代码随想录–二叉树章节总结 Part I
1.Leetcode144 前序遍历二叉树
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它节点值的 前序 遍历
解题思路1:使用递归解决。
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return list;
preorder(root, list);
return list;
}
private void preorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) return;
// 先遍历根
list.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, list);
preorder(root.right, list);
}
解题思路2: 利用栈来模拟递归实现非迭代遍历二叉树
- 创建一个栈,让根结点入栈
- 然后开始循环,循环条件是栈不为空。首先让栈中元素出栈,将元素保存list中
- 然后判断元素是否有右孩子,如果有,则右孩子入栈。
- 然后判断元素是否有左孩子,如果有,则左孩子入栈。
- 循环结束后,list中保存了前序遍历的序列
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 如果树为空那么直接返回
if (root == null) return list;
// 创建一个栈
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
// 根结点入栈
stack.push(root);
// 循环
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
// 出栈
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
// 保存结点
list.add(node.val);
// 判断这个结点是否有右孩子
if (node.right != null)
stack.push(node.right);
if (node.left != null)
stack.push(node.left);
}
return list;
}

2.Leetcode145 后序遍历
解题思路1:利用递归实现后序遍历
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root, list);
return list;
}
private void postorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) return;
postorder(root.left, list);
postorder(root.right, list);
list.add(root.val);
}
解题思路2: 使用前序遍历的序列进行一些加工。前序遍历序列为根左右,如果我们变成根右左,然后在进行一次反转,就变成了左右根,就是后序遍历的顺序了。
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 如果树为空那么直接返回
if (root == null) return list;
// 创建一个栈
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
// 根结点入栈
stack.push(root);
// 循环
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
// 出栈
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
// 保存结点
list.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null)
stack.push(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
stack.push(node.right);
}
Collections.reverse(list);
return list;
}
这种遍历方式并不是真正意义的后序遍历,因为访问结点的顺序实际上是根右左
3.Leetcode94 中序遍历
解题思路1: 利用递归实现
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, list);
return list;
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) return;
inorder(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, list);
}
解题思路2:利用栈实现非递归方式
- 创建一个指针,指向根结点,创建一个栈
- 如果指针不为空,或者栈不空,那么进行循环
- 在循环中,如果指针不为空,那么就将元素入栈,并将cur指向它的左子树
- 如果指针为空,那么说明cur指向的元素要么已经没有左子树了,说明cur是当前子二叉树的根结点,因此保存cur到list,并判断cur是否有右子树,如果有,则将cur指向右子树
- 或者cur可能是某一个子二叉树的右子树,如果此时cur为空,则说明这个子二叉树已经被遍历完毕,需要从栈汇总取新的元素。
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return list;
TreeNode cur = root;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// cur 为空的情况主要有遍历到最左边了,已经到头了
// 或者弹出的元素没有右子树
if (cur != null) {
// cur 入栈
stack.push(cur);
// 遍历cur是否还有左子树
cur = cur.left;
} else {
// 如果cur已经为空 要么cur没有左子树,那么cur就是当前二叉树的根
// 既然是中序,并且左子树为空,那么就改轮到cur了
// 要么cur是某一个结点的右子树,右子树为空,说明这个子树已经遍历完了
// 那么要从栈中取出新元素
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null)
cur = node.right;
}
}
return list;
}

4.Leetcode102 层序遍历
解题思路:利用队列实现层序遍历
- 首先将根结点加入队列
- 只要队列不为空,就出队列,然后将左右子树入队
- 直到队列为空
需要注意的是,如果需要分层输出每次层的结点,那么就需要记录一下每次入队后队的size,size的目的就是记录每一层的元素个数。如果单纯输出一个层序遍历序列,则不需要记录size
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return list;
// 创建队列,根结点入队
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
ArrayList level = new ArrayList(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null)
queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
queue.offer(node.right);
}
list.add(level);
}
return list;
}
5.Leetcode226 反转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
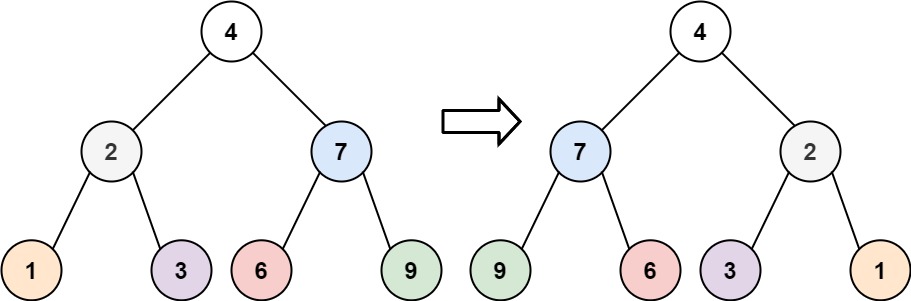
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
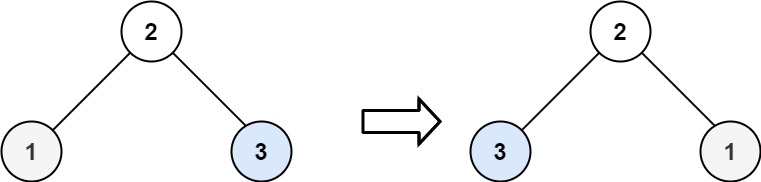
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:[2,3,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
解题思路1: 利用递归
- 如果传入的结点是一个空结点,那么直接返回空即可
- 否则就判断当前结点是否是叶子结点,如果是叶子结点,则直接返回该结点
- 否则就递归的先去反转当前结点的左右子树
- 等左右子树都反转完成后,然后在交换以当前结点为根的树的左右子树即可。
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
// 如果树为空或者这个树只有一个结点,直接返回
if (root == null) return null;
// 如果目前root是一个叶子结点,则直接返回
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return root;
// 否则就先让其左右子树都进行反转
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
// 都反转完了以后,在反转以root为根的二叉树
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
return root;
}
上面的方法是使用后序遍历实现的,这个题也可以使用前序遍历
只需要把invertTree写在交换代码的后面即可。
这个题实际上还可以使用中序遍历。但是两次遍历都需要遍历左子树。图解如下:
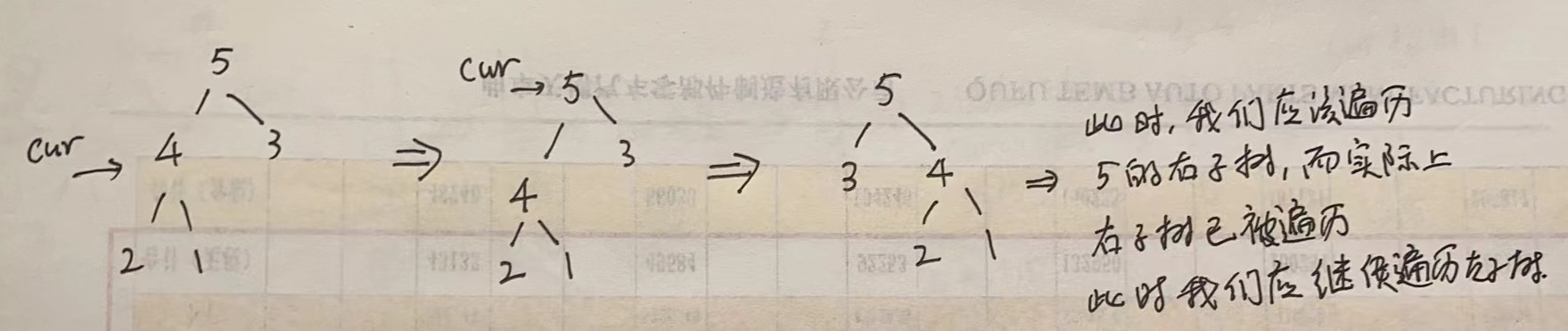
伪代码如下:
invertTree(root.left);
swap(root.left, root.right)
invertTree(root.left);
解题思路2: 利用层序遍历实现
和普通的层序遍历代码相同,只不过在出队的时候需要交换出队元素的左右子树
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
// 交换
TreeNode temp = node.left;
node.left = node.right;
node.right = temp;
if (node.left != null)
queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
queue.offer(node.right);
}
return root;
}
6.Leetcode101 对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
提示:树中节点数目在范围 [1, 1000] 内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
解题思路1:利用二叉树层序遍历。但是需要注意的是,即使遍历的某一个结点没有左子树或者右子树,也要入队,就入队一个标志位,标志这个地方为空。然后每一层都所有元素都收集起来,存放到list中。然后判断list是否位回文。如果不是,则返回false。否则等队中元素为空以后,返回true。
public static boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
// 如果树中只有一个结点 返回true
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return true;
// 创建队列 层序遍历
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
ArrayList<Integer> list;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 获取这一层的元素个数
int size = queue.size();
list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node == null)
list.add(-1000);
else
list.add(node.val);
if (node != null) {
queue.offer(node.left != null ? node.left : null);
queue.offer(node.right != null ? node.right : null);
}
}
if (!check(list)) return false;
}
return true;
}
private static boolean check(ArrayList<Integer> list) {
// 判断字符串是不是回文
int left = 0, right = list.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
int l = list.get(left);
int r = list.get(right);
if (l != r)
return false;
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
这个题最一开始想的是用字符串来存储每一层的值,然后空的位置填写null。然后判断是否为回文。这样不可行,因为这个循环会遍历到二叉树高度+1的位置,也就是说,最后一次队列中所有元素都为null元素,那么输出的字符串就是nullnullnull,显然不是回文,返回false。而实际上应该返回true。
所以后来使用list代替,根据结点val的取值范围,选择使用-1000来代表空结点。
解题思路2: 利用递归中的后序遍历实现。
- 首先要比较当前传入的结点的左右子树。
- 如果左右子树都为空,则返回true
- 如果左子树为空右子树不为空,或者左子树不为空,右子树为空,则返回false
- 如果左右子树都不为空,但是值不相等,则返回false
- 否则就去判断传入结点的左右子树是否满足上述条件。
- 只有当左右子树都满足条件的时候,以传入结点为根的二叉树才满足条件,返回true
public boolean isSymmetric1(TreeNode root) {
return compare(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean compare(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
if (left == null && right != null) {
return false;
}
if (left != null && right == null) {
return false;
}
if (left == null && right == null) {
return true;
}
if (left.val != right.val) {
return false;
}
// 比较外侧
boolean compareOutside = compare(left.left, right.right);
// 比较内侧
boolean compareInside = compare(left.right, right.left);
return compareOutside && compareInside;
}
下面通过画图展示递归过程,展示了满足条件的树和不满足条件的树。
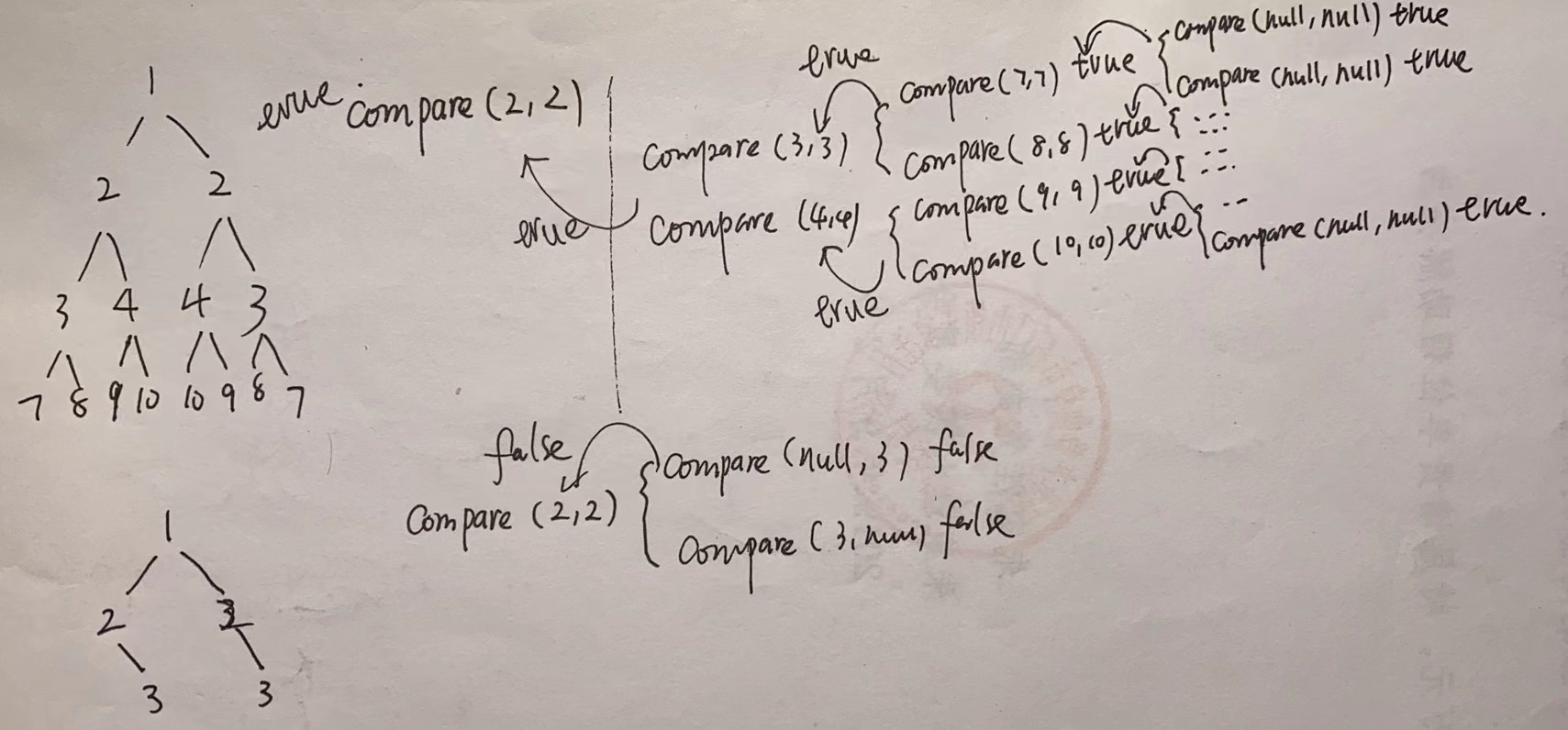
7.Leetcode104 求二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
关于二叉树的深度和二叉树的高度
- 二叉树中一个结点的高度,指的是从叶子结点到该结点经过的路径数
- 二叉树中一个结点的深度,指的是从根结点到该结点的的经过的路径数
根结点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度
解题思路1: 利用递归。
- 如果当前结点为叶子结点,则返回高度为1
- 否则,则高度就为1+max(当前结点左子树高度,当前结点的右子树高度)
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
// 如果是叶子结点,直接返回1
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
int left = maxDepth(root.left); // 左
int right = maxDepth(root.right); // 右
return 1 + Math.max(left, right); // 中
}
从理论上来说,求二叉树的高度是自底向上进行计算,因此适用于后序遍历;而求深度是从根向下遍历,适用于先序遍历。这个题是求深度,但是使用了后续遍历,主要原因是根结点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度
解题思路2:利用层序遍历来做,对层序遍历代码简单修改即可。
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int count = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null ) queue.offer(node.right);
}
count++;
}
return count;
}
8.Leetcode111 求二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
解题思路1: 利用层序遍历,使用一个变量记录层数,只要看这一层是不是满元素状态就可以,如果不是满的,那么就直接返回层数。这个方式实际上不可行,考虑示例2的情况,按照这个方法返回的结果是1,而正确答案是5。
实际上这道题可以使用层序遍历来做,我们使用层序遍历每一个结点,当遍历到第一个叶子结点的时候,直接返回层数,就是这棵树的最小深度。
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int count = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
// 如果遍历到叶子结点,则直接返回层数即可
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) return count;
if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
return count;
}
解题思路2: 利用递归的方式。
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
// 如果是叶子结点,直接返回1
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
int left = minDepth(root.left); // 左
int right = minDepth(root.right); // 右
return 1 + Math.min(left, right); // 中
}
本来的想法是和上面那道题一样,只需要修改max为min即可,但是发现示例2的结果不对。经过原因分析发现,当输入结点是root的时候,会计算left和right,left为0,right为4,那么最后的结果输出为1,这不不对。也就是说,如果某一个结点只有左孩子或者只有有孩子的时候,我们就不需要再求左右子树深度的最小值了,二是直接返回左孩子或者有孩子深度+1。
正确的递归代码如下:
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
// 如果树为空
if (root == null) return 0;
// 如果树中只有一个结点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
// 如果这个结点只有左孩子
if (root.left != null && root.right == null)
return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
// 如果这个结点只有右子树
if (root.left == null && root.right != null)
return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
// 如果这个结点左右子树都存在
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
return 1 + Math.min(left, right);
}







![LeetCode[128]最长连续序列](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/4a9c21f5065a408b9d734535377699c0.png)