Conference:ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS)
CCF level:CCF A
Categories:network and information security
Year:2023
Num:25
第1~7篇区块链文章请点击此处查看
第8~13篇区块链文章请点击此处查看
第14~19篇区块链文章请点击此处查看
20
Title:
Interchain Timestamping for Mesh Security
网格安全的链间时间戳
Authors:

Key words:
Interchain timestamping; mesh security
链间时间戳;网格安全
Abstract:
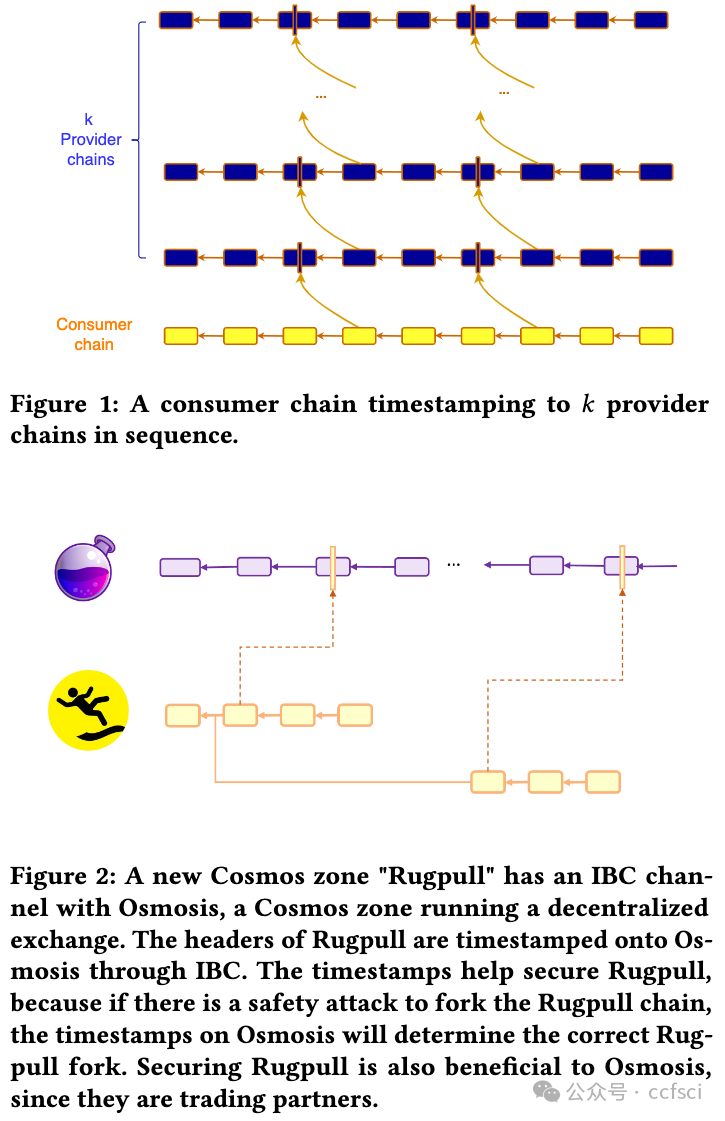
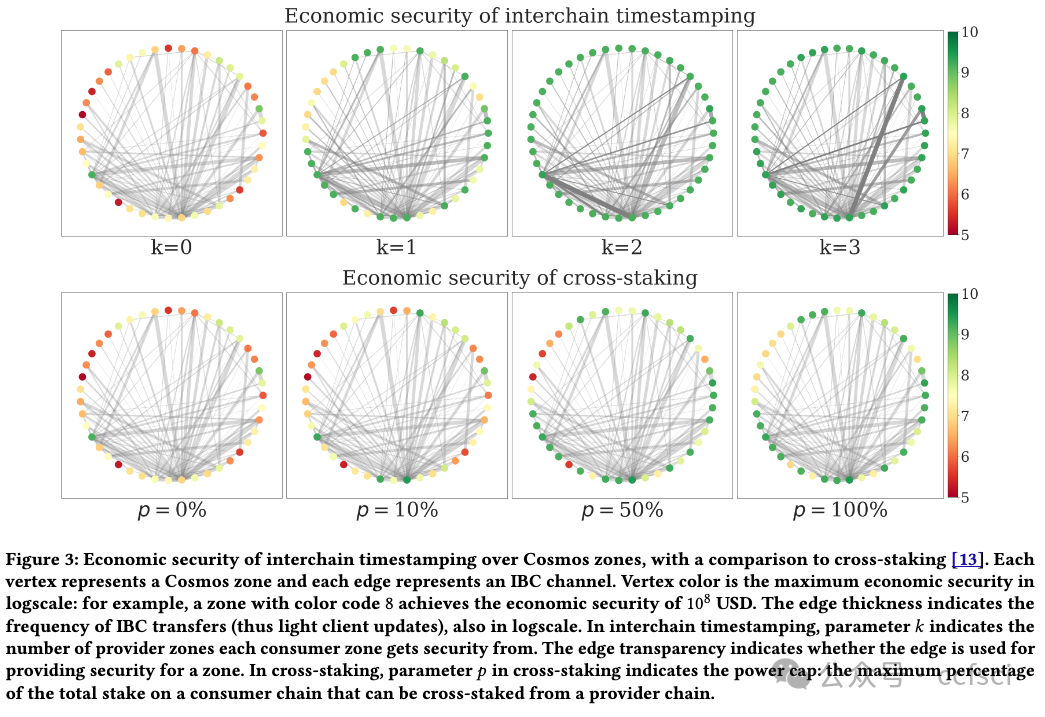
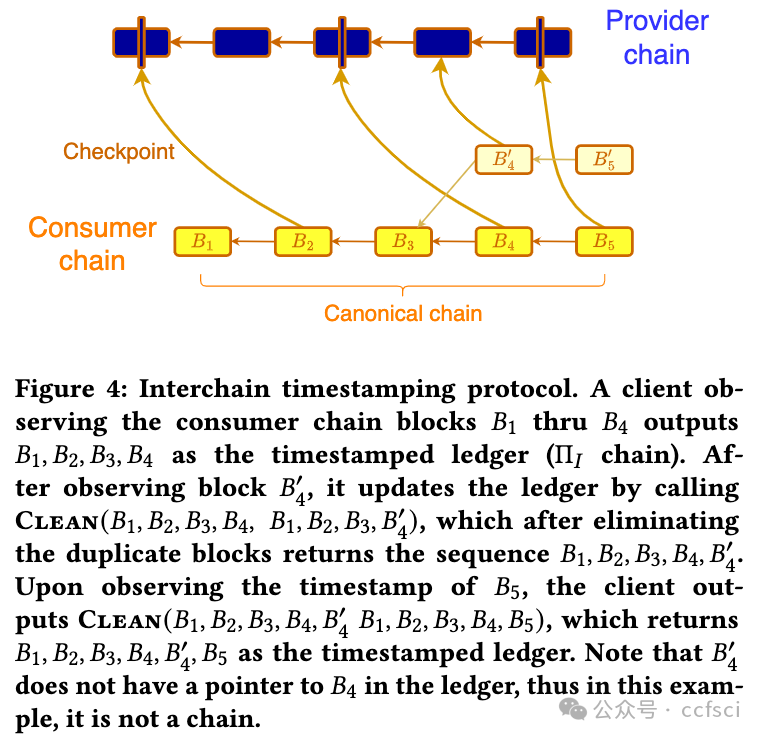
Fourteen years after the invention of Bitcoin, there has been a proliferation of many permissionless blockchains. Each such chain provides a public ledger that can be written to and read from by anyone. In this multi-chain world, a natural question arises: what is the optimal security an existing blockchain, a consumer chain, can extract by only reading and writing to k other existing blockchains, the provider chains? We design a protocol, called interchain timestamping, and show that it extracts the maximum economic security from the provider chains, as quantified by the slashable safety resilience. We observe that interchain timestamps are already provided by light-client based bridges, so interchain timestamping can be readily implemented for Cosmos chains connected by the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. We compare interchain timestamping with cross-staking, the original solution to mesh security, as well as with Trustboost, another recent security sharing protocol.
比特币发明 14 年后,许多无许可区块链如雨后春笋般涌现。每个区块链都提供了一个公共账本,任何人都可以写入和读取。在这个多链的世界里,一个自然而然的问题出现了:一个现有的区块链(即消费者链),通过只读写 k 个其他现有的区块链(即提供者链),可以获得怎样的最佳安全性?我们设计了一种称为链间时间戳的协议,并表明它可以从提供者链中提取最大的经济安全性,这可以通过可削减的安全弹性来量化。我们观察到,轻客户端桥已经提供了链间时间戳,因此可以通过跨区块链通信 (IBC) 协议连接的 Cosmos 链轻松实现链间时间戳。我们将链间时间戳与交叉质押(网格安全的原始解决方案)以及另一种最近的安全共享协议 Trustboost 进行了比较。
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3616612
21
Title:
FlexiRand: Output Private (Distributed) VRFs and Application to Blockchains
FlexiRand:输出私有(分布式)VRF 及其在区块链中的应用
Authors:

Key words:
Verifiable Random Functions, Distributed VRFs, Privacy
可验证随机函数、分布式 VRF、隐私
Abstract:
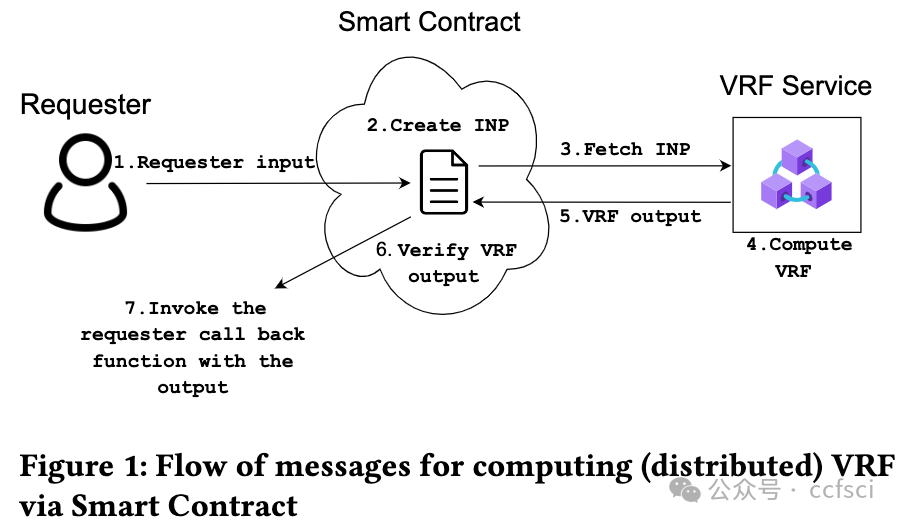
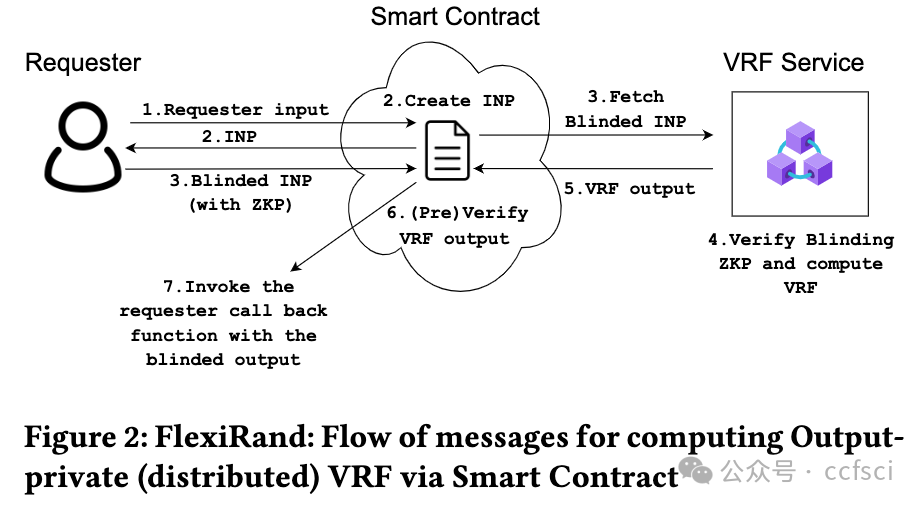
Web3 applications based on blockchains regularly need access to randomness that is unbiased, unpredictable, and publicly verifiable. For Web3 gaming applications, this becomes a crucial selling point to attract more users by providing credibility to the "random reward" distribution feature. A verifiable random function (VRF) protocol satisfies these requirements naturally, and there is a tremendous rise in the use of VRF services. As most blockchains cannot maintain the secret keys required for VRFs, Web3 applications interact with external VRF services via a smart contract where a VRF output is exchanged for a fee. While this smart contract-based plain-text exchange offers the much-needed public verifiability immediately, it severely limits the way the requester can employ the VRF service: the requests cannot be made in advance, and the output cannot be reused. This introduces significant latency and monetary overhead. This work overcomes this crucial limitation of the VRF service by introducing a novel privacy primitive Output Private VRF ( Pri-VRF) and thereby adds significantly more flexibility to the Web3-based VRF services. We call our framework FlexiRand. While maintaining the pseudo-randomness and public verifiability properties of VRFs, FlexiRand ensures that the requester alone can observe the VRF output. The smart contract and anybody else can only observe a blinded-yet-verifiable version of the output. We formally define Pri-VRF, put forward a practically efficient design, and provide provable security analysis in the universal composability (UC) framework (in the random oracle model) using a variant of one-more Diffie-Hellman assumption over bilinear groups. As the VRF service, with its ownership of the secret key, becomes a single point of failure, it is realized as a distributed VRF with the key secret-shared across distinct nodes in our framework. We develop our distributed Pri-VRF construction by combining approaches from Distributed VRF and Distributed Oblivious PRF literature. We provide provable security analysis (in UC), implement it and compare its performance with existing distributed VRF schemes. Our distributed Pri-VRF only introduces a minimal computation and communication overhead for the VRF service, the requester, and the contract.
基于区块链的 Web3 应用程序经常需要访问无偏、不可预测且可公开验证的随机数。对于 Web3 游戏应用程序而言,这成为吸引更多用户的关键卖点,因为它为“随机奖励”分配功能提供了可信度。可验证随机函数 (VRF) 协议自然满足了这些要求,VRF 服务的使用量也大幅增加。由于大多数区块链无法维护 VRF 所需的密钥,Web3 应用程序通过智能合约与外部 VRF 服务进行交互,其中 VRF 输出需要付费交换。虽然这种基于智能合约的纯文本交换可以立即提供急需的公开可验证性,但它严重限制了请求者使用 VRF 服务的方式:无法提前发出请求,也无法重复使用输出。这会带来显著的延迟和金钱开销。这项工作通过引入一种新颖的隐私原语输出私有 VRF (Pri-VRF) 克服了 VRF 服务的这一关键限制,从而为基于 Web3 的 VRF 服务增加了更大的灵活性。我们将我们的框架称为 FlexiRand。在保持 VRF 的伪随机性和公开可验证性属性的同时,FlexiRand 确保只有请求者才能观察到 VRF 输出。智能合约和任何其他人只能观察到输出的盲化但可验证的版本。我们正式定义了 Pri-VRF,提出了一种实用有效的设计,并使用双线性群上的一个 Diffie-Hellman 假设的变体在通用可组合性 (UC) 框架(在随机预言模型中)中提供可证明的安全性分析。由于 VRF 服务及其对密钥的所有权成为单点故障,因此它被实现为分布式 VRF,密钥秘密在我们的框架中跨不同节点共享。我们结合了分布式 VRF 和分布式 Oblivious PRF 文献中的方法来开发我们的分布式 Pri-VRF 构造。我们提供可证明的安全性分析(在 UC 中),实现它并将其性能与现有的分布式 VRF 方案进行比较。我们的分布式 Pri-VRF 仅为 VRF 服务、请求者和合同引入了最少的计算和通信开销。

Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3616601
22
Title:
The Locality of Memory Checking
内存检查的局部性
Authors:

Key words:
Memory checking; foundations of cryptography
内存检查;密码学基础
Abstract:
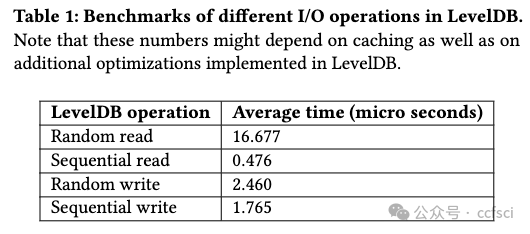
Motivated by the extended deployment of authenticated data structures (e.g., Merkle Patricia Tries) for verifying massive amounts of data in blockchain systems, we begin a systematic study of the I/O efficiency of such systems. We first explore the fundamental limitations of memory checking, a previously-proposed abstraction for verifiable storage, in terms of its locality-a complexity measure that we introduce for the first time and is defined as the number of non-contiguous memory regions a checker must query to verifiably answer a read or a write query. Our central result is an Ω(log n/log log n) lower bound for the locality of any memory checker. Then we turn our attention to (dense and sparse) Merkle trees, one of the most celebrated memory checkers, and provide stronger lower bounds for their locality. For example, we show that any dense Merkle tree layout will have average locality at least (1/3)log n. Furthermore, if we allow node duplication, we show that if any write operation has at most polylog complexity, then the read locality cannot be less than log n/log log n. Our lower bounds help us construct two new locality-optimized authenticated data structures (DupTree and PrefixTree) which we implement and evaluate on random operations and real workloads, and which are shown to outperform traditional Merkle trees, especially as the number of leaves increases.
用于验证区块链系统中大量数据的认证数据结构(例如 Merkle Patricia Tries)被广泛部署,受此启发,我们开始对此类系统的 I/O 效率进行系统研究。我们首先探讨内存检查的基本局限性,内存检查是一种先前提出的可验证存储的抽象,就其局部性而言,这是我们首次引入的复杂性度量,被定义为检查器必须的非连续内存区域的数量 查询以可验证地回答读取或写入查询。我们的中心结果是任何内存检查器局部性的 Ω(log n/log log n) 下界。然后我们将注意力转向(密集和稀疏)Merkle 树,这是最著名的内存检查器之一,并为其局部性提供更强的下界。例如,我们证明任何密集的 Merkle 树布局都将具有至少 (1/3)log n 的平均局部性。此外,如果我们允许节点重复,我们会表明,如果任何写入操作最多具有 polylog 复杂度,则读取局部性不能小于 log n/log log n。我们的下限帮助我们构建了两个新的局部性优化认证数据结构(DupTree 和 PrefixTree),我们在随机操作和实际工作负载上实施和评估了这两个结构,结果表明它们优于传统的 Merkle 树,尤其是在叶子数量增加的情况下。
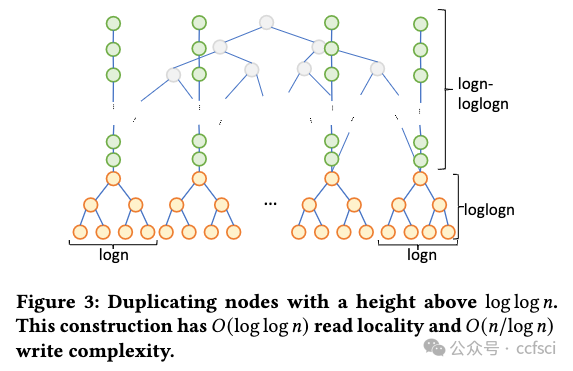
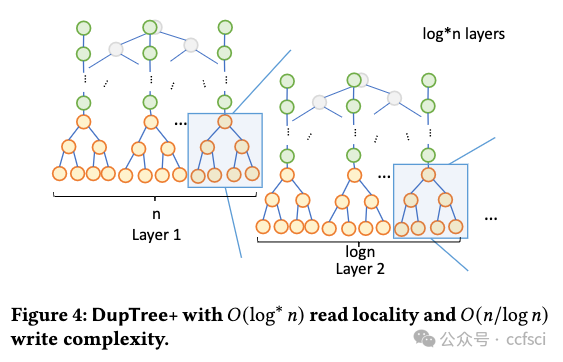
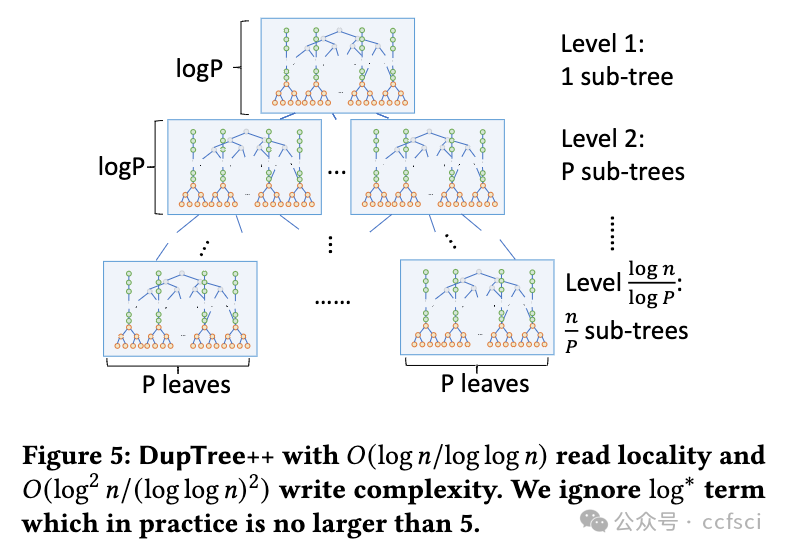
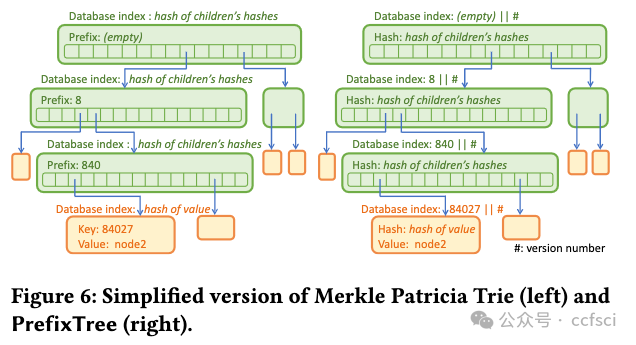
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3623195
23
Title:
Uncovering Impact of Mental Models towards Adoption of Multi-device Crypto-Wallets
揭示心理模型对多设备x密x币钱包采用的影响
Authors:

Key words:
Cryptocurrency wallets, security, usability, multi-device wallets
x密x币钱包、安全性、可用性、多设备钱包
Abstract:
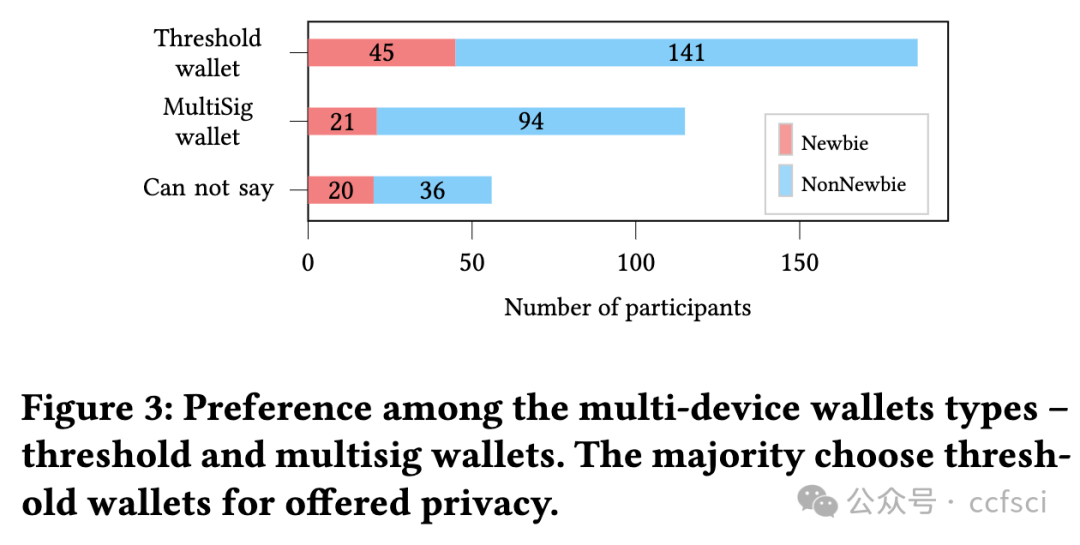
Cryptocurrency users saw a sharp increase in different types of crypto wallets in the past decade. However, the emerging multi-device wallets, even with improved security guarantees over their single-device counterparts, are yet to receive proportionate adoption. This work presents a data-driven investigation into the perceptions of users towards multi-device wallets, using a survey of 357 crypto-wallet users. Our results revealed two significant groups among our participants-Newbies and Non-newbies. Our follow-up qualitative analysis, after educating, revealed a gap between the mental model for these participants and actual security guarantees. Furthermore, we investigated preferred default settings for crypto-wallets across our participants over different key-share distribution settings of multi-device wallets-the threat model considerations affected user preferences, signifying a need for contextualizing default settings. We identified concrete, actionable design avenues for future multi-device wallet developers to improve adoption.
过去十年,x密x币用户看到不同类型的钱包急剧增加。然而,新兴的多设备钱包即使比单设备钱包具有更好的安全保障,也尚未得到相应的采用。这项研究通过对 357 名加密钱包用户的调查,对用户对多设备钱包的看法进行了数据驱动的调查。我们的结果显示,我们的参与者中有两个重要的群体——新手和非新手。在教育之后,我们进行的后续定性分析揭示了这些参与者的心理模型与实际安全保障之间的差距。此外,我们调查了参与者对多设备钱包的不同密钥共享分发设置的加密钱包的首选默认设置——威胁模型考虑因素影响了用户偏好,这表明需要将默认设置情境化。我们为未来的多设备钱包开发人员确定了具体的、可操作的设计途径,以提高采用率。
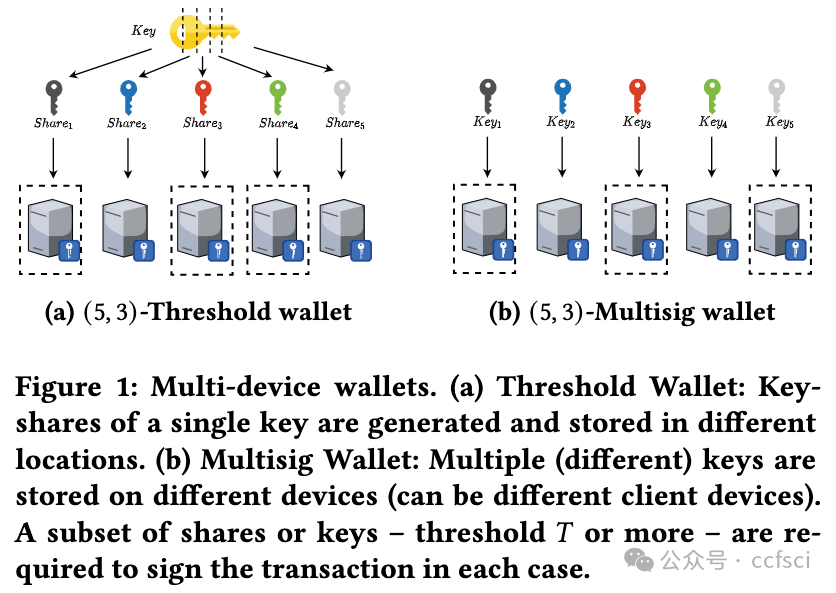
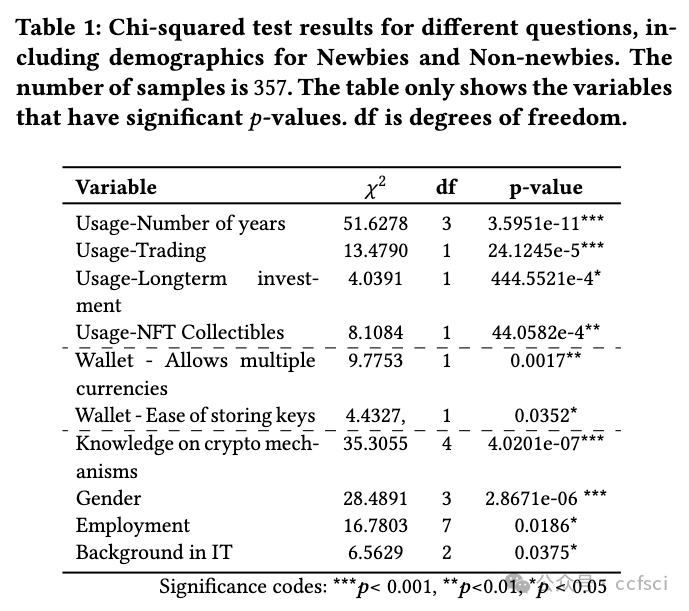
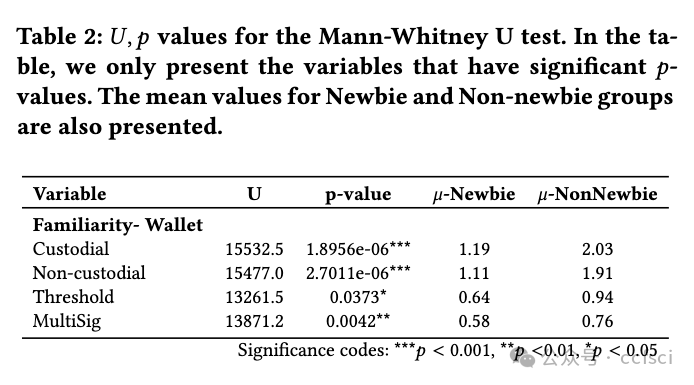
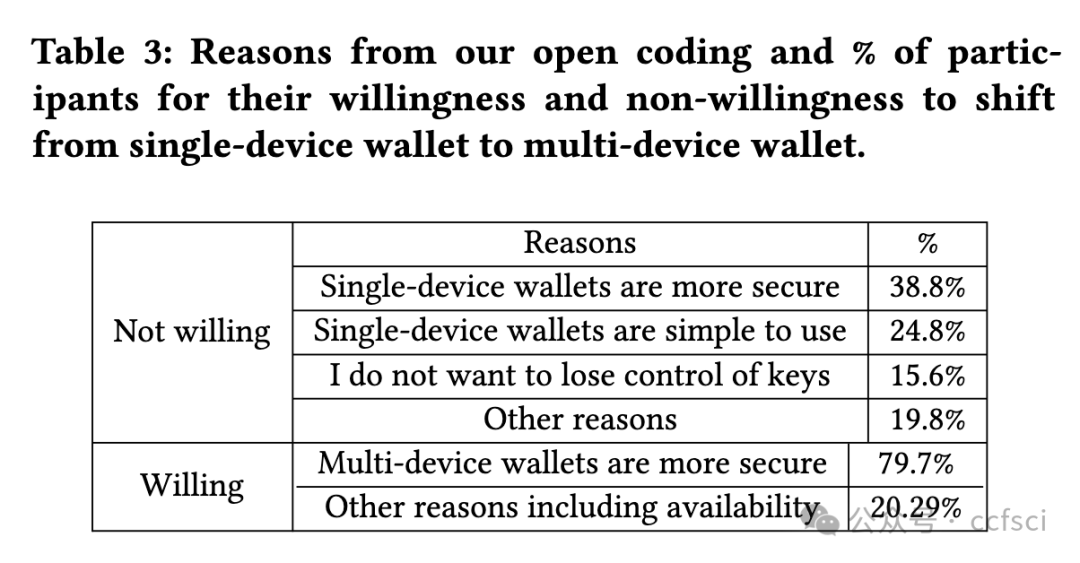
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3623218
24
Title:
Poster: WIP: Account ZK-Rollups from Sumcheck Arguments
海报:WIP:来自 Sumcheck 参数的帐户 ZK-Rollups
Authors:

Key words:
Cryptography, Argument Systems
密码学、论证系统
Abstract:
Traditional blockchains execute transactions through the use of consensus mechanisms that guarantee reasonable expectations of integrity and finality. However, often these incur costs making the throughput of transactions orders of magnitude slower than their web2 counterparts. To address this drawback, so called L2 layers offload transactions from the main chain, called L1, execute these fast and anchor back the result of these transaction through succinct checkpoints. ZK-Rollups are emerging as compelling methods to establish the integrity of such checkpoints, by the use of compressed cryptographic proofs. However, the use of general purpose SNARKs still suffers from efficiency issues. We define a simple, but ubiquitous, account integrity constraint defined over a series of transactions and design a ZK-Rollup for transaction integrity using sumcheck arguments that exploits its simple structure and provides attractive efficiency benefits.
传统区块链通过使用共识机制来执行交易,这些机制可保证对完整性和最终性的合理预期。然而,这些机制通常会产生成本,使得交易的吞吐量比 Web2 交易慢几个数量级。为了解决这一缺点,所谓的 L2 层将交易从主链(称为 L1)卸载,快速执行这些交易并通过简洁的检查点将这些交易的结果锚定回来。ZK-Rollup 正在成为一种引人注目的方法,通过使用压缩加密证明来建立此类检查点的完整性。然而,使用通用 SNARK 仍然存在效率问题。我们定义了一个简单但普遍存在的帐户完整性约束,该约束定义在一系列交易上,并使用 sumcheck 参数设计了一个用于交易完整性的 ZK-Rollup,利用其简单的结构并提供有吸引力的效率优势。
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3624405
25
Title:
Poster: A Privacy-Preserving Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection Framework for Permissioned Blockchain
海报:用于许可区块链的隐私保护智能合约漏洞检测框架
Authors:

Key words:
Smart Contract, Privacy-preserving, Vulnerability Detection, Blockchain
智能合约、隐私保护、漏洞检测、区块链
Abstract:
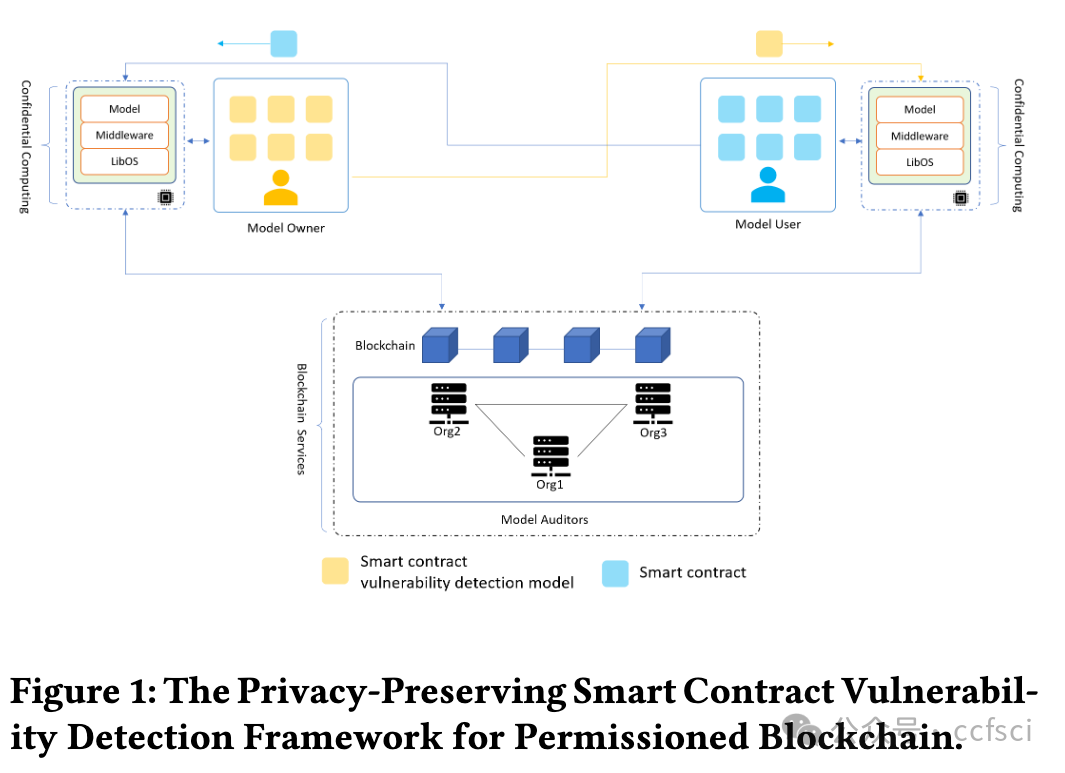
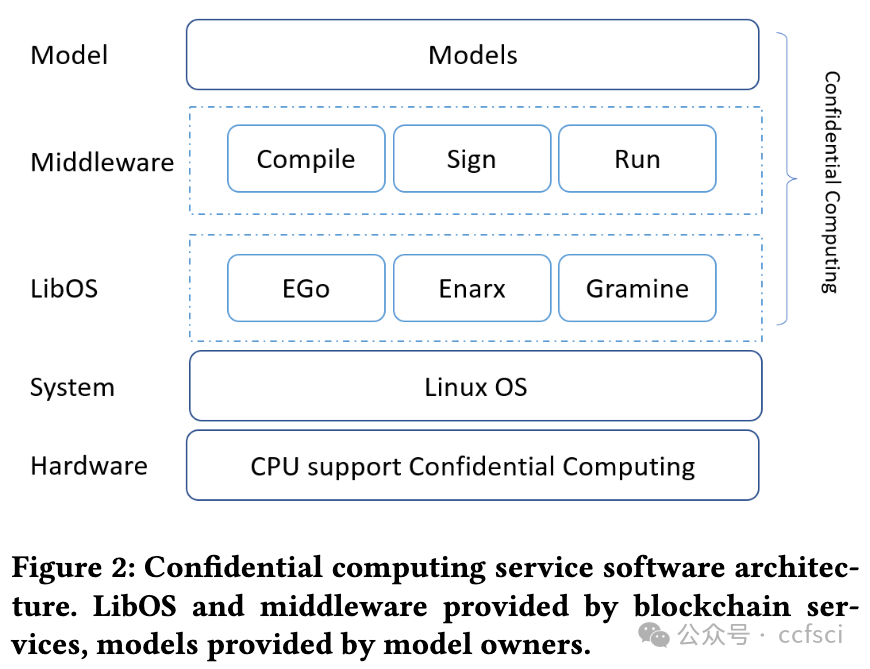
The two main types of blockchains that are currently widely deployed are public blockchains and permissioned blockchains. The research that has been conducted for blockchain vulnerability detection is mainly oriented to public blockchains. Less consideration is given to the unique requirements of the permissioned blockchains, which cannot be directly migrated to the application scenarios of the permissioned blockchains. The permissioned blockchain is deployed between verified organizations, and its smart contracts may contain sensitive information such as the transaction flow of the contracts, transaction algorithms, etc. The sensitive information can be considered as the private information of the smart contracts themselves, which should be kept confidential to users outside the blockchain. In this paper, a privacy-preserving smart contract vulnerability detection framework is proposed. The framework leverages blockchain and confidential computing technologies to enable vulnerability detection in permissioned blockchain smart contracts while protecting the privacy of smart contracts. The framework is also able to protect the interests of vulnerability detection model owners. We experimentally validate the detection performance of our framework in a confidential computing environment.
目前广泛部署的区块链主要分为公有链和许可链两大类。目前对区块链漏洞检测的研究主要面向公有链,较少考虑许可链的独特需求,无法直接迁移到许可链的应用场景中。许可链部署在经过验证的组织之间,其智能合约中可能包含合约的交易流、交易算法等敏感信息,这些敏感信息可以视为智能合约本身的隐私信息,对链外用户应当保密。本文提出了一种隐私保护的智能合约漏洞检测框架,该框架利用区块链和机密计算技术,在保护智能合约隐私的同时实现许可链智能合约的漏洞检测,并保护漏洞检测模型所有者的利益。我们在机密计算环境中通过实验验证了框架的检测性能。
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3624366
若想投稿CCS,录用率请点击此处查看

关注我们,持续接收区块链最新论文
洞察区块链技术发展趋势
Follow us to keep receiving the latest blockchain papers
Insight into Blockchain Technology Trends