无名管道与有名管道的区别
无名管道:
它是半双工的,具有固定的读端和写端。
只能用于具有亲缘关系的进程之间的通信(也是父子进程或者兄弟进程之间)。
不是普通的文件,不属于其他任何文件系统,并且只存在于内存中。
有名管道FIFO:
FIFO可以在无关的进程之间交换数据。
FIFO有路径名与之相关联,它以一种特殊设备文件形式存在于文件系统中。
思路
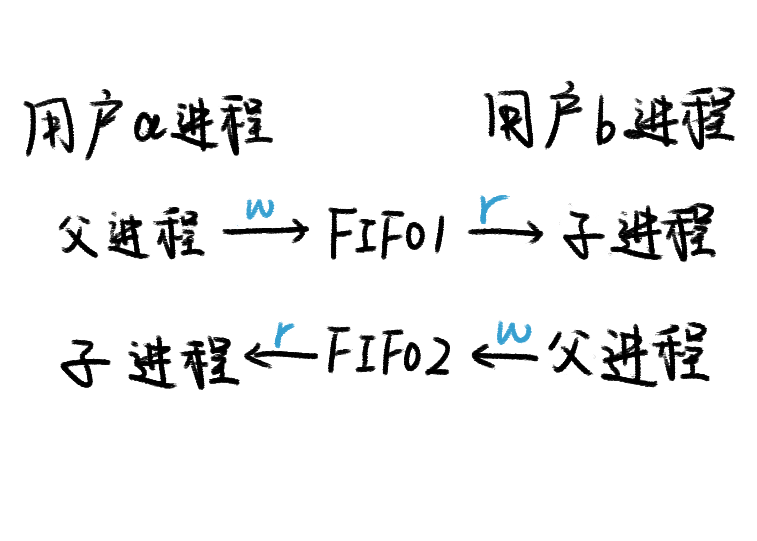
父进程负责写,子进程负责读。
FIFO1负责存储用户a发出的消息,
FIFO2负责存储用户b发出的消息。
代码
chat_a.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid > 0)
{
//a的父进程写FIFO1
char *fifo1 = "./fifo1";
//判断fifo1是否存在
int ret = access(fifo1, F_OK);
if (ret == -1){
//文件不存在,需要创建
ret = mkfifo(fifo1, 0664);
if (ret == -1){
//创建失败
perror("mkfifo error");
exit(-1);
}
}
//文件fifo1存在,以只写方式打开
int fdw = open(fifo1, O_WRONLY);
if (fdw == -1)
{
perror("open error");
exit(-1);
}
printf("a:successfully opened fifo1\n");
//循环写入数据
char buf[256];
while (1){
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
//获取标准输入的数据
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);
//写数据到fifo1
int len = write(fdw, buf, strlen(buf));
if (len == -1){
perror("write error");
break;
}
printf("\n");
}
close(fdw);
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
//a的子进程读FIFO2
char *fifo2 = "./fifo2";
//判断FIFO2是否存在
int ret = access(fifo2, F_OK);
if (ret == -1)
{
//文件不存在,需要创建
ret = mkfifo(fifo2, 0664);
if (ret == -1)
{
//创建失败
perror("mkfifo error");
exit(-1);
}
}
//文件FIFO2存在,以只读方式打开
int fdr = open(fifo2, O_RDONLY);
if (fdr == -1)
{
perror("open error");
exit(-1);
}
printf("a:successfully opened fifo2\n");
//循环读数据
char buf[256];
while (1)
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
int len = read(fdr, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (len <= 0)
{
perror("read");
break;
}
printf("b: %s\n", buf);
}
close(fdr);
}
return 0;
}chat_b.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid > 0){
//b的父进程写FIFO2
char *fifo2 = "./fifo2";
//判断文件fifo2是否存在
int ret = access(fifo2, F_OK);
if (ret == -1)
{
//文件不存在,需要创建
ret = mkfifo(fifo2, 0664);
if (ret == -1)
{
perror("mkfifo error");
exit(-1);
}
}
//文件fifo2存在,以只写方式打开
int fdw = open(fifo2, O_WRONLY);
if (fdw == -1)
{
perror("open error");
exit(-1);
}
printf("b:successfully opened fifo2\n");
//循环写入数据
char buf[256];
while (1)
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
//获取标准输入的数据
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);
//写数据到fifo2
int len = write(fdw, buf, strlen(buf));
if (len == -1)
{
perror("write error");
break;
}
printf("\n");
}
close(fdw);
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
//b的子进程读FIFO1
char *fifo1 = "./fifo1";
int ret = access(fifo1, F_OK);
if (ret == -1)
{
//文件不存在,需要创建
ret = mkfifo(fifo1, 0664);
if (ret == -1)
{
perror("mkfifo error");
exit(-1);
}
}
//文件FIFO1存在,以只读方式打开
int fdr = open(fifo1, O_RDONLY);
if (fdr == -1)
{
perror("open error");
exit(-1);
}
printf("b:successfully opened fifo1\n");
// 循环读数据
char buf[256];
while (1)
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
int len = read(fdr, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (len <= 0)
{
perror("read");
break;
}
printf("a: %s\n", buf);
}
close(fdr);
}
return 0;
}


![Erlang程序设计[Part2 chapter5-chapter8]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5d1ecc60e0e541f9a0ba10e20989be64.png)