序言
之前文章有介绍采用FactoryBean的方式创建对象,以及使用反射创建对象。
这篇文章继续介绍Spring中创建Bean的形式之一——自定义BeanPostProcessor。
之前在介绍BeanPostProcessor的文章中有提到,BeanPostProcessor接口的实现中有一个InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
而在Spirng源码中的doGetBean方法中就有针对该接口的判断逻辑,如果有类实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor则可以在对应的方法中进行Bean对象的创建。
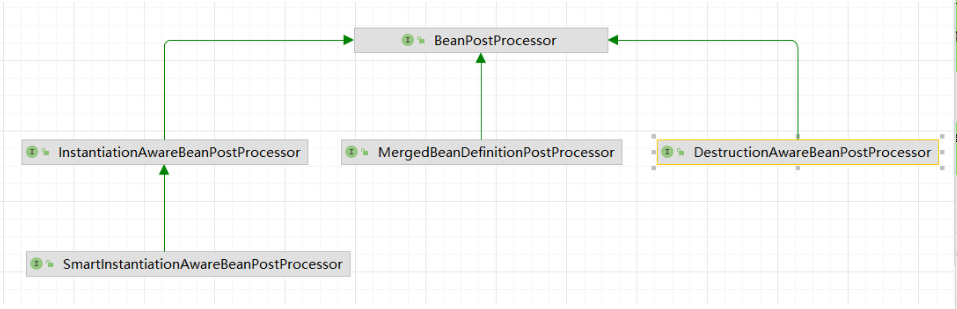
源码
去除无用代码,我们这里主要看resolveBeforeInstantiation方法。如果通过resolveBeforeInstantiation创建了Bean示例,则return该Bean 不在继续往下走其他流程。
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
//锁定class,根据设置的class属性或者根据className来解析class
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
// 给BeanPostProcessors一个机会来返回代理来替代真正的实例,
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
}
resolveBeforeInstantiation
如果满足if条件,则会走applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation方法进行对象的创建。
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
//如果beforeInstantiationResolved值为null或者true,那么表示尚未被处理,进行后续的处理
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
// 确保Bean确实在此处进行处理
// 判断当前mbd是否是合成的,只有在实现aop的时候synthetic的值才为true,并且是否实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
//确定目标类型
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation
获取所有实现了BeanPostProcessors的类,并强转成InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 类型,调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法进行Bean的创建。
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
测试类
我们针对上面的源码流程,扩展自定义的BeanPostProcessor进行类的创建。我们这里依然采用上篇文章提到的Cglib动态代理的方式创建我们的对象。
BeforeInstantiation
BeforeInstantiation 是我们想要最终创建的实例对象。
public class BeforeInstantiation {
public void doSomeThing(){
System.out.println("执行do some thing....");
}
}
MyMethodInterceptor
拦截器类,对目标方法进行中间拦截,上篇文章在讲lookup-method标签时,里面采用Cglib动态代理生成对象的固定写法,创建Enhancer对象并设置CallBack。
因为我们这里也采用Cglib的方式进行对象的创建,所以也需要设置CallBack。
public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("目标方法执行之前:" + method);
Object o1 = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
System.out.println("目标方法执行之后:" + method);
return o1;
}
}
MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
自定义InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的扩展类,调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法,采用Cglib的固定写法实现对BeforeInstantiation 对象的创建。
其余方法因为用不到,所以直接return对应类型,没有具体业务逻辑。
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanClass == BeforeInstantiation.class) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(beanClass);
enhancer.setCallback(new MyMethodInterceptor());
BeforeInstantiation beforeInstantiation = (BeforeInstantiation) enhancer.create();
return beforeInstantiation;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return true;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return pvs;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return pvs;
}
resolveBeforeInstantiation.xml
xml中声明MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor对象和BeforeInstantiation对象。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor" class="org.springframework.resolveBeforeInstantiation.MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor" />
<bean id="beforeInstantiation" class="org.springframework.resolveBeforeInstantiation.BeforeInstantiation"/>
</beans>
main
执行refresh()主流程调用registerBeanPostProcessors方法创建MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后,会调用addBeanPostProcessor方法将hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()变量设置为true,当beforeInstantiation创建时,if 判断 整体为 true,调用我们自定义的扩展类创建beforeInstantiation对象。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("resolveBeforeInstantiation.xml");
BeforeInstantiation beanInstantiation = (BeforeInstantiation)ac.getBean("beforeInstantiation");
beanInstantiation.doSomething();
}