序言
目前介绍几种Spring创建对象的方式,其中包括 FactoryBean、Cglib动态代理、自定义BeanPostProcessor(InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor)。
这篇文章会继续扩展Spring中Bean的创建方式——Supplier。
Supplier
先看下我们的Supplier类,在前面的ObjectFactory中有提到过,类上有@FunctionalInterface注解相当于函数式编程,而当我们调用get()方法时,才会调用我们自定义实现的方法。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {
/**
* Gets a result.
*
* @return a result
*/
T get();
}
测试类
SupplierBeanFactoryPostProcessor
自定义类实现了BFPP,并在方法中设置InstanceSupplier变量。
public class SupplierBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
GenericBeanDefinition gbd = (GenericBeanDefinition)beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("user");
gbd.setInstanceSupplier(CreateSupplier::createUser);
gbd.setBeanClass(User.class);
}
}
// 或者
public class SupplierBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
registry.registerBeanDefinition("user", new RootBeanDefinition(User.class,CreateSupplier::createUser));
}
}
CreateSupplier
返回User对象。
public class CreateSupplier {
public static User createUser(){
return new User("zhangsan");
}
}
User
简单的一个User类。
public class User {
private String name;
public User() {
}
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
supplier.xml
xml文件中定义了SupplierBeanFactoryPostProcessor和准备创建的User类。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="supplierBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class="org.springframework.supplier.SupplierBeanFactoryPostProcessor"/>
<bean id="user" class="org.springframework.supplier.User"/>
<bean id="supplierBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor" class="org.springframework.supplier.SupplierBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor" />
</beans>
main
当代码运行,refresh()主流程方法中调用invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法时,就会执行我们自定义的类中方法,从而设置instanceSupplier变量,当调用getBean方法生成User对象时,instanceSupplier不为null,调用createBean方法,生成User对象。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("supplier.xml");
User user = ac.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
doCreateBean
回到我们的源码doCreateBean方法中,我们重点关注createBeanInstance()方法。
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
//这个beanWrapper是用来持有创建出来的bean对象的
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
//如果是单例对象,从factoryBeanInstanceCache缓存中移除该信息
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 如果是单例对象,从factoryBean实例缓存中移除当前bean定义信息
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
// 没有就创建实例
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 根据执行bean使用对应的策略创建新的实例,如,工厂方法,构造函数主动注入、简单初始化
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// 去除无用代码.....
}
createBeanInstance
在createBeanInstance方法中,会获取我们自定义的getInstanceSupplier,如果不为 null, 则调用obtainFromSupplier
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
// 锁定class,根据设置的class属性或者根据className来解析class
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
// 如果beanClass != null
// 并且,访问修饰符不是public修饰, 抛异常
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
// 获取定义的Supplier
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
此时创建我们的User对象时,可以进到判断中。
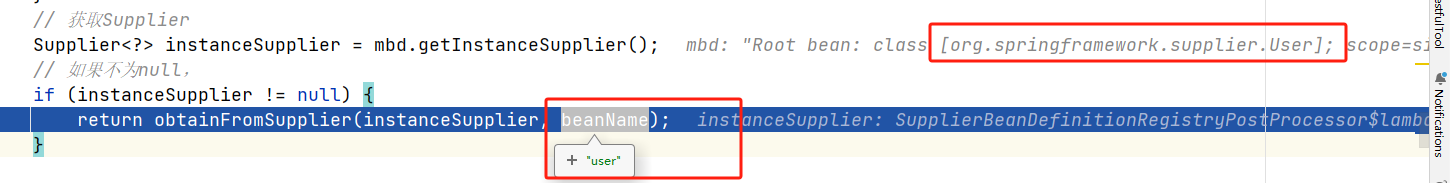
obtainFromSupplier
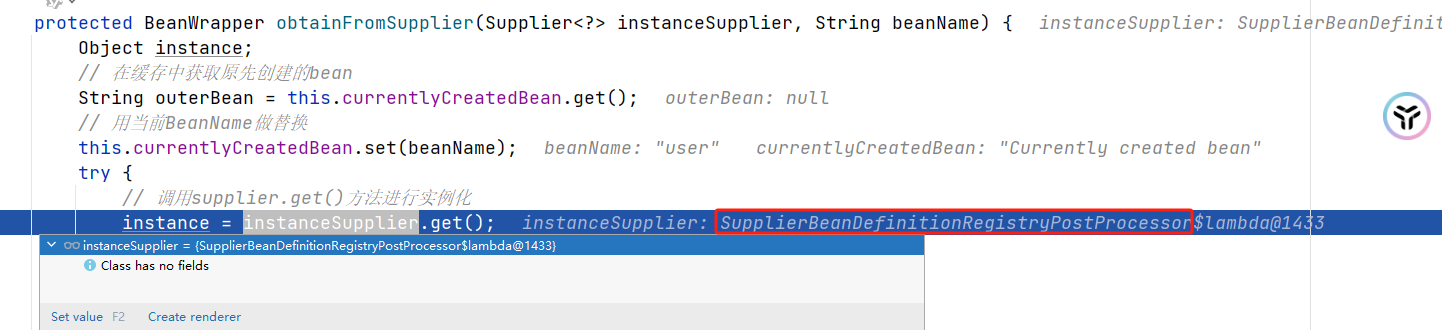
此时instanceSupplier.get()方法就会执行我们定义的createUser,从而进行User对象的创建。
protected BeanWrapper obtainFromSupplier(Supplier<?> instanceSupplier, String beanName) {
Object instance;
// 在缓存中获取原先创建的bean
String outerBean = this.currentlyCreatedBean.get();
// 用当前BeanName做替换
this.currentlyCreatedBean.set(beanName);
try {
// 调用supplier.get()方法进行实例化
instance = instanceSupplier.get();
}
finally {
//
if (outerBean != null) {
this.currentlyCreatedBean.set(outerBean);
}
else {
this.currentlyCreatedBean.remove();
}
}
// 如果instance == null,则返回NullBean
if (instance == null) {
instance = new NullBean();
}
// 将创建好的示例封装到wrapper包装类
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(instance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
Supplier对象是我们自定义的Supplier。