常见的触发更新的方式
- 创建 React 应用的根对象
ReactDOM.creatRoot().render(); - 类组件
this.setState(); - 函数组件
useState useEffect;
我们希望实现一套统一的更新机制,他的特点是:
- 兼容上述触发更新的方式
- 方便后续拓展(优先级机制)
更新机制的组成部分
- 代表更新的数据结构
Update - 消费update的数据结构——
UpdateQueue

实现 Update 和 UpdateQueue
在 packages/react-reconciler/src/ 目录下新建 updateQueue.ts 文件:
// packages/react-reconciler/src/updateQueue.ts
import { Action } from '@/shared/ReactTypes'
import { Update } from './fiberFlags'
export interface Update<State> {
action: Action<State>
}
export interface UpdateQueue<State> {
shared: {
pending: Update<State> | null
}
}
/** 创建 Update */
export const createUpdate = <State>(action: Action<State>): Update<State> => {
return {
action,
}
}
/** 创建 UpdateQueue */
export const createUpdateQueue = <Action>() => {
return {
shared: {
pending: null,
},
} as UpdateQueue<Action>
}
/** updateQueue添加update */
export const enqueueUpdate = <Action>(
updateQueue: UpdateQueue<Action>,
update: Update<Action>
) => {
updateQueue.shared.pending = update
}
/** updateQueue消费update */
export const processUpdateQueue = <State>(
baseState: State, // 初始状态
pendingUpdate: Update<State> | null // 要消费的Update
): { memoizedState: State } => {
const result: ReturnType<typeof processUpdateQueue<State>> = {
memoizedState: baseState,
}
if (pendingUpdate !== null) {
const action = pendingUpdate.action
if (action instanceof Function) {
// baseState:1, update:(x)=>4*x ——> memoizedState:4
result.memoizedState = action(baseState)
} else {
// baseState:1, update:2 ——> memoizedState:2
result.memoizedState = action
}
}
return result
}
// packages/shared/ReactTypes.ts
// ...
/** useState支持的两种dispatch参数 */ export type Action<State> = State | ((prevState: State) => State)
实现触发更新
接下来的工作包括:
- 实现
ReactDOM.createRoot().render()时调用的API - 将该API接入上述更新机制中
需要考虑的事情:
- 更新可能发生于任意组件,而更新流程是从根节点递归
- 需要一个统一的根节点保存通用信息

ReactDOM.createRoot()函数生成一个新的Root对象,它在源码中是FiberRootNode类型,充当了 React 应用的根节点。rootElement则是要渲染到的 DOM 节点,它在源码中是hostRootFiber类型,作为 React 应用的根 DOM 节点。render()方法将组件<App/>渲染到根节点上。在这个过程中,React 会创建一个代表<App/>组件的FiberNode,并将其添加到Root对象的 Fiber 树上。
实现 FiberRootNode
根据上图,我们先来实现 FiberRootNode 类型:
// packages/react-reconciler/src/fiber.ts
// ...
export class FiberRootNode {
container: Container // 保存挂载节点 FiberRootNode
current: FiberNode // 指向 hostRootFiber
finishedWork: FiberNode | null // 最后递归完成的 fiber
constructor(container: Container, hostRootFiber: FiberNode) {
this.container = container
this.current = hostRootFiber
hostRootFiber.stateNode = this
this.finishedWork = null
}
}
实现 render 调用的 API
接着我们来实现 ReactDOM.createRoot().render() 过程中调用的 API:
- createContainer 函数: 用于创建一个新的容器(container),该容器包含了 React 应用的根节点以及与之相关的一些配置信息。
createContainer函数会创建一个新的Root对象,该对象用于管理整个 React 应用的状态和更新。 - updateContainer 函数: 用于更新已经存在的容器中的内容。在内部,
updateContainer函数会调用scheduleUpdateOnFiber等方法,通过 Fiber 架构中的协调更新过程,将新的 React 元素(element)渲染到容器中,并更新整个应用的状态。
新建文件 fiberReconciler.ts,里面有 createContainer 和 updateContainer 两个函数
import { Container } from 'hostConfig'
import { FiberNode, FiberRootNode } from './fiber'
import { HostRoot } from './workTags'
import {
UpdateQueue,
createUpdate,
createUpdateQueue,
enqueueUpdate,
} from './updateQueue'
import { ReactElementType } from 'shared/ReactTypes'
export function createContainer(container: Container) {
// 1.新建 hostRootFiber
const hostRootFiber = new FiberNode(HostRoot, {}, null)
// 2.新建 fiberRootNode
const root = new FiberRootNode(container, hostRootFiber)
// 3.初始化hostRootFiber的updateQueue
hostRootFiber.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue()
return root
}
export function updateContainer(
element: ReactElementType | null,
root: FiberRootNode
) {
// 1.获取 hostRootFiber
const hostRootFiber = root.current
// 2.新建 update
const update = createUpdate<ReactElementType | null>(element)
// 3.将该 update 插入到 hostRootFiber的updateQueue中
enqueueUpdate(
hostRootFiber.updateQueue as UpdateQueue<ReactElementType | null>,
update
)
return element
}
实现在 updateContainer后进入wordLoop更新流程
将updateContainer方法与wordLoop的renderRoot更新流程连接:
在 workLoop.ts 文件中实现 scheduleUpdateOnFiber函数:
/** 实现在 updateContainer后进入wordLoop更新流程 */
export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber: FiberNode) {
// TODO 调度功能
// 先找到触发更新节点的根节点
const root = markUpdateFromFiberToRoot(fiber)
// 然后执行 renderRoot
renderRoot(root)
}
然后在updateContainer中执行scheduleUpdateOnFiber(hostRootFiber)
export function updateContainer(
element: ReactElementType | null,
root: FiberRootNode
) {
// ...
// 进入wordLoop更新流程
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(hostRootFiber)
return element
}
另外,在上一节中,我们在实现 prepareFreshStack 函数时,直接将 root 作为参数赋值给了 workInProgress,但现在我们知道了,root 其实是 FiberRootNode 类型的,不能直接赋值给 FiberNode 类型的 workInProgress,所以需要写一个 createWorkInProgress 函数处理一下:
// fiber.ts
/** 创建 WorkInProgress*/
export const createWorkInProgress = (
current: FiberNode,
pendingProps: Props
): FiberNode => {
let wip = current.alternate
if (wip === null) {
// mount
wip = new FiberNode(current.tag, pendingProps, current.key)
wip.stateNode = current.stateNode
wip.alternate = current
current.alternate = wip
} else {
// update
wip.pendingProps = pendingProps
wip.flags = NoFlags // 清除副作用
}
wip.type = current.type
wip.updateQueue = current.updateQueue
wip.children = current.children
wip.memoizedProps = current.memoizedProps
wip.memoizedState = current.memoizedState
return wip
}
然后更新wordLoop初始化:
// workLoop.ts
/** 初始化 */
function prepareFreshStack(root: FiberRootNode) {
workInProgress = createWorkInProgress(root.current, {})
}
至此,我们已经实现了 React 应用在首次渲染或后续更新时的大致更新流程,一起来回顾一下:
- 首先,我们通过
createContainer函数创建了 React 应用的根节点FiberRootNode,并将其与 DOM 节点(hostFiberRoot)连接起来;
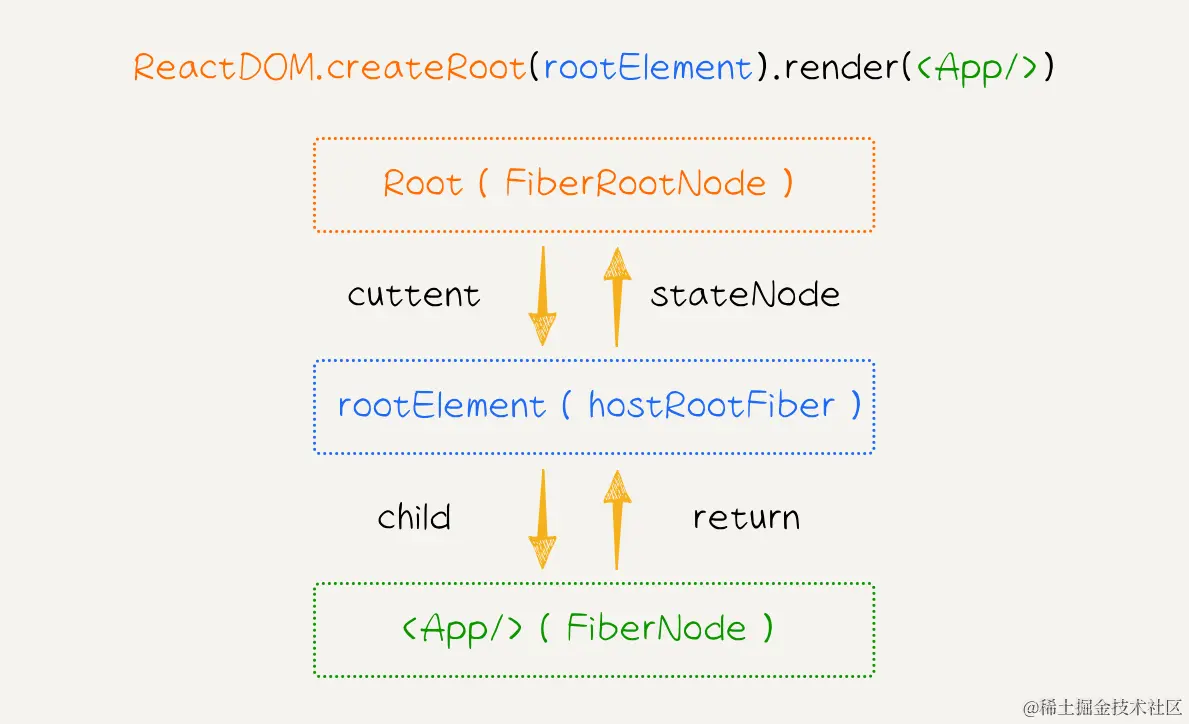
- 然后,通过
updateContainer函数创建了一个更新(update),并将其加入到更新队列(updateQueue)中,启动了首屏渲染或后续更新的机制; - 接着会调用
scheduleUpdateOnFiber函数开始调度更新,从触发更新的节点开始向上遍历,直到达到根节点FiberRootNode; - 接着会调用
renderRoot函数,初始化workInProgress变量,生成与hostRootFiber对应的workInProgress; - 接着就开始
Reconciler的更新流程,即workLoop函数,对 Fiber 树进行深度优先遍历(DFS); - 在向下遍历阶段会调用
beginWork方法,在向上返回阶段会调用completeWork方法,这两个方法负责 Fiber 节点的创建、更新和处理,具体实现会在下一节会讲到。





![[SAP ABAP] 排序内表数据](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/cc8b2d9a9eec4ebc85a6933e6ec9b4a5.png)