TypeScript 笔记记录,侧重于接口,对象等内容。
文章目录
- 一、 TS 面向对象
- 二、TS 类
- 三、TS 继承
- 四、TS super关键字
- 五、TS 抽象类
- 六、TS 接口
- 七、TS 属性封装
- 八、TS 泛型
一、 TS 面向对象
js也是面向对象的,并不是面向过程的。
下面,简单看看就行。

二、TS 类
类就是对象的模型,要想面对操作对象,就要定义对应的类。
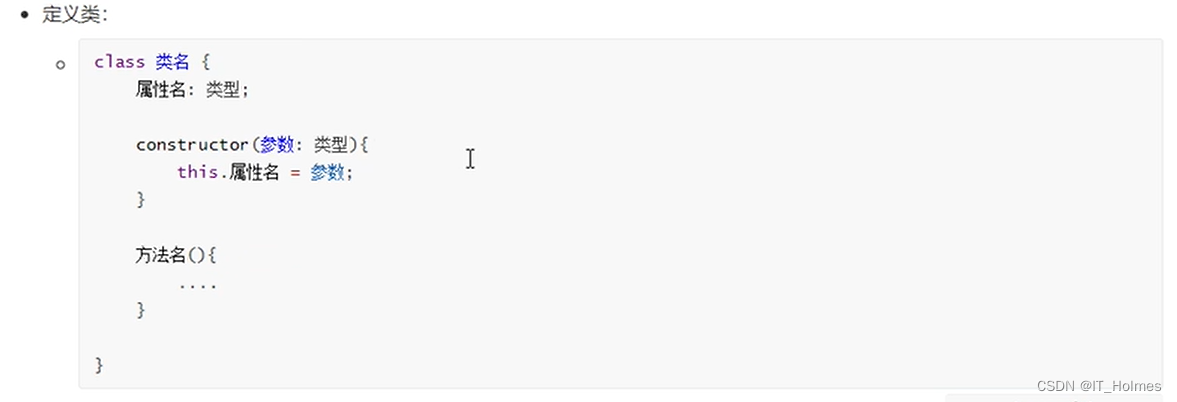
类格式:
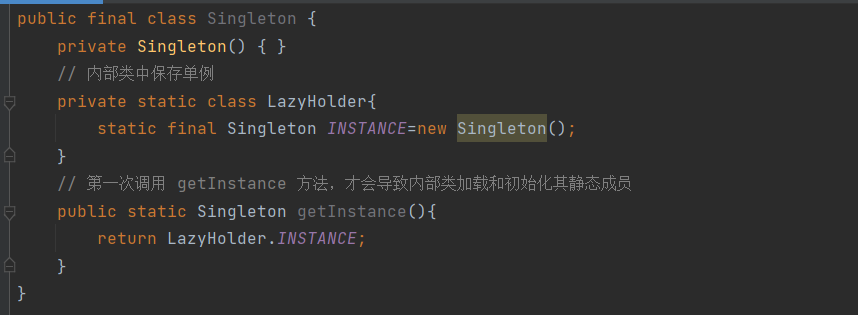
其实TS类 转换成了这种类似的 立即执行函数的效果。
class Person {
name: string = 'demo'
// 构造函数
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
// static 静态属性
static age: number = 18
sayHello(){
console.log('123456')
}
}
const per = new Person('aa')
// 静态属性必须通过类型才能获得
console.log(Person.age)
三、TS 继承
和Java 继承差不多,简单看看就行。

四、TS super关键字
super关键字 相关内容:
class Animal {
name: string = 'demo'
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
sayHello(){
console.log('123456')
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
constructor(props) {
// 如果在子类中写了构造函数,在子类的构造函数中必须要调用super父类的构造函数。
super(props);
}
sayHello() {
// 在类的方法中 super就表示当前类的父类。
super.sayHello();
console.log('hello,world')
}
}
五、TS 抽象类
同样和Java差不多。
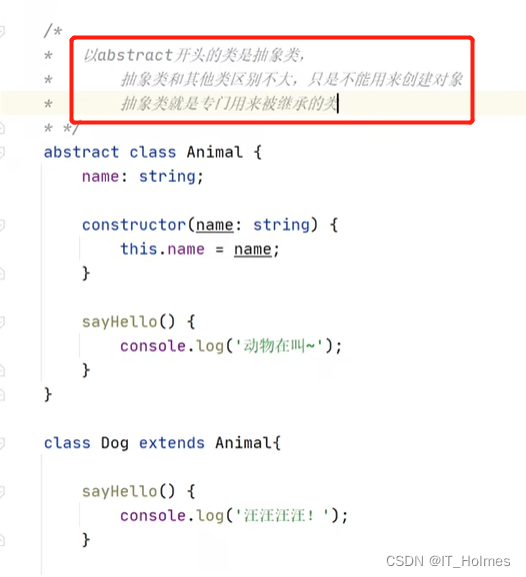
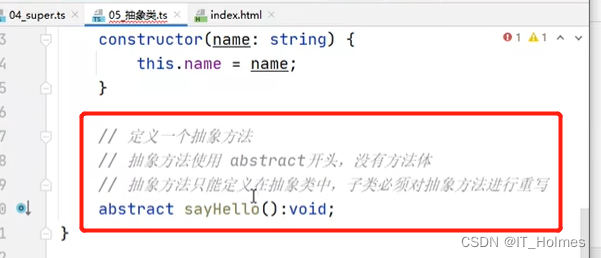
注意抽象方法的使用就行:
六、TS 接口
指定类型:

限制类结构:

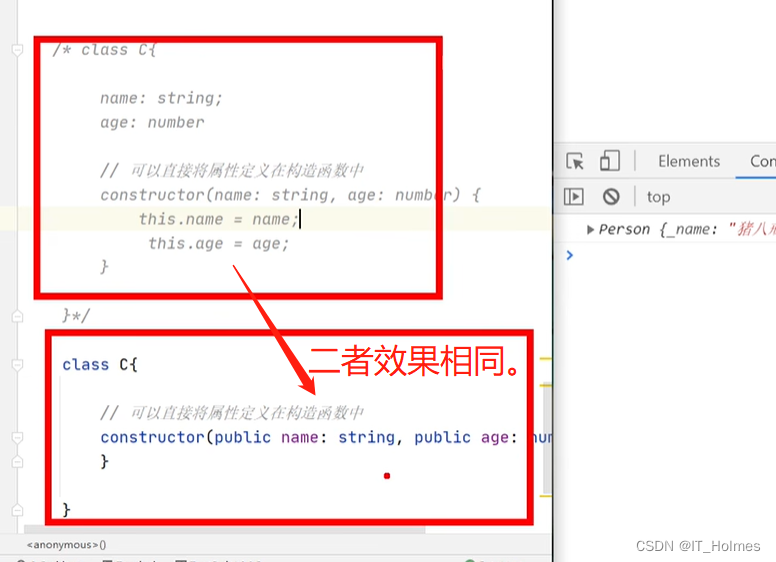
七、TS 属性封装
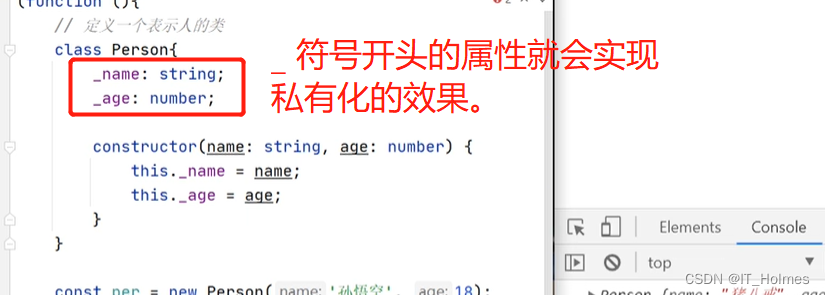
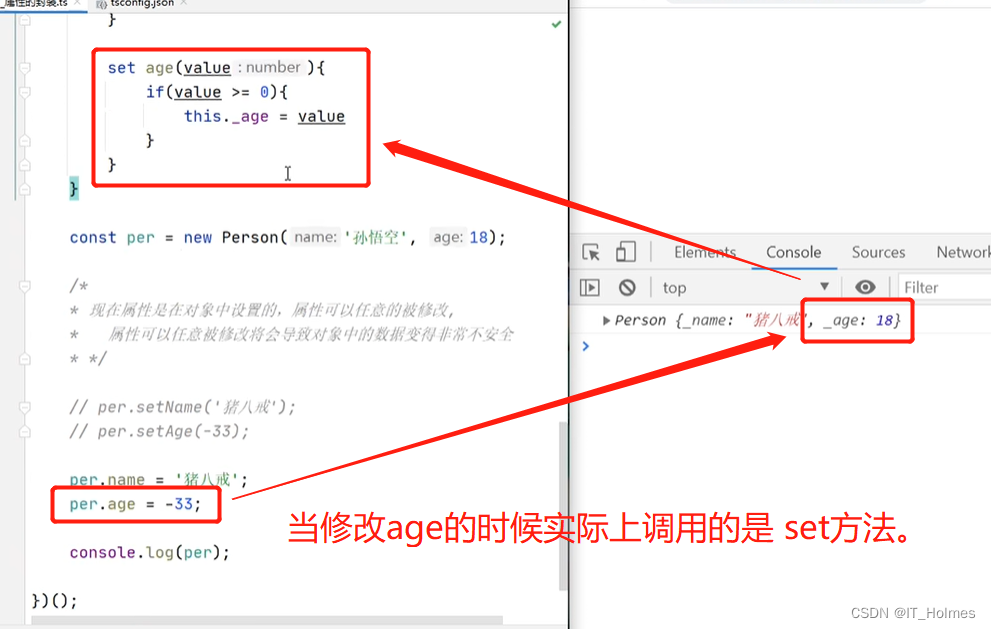
配合public 、private 来进行属性的封装效果。同样也可以通过定义 get 、set方法对应的属性来操作。
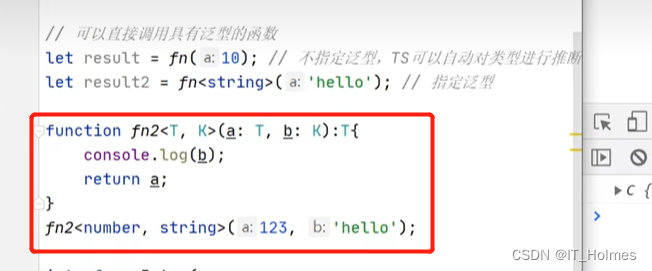
八、TS 泛型
泛型效果也是和Java相同:
- 关注:函数、类、extends用法就可以。


![Linux[安装gitlab笔记]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20201103110304970.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L2x4eTg2OTcxODA2OQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70#pic_center)