🍭 大家好这里是清隆学长 ,一枚热爱算法的程序员
✨ 本系列打算持续跟新华为OD-C/D卷的三语言AC题解
💻 ACM银牌🥈| 多次AK大厂笔试 | 编程一对一辅导
👏 感谢大家的订阅➕ 和 喜欢💗
📎在线评测链接
https://app5938.acapp.acwing.com.cn/contest/2/problem/OD1066
🌍 评测功能需要 ⇒ 订阅专栏 ⇐ 后私信联系清隆解锁~
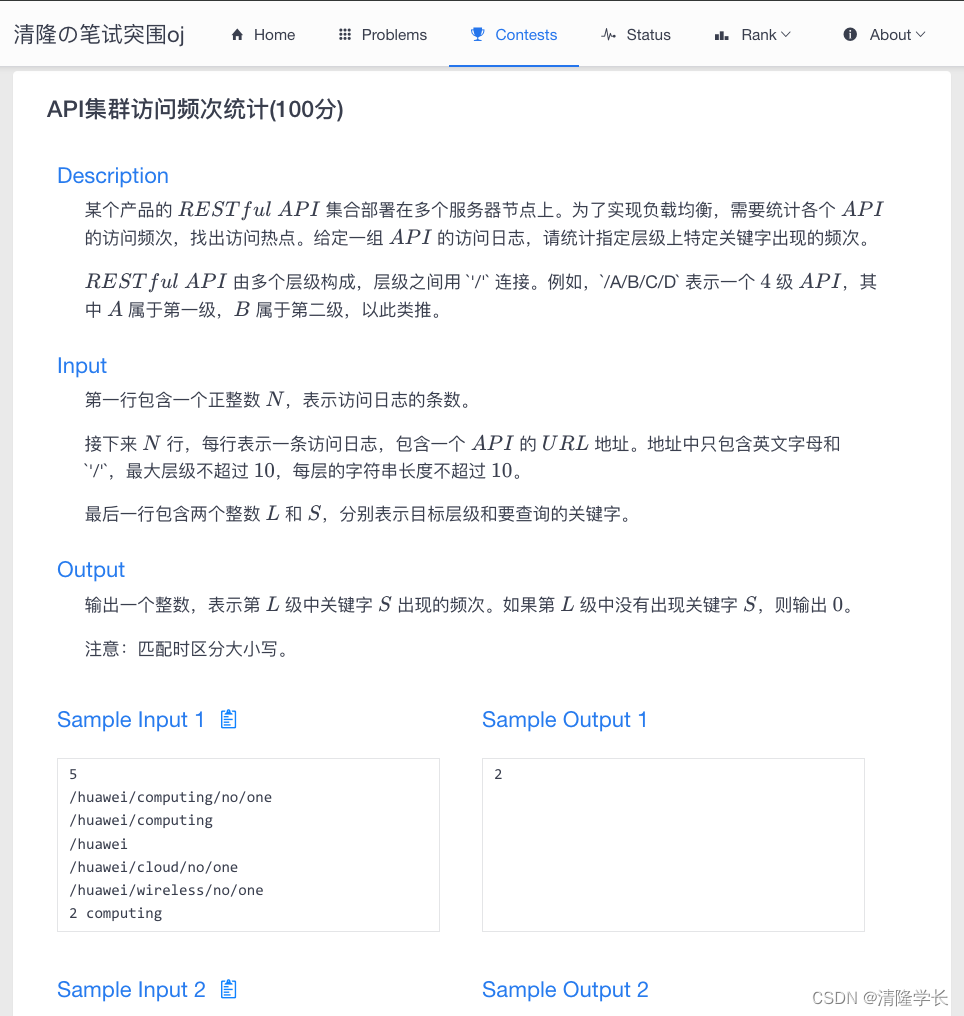
🍓OJ题目截图
文章目录
- 📎在线评测链接
- 🍓OJ题目截图
- ✨ API集群访问频次统计
- 问题描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例输入
- 样例输出
- 样例输入
- 样例输出
- 数据范围
- 题解
- 参考代码
✨ API集群访问频次统计
问题描述
某个产品的 R E S T f u l RESTful RESTful A P I API API 集合部署在多个服务器节点上。为了实现负载均衡,需要统计各个 A P I API API 的访问频次,找出访问热点。给定一组 A P I API API 的访问日志,请统计指定层级上特定关键字出现的频次。
R
E
S
T
f
u
l
RESTful
RESTful
A
P
I
API
API 由多个层级构成,层级之间用 '/' 连接。例如,/A/B/C/D 表示一个
4
4
4 级
A
P
I
API
API,其中
A
A
A 属于第一级,
B
B
B 属于第二级,以此类推。
输入格式
第一行包含一个正整数 N N N,表示访问日志的条数。
接下来
N
N
N 行,每行表示一条访问日志,包含一个
A
P
I
API
API 的
U
R
L
URL
URL 地址。地址中只包含英文字母和 '/',最大层级不超过
10
10
10,每层的字符串长度不超过
10
10
10。
最后一行包含两个整数 L L L 和 S S S,分别表示目标层级和要查询的关键字。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示第 L L L 级中关键字 S S S 出现的频次。如果第 L L L 级中没有出现关键字 S S S,则输出 0 0 0。
注意:匹配时区分大小写。
样例输入
5
/huawei/computing/no/one
/huawei/computing
/huawei
/huawei/cloud/no/one
/huawei/wireless/no/one
2 computing
样例输出
2
样例输入
5
/huawei/computing/no/one
/huawei/computing
/huawei
/huawei/cloud/no/one
/huawei/wireless/no/one
4 two
样例输出
0
数据范围
- 1 ≤ N ≤ 1000 1 \le N \le 1000 1≤N≤1000
- 1 ≤ L ≤ 10 1 \le L \le 10 1≤L≤10
- 1 ≤ l e n g t h ( S ) ≤ 10 1 \le length(S) \le 10 1≤length(S)≤10
题解
这道题可以用哈希表来解决。具体步骤如下:
-
用一个哈希表 c n t cnt cnt 统计每个层级上各关键字的出现频次。哈希表的键为
(level, word)二元组,表示层级和关键字,值为该关键字在该层级出现的频次。 -
遍历访问日志中的每个 U R L URL URL:
- 将
U
R
L
URL
URL 按
'/'切分成多个部分,每个部分对应一个层级。 - 对于每个层级 i i i 和关键字 w o r d word word,将 c n t [ ( i , w o r d ) ] cnt[(i, word)] cnt[(i,word)] 的值加 1 1 1,表示 ( i , w o r d ) (i, word) (i,word) 这个键值对出现了一次。
- 将
U
R
L
URL
URL 按
-
查询目标层级 L L L 和关键字 S S S 在哈希表中的值,即 c n t [ ( L , S ) ] cnt[(L, S)] cnt[(L,S)] 的值,输出即可。如果哈希表中不存在键 ( L , S ) (L, S) (L,S),说明第 L L L 级中没有出现过关键字 S S S,输出 0 0 0。
时间复杂度 O ( N × L ) O(N \times L) O(N×L),其中 N N N 为访问日志的条数, L L L 为 U R L URL URL 的最大层级。空间复杂度 O ( N × L ) O(N \times L) O(N×L)。
参考代码
- Python
from collections import defaultdict
n = int(input())
cnt = defaultdict(int)
for _ in range(n):
levels = input().split('/')
for i in range(1, len(levels)):
cnt[(i, levels[i])] += 1
target_level, target_word = input().split()
target_level = int(target_level)
print(cnt[(target_level, target_word)])
- Java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
Map<String, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String[] levels = sc.next().split("/");
for (int j = 1; j < levels.length; j++) {
String key = j + "," + levels[j];
cnt.put(key, cnt.getOrDefault(key, 0) + 1);
}
}
int targetLevel = sc.nextInt();
String targetWord = sc.next();
String targetKey = targetLevel + "," + targetWord;
System.out.println(cnt.getOrDefault(targetKey, 0));
}
}
- Cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
unordered_map<string, int> cnt;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string url;
cin >> url;
int pos = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < url.size(); j++) {
if (url[j] == '/') {
string key = to_string(j) + "," + url.substr(pos + 1, j - pos - 1);
cnt[key]++;
pos = j;
}
}
}
int targetLevel;
string targetWord;
cin >> targetLevel >> targetWord;
string targetKey = to_string(targetLevel) + "," + targetWord;
cout << cnt[targetKey] << endl;
return 0;
}