76. 最小覆盖子串
- 1. 题目描述
- 2.详细题解
- 3.代码实现
- 3.1 Python
- 3.2 Java
1. 题目描述
题目中转:76. 最小覆盖子串


2.详细题解
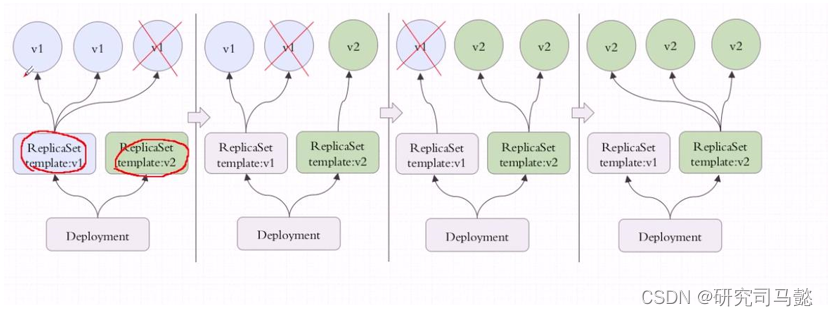
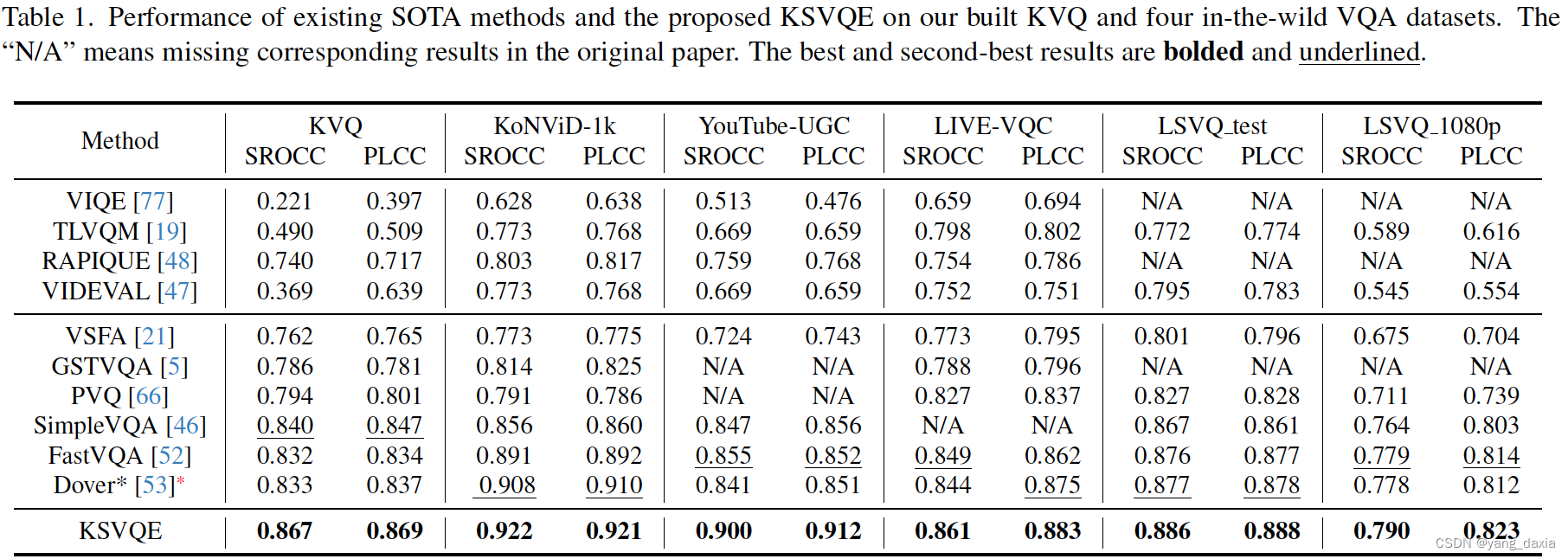
在s中寻找一个最短的子串,使之包含t中的所有字符,t中可能存在多个相同字符,寻找的子串也应至少含有相同数量的相同字符(示例3可以进一步确认)。子串即连续的一段子字符串区间,可以进一步总结为寻找一个区间,该区间内的字符包含t中的所有字符,即双指针,左指针指向子串的起始索引,右指针指向子串的结束索引,初始时,左右指针均指向s起始索引,两个指针均从左至右移动。
step1:右指针开始移动,直至包含了t中的所有字符【需要注意的视,t中的单一字符可能会出现多次,因此首先需要统计各字符出现的次数】;
step2:左指针开始移动,移除左端所有非t中出现的字符,计算此时寻找的子串长度并与已知子串长度对比,若更小则更新子串长度和记录左右位置;
step3:左指针指向的字符为t中存在的字符,移除该字符,则此时子串不再包含t中所有字符,重复步骤step1——step3。
3.代码实现
3.1 Python
class Solution:
def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:
t_count = Counter(t)
l, r, n = 0, 0, len(t)
res = [0, -1, len(s)+1]
cnt = 0
indexs = []
while r < len(s):
c = s[r]
if c in t_count:
t_count[c] -= 1
cnt += 1 if t_count[c] >= 0 else 0 # 每覆盖一个字符则加1
indexs.append(r)
while cnt == n and len(indexs) > 0:
l = indexs.pop(0)
if r - l + 1 < res[-1]:
res = [l, r, r-l+1]
cnt -= 1 if t_count[s[l]] >= 0 else 0 # 减少一个覆盖字符
t_count[s[l]] += 1
r += 1
return s[res[0]: res[1]+1]

为缩短左指针遍历的次数,使用了一个列表存储包含t符号的索引,但这样忽略了一个问题,列表的插入和删除的时间,尽管末尾插入时间复杂度为常数,但队首删除时间复杂度为O(N),为进一步优化,不再使用删除,直接记录下所有的位置,牺牲空间换取时间:
class Solution:
def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:
t_count = Counter(t)
l, r, n = 0, 0, len(t)
res = [0, -1, len(s)+1]
cnt = 0
indexs = []
ptr = -1
while r < len(s):
c = s[r]
if c in t_count:
t_count[c] -= 1
cnt += 1 if t_count[c] >= 0 else 0 # 每覆盖一个字符则加1
indexs.append(r)
while cnt == n:
ptr += 1
l = indexs[ptr]
if r - l + 1 < res[-1]:
res = [l, r, r-l+1]
cnt -= 1 if t_count[s[l]] >= 0 else 0 # 减少一个覆盖字符
t_count[s[l]] += 1
r += 1
return s[res[0]: res[1]+1]
3.2 Java
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
Map<Character, Integer> t_count = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
t_count.put(c, t_count.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
int l = 0, r = 0, n = t.length();
int[] res = {0, -1, s.length() + 1};
int cnt = 0;
int head = 0;
int ptr = -1;
int[] indexs = new int[s.length()]; // use an array to store indices
while (r < s.length()) {
char c = s.charAt(r);
if (t_count.containsKey(c)) {
t_count.put(c, t_count.get(c) - 1);
if (t_count.get(c) >= 0)cnt++;
indexs[head++] = r; // store the index
}
while (cnt == n) {
ptr++;
l = indexs[ptr];
if (r - l + 1 < res[2]) {
res[0] = l;
res[1] = r;
res[2] = r - l + 1;
}
t_count.put(s.charAt(l), t_count.get(s.charAt(l)) + 1);
if (t_count.get(s.charAt(l)) > 0) cnt--;
}
r++;
}
return res[1] == -1 ? "" : s.substring(res[0], res[1] + 1);
}
}

执行用时不必过于纠结,对比可以发现,对于python和java完全相同的编写,java的时间一般是优于python的;至于编写的代码的执行用时击败多少对手,执行用时和网络环境、当前提交代码人数等均有关系,可以尝试完全相同的代码多次执行用时也不是完全相同,只要确保自己代码的算法时间复杂度满足相应要求即可,也可以通过点击分布图查看其它coder的code