color indicates a larger error).
图 4. 对1/4剂量输入的临床数据集上重建结果的视觉比较。第一行展示了SPET图像、LPET图像和重建图像,第二行展示了图像的放大区域以进行更细致的检查,第三行是重建图像与SPET图像之间的绝对误差图(较暗的颜色表示较大的误差)。
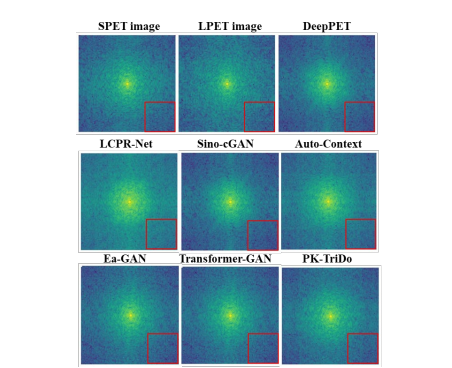
Fig. 5. Visualization of the 2D spectrum of the SPET image, the LPETimage, and the reconstructed images.
图 5. 展示了SPET图像、LPET图像和重建图像的2D频谱可视化。
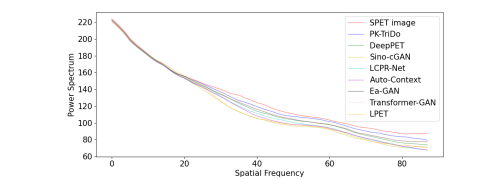
Fig. 6. The 1D power spectrum of the SPET image, the LPET image, and the reconstructed images.
图 6. SPET图像、LPET图像和重建图像的1D功率谱。
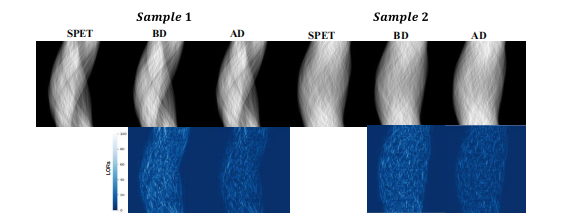
Fig. 7. Two typical examples of the sinograms before and after denoising on clinical dataset are shown in the first row. The corresponding absolute error maps are presented in the second row.“BD” refers to “before denoising” and “AD” refers to “after denoising”.
图 7. 在临床数据集上显示的两个典型示例的正电子发射断层扫描图(sinogram)在去噪前后的比较显示在第一行。对应的绝对误差图显示在第二行。“BD”表示“去噪前”,“AD”表示“去噪后”。
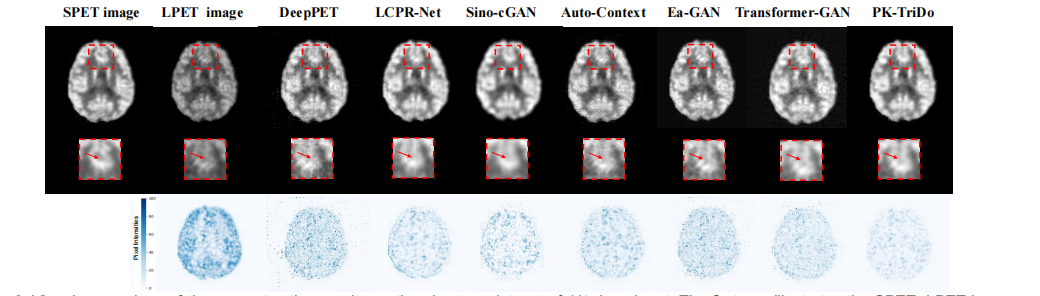
Fig. 8. Visual comparison of the reconstruction results on the phantom dataset of 1/4 dose input. The first row illustrates the SPET, LPET image, and the reconstructed images, the second row presents the zoom-in areas of the images for closer inspection, and the third row is the absolute error maps between the reconstructed and the SPET images (with darker color indicating a larger error).
图 8. 对1/4剂量输入的模拟数据集上重建结果的视觉比较。第一行展示了SPET图像、LPET图像和重建图像,第二行展示了图像的放大区域以进行更细致的检查,第三行是重建图像与SPET图像之间的绝对误差图(较暗的颜色表示较大的误差)。
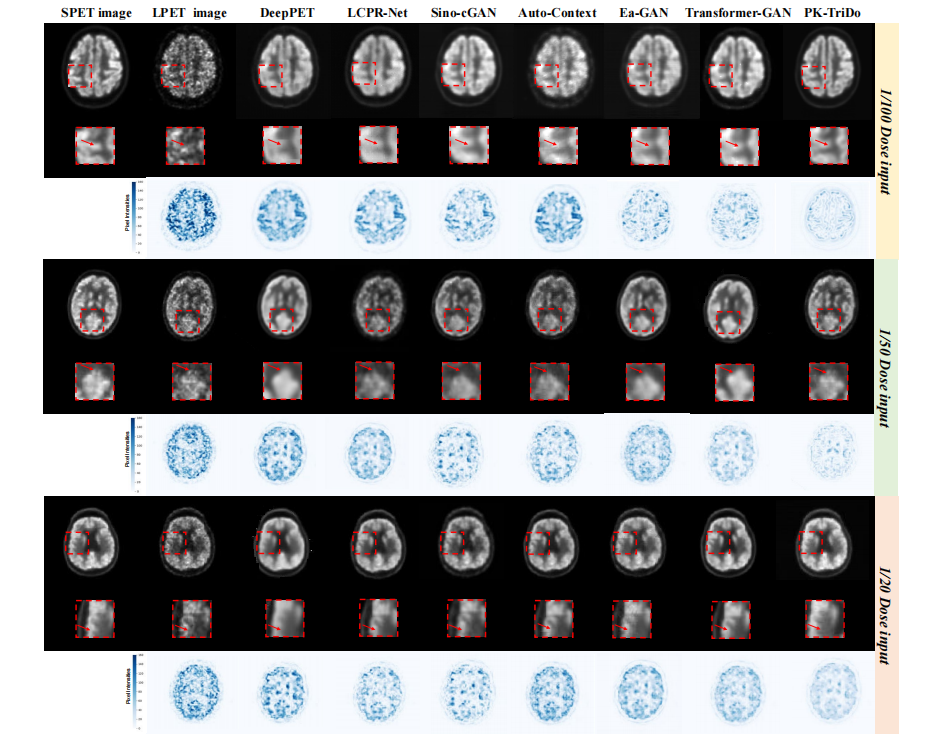
Fig. 9. Visual comparison of the reconstruction results on the brain region of the UDPET dataset at 1/100, 1/50, and 1/20 doses (from top to bottom). For each dose level, the first row illustrates the SPET, LPET image, and the reconstructed images, the second row presents the zoom-in areas of the images for closer inspection, and the third row represents the absolute error maps between the reconstructed and the SPET images (with darker color indicating a larger error).
图 9. 在UDPET数据集上不同剂量(从上到下为1/100、1/50和1/20剂量)的脑部区域重建结果的视觉比较。每个剂量水平,第一行展示了SPET图像、LPET图像和重建图像,第二行展示了图像的放大区域以进行更细致的检查,第三行是重建图像与SPET图像之间的绝对误差图(较暗的颜色表示较大的误差)。
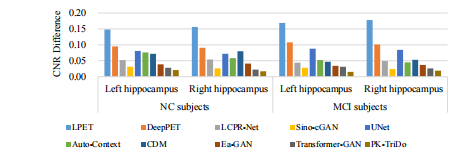
Fig. 10. Average CNR differences in left/right hippocampal regions on clinical dataset.
图 10. 临床数据集左右海马区域的平均对比噪声比(CNR)差异。
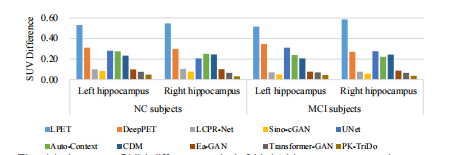
Fig. 11. Average SUV differences in left/right hippocampus regions on clinical dataset.
图 11. 临床数据集左右海马区域的平均标准摄取值(SUV)差异。
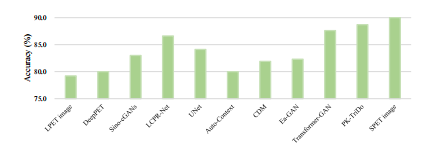
Fig. 12. Comparison results on clinical diagnosis experiment.
图 12. 临床诊断实验的比较结果。
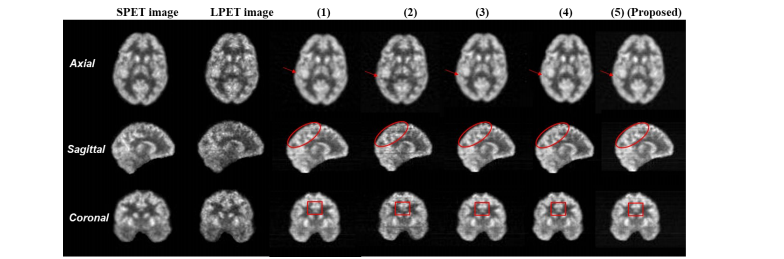
Fig. 13. Visual comparison results of the images reconstructed by different ablation variants of the proposed PK-TriDo model.
图 13. 不同消融变体的提出的PK-TriDo模型重建图像的视觉比较结果。
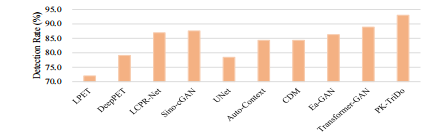
Fig. 14. Lesion detectability on the UDPET dataset
图 14. UDPET数据集上的病变可检测性
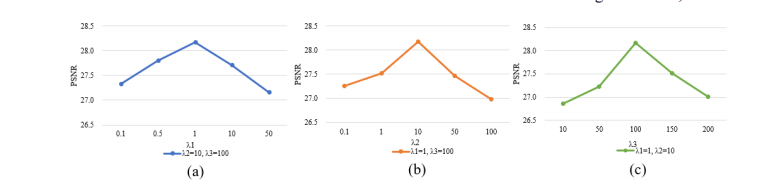
Fig. 15. The influence of different hyper-parameters in terms of PSNR on the phantom dataset.
图 15. 不同超参数对幻影数据集上PSNR的影响。
Table
表
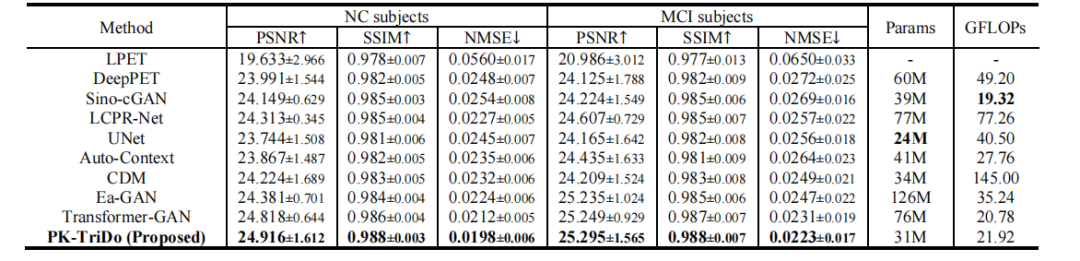
TABLE Ⅰ quantitative comparison with other state-of-the-art methods on clinical dataset in terms of psnr, ssim, and nmse, as well as the number of parameters and glops.
表 I在临床数据集上,基于PSNR、SSIM和NMSE以及参数数量和GLOPS的定量比较与其他最先进方法的比较。
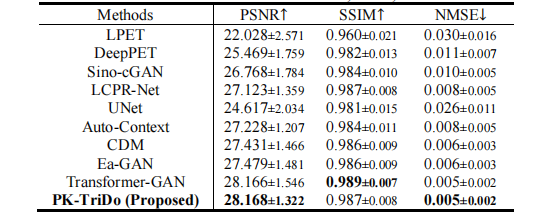
TABLE ⅠI quantitative comparison with other state-of-the-art methods on phantom dataset in terms of psnr, ssim, and nmse.
表 II在模拟数据集上,基于PSNR、SSIM和NMSE的定量比较与其他最先进方法的比较。
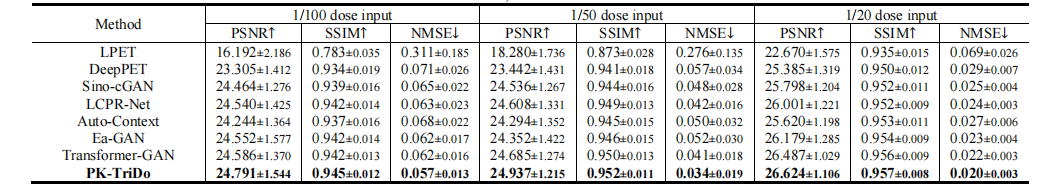
TABLE ⅠII quantitative comparison with other state-of-the-art methods on the UDPET dataset at 1/100, 1/50, and 1/20 doses in terms of psnr, ssim, and nmse.
表 III在UDPET数据集上,以1/100、1/50和1/20剂量进行的PSNR、SSIM和NMSE的定量比较与其他最先进方法的比较。
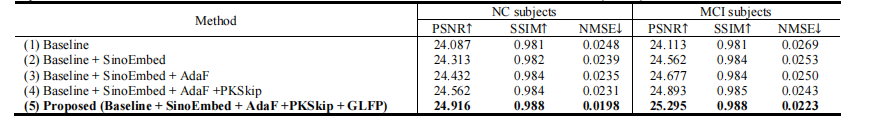
TABLE ⅠV quantitative comparisons of our proposed method and its ablation variants in terms of psnr, ssim, and nmse on clinical dataset.
表 IV在临床数据集上,基于PSNR、SSIM和NMSE的定量比较我们提出的方法及其消融变体之间的比较
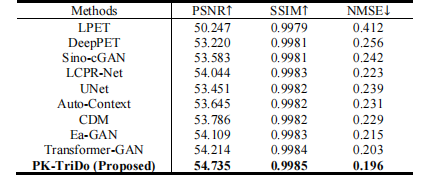
TABLE V quantitative comparison with other state-of-the-art methods on UDPET dataset at 1/50 dose level under whole-body imaging scenario in terms of psnr, ssim, and nmse.
表 V在UDPET数据集上,全身成像场景下1/50剂量水平的PSNR、SSIM和NMSE定量比较与其他最先进方法的比较。