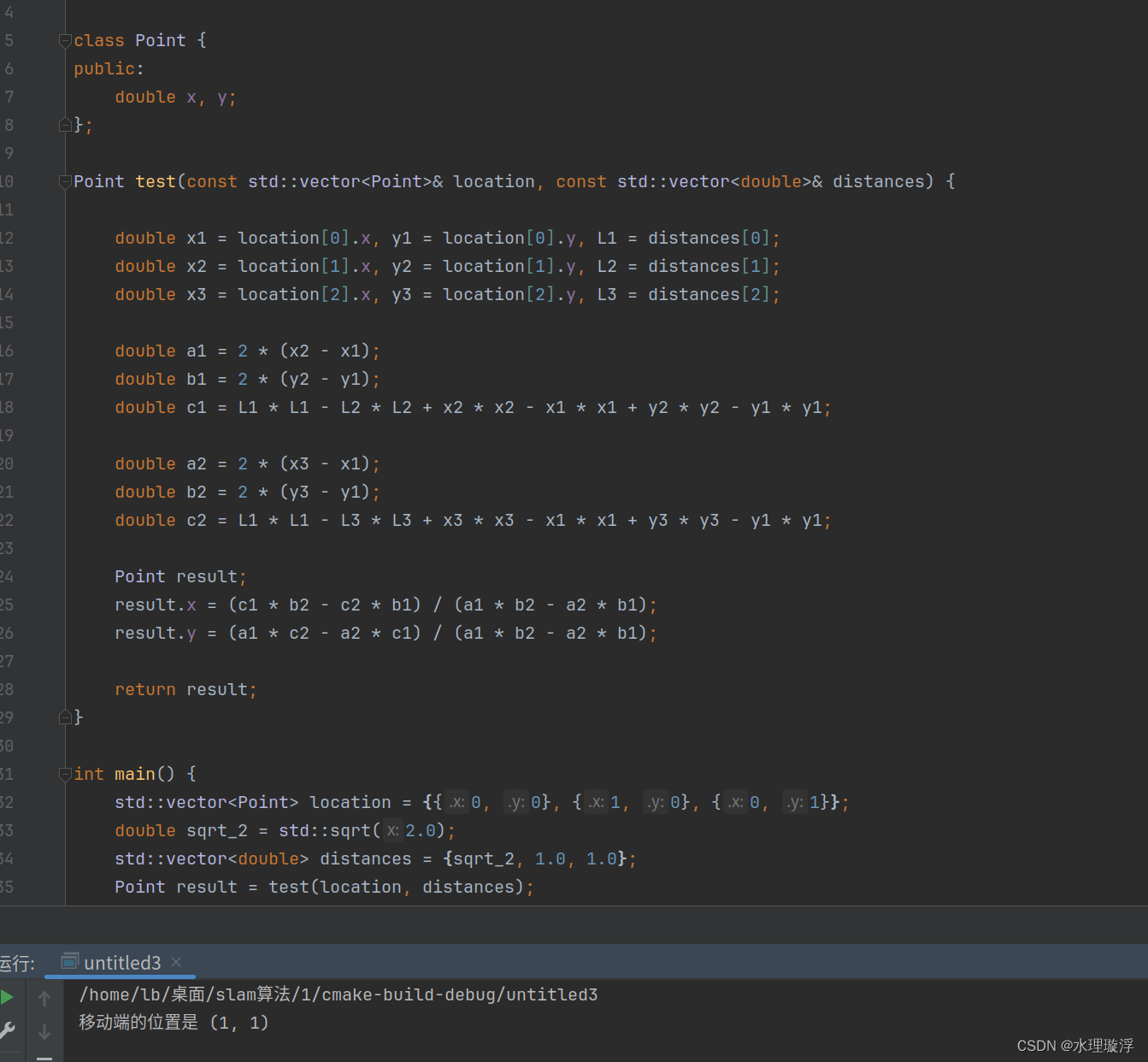
1、最小二乘题目:
假设有三个WIFI热点,位置分别在(x1,y1), (x2,y2), (x3,y3), 移动端测量到每一个热点的距离L1,L2和L3,要求解移动端的位置.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
};
Point test(const std::vector<Point>& location, const std::vector<double>& distances) {
double x1 = location[0].x, y1 = location[0].y, L1 = distances[0];
double x2 = location[1].x, y2 = location[1].y, L2 = distances[1];
double x3 = location[2].x, y3 = location[2].y, L3 = distances[2];
double a1 = 2 * (x2 - x1);
double b1 = 2 * (y2 - y1);
double c1 = L1 * L1 - L2 * L2 + x2 * x2 - x1 * x1 + y2 * y2 - y1 * y1;
double a2 = 2 * (x3 - x1);
double b2 = 2 * (y3 - y1);
double c2 = L1 * L1 - L3 * L3 + x3 * x3 - x1 * x1 + y3 * y3 - y1 * y1;
Point result;
result.x = (c1 * b2 - c2 * b1) / (a1 * b2 - a2 * b1);
result.y = (a1 * c2 - a2 * c1) / (a1 * b2 - a2 * b1);
return result;
}
int main() {
std::vector<Point> location = {{0, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}};
double sqrt_2 = std::sqrt(2.0);
std::vector<double> distances = {sqrt_2, 1.0, 1.0};
Point result = test(location, distances);
std::cout << "移动端的位置是 (" << result.x << ", " << result.y << ")" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
2、图像题目
已知相机内参:520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1。求解两帧图像之间的运动。
a.部署OpenCV等环境,使用熟悉的特征点匹配后计算。
b.运动求解过程需要亲自编写程序,不允许调用第三方库。
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(vo1)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
add_definitions("-DENABLE_SSE")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++14 -O2 ${SSE_FLAGS} -msse4")
#list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
find_package(OpenCV 3.4.15 REQUIRED)
#find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
#find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
include_directories(
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
# ${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS}
# ${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS}
"/usr/include/eigen3/"
)
# add_executable( pose_estimation_2d2d pose_estimation_2d2d.cpp extra.cpp ) # use this if in OpenCV2
add_executable(pose_estimation_2d2d pose_estimation_2d2d.cpp)
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_2d2d ${OpenCV_LIBS})主函数
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <vector>
#include <random>
#include <ctime>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace Eigen;
void find_feature_matches(
const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,
std::vector<DMatch> &matches);
void pose_estimation_2d2d(
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_2,
std::vector<DMatch> matches,
Mat &R, Mat &t);
const int MAX_ITER = 100000; // 最大迭代次数
const float THRESHOLD = 0.001; // 内点距离阈值
float calculateError(const Matrix3f& F, const Point2f& pt1, const Point2f& pt2) {
Vector3f p1(pt1.x, pt1.y, 1.0);
Vector3f p2(pt2.x, pt2.y, 1.0);
Vector3f line = F * p1;
return fabs(p2.dot(line)) / sqrt(line[0] * line[0] + line[1] * line[1]);
}
Matrix3f ransacFundamentalMat(const vector<Point2f>& points1, const vector<Point2f>& points2) {
int bestInliersCount = 0;
Matrix3f bestF;
std::default_random_engine rng(time(0));
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> uniDist(0, points1.size() - 1);
for (int iter = 0; iter < MAX_ITER; ++iter) {
vector<Point2f> samplePoints1, samplePoints2;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int idx = uniDist(rng);
samplePoints1.push_back(points1[idx]);
samplePoints2.push_back(points2[idx]);
}
int N = samplePoints1.size();
MatrixXf A(N, 9);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
float x1 = samplePoints1[i].x;
float y1 = samplePoints1[i].y;
float x2 = samplePoints2[i].x;
float y2 = samplePoints2[i].y;
A.row(i) << x2 * x1, x2 * y1, x2, y2 * x1, y2 * y1, y2, x1, y1, 1;
}
JacobiSVD<MatrixXf> svd(A, ComputeFullV);
VectorXf f = svd.matrixV().col(8);
Matrix3f F;
F << f(0), f(1), f(2),
f(3), f(4), f(5),
f(6), f(7), f(8);
JacobiSVD<Matrix3f> svdF(F, ComputeFullU | ComputeFullV);
Vector3f singularValues = svdF.singularValues();
singularValues[2] = 0;
F = svdF.matrixU() * singularValues.asDiagonal() * svdF.matrixV().transpose();
int inliersCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points1.size(); ++i) {
if (calculateError(F, points1[i], points2[i]) < THRESHOLD) {
++inliersCount;
}
}
if (inliersCount > bestInliersCount) {
bestInliersCount = inliersCount;
cout<<bestInliersCount<<endl;
bestF = F;
}
}
return bestF;
}
void recoverPose_my(const Matrix3f& essential_matrix, const vector<Point2f>& points1, const vector<Point2f>& points2, Matrix3f& R, Vector3f& t, double focal_length, const Point2d& principal_point) {
// SVD分解本质矩阵
JacobiSVD<Matrix3f> svd(essential_matrix, ComputeFullU | ComputeFullV);
Matrix3f U = svd.matrixU();
Matrix3f Vt = svd.matrixV().transpose();
// 构造W矩阵和Z矩阵
Matrix3f W;
W << 0, -1, 0,
1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1;
Matrix3f Z;
Z << 0, 1, 0,
-1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0;
// 可能的两种旋转矩阵
Matrix3f R1 = U * W * Vt;
if (R1.determinant() < 0) {
R1 = -R1;
}
Matrix3f R2 = U * W.transpose() * Vt;
if (R2.determinant() < 0) {
R2 = -R2;
}
// 平移向量
Vector3f t1 = U.col(2);
Vector3f t2 = -U.col(2);
// 对两个可能的解进行验证,选择最合适的那个
int valid_count1 = 0;
int valid_count2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points1.size(); ++i) {
Vector3f p1(points1[i].x, points1[i].y, 1.0);
Vector3f p2(points2[i].x, points2[i].y, 1.0);
p1[0] = (p1[0] - principal_point.x) / focal_length;
p1[1] = (p1[1] - principal_point.y) / focal_length;
p2[0] = (p2[0] - principal_point.x) / focal_length;
p2[1] = (p2[1] - principal_point.y) / focal_length;
// 计算重投影误差来判断是否在相机前方
Vector3f p1_proj = R1 * p2 + t1;
if (p1_proj[2] > 0) {
++valid_count1;
}
p1_proj = R2 * p2 + t2;
if (p1_proj[2] > 0) {
++valid_count2;
}
}
if (valid_count1 > valid_count2) {
R = R1;
t = t1;
} else {
R = R2;
t = t2;
}
}
int main() {
//-- 读取图像
Mat img_1 = imread("../1.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
Mat img_2 = imread("../2.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR);
if (img_1.empty() || img_2.empty()) {
cerr << "无法加载图片" << endl;
return -1;
}
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector<DMatch> matches;
find_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches);
cout << "一共找到了" << matches.size() << "组匹配点" << endl;
//-- 估计两张图像间运动
Mat R, t;
pose_estimation_2d2d(keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches, R, t);
return 0;
}
void find_feature_matches(const Mat &img_1, const Mat &img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints_2,
std::vector<DMatch> &matches) {
//-- 初始化
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
// used in OpenCV3
Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();
Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
detector->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);
detector->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector<DMatch> match;
//BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
double min_dist = 10000, max_dist = 0;
//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
double dist = match[i].distance;
if (dist < min_dist) min_dist = dist;
if (dist > max_dist) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist);
printf("-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist);
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for (int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++) {
if (match[i].distance <= max(2 * min_dist, 30.0)) {
matches.push_back(match[i]);
}
}
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches(img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2, matches, img_matches);
// 显示匹配结果
imshow("按任意键继续!", img_matches);
waitKey();
}
void pose_estimation_2d2d(std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_2,
std::vector<DMatch> matches,
Mat &R, Mat &t) {
// 相机内参,TUM Freiburg2
Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);
//-- 把匹配点转换为vector<Point2f>的形式
vector<Point2f> points1;
vector<Point2f> points2;
for (int i = 0; i < (int) matches.size(); i++) {
points1.push_back(keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
points2.push_back(keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
//-- 计算本质矩阵
Point2d principal_point(325.1, 249.7); //相机光心
double focal_length = 521; //相机焦距
Mat essential_matrix;
essential_matrix = findEssentialMat(points1, points2, focal_length, principal_point);
// 内参矩阵K
Matrix3f k;
k << focal_length, 0, principal_point.x,
0, focal_length, principal_point.y,
0, 0, 1;
// 计算本质矩阵
Matrix3f fundamental_matrix_ransac;
fundamental_matrix_ransac = ransacFundamentalMat(points1, points2);
Matrix3f E = k.transpose() * fundamental_matrix_ransac * k;
JacobiSVD<Matrix3f> svdE(E, ComputeFullU | ComputeFullV);
Vector3f singularValues = svdE.singularValues();
singularValues[2] = 0;
E = svdE.matrixU() * singularValues.asDiagonal() * svdE.matrixV().transpose();
//-- 从本质矩阵中恢复旋转和平移信息.
recoverPose(essential_matrix, points1, points2, R, t, focal_length, principal_point);
Matrix3f R1;
Vector3f t1;
recoverPose_my( E , points1, points2, R1, t1, focal_length, principal_point);
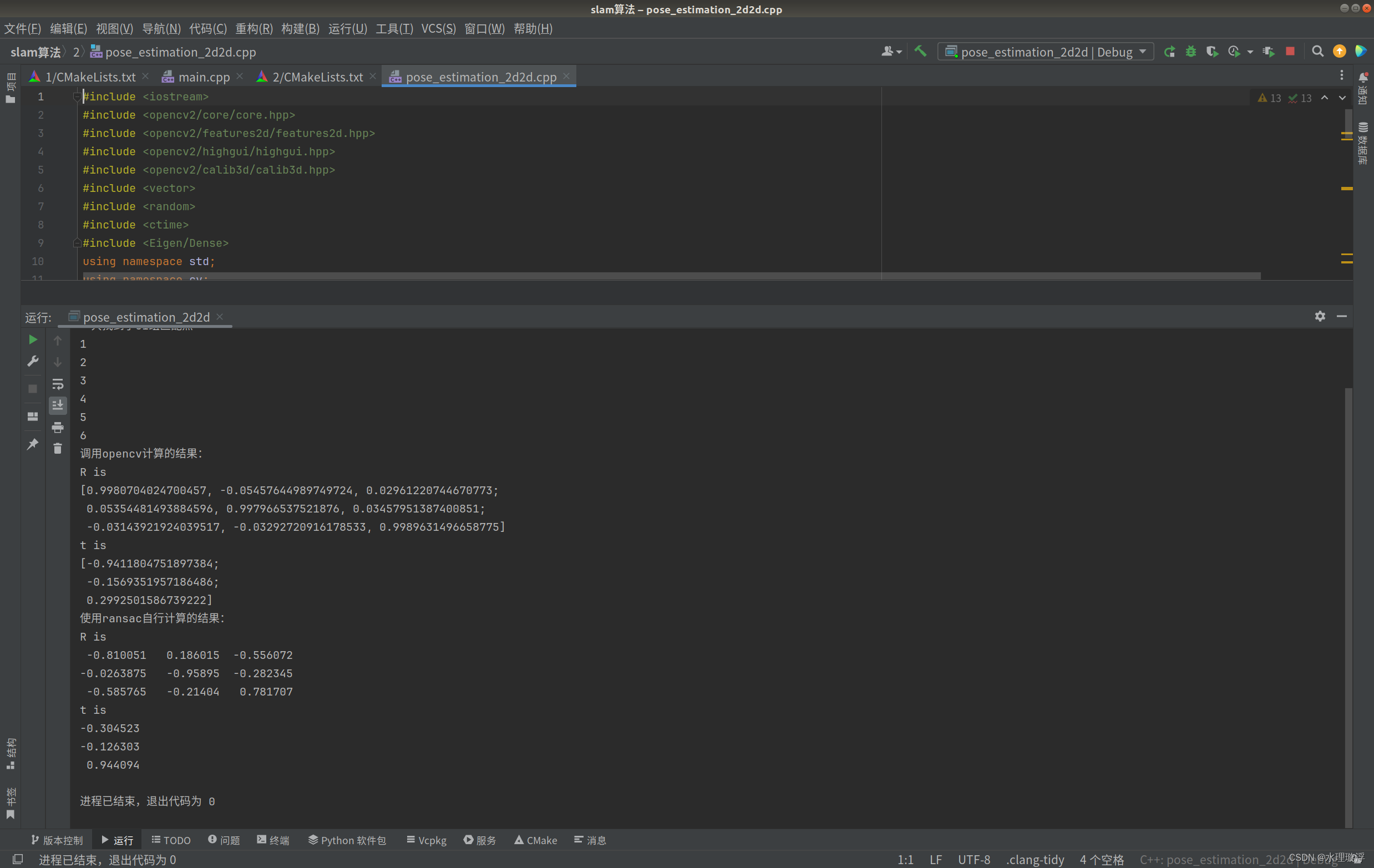
cout << "调用opencv计算的结果: " << endl;
cout << "R is " << endl << R << endl;
cout << "t is " << endl << t << endl;
cout << "使用ransac自行计算的结果: " << endl;
cout << "R is " << endl << R1 << endl;
cout << "t is " << endl << t1 << endl;
}