文章目录
- VIT 模型搭建
- Swin-T 模型搭建
- 参考
这里使用 VIT 和 Swin-T 在数据集 cifar10 上进行训练
![![[5f5e5055bc1149e4bb1fa2961cc71434.gif]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5bfa9859e5244f879337110cc6bb553a.gif)
VIT 模型搭建
导入需要的外部库
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
这里我们接着使用 cifar10 的数据,导入数据如下
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.cifar10.load_data()
# x_train.shape, y_train.shape
# ((50000, 32, 32, 3), (50000, 1))
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test))
# 图片处理
image_size = 72 # 把图片尺寸固定为 image_size
def process_data(image, label):
image = tf.image.resize(image, [image_size, image_size])
image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image)
image = tf.image.random_flip_up_down(image)
image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, 0.2)
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32) / 255.0
return image, label
# 这里batchsize定位128
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(process_data).batch(128)
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(process_data).batch(128)
图片展示
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
for i in range(25):
plt.subplot(5, 5, i + 1)
plt.imshow(x_train[i])
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
得到图片效果
![![[Pasted image 20240611175813.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1f654884e01b4f5b87e5f902637722fd.png)
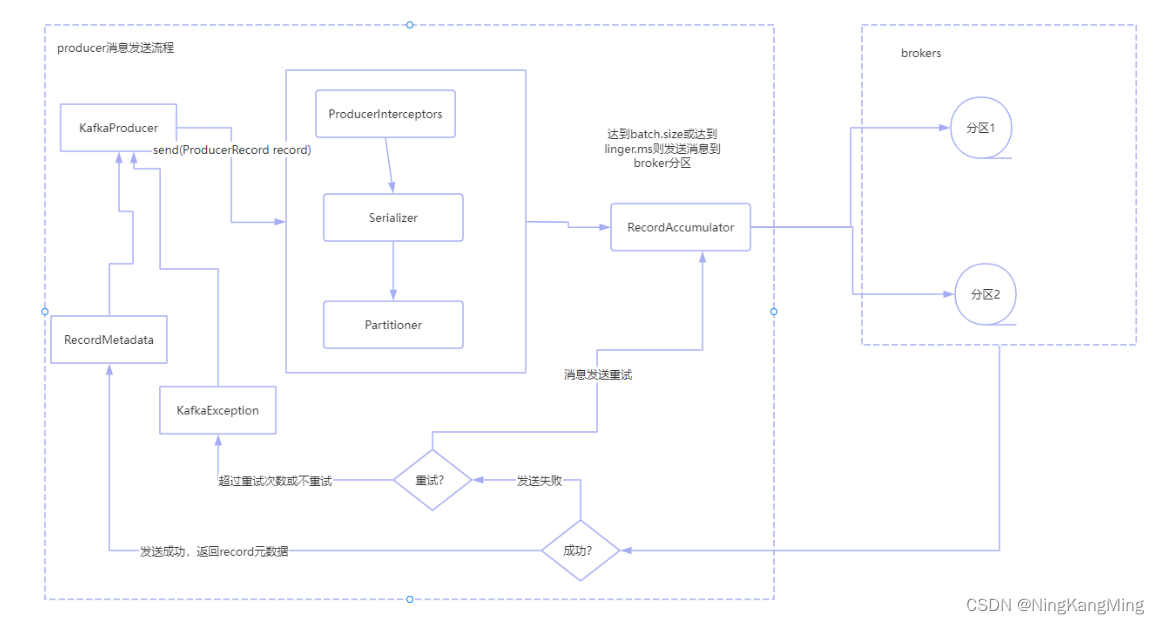
VIT 模型架构如图所示:
![![[Pasted image 20240605185215.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/13027d4257f04d1e849255fe3321d3f8.png)
从中可以看到,其创新点主要是将图片进行拆分作为序列数据带入 Transformer 中,这里先实现拆分图片类 PatchExtract 和 分块编码类 PatchEmbedding
class PatchExtract(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, patch_size):
"""patch_size 每一块图片的长宽"""
super(PatchExtract, self).__init__()
self.patch_size = patch_size
def call(self, images):
patches = tf.image.extract_patches(
images,
sizes=[1, self.patch_size, self.patch_size, 1],
strides=[1, self.patch_size, self.patch_size, 1],
rates=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='VALID'
)
patches = tf.reshape(patches, [tf.shape(patches)[0], -1, tf.shape(patches)[-1]])
return patches
class PatchEmbedding(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, patch_size, patch_nums, d_model):
super(PatchEmbedding, self).__init__()
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.patch_nums = patch_nums
self.d_model = d_model
self.patches = PatchExtract(self.patch_size)
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(self.patch_nums + 1, self.d_model)
self.dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model)
self.learnabel_parameters = self.add_weight(shape=[1, 1, d_model])
def call(self, x):
# 处理 patches
x = self.patches(x)
x = self.dense(x)
x = tf.concat([tf.repeat(self.learnabel_parameters, tf.shape(x)[0], axis=0), x], axis=1)
# 处理位置编码
p = tf.range(self.patch_nums + 1)
p = self.embedding(p)
output = x + p
return output
可视化 Patches ,代码如下
image_size = 72
patch_size = 6
# 定义图片
img = x_train[0]
# 原图
plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis("off")
# 放大图片 并 切分 patches
patches = tf.image.resize(img[tf.newaxis, :], [image_size, image_size])
patches = PatchExtract(patch_size)(patches)
# 由于patches的行数和列数相同,这里采取开根号的形式
n = int(np.sqrt(patches.shape[1]))
# patches 图
plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
for i, patch in enumerate(patches[0]):
ax = plt.subplot(n, n, i + 1)
patch_img = tf.reshape(patch, (patch_size, patch_size, 3))
plt.imshow(tf.cast(patch_img, dtype=tf.int32))
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
得到效果如下
![![[Pasted image 20240605185037.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ba2a65280f0346f7bbc03090afec3aed.png)
定义一个多头注意力机制类 MultiHeadAttention 如下
class MultiHeadAttention(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_heads, d_model):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.d_model = d_model
## 判断能否被整除
assert self.d_model % self.num_heads == 0
## 定义需要用到的 layer
self.query_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model)
self.key_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model)
self.value_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model)
self.output_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model)
def call(self, x_query, x_key, x_value, use_casual_mask=False):
query = self._split_heads(self.query_dense(x_query))
key = self._split_heads(self.key_dense(x_key))
value = self._split_heads(self.value_dense(x_value))
output, attention_weights = self._scaled_dot_product_attention(query, key, value, use_casual_mask)
output = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda output: tf.transpose(output, perm=[0, 2, 1, 3]))(output)
output = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda output: tf.reshape(output, [tf.shape(output)[0], -1, self.d_model]))(output)
output = self.output_dense(output)
return output
def _split_heads(self, x):
# x = tf.reshape(x, [tf.shape(x)[0], -1, self.num_heads, self.d_model / self.num_heads])
# x = tf.transpose(x, perm=[0, 2, 1, 3])
x = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.reshape(x, [tf.shape(x)[0], -1, self.num_heads, self.d_model // self.num_heads]))(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.transpose(x, perm=[0, 2, 1, 3]))(x)
return x
def _scaled_dot_product_attention(self, query, key, value, use_casual_mask):
dk = tf.cast(tf.shape(key)[-1], tf.float32)
scaled_attention_logits = tf.matmul(query, key, transpose_b=True) / tf.math.sqrt(dk)
if use_casual_mask:
casual_mask = 1 - tf.linalg.band_part(tf.ones_like(scaled_attention_logits), -1, 0)
scaled_attention_logits += casual_mask * -1e9
attention_weights = tf.nn.softmax(scaled_attention_logits, axis=-1)
output = tf.matmul(attention_weights, value)
return output, attention_weights
再定义一个 MLP 网络层如下:
class MLP(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, d_model, dropout_rate=0.1):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.dense_layers = [tf.keras.layers.Dense(units, activation='gelu') for units in [d_model * 2, d_model]]
self.dropout = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(rate=dropout_rate)
def call(self, x):
for dense_layer in self.dense_layers:
x = dense_layer(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
return x
构建一个 EncoderLayer 来结合 MultiHeadAttention 和 MLP,并利用 EncoderLayer 来构建 VIT
class EncoderLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_heads, d_model):
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.mha = MultiHeadAttention(num_heads, d_model)
self.mlp = MLP(d_model)
self.layernorm_mha = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
self.layernorm_mlp = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
def call(self, x):
# 注意力部分
x = self.layernorm_mha(x)
x = x + self.mha(x, x, x)
# 多重感知机部分
x = x + self.mlp(self.layernorm_mlp(x))
return x
class VIT(tf.keras.models.Model):
def __init__(self, patch_size, patch_nums, encoder_layer_nums, num_heads, d_model):
super(VIT, self).__init__()
self.embedding = PatchEmbedding(patch_size, patch_nums, d_model)
self.encoder_layers = [EncoderLayer(num_heads, d_model) for _ in range(encoder_layer_nums)]
self.final_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
def call(self, x):
x = self.embedding(x)
for encoder_layer in self.encoder_layers:
x = encoder_layer(x)
x = self.final_dense(x[:, 0, :])
return x
模型定义完毕后,初始化模型并开始训练
# 定义超参数
patch_size = 6
patch_nums = 144
encoder_layer_nums = 3
num_heads = 8
d_model = 256
model = VIT(patch_size, patch_nums, encoder_layer_nums, num_heads, d_model)
# 定义学习率
learning_rate = 1e-3
model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(
learning_rate=learning_rate
),
metrics=[
tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name="accuracy"),
tf.keras.metrics.SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy(5, name="top-5-accuracy"),
],
)
# 开始训练
history = model.fit(train_dataset, epochs=20, validation_data=test_dataset)
训练过程如下
Epoch 1/20
391/391 [==============================] - 23s 47ms/step - loss: 2.1613 - accuracy: 0.2516 - top-5-accuracy: 0.7557 - val_loss: 1.6115 - val_accuracy: 0.3989 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.8984
Epoch 2/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 46ms/step - loss: 1.5517 - accuracy: 0.4297 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9031 - val_loss: 1.3938 - val_accuracy: 0.4899 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9331
Epoch 3/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 46ms/step - loss: 1.3867 - accuracy: 0.4973 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9304 - val_loss: 1.2830 - val_accuracy: 0.5353 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9457
Epoch 4/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 45ms/step - loss: 1.2876 - accuracy: 0.5326 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9437 - val_loss: 1.2664 - val_accuracy: 0.5308 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9513
Epoch 5/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 45ms/step - loss: 1.2138 - accuracy: 0.5618 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9505 - val_loss: 1.2320 - val_accuracy: 0.5522 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9483
Epoch 6/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 46ms/step - loss: 1.1558 - accuracy: 0.5821 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9567 - val_loss: 1.2069 - val_accuracy: 0.5682 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9536
Epoch 7/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 46ms/step - loss: 1.1135 - accuracy: 0.5980 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9608 - val_loss: 1.1252 - val_accuracy: 0.5982 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9601
Epoch 8/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 46ms/step - loss: 1.0649 - accuracy: 0.6175 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9645 - val_loss: 1.0961 - val_accuracy: 0.6041 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9625
Epoch 9/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 45ms/step - loss: 1.0353 - accuracy: 0.6285 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9674 - val_loss: 1.0793 - val_accuracy: 0.6174 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9640
Epoch 10/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 45ms/step - loss: 1.0059 - accuracy: 0.6390 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9689 - val_loss: 1.0667 - val_accuracy: 0.6221 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9638
Epoch 11/20
391/391 [==============================] - 18s 46ms/step - loss: 0.9743 - accuracy: 0.6491 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9717 - val_loss: 1.0402 - val_accuracy: 0.6284 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9653
Epoch 12/20
391/391 [==============================] - 23s 58ms/step - loss: 0.9518 - accuracy: 0.6601 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9735 - val_loss: 1.0703 - val_accuracy: 0.6240 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.
Swin-T 模型搭建
Swin-T 的思想核心和 CNN 差不多,主要实现的是一个下采样的算法过程;
首先导入外部库
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
导入数据,这里同样用 cifar10 的数据集
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.cifar10.load_data()
# x_train.shape, y_train.shape # ((50000, 32, 32, 3), (50000, 1))
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test))
def process_data(image, label):
image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image)
image = tf.image.random_flip_up_down(image)
image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, 0.2)
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32) / 255.0
return image, label
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(process_data).batch(128)
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(process_data).batch(128)
数据可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
for i in range(25):
plt.subplot(5, 5, i + 1)
plt.imshow(x_train[i])
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
得到图片效果
![![[Pasted image 20240611180840.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d386a88d34fb480b9ee5bb874e7d3b00.png)
在对 Patch 进行操作时我们定义三个类 PatchExtract, PatchEmbedding, PatchMerging,前面两个和 VIT 模型相似,第三个 PatchMerging 是将 PatchExtract 后的 Patch 相同位置的像素绑定到一起构成一张新的 Patch;
## 这里可以直接使用 Conv2D 实现 `PatchExtract` 和 `PatchEmbedding`
## self.proj = Conv2D(filters=embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, strides=patch_size)
class PatchExtract(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, patch_size, **kwargs):
"""patch_size 每一块图片的长宽"""
super(PatchExtract, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.patch_size = patch_size
def call(self, images):
patches = tf.image.extract_patches(
images,
sizes=[1, self.patch_size, self.patch_size, 1],
strides=[1, self.patch_size, self.patch_size, 1],
rates=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='VALID'
)
patches = tf.reshape(patches, [tf.shape(patches)[0], -1, tf.shape(patches)[-1]])
return patches
class PatchEmbedding(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, d_model, patch_size, patch_nums, **kwargs):
super(PatchEmbedding, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.patch_nums = patch_nums
self.proj = tf.keras.layers.Dense(d_model, activation='relu')
self.patches = PatchExtract(patch_size)
self.pos_embed = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(input_dim=patch_nums, output_dim=d_model)
def call(self, x):
patch = self.patches(x)
pos = tf.range(start=0, limit=self.patch_nums, delta=1)
return self.proj(patch) + self.pos_embed(pos)
class PatchMerging(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, input_resolution, d_model, **kwargs):
super(PatchMerging, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.d_model = d_model
self.input_resolution = input_resolution
self.dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model * 2, use_bias=False, activation='relu')
self.norm = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
def call(self, x):
# assert tf.shape(x)[1] == self.input_resolution[0] * self.input_resolution[1]
# assert tf.shape(x)[-1] == self.d_model
x = tf.reshape(x, [tf.shape(x)[0], self.input_resolution[0], self.input_resolution[1], -1])
x1 = x[:, 0::2, 0::2, :]
x2 = x[:, 1::2, 0::2, :]
x3 = x[:, 0::2, 1::2, :]
x4 = x[:, 1::2, 1::2, :]
x = tf.concat([x1, x2, x3, x4], axis=-1)
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, self.input_resolution[0]*self.input_resolution[1]//4, 4 * self.d_model])
# x = self.norm(x)
x = self.dense(x)
return x
## 代码中的 https://github.com/VcampSoldiers/Swin-Transformer-Tensorflow/blob/main/models/swin_transformer.py 中并没有使用 Embedding(range) 的方式进行添加
定义窗口注意力机制,与普通的注意力机制不同,其是在各个窗口中执行注意力机制
class WindowAttention(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, d_model, window_size, num_heads, **kwargs):
super(WindowAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.d_model = d_model
self.window_size = window_size
self.num_heads = num_heads
assert self.d_model % self.num_heads == 0
self.head_dim = self.d_model // self.num_heads
self.scale = self.head_dim ** -0.5
self.relative_position_bias_table = self.add_weight(shape=[(2*self.window_size[0]-1)*(2*self.window_size[1]-1), self.num_heads])
# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window
coords_h = tf.range(self.window_size[0])
coords_w = tf.range(self.window_size[1])
coords = tf.stack(tf.meshgrid(coords_h, coords_w)) # 2, Wh, Ww
coords_flatten = tf.reshape(coords, [2, -1]) # 2, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
relative_coords = tf.transpose(relative_coords, perm=[1,2,0]) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2
relative_coords = relative_coords + [self.window_size[0] - 1, self.window_size[1] - 1] # shift to start from 0
relative_coords = relative_coords * [2*self.window_size[0] - 1, 1]
self.relative_position_index = tf.math.reduce_sum(relative_coords,-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww
self.qkv = tf.keras.layers.Dense(3 * self.d_model, activation='relu', use_bias=True)
self.output_dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.d_model, activation='relu', use_bias=True)
def call(self, x, mask=None):
qkv = self.qkv(x) # x.shape = B, L, C -> qkv.shape = B, L, 3 * C
qkv = tf.reshape(qkv, [tf.shape(x)[0], tf.shape(x)[1], 3, self.num_heads, self.head_dim]) # B, L, 3, num_heads, C // num_heads
qkv = tf.transpose(qkv, perm=[2, 0, 3, 1, 4]) # 3, B, num_heads, L, C // num_heads
q, k, v = tf.unstack(qkv, axis=0) # q,k,v -> B, num_heads, L, C // num_heads
scaled_attention_logits = tf.matmul(q, k, transpose_b=True) * self.scale # B, num_heads, L, L
# 获得 relative_position_bias
relative_position_bias = tf.reshape(tf.gather(self.relative_position_bias_table, tf.reshape(self.relative_position_index, [-1])),
[self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1]) # L, L, num_heads
relative_position_bias = tf.transpose(relative_position_bias, perm=[2, 0, 1]) # num_heads, L, L
scaled_attention_logits = scaled_attention_logits + relative_position_bias[tf.newaxis, :] # B, num_heads, L, L
if mask is not None:
nW = mask.shape[0] # every window has different mask [num_heads, L, L]
scaled_attention_logits = tf.reshape(scaled_attention_logits,
[tf.shape(x)[0] // nW, nW, self.num_heads, tf.shape(x)[1], tf.shape(x)[1]]
) + mask[:, None, :, :] # add mask: make each component -inf or just leave it
scaled_attention_logits = tf.reshape(scaled_attention_logits, [-1, self.num_heads, tf.shape(x)[1], tf.shape(x)[1]])
# scaled_attention_logits -> B, num_heads, L, L
attention_weights = tf.nn.softmax(scaled_attention_logits, axis=-1) # B, num_heads, L, L
output = tf.matmul(attention_weights, v) # B, num_heads, L, L and B, num_heads, L, C // num_heads -> B, num_heads, L, C // num_heads
output = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda output: tf.transpose(output, perm=[0, 2, 1, 3]))(output)
output = tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda output: tf.reshape(output, [tf.shape(output)[0], tf.shape(x)[1], self.d_model]))(output)
output = self.output_dense(output)
return output
定义一个 MLP 模块
class MLP(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, d_model, **kwargs):
super(MLP, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dense_1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(4 * d_model, activation='gelu')
self.dense_2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(d_model, activation='gelu')
def call(self, x):
x = self.dense_1(x)
x = self.dense_2(x)
return x
定义一个 SwinTransformerBlock
class SwinTransformerBlock(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
r""" Swin Transformer Block.
Args:
d_model (int): Number of input channels.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resulotion.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Window size.
shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA.
drop_path (float, optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0
"""
def __init__(self, d_model, input_resolution, num_heads, window_size=7, shift_size=0):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.input_resolution = input_resolution
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.window_size = window_size
self.shift_size = shift_size
# if window size is larger than input resolution, we don't partition windows
if min(self.input_resolution) <= self.window_size:
self.shift_size = 0
self.window_size = min(self.input_resolution)
assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-window_size"
self.norm1 = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
self.attn = WindowAttention(
self.d_model, window_size=[self.window_size, self.window_size], num_heads=num_heads)
# 来一个drop_path
# self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path)
self.norm2 = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
self.mlp = MLP(d_model=self.d_model)
# calculate attention mask for SW-MSA
if self.shift_size > 0:
self.attn_mask = self.calculate_attention_mask(self.window_size, self.shift_size)
else:
self.attn_mask = None
def call(self, x):
H, W = self.input_resolution
B, L, C = tf.shape(x)[0], tf.shape(x)[1], tf.shape(x)[2]
# assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x)
x = tf.reshape(x, [B, H, W, C])
# cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
shifted_x = tf.roll(x, shift=[-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size], axis=(1, 2))
else:
shifted_x = x
# partition windows
x_windows = self.window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, C
x_windows = tf.reshape(x_windows, [-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C]) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# W-MSA/SW-MSA
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=self.attn_mask) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C
# merge windows
attn_windows = tf.reshape(attn_windows, [-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C])
shifted_x = self.window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, H, W) # B H' W' C
# reverse cyclic shift
if self.shift_size > 0:
x = tf.roll(shifted_x, shift=[self.shift_size, self.shift_size], axis=(1, 2))
else:
x = shifted_x
x = tf.reshape(x, [B, H * W, C])
x = shortcut + x
# FFN
x = x + self.mlp(self.norm2(x))
return x
def calculate_attention_mask(self, window_size, shift_size):
H, W = self.input_resolution
img_mask = np.zeros([1, H, W, 1]) # 1 H W 1
h_slices = (slice(0, -window_size),
slice(-window_size, -shift_size),
slice(-shift_size, None))
w_slices = (slice(0, -window_size),
slice(-window_size, -shift_size),
slice(-shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt
cnt += 1
img_mask = tf.convert_to_tensor(img_mask)
mask_windows = self.window_partition(img_mask, window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1
mask_windows = tf.reshape(mask_windows, [-1, window_size * window_size])
attn_mask = mask_windows[:, None, :] - mask_windows[:, :, None]
attn_mask = tf.where(attn_mask==0, -100., 0.)
return attn_mask
def window_partition(self, x, window_size):
"""
Args:
x: (B, H, W, C)
window_size (int): window size
Returns:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
"""
B, H, W, C = tf.shape(x)[0], tf.shape(x)[1], tf.shape(x)[2], tf.shape(x)[3]
x = tf.reshape(x, [B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C])
# TODO contiguous memory access?
windows = tf.reshape(tf.transpose(x, perm=[0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5]), [-1, window_size, window_size, C])
return windows
@tf.function
def window_reverse(self, windows, window_size, H, W):
"""
Args:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)
window_size (int): Window size
H (int): Height of image
W (int): Width of image
Returns:
x: (B, H, W, C)
"""
B = tf.shape(windows)[0] * window_size ** 2 // (H * W)
x = tf.reshape(windows, [B, H // window_size, W // window_size, window_size, window_size, -1])
x = tf.reshape(tf.transpose(x, perm=[0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5]), [B, H, W, -1])
return x
由于层之间重复性出现,可以定义一个 BasicLayer 简化模型定义操作
![![[Pasted image 20240611182658.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/081c01d04ab940f19e8e75e0213a2381.png)
class BasicLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
""" A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage.
Args:
d_model (int): Number of input channels.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resolution.
depth (int): Number of blocks.
num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.
window_size (int): Local window size.
downsample (tf.keras.layers.Layer | None, optional): Downsample layer at the end of the layer. Default: None
"""
def __init__(self, d_model, input_resolution, depth, num_heads, window_size, downsample=None, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.d_model = d_model
self.input_resolution = input_resolution
self.depth = depth
# build blocks
self.blocks = [
SwinTransformerBlock(d_model=d_model,
input_resolution=input_resolution,
num_heads=num_heads,
window_size=window_size,
shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else window_size // 2) for i in range(depth)]
# patch merging layer
if downsample is not None:
self.downsample = downsample(input_resolution=input_resolution, d_model=d_model)
else:
self.downsample = None
def call(self, x):
for blk in self.blocks:
x = blk(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
x = self.downsample(x)
return x
利用 BasicLayer 定义最后的模型结构 SwinTransformer
class SwinTransformer(tf.keras.models.Model):
r""" Swin Transformer
A Tensorflow impl of : `Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows` -
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.14030
Args:
img_size (int | tuple(int)): Input image size. Default 224
patch_size (int | tuple(int)): Patch size. Default: 4
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3
num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000
embed_dim (int): Patch embedding dimension. Default: 96
depths (tuple(int)): Depth of each Swin Transformer layer.
num_heads (tuple(int)): Number of attention heads in different layers.
window_size (int): Window size. Default: 7
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=32, patch_size=2, num_classes=10, d_model=256,
depths=[2, 2], num_heads=[4, 8], window_size=4, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_layers = len(depths)
self.d_model = d_model
self.patches_resolution = [img_size // patch_size, img_size // patch_size]
self.patch_nums = self.patches_resolution[0] ** 2
# split image into non-overlapping patches
self.embedding = PatchEmbedding(d_model=d_model, patch_size=patch_size, patch_nums=self.patch_nums)
# build layers
self.sequence = tf.keras.models.Sequential(name="basic_layers_seq")
for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):
self.sequence.add(BasicLayer(d_model=int(self.d_model * 2 ** i_layer),
input_resolution=(self.patches_resolution[0] // (2 ** i_layer),
self.patches_resolution[1] // (2 ** i_layer)),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
window_size=window_size,
downsample=PatchMerging if (i_layer < self.num_layers - 1) else None))
self.norm = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)
self.avgpool = tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D()
self.head = tf.keras.layers.Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax')
def forward_features(self, x):
x = self.embedding(x)
x = self.sequence(x)
x = self.norm(x) # B L C
x = self.avgpool(x)
return x
def call(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.head(x)
return x
初始化模型
model = SwinTransformer(img_size=32, patch_size=2, num_classes=10, d_model=256,
depths=[2, 2], num_heads=[4, 8], window_size=4)
# 定义学习率
learning_rate = 1e-3
model.compile(
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(),
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(
learning_rate=learning_rate
),
metrics=[
tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name="accuracy"),
tf.keras.metrics.SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy(5, name="top-5-accuracy"),
],
)
history = model.fit(train_dataset, epochs=20, validation_data=test_dataset)
得到训练过程
Epoch 1/20
391/391 [==============================] - 40s 83ms/step - loss: 2.1053 - accuracy: 0.2078 - top-5-accuracy: 0.7266 - val_loss: 1.8410 - val_accuracy: 0.2724 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.8481
Epoch 2/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 80ms/step - loss: 1.6857 - accuracy: 0.3554 - top-5-accuracy: 0.8823 - val_loss: 1.5863 - val_accuracy: 0.4000 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9075
Epoch 3/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 80ms/step - loss: 1.5168 - accuracy: 0.4359 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9137 - val_loss: 1.4614 - val_accuracy: 0.4630 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9228
Epoch 4/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 79ms/step - loss: 1.4073 - accuracy: 0.4840 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9285 - val_loss: 1.3463 - val_accuracy: 0.5183 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9394
Epoch 5/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 79ms/step - loss: 1.3172 - accuracy: 0.5221 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9390 - val_loss: 1.2881 - val_accuracy: 0.5345 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9431
Epoch 6/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 79ms/step - loss: 1.2394 - accuracy: 0.5539 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9474 - val_loss: 1.2543 - val_accuracy: 0.5536 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9410
Epoch 7/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 80ms/step - loss: 1.1807 - accuracy: 0.5765 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9522 - val_loss: 1.1820 - val_accuracy: 0.5759 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9536
Epoch 8/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 79ms/step - loss: 1.1309 - accuracy: 0.5942 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9583 - val_loss: 1.1263 - val_accuracy: 0.5941 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9560
Epoch 9/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 78ms/step - loss: 1.0864 - accuracy: 0.6095 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9606 - val_loss: 1.0998 - val_accuracy: 0.6105 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9589
Epoch 10/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 80ms/step - loss: 1.0537 - accuracy: 0.6250 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9638 - val_loss: 1.0706 - val_accuracy: 0.6213 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9638
Epoch 11/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 78ms/step - loss: 1.0157 - accuracy: 0.6360 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9660 - val_loss: 1.0507 - val_accuracy: 0.6303 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9630
Epoch 12/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 78ms/step - loss: 0.9869 - accuracy: 0.6457 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9685 - val_loss: 1.0682 - val_accuracy: 0.6241 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9623
Epoch 13/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 78ms/step - loss: 0.9490 - accuracy: 0.6589 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9714 - val_loss: 1.0055 - val_accuracy: 0.6473 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9681
Epoch 14/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 78ms/step - loss: 0.9187 - accuracy: 0.6729 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9741 - val_loss: 1.0054 - val_accuracy: 0.6504 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9677
Epoch 15/20
391/391 [==============================] - 31s 79ms/step - loss: 0.8934 - accuracy: 0.6836 - top-5-accuracy: 0.9765 - val_loss: 0.9728 - val_accuracy: 0.6575 - val_top-5-accuracy: 0.9696
参考
Swin-Transformer网络结构详解_swin transformer-CSDN博客