消息中间件 RocketMQ 高级功能和源码分析(十一)
一、消息中间件 RocketMQ 源码分析: 拉取消息长轮询机制
1、消息拉取长轮询机制分析
RocketMQ 未真正实现消息推模式,而是消费者主动向消息服务器拉取消息,RocketMQ 推模式是循环向消息服务端发起消息拉取请求,如果消息消费者向 RocketMQ 拉取消息时,消息未到达消费队列时,如果不启用长轮询机制,则会在服务端等待shortPollingTimeMills 时间后(挂起)再去判断消息是否已经到达指定消息队列,如果消息仍未到达则提示拉取消息客户端PULL—NOT—FOUND(消息不存在);如果开启长轮询模式,RocketMQ 一方面会每隔 5s 轮询检查一次消息是否可达,同时一有消息达到后立马通知挂起线程再次验证消息是否是自己感兴趣的消息,如果是则从 CommitLog 文件中提取消息返回给消息拉取客户端,否则直到挂起超时,超时时间由消息拉取方在消息拉取是封装在请求参数中,PUSH 模式为 15s,PULL 模式通过 DefaultMQPullConsumer#setBrokerSuspendMaxTimeMillis 设置。RocketMQ 通过在 Broker 客户端配置 longPollingEnable 为 true 来开启长轮询模式。
2、 代码:PullMessageProcessor#processRequest
//当没有拉取到消息时,通过长轮询方式继续拉取消息
case ResponseCode.PULL_NOT_FOUND:
if (brokerAllowSuspend && hasSuspendFlag) {
long pollingTimeMills = suspendTimeoutMillisLong;
if (!this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().isLongPollingEnable()) {
pollingTimeMills = this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().getShortPollingTimeMills();
}
String topic = requestHeader.getTopic();
long offset = requestHeader.getQueueOffset();
int queueId = requestHeader.getQueueId();
//构建拉取请求对象
PullRequest pullRequest = new PullRequest(request, channel, pollingTimeMills,
this.brokerController.getMessageStore().now(), offset, subscriptionData, messageFilter);
//处理拉取请求
this.brokerController.getPullRequestHoldService().suspendPullRequest(topic, queueId, pullRequest);
response = null;
break;
}
3、 PullRequestHoldService方式实现长轮询
代码:PullRequestHoldService#suspendPullRequest
//将拉取消息请求,放置在ManyPullRequest集合中
public void suspendPullRequest(final String topic, final int queueId, final PullRequest pullRequest) {
String key = this.buildKey(topic, queueId);
ManyPullRequest mpr = this.pullRequestTable.get(key);
if (null == mpr) {
mpr = new ManyPullRequest();
ManyPullRequest prev = this.pullRequestTable.putIfAbsent(key, mpr);
if (prev != null) {
mpr = prev;
}
}
mpr.addPullRequest(pullRequest);
}
4、 代码:PullRequestHoldService#run
public void run() {
log.info("{} service started", this.getServiceName());
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
//如果开启长轮询每隔5秒判断消息是否到达
if (this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().isLongPollingEnable()) {
this.waitForRunning(5 * 1000);
} else {
//没有开启长轮询,每隔1s再次尝试
this.waitForRunning(this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().getShortPollingTimeMills());
}
long beginLockTimestamp = this.systemClock.now();
this.checkHoldRequest();
long costTime = this.systemClock.now() - beginLockTimestamp;
if (costTime > 5 * 1000) {
log.info("[NOTIFYME] check hold request cost {} ms.", costTime);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
log.info("{} service end", this.getServiceName());
}
5、 代码:PullRequestHoldService#checkHoldRequest
//遍历拉取任务
private void checkHoldRequest() {
for (String key : this.pullRequestTable.keySet()) {
String[] kArray = key.split(TOPIC_QUEUEID_SEPARATOR);
if (2 == kArray.length) {
String topic = kArray[0];
int queueId = Integer.parseInt(kArray[1]);
//获得消息偏移量
final long offset = this.brokerController.getMessageStore().getMaxOffsetInQueue(topic, queueId);
try {
//通知有消息达到
this.notifyMessageArriving(topic, queueId, offset);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("check hold request failed. topic={}, queueId={}", topic, queueId, e);
}
}
}
}
6、 代码:PullRequestHoldService#notifyMessageArriving
//如果拉取消息偏移大于请求偏移量,如果消息匹配调用executeRequestWhenWakeup处理消息
if (newestOffset > request.getPullFromThisOffset()) {
boolean match = request.getMessageFilter().isMatchedByConsumeQueue(tagsCode,
new ConsumeQueueExt.CqExtUnit(tagsCode, msgStoreTime, filterBitMap));
// match by bit map, need eval again when properties is not null.
if (match && properties != null) {
match = request.getMessageFilter().isMatchedByCommitLog(null, properties);
}
if (match) {
try {
this.brokerController.getPullMessageProcessor().executeRequestWhenWakeup(request.getClientChannel(),
request.getRequestCommand());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("execute request when wakeup failed.", e);
}
continue;
}
}
//如果过期时间超时,则不继续等待将直接返回给客户端消息未找到
if (System.currentTimeMillis() >= (request.getSuspendTimestamp() + request.getTimeoutMillis())) {
try {
this.brokerController.getPullMessageProcessor().executeRequestWhenWakeup(request.getClientChannel(),
request.getRequestCommand());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("execute request when wakeup failed.", e);
}
continue;
}
二、消息中间件 RocketMQ 源码分析: 消息达到后实时推送机制
1、消息达到后实时推送机制
如果开启了长轮询机制,PullRequestHoldService 会每隔 5s 被唤醒去尝试检测是否有新的消息的到来才给客户端响应,或者直到超时才给客户端进行响应,消息实时性比较差,为了避免这种情况,RocketMQ 引入另外一种机制:当消息到达时唤醒挂起线程触发一次检查。
2、 DefaultMessageStore$ReputMessageService机制
代码:DefaultMessageStore#start
//长轮询入口
this.reputMessageService.setReputFromOffset(maxPhysicalPosInLogicQueue);
this.reputMessageService.start();
3、 代码:DefaultMessageStore$ReputMessageService#run
public void run() {
DefaultMessageStore.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
//长轮询核心逻辑代码入口
this.doReput();
} catch (Exception e) {
DefaultMessageStore.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
DefaultMessageStore.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
4、 代码:DefaultMessageStore$ReputMessageService#deReput
//当新消息达到是,进行通知监听器进行处理
if (BrokerRole.SLAVE != DefaultMessageStore.this.getMessageStoreConfig().getBrokerRole()
&& DefaultMessageStore.this.brokerConfig.isLongPollingEnable()) {
DefaultMessageStore.this.messageArrivingListener.arriving(dispatchRequest.getTopic(),
dispatchRequest.getQueueId(), dispatchRequest.getConsumeQueueOffset() + 1,
dispatchRequest.getTagsCode(), dispatchRequest.getStoreTimestamp(),
dispatchRequest.getBitMap(), dispatchRequest.getPropertiesMap());
}
5、 代码:NotifyMessageArrivingListener#arriving
public void arriving(String topic, int queueId, long logicOffset, long tagsCode,
long msgStoreTime, byte[] filterBitMap, Map<String, String> properties) {
this.pullRequestHoldService.notifyMessageArriving(topic, queueId, logicOffset, tagsCode,
msgStoreTime, filterBitMap, properties);
}
三、消息中间件 RocketMQ 源码分析: 消息消费负载和重新分布机制
1、消息队列负载与重新分布机制
RocketMQ 消息队列重新分配是由 RebalanceService 线程来实现。一个 MQClientInstance 持有一个 RebalanceService 实现,并随着 MQClientInstance 的启动而启动。
2、 代码:RebalanceService#run
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
//RebalanceService线程默认每隔20s执行一次mqClientFactory.doRebalance方法
while (!this.isStopped()) {
this.waitForRunning(waitInterval);
this.mqClientFactory.doRebalance();
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
3、 代码:MQClientInstance#doRebalance
public void doRebalance() {
//MQClientInstance遍历以注册的消费者,对消费者执行doRebalance()方法
for (Map.Entry<String, MQConsumerInner> entry : this.consumerTable.entrySet()) {
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
try {
impl.doRebalance();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("doRebalance exception", e);
}
}
}
}
4、 代码:RebalanceImpl#doRebalance
//遍历订阅消息对每个主题的订阅的队列进行重新负载
public void doRebalance(final boolean isOrder) {
Map<String, SubscriptionData> subTable = this.getSubscriptionInner();
if (subTable != null) {
for (final Map.Entry<String, SubscriptionData> entry : subTable.entrySet()) {
final String topic = entry.getKey();
try {
this.rebalanceByTopic(topic, isOrder);
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (!topic.startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
log.warn("rebalanceByTopic Exception", e);
}
}
}
}
this.truncateMessageQueueNotMyTopic();
}
5、 代码:RebalanceImpl#rebalanceByTopic
//从主题订阅消息缓存表中获取主题的队列信息
Set<MessageQueue> mqSet = this.topicSubscribeInfoTable.get(topic);
//查找该主题订阅组所有的消费者ID
List<String> cidAll = this.mQClientFactory.findConsumerIdList(topic, consumerGroup);
//给消费者重新分配队列
if (mqSet != null && cidAll != null) {
List<MessageQueue> mqAll = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
mqAll.addAll(mqSet);
Collections.sort(mqAll);
Collections.sort(cidAll);
AllocateMessageQueueStrategy strategy = this.allocateMessageQueueStrategy;
List<MessageQueue> allocateResult = null;
try {
allocateResult = strategy.allocate(
this.consumerGroup,
this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(),
mqAll,
cidAll);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("AllocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate Exception. allocateMessageQueueStrategyName={}", strategy.getName(),
e);
return;
}
6、 RocketMQ 默认提供5中负载均衡分配算法
AllocateMessageQueueAveragely:平均分配
举例:8个队列q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,a6,q7,q8,消费者3个:c1,c2,c3
分配如下:
c1:q1,q2,q3
c2:q4,q5,a6
c3:q7,q8
AllocateMessageQueueAveragelyByCircle:平均轮询分配
举例:8个队列q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,a6,q7,q8,消费者3个:c1,c2,c3
分配如下:
c1:q1,q4,q7
c2:q2,q5,a8
c3:q3,q6
7、 注意:消息队列的分配遵循一个消费者可以分配到多个队列,但同一个消息队列只会分配给一个消费者,故如果出现消费者个数大于消息队列数量,则有些消费者无法消费消息。
四、消息中间件 RocketMQ 源码分析: 消息并发处理
1、消息消费过程–消息并发处理
PullMessageService 负责对消息队列进行消息拉取,从远端服务器拉取消息后将消息存储 ProcessQueue 消息队列处理队列中,然后调用 ConsumeMessageService#submitConsumeRequest 方法进行消息消费,使用线程池来消费消息,确保了消息拉取与消息消费的解耦。ConsumeMessageService 支持顺序消息和并发消息,核心类图如下:
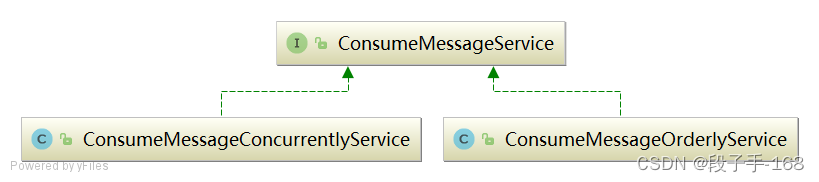
2、 并发消息消费
代码:ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService#submitConsumeRequest
//消息批次单次
final int consumeBatchSize = this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeMessageBatchMaxSize();
//msgs.size()默认最多为32条。
//如果msgs.size()小于consumeBatchSize,则直接将拉取到的消息放入到consumeRequest,然后将consumeRequest提交到消费者线程池中
if (msgs.size() <= consumeBatchSize) {
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(msgs, processQueue, messageQueue);
try {
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(consumeRequest);
}
}else{ //如果拉取的消息条数大于consumeBatchSize,则对拉取消息进行分页
for (int total = 0; total < msgs.size(); ) {
List<MessageExt> msgThis = new ArrayList<MessageExt>(consumeBatchSize);
for (int i = 0; i < consumeBatchSize; i++, total++) {
if (total < msgs.size()) {
msgThis.add(msgs.get(total));
} else {
break;
}
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(msgThis, processQueue, messageQueue);
try {
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
for (; total < msgs.size(); total++) {
msgThis.add(msgs.get(total));
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(consumeRequest);
}
}
}
3、 代码:ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService$ConsumeRequest#run
//检查processQueue的dropped,如果为true,则停止该队列消费。
if (this.processQueue.isDropped()) {
log.info("the message queue not be able to consume, because it's dropped. group={} {}", ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.consumerGroup, this.messageQueue);
return;
}
...
//执行消息处理的钩子函数
if (ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.hasHook()) {
consumeMessageContext = new ConsumeMessageContext();
consumeMessageContext.setNamespace(defaultMQPushConsumer.getNamespace());
consumeMessageContext.setConsumerGroup(defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
consumeMessageContext.setProps(new HashMap<String, String>());
consumeMessageContext.setMq(messageQueue);
consumeMessageContext.setMsgList(msgs);
consumeMessageContext.setSuccess(false);
ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.executeHookBefore(consumeMessageContext);
}
...
//调用应用程序消息监听器的consumeMessage方法,进入到具体的消息消费业务处理逻辑
status = listener.consumeMessage(Collections.unmodifiableList(msgs), context);
//执行消息处理后的钩子函数
if (ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.hasHook()) {
consumeMessageContext.setStatus(status.toString());
consumeMessageContext.setSuccess(ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS == status);
ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.executeHookAfter(consumeMessageContext);
}
五、消息中间件 RocketMQ 源码分析: 定时消息处理机制
1、消息中间件 RocketMQ 源码分析:定时消息处理机制
1、定时消息处理机制
定时消息是消息发送到 Broker 后,并不立即被消费者消费而是要等到特定的时间后才能被消费,RocketMQ 并不支持任意的时间精度,如果要支持任意时间精度定时调度,不可避免地需要在Broker 层做消息排序,再加上持久化方面的考量,将不可避免的带来巨大的性能消耗,所以 RocketMQ 只支持特定级别的延迟消息。消息延迟级别在 Broker 端通过 messageDelayLevel 配置,默认为“1s 5s 10s 30s 1m 2m 3m 4m 5m 6m 7m 8m 9m 10m 20m 30m 1h 2h”,delayLevel=1 表示延迟消息 1s,delayLevel=2 表示延迟 5s,依次类推。
RocketMQ 定时消息实现类为 ScheduleMessageService,该类在 DefaultMessageStore 中创建。通过在 DefaultMessageStore 中调用 load 方法加载该类并调用 start 方法启动。
2、 代码:ScheduleMessageService#load
//加载延迟消息消费进度的加载与delayLevelTable的构造。延迟消息的进度默认存储路径为/store/config/delayOffset.json
public boolean load() {
boolean result = super.load();
result = result && this.parseDelayLevel();
return result;
}
3、 代码:ScheduleMessageService#start
//遍历延迟队列创建定时任务,遍历延迟级别,根据延迟级别level从offsetTable中获取消费队列的消费进度。如果不存在,则使用0
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Long> entry : this.delayLevelTable.entrySet()) {
Integer level = entry.getKey();
Long timeDelay = entry.getValue();
Long offset = this.offsetTable.get(level);
if (null == offset) {
offset = 0L;
}
if (timeDelay != null) {
this.timer.schedule(new DeliverDelayedMessageTimerTask(level, offset), FIRST_DELAY_TIME);
}
}
//每隔10s持久化一次延迟队列的消息消费进度
this.timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if (started.get()) ScheduleMessageService.this.persist();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("scheduleAtFixedRate flush exception", e);
}
}
}, 10000, this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDelayOffsetInterval());
4、 调度机制
ScheduleMessageService 的 start 方法启动后,会为每一个延迟级别创建一个调度任务,每一个延迟级别对应 SCHEDULE_TOPIC_XXXX 主题下的一个消息消费队列。定时调度任务的实现类为 DeliverDelayedMessageTimerTask,核心实现方法为 executeOnTimeup
5、 代码:ScheduleMessageService$DeliverDelayedMessageTimerTask#executeOnTimeup
//根据队列ID与延迟主题查找消息消费队列
ConsumeQueue cq =
ScheduleMessageService.this.defaultMessageStore.findConsumeQueue(SCHEDULE_TOPIC,
delayLevel2QueueId(delayLevel));
...
//根据偏移量从消息消费队列中获取当前队列中所有有效的消息
SelectMappedBufferResult bufferCQ = cq.getIndexBuffer(this.offset);
...
//遍历ConsumeQueue,解析消息队列中消息
for (; i < bufferCQ.getSize(); i += ConsumeQueue.CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE) {
long offsetPy = bufferCQ.getByteBuffer().getLong();
int sizePy = bufferCQ.getByteBuffer().getInt();
long tagsCode = bufferCQ.getByteBuffer().getLong();
if (cq.isExtAddr(tagsCode)) {
if (cq.getExt(tagsCode, cqExtUnit)) {
tagsCode = cqExtUnit.getTagsCode();
} else {
//can't find ext content.So re compute tags code.
log.error("[BUG] can't find consume queue extend file content!addr={}, offsetPy={}, sizePy={}",
tagsCode, offsetPy, sizePy);
long msgStoreTime = defaultMessageStore.getCommitLog().pickupStoreTimestamp(offsetPy, sizePy);
tagsCode = computeDeliverTimestamp(delayLevel, msgStoreTime);
}
}
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
long deliverTimestamp = this.correctDeliverTimestamp(now, tagsCode);
...
//根据消息偏移量与消息大小,从CommitLog中查找消息.
MessageExt msgExt =
ScheduleMessageService.this.defaultMessageStore.lookMessageByOffset(
offsetPy, sizePy);
}
六、消息中间件 RocketMQ 源码分析: 顺序消息原理
1、顺序消息原理
顺序消息实现类是 org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.ConsumeMessageOrderlyService
2、 代码:ConsumeMessageOrderlyService#start
public void start() {
//如果消息模式为集群模式,启动定时任务,默认每隔20s执行一次锁定分配给自己的消息消费队列
if (MessageModel.CLUSTERING.equals(ConsumeMessageOrderlyService.this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.messageModel())) {
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ConsumeMessageOrderlyService.this.lockMQPeriodically();
}
}, 1000 * 1, ProcessQueue.REBALANCE_LOCK_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
3、 代码:ConsumeMessageOrderlyService#submitConsumeRequest
//构建消息任务,并提交消费线程池中
public void submitConsumeRequest(
final List<MessageExt> msgs,
final ProcessQueue processQueue,
final MessageQueue messageQueue,
final boolean dispathToConsume) {
if (dispathToConsume) {
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(processQueue, messageQueue);
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
}
}
4、 代码:ConsumeMessageOrderlyService$ConsumeRequest#run
//如果消息队列为丢弃,则停止本次消费任务
if (this.processQueue.isDropped()) {
log.warn("run, the message queue not be able to consume, because it's dropped. {}", this.messageQueue);
return;
}
//从消息队列中获取一个对象。然后消费消息时先申请独占objLock锁。顺序消息一个消息消费队列同一时刻只会被一个消费线程池处理
final Object objLock = messageQueueLock.fetchLockObject(this.messageQueue);
synchronized (objLock) {
...
}
5、 消费消息 小结
-
1)RocketMQ 消息消费方式分别为集群模式、广播模式。
-
2)消息队列负载由 RebalanceService 线程默认每隔 20s 进行一次消息队列负载,根据当前消费者组内消费者个数与主题队列数量按照某一种负载算法进行队列分配,分配原则为同一个消费者可以分配多个消息消费队列,同一个消息消费队列同一个时间只会分配给一个消费者。
-
3)消息拉取由 PullMessageService 线程根据 RebalanceService 线程创建的拉取任务进行拉取,默认每次拉取 32 条消息,提交给消费者消费线程后继续下一次消息拉取。如果消息消费过慢产生消息堆积会触发消息消费拉取流控。
-
4)并发消息消费指消费线程池中的线程可以并发对同一个消息队列的消息进行消费,消费成功后,取出消息队列中最小的消息偏移量作为消息消费进度偏移量存储在于消息消费进度存储文件中,集群模式消息消费进度存储在 Broker(消息服务器),广播模式消息消费进度存储在消费者端。
-
5)RocketMQ 不支持任意精度的定时调度消息,只支持自定义的消息延迟级别,例如 1s、2s、5s 等,可通过在 broker 配置文件中设置 messageDelayLevel。
-
6)顺序消息一般使用集群模式,是指对消息消费者内的线程池中的线程对消息消费队列只能串行消费。并并发消息消费最本质的区别是消息消费时必须成功锁定消息消费队列,在 Broker 端会存储消息消费队列的锁占用情况。
上一节关联链接请点击:
# 消息中间件 RocketMQ 高级功能和源码分析(十)