- 🍨 本文為🔗365天深度學習訓練營 中的學習紀錄博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊 | 接輔導、項目定制
一、我的環境
-
電腦系統:Windows 10
-
顯卡:NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1060 6GB
-
語言環境:Python 3.7.0
-
開發工具:Sublime Text,Command Line(CMD)
-
深度學習環境:1.12.1+cu113
二、準備套件
# PyTorch 的核心模組,包含了張量操作、自動微分、神經網絡構建、優化器等
import torch
# PyTorch 的神經網絡模組,包含了各種神經網絡層和相關操作的類別和函數
import torch.nn as nn
# Matplotlib 的繪圖模組,用於創建各種圖表和視覺化數據
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# PyTorch 的計算機視覺工具包,包含了常用的數據集、模型和圖像轉換操作
import torchvision
# 一個用於數值計算的 Python 庫,提供了高效的數組和矩陣操作功能
import numpy as np
# PyTorch 的函數式神經網絡操作模組,包含了神經網絡中常用的操作,例如激活函數、損失函數等
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 提供 PyTorch 模型的詳細摘要信息,包括層數、參數數量和輸出形狀等,類似於 Keras 的 model.summary()
from torchinfo import summary
# 隱藏警告
import warnings
三、環境準備
# 忽略警告訊息
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 輸出 PyTorch 的版本號
print(torch.__version__)
# 檢查是否有可用的CUDA設備,否則使用CPU
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 打印出當前使用的設備
print(device)![]()
四、載入數據
# 載入CIFAR-10訓練數據集
train_ds = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
'data', # 數據下載後保存的目錄
train=True, # 指定載入訓練數據集
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # 將圖像轉換為Tensor
download=True # 如果數據集不存在,則從網絡下載
)
test_ds = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
'data', # 數據下載後保存的目錄
train=False, # 指定載入測試數據集
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # 將圖像轉換為Tensor
download=True # 如果數據集不存在,則從網絡下載
)![]()
五、數據預處理
# 定義每個批次的大小為32
batch_size = 32
# 創建訓練數據的DataLoader
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_ds, # 訓練數據集
batch_size=batch_size, # 每個批次包含32個樣本
shuffle=True # 在每個epoch開始時打亂數據
)
# 創建測試數據的DataLoader
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
test_ds, # 測試數據集
batch_size=batch_size # 每個批次包含32個樣本
# 測試數據集不需要shuffle,默認為False
)
# 從訓練數據加載器中取出一個批次的圖像和標籤
imgs, labels = next(iter(train_dl))
# 打印圖像的形狀 (batch_size, channels, height, width)
print(imgs.shape)![]()
六、圖片可視化
# 創建一個大小為 (20, 5) 的圖形
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
# 遍歷前20個圖像
for i, imgs in enumerate(imgs[:20]):
# 將圖像從 (channels, height, width) 轉換為 (height, width, channels) 以便於顯示
npimg = imgs.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))
# 在2行10列的子圖中繪製圖像
plt.subplot(2, 10, i+1)
# 顯示圖像,使用灰度色彩映射
plt.imshow(npimg, cmap=plt.cm.binary)
# 隱藏坐標軸
plt.axis('off')
# 顯示圖形
plt.show()
七、定義模型
# 定義分類數量(CIFAR-10有10個類別)
num_classes = 10
# 定義模型類
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# 定義第一個卷積層,輸入通道為3(CIFAR-10圖像的RGB通道),輸出通道為64,卷積核大小為3x3
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3)
# 定義第一個池化層,使用2x2的最大池化
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# 定義第二個卷積層,輸入通道為64,輸出通道為64,卷積核大小為3x3
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3)
# 定義第二個池化層,使用2x2的最大池化
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# 定義第三個卷積層,輸入通道為64,輸出通道為128,卷積核大小為3x3
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3)
# 定義第三個池化層,使用2x2的最大池化
self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# 定義第一個全連接層,輸入大小為512,輸出大小為256
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
# 定義第二個全連接層,輸出大小為 num_classes(分類的數量)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, num_classes)
# 定義前向傳播
def forward(self, x):
# 通過第一個卷積層、ReLU激活函數和池化層
x = self.pool1(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
# 通過第二個卷積層、ReLU激活函數和池化層
x = self.pool2(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
# 通過第三個卷積層、ReLU激活函數和池化層
x = self.pool3(F.relu(self.conv3(x)))
# 將特徵圖展平為一維向量
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
# 通過第一個全連接層和ReLU激活函數
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
# 通過第二個全連接層,輸出為分類結果
x = self.fc2(x)
# 返回輸出
return x
# 將模型移動到指定設備(GPU或CPU)
model = Model().to(device)
# 打印模型結構摘要
summary(model)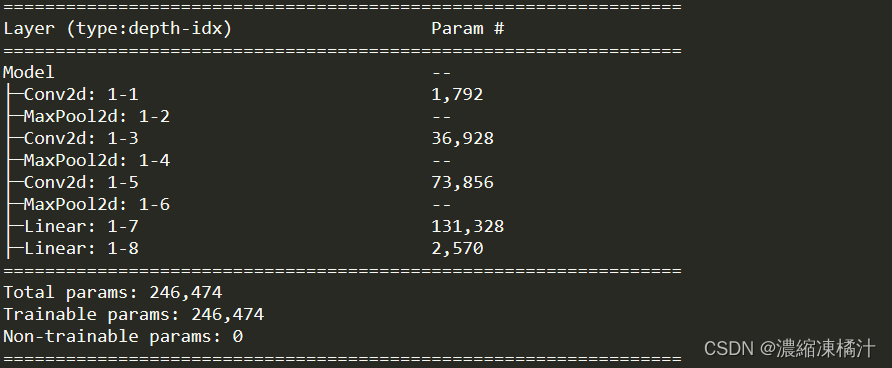
八、定義訓練函數
# 定義損失函數為交叉熵損失
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 設定學習率為0.01
learn_rate = 1e-2
# 使用隨機梯度下降(SGD)優化器
opt = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learn_rate)
# 定義訓練函數
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
# 獲取訓練集的大小
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
# 獲取批次數量
num_batches = len(dataloader)
# 初始化訓練損失和準確率
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0
# 遍歷訓練數據
for X, y in dataloader:
# 將輸入和標籤移動到指定設備(GPU或CPU)
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 前向傳播:計算模型預測
pred = model(X)
# 計算損失
loss = loss_fn(pred, y)
# 反向傳播前清零梯度
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 反向傳播:計算梯度
loss.backward()
# 更新模型參數
optimizer.step()
# 計算訓練準確率
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
# 累加訓練損失
train_loss += loss.item()
# 計算平均訓練準確率
train_acc /= size
# 計算平均訓練損失
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss九、定義測試函數
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
# 獲取測試集的大小
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
# 獲取批次數量
num_batches = len(dataloader)
# 初始化測試損失和準確率
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# 禁用梯度計算(加速推理過程)
with torch.no_grad():
# 遍歷測試數據
for imgs, target in dataloader:
# 將輸入和標籤移動到指定設備(GPU或CPU)
imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
# 前向傳播:計算模型預測
target_pred = model(imgs)
# 計算損失
loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
# 累加測試損失
test_loss += loss.item()
# 計算測試準確率
test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
# 計算平均測試準確率
test_acc /= size
# 計算平均測試損失
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss十、模型訓練
epochs = 10 # 訓練的回合數
train_loss = [] # 存儲每個回合的訓練損失
train_acc = [] # 存儲每個回合的訓練準確率
test_loss = [] # 存儲每個回合的測試損失
test_acc = [] # 存儲每個回合的測試準確率
# 訓練和測試循環
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train() # 將模型設置為訓練模式
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, opt) # 訓練模型並返回訓練準確率和損失
model.eval() # 將模型設置為評估模式
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn) # 測試模型並返回測試準確率和損失
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc) # 存儲訓練準確率
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss) # 存儲訓練損失
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc) # 存儲測試準確率
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss) # 存儲測試損失
# 格式化並輸出當前回合的訓練和測試結果
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%,Test_loss:{:.3f}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss, epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss))
print('Done')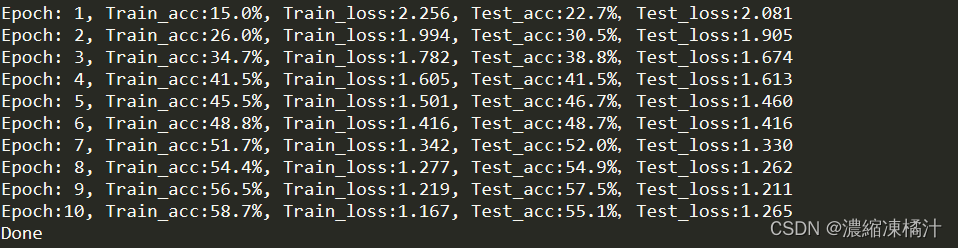
十一、結果可視化
# 設定 Matplotlib 的參數以支援中文和負號的顯示
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用來正常顯示中文標籤
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用來正常顯示負號
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100 # 設定圖表的解析度
epochs_range = range(epochs) # 訓練回合的範圍
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3)) # 設置圖表大小
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) # 創建一個2行1列的子圖佈局,這裡畫第一個圖
# 畫出訓練和測試的準確率曲線
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_acc, label='Test Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right') # 顯示圖例
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy') # 設定標題
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) # 畫第二個圖
# 畫出訓練和測試的損失曲線
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_loss, label='Test Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right') # 顯示圖例
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss') # 設定標題
plt.show() # 顯示圖表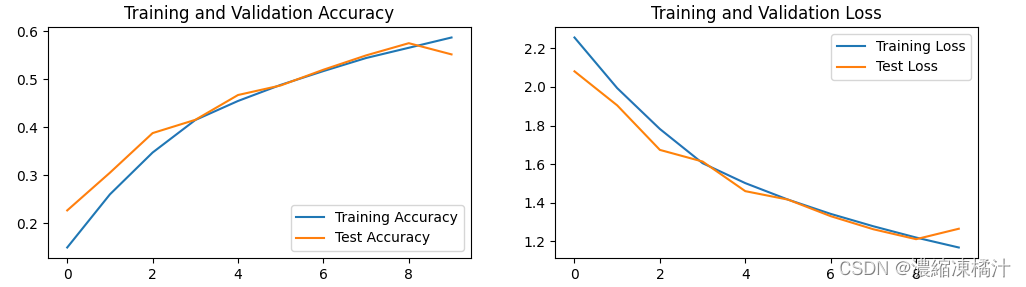
十二、心得
最近開始使用 PyTorch 框架來訓練模型,以下是 PyTorch 和 TensorFlow 2 的差異說明
-
動態圖 vs 靜態圖:
- PyTorch 使用動態計算圖:這意味著計算圖是即時定義的,每次迭代可以根據需要改變結構,更靈活,更容易進行調試和編程
- TensorFlow 2 則引入了即時執行(Eager Execution),類似於 PyTorch 的動態圖模式,使得模型的建立和調試更加直觀和靈活,此外,TensorFlow 2 也可以使用靜態圖來進行更高效的低級優化和部署
-
API 設計:
- PyTorch 的 API 設計更直觀和簡潔,更貼近 Python 編程風格,使得學習曲線較平緩,特別適合研究和實驗
- TensorFlow 2 則採用了 Keras 作為其主要高級 API,提供了更高層次的抽象和簡化,使得模型的定義和訓練更加容易,特別適合生產環境和大規模部署
-
模型部署:
- TensorFlow 2 在模型訓練後的部署和生產環境中表現更加優異,支持較多的低級優化和部署工具(如 TensorFlow Serving)
- PyTorch 雖然近年來在這方面有所改進,但相對而言仍有一定的差距,部署需要更多的自定義和額外的工作
-
社區和生態系統:
- TensorFlow 擁有更大的社區支持和更成熟的生態系統,有更多的文檔、教程和預訓練模型可用
- PyTorch 的社區雖然較小,但在學術界和研究領域中得到了廣泛的應用和支持,並且快速增長
這次作業中,我學到如何使用 PyTorch 的 torchvision 模組來加載 CIFAR-10 數據集,這個過程包括對圖片進行標準化和轉換,使其適合訓練模型,載入數據後使用 PyTorch 定義一個簡單的卷積神經網絡(CNN)來處理圖像分類任務,這裡使用了幾個卷積層和池化層,以及全連接層,之後定義損失函數和優化器,然後訓練模型,這裡使用交叉熵損失和隨機梯度下降(SGD)優化器,最後使用測試集來評估模型的表現,計算準確率和其他指標
通過調整不同的超參數和嘗試不同的模型架構,也意識到了如何優化模型以達到更好的性能,這個過程不僅加深了我對深度學習的理解,還增強了我解決實際問題的能力