文章目录
- windows
- linux
C语言调用动态链接库
windows
C语言调用windows下的动态库dll;
待实现
linux
C语言调用linux下的动态库so;
- 准备C代码,并编译为so
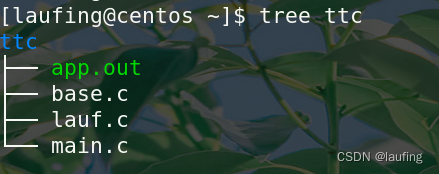
base.c
#include <stdio.h>
int funcBase(){
printf("func base is running...");
return 10;
}
lauf.c
#include <stdio.h>
// 定义变量
char *username = "jack";
char *funcLauf(char* ptr){
printf("%s-username:%s\n", __FILE__, ptr);
return ptr;
}
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
// declare func defined in other c source.
extern int funcBase();
extern char* funcLauf(char* ptr);
// declare global variable
extern char* username;
// 入口函数
int main(){
int result = funcBase();
printf("%s-result:%d\n", __FILE__, result);
char* name = funcLauf(username);
printf("%s-name: %s\n", __FILE__, name);
return 0;
}
编译可执行程序:
# 命令行下编译,指定需要编译的所有C源文件,其他目录下的也可以指定
gcc ./*.c -o app.out
# 编译为动态共享库
gcc -fPIC ./*.c -shared -o app.so
图中的app.out 是在linux下编译的可执行程序, ./app.out 即可执行
- 编写C代码,调用上一步的so(共享库、动态库);
- 使用头文件
<
d
l
f
c
n
.
h
>
<dlfcn.h>
<dlfcn.h>
- void *dlopen(const char *filename, int flag),打开一个动态库;如dlopen(“xxx.so”, RTLD_LAZY)
- void *dlsym(void *handle, const char *symbolName),获取动态库中的函数/变量(符号);如dlsym(ptr, “func”)
- int dlclose(void *handle),关闭一个动态库;
- char *dlerror(void): 返回上一个动态链接库错误的字符串描述。
- 使用 LD_PRELOAD 环境变量
- 使用 -l 编译器选项链接库文件
- 使用头文件
<
d
l
f
c
n
.
h
>
<dlfcn.h>
<dlfcn.h>
// 这里用 <dlfcn.h> 使用动态库的头文件方式
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dlfcn.h> // 使用动态库的头文件
int main() {
void *handle = NULL;
char* (*func)(char*); // ptr of func
char *error = NULL;
char* username = "jack";
// load lib
handle = dlopen("app.so", RTLD_LAZY); // lazy load
if (!handle) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", dlerror()); // 错误信息输入到dlerror
return 1;
}
// get func inner so
func = dlsym(handle, "funcLauf");
if ((error = dlerror()) != NULL) { // 有错误输出
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", error);
return 1;
}
// 函数调用
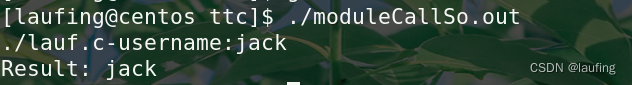
printf("Result: %s\n", func(username));
// close so ptr
dlclose(handle);
return 0;
}
编译可执行文件:
# compile
gcc moduleCallSo.c -o moduleCallSo.out -ldl
# gcc, compiler
# moduleCallSo.c, C source file
# -o, output to a file
# -l, to include dynamic lib, 'dl' is dynamic linked lib
执行结果: