目录
- 1.算法原理
- 2.代码讲解
- 3.结果展示
- 4.代码获取
1.算法原理
A* 算法是一种基于传统图搜索的智能启发式算法,它具有稳定性高、节点搜索效率高等优点。主要原理为:以起点作为初始节点,搜索初始节点旁 8 个邻域,并通过启发函数评估后选择代价最小的节点,然后搜索这个节点的 8 个邻域,选择下一个代价最小的节点,重复上述步骤,直到选择的节点与目标点重合,将这些代价最小的节点连接起来就得到一条最优路径。
A*算法代价函数:
f
(
n
)
=
g
(
n
)
+
h
(
n
)
(1)
f\begin{pmatrix}n\end{pmatrix}=g\begin{pmatrix}n\end{pmatrix}+h\begin{pmatrix}n\end{pmatrix}\tag{1}
f(n)=g(n)+h(n)(1)
其中, f(n)为n节点的总代价值, g(n)代表从n节点到初始节点的最短路径代价值, h(n)代表从n节点到目标节点代价的估计值。

2.代码讲解
地图参数初始化
start_node = [1, 1]; %起点
target_node = [20, 20];%坐标
% 栅格地图的行数、列数定义
m = 20;
n = 20;
% 加载地图
MAP = [0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0;
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0;
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0;
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0;
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0;
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0;
1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;];
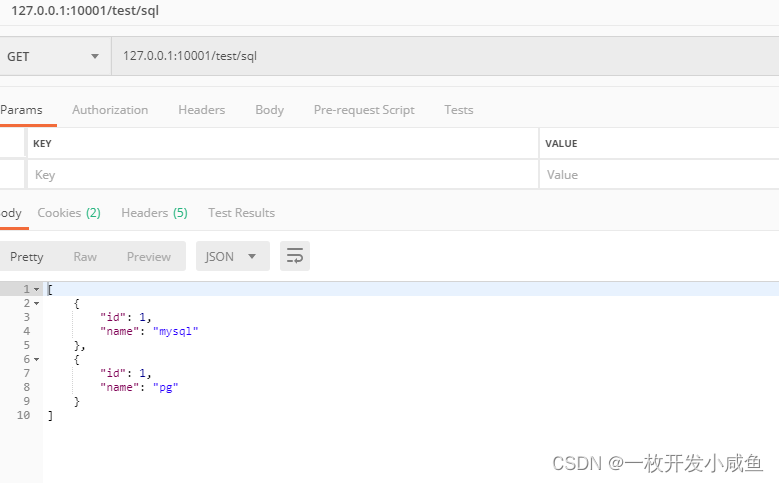
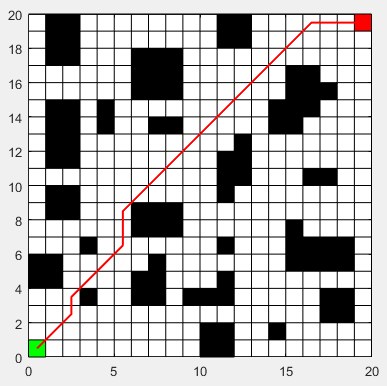
地图中1代表障碍物,0代表可行区域,绿色代表起点,红色代表终点:

获得父结点的可行子结点列表
function child_nodes = child_nodes_cal(parent_node, m, n, obs, closeList)
child_nodes = [];
field = [1,1; n,1; n,m; 1,m]; %边界
% 左上结点
child_node = [parent_node(1)-1, parent_node(2)+1];
if inpolygon(child_node(1), child_node(2), field(:,1), field(:,2)) %判断是否在地图内
if ~ismember(child_node, obs, 'rows') %如果子结点不是障碍物
child_nodes = [child_nodes; child_node];
end
end
% 上结点
child_node = [parent_node(1), parent_node(2)+1];
if inpolygon(child_node(1), child_node(2), field(:,1), field(:,2))
if ~ismember(child_node, obs, 'rows')
child_nodes = [child_nodes; child_node];
end
end
% 右上结点
child_node = [parent_node(1)+1, parent_node(2)+1];
if inpolygon(child_node(1), child_node(2), field(:,1), field(:,2))
if ~ismember(child_node, obs, 'rows')
child_nodes = [child_nodes; child_node];
end
end
% 左结点
child_node = [parent_node(1)-1, parent_node(2)];
if inpolygon(child_node(1), child_node(2), field(:,1), field(:,2))
if ~ismember(child_node, obs, 'rows')
child_nodes = [child_nodes; child_node];
end
end
% 右结点
child_node = [parent_node(1)+1, parent_node(2)];
if inpolygon(child_node(1), child_node(2), field(:,1), field(:,2))
if ~ismember(child_node, obs, 'rows')
child_nodes = [child_nodes; child_node];
end
end
% 左下结点
child_node = [parent_node(1)-1, parent_node(2)-1];
if inpolygon(child_node(1), child_node(2), field(:,1), field(:,2))
if ~ismember(child_node, obs, 'rows')
child_nodes = [child_nodes; child_node];
end
end
% 下结点
child_node = [parent_node(1), parent_node(2)-1];
if inpolygon(child_node(1), child_node(2), field(:,1), field(:,2))
if ~ismember(child_node, obs, 'rows')
child_nodes = [child_nodes; child_node];
end
end
% 右下结点
child_node = [parent_node(1)+1, parent_node(2)-1];
if inpolygon(child_node(1), child_node(2), field(:,1), field(:,2))
if ~ismember(child_node, obs, 'rows')
child_nodes = [child_nodes; child_node];
end
end
%% 排除已经存在于closeList的节点
delete_idx = [];
for i = 1:size(child_nodes, 1)
if ismember(child_nodes(i,:), closeList , 'rows')
delete_idx(end+1,:) = i;
end
end
child_nodes(delete_idx, :) = [];
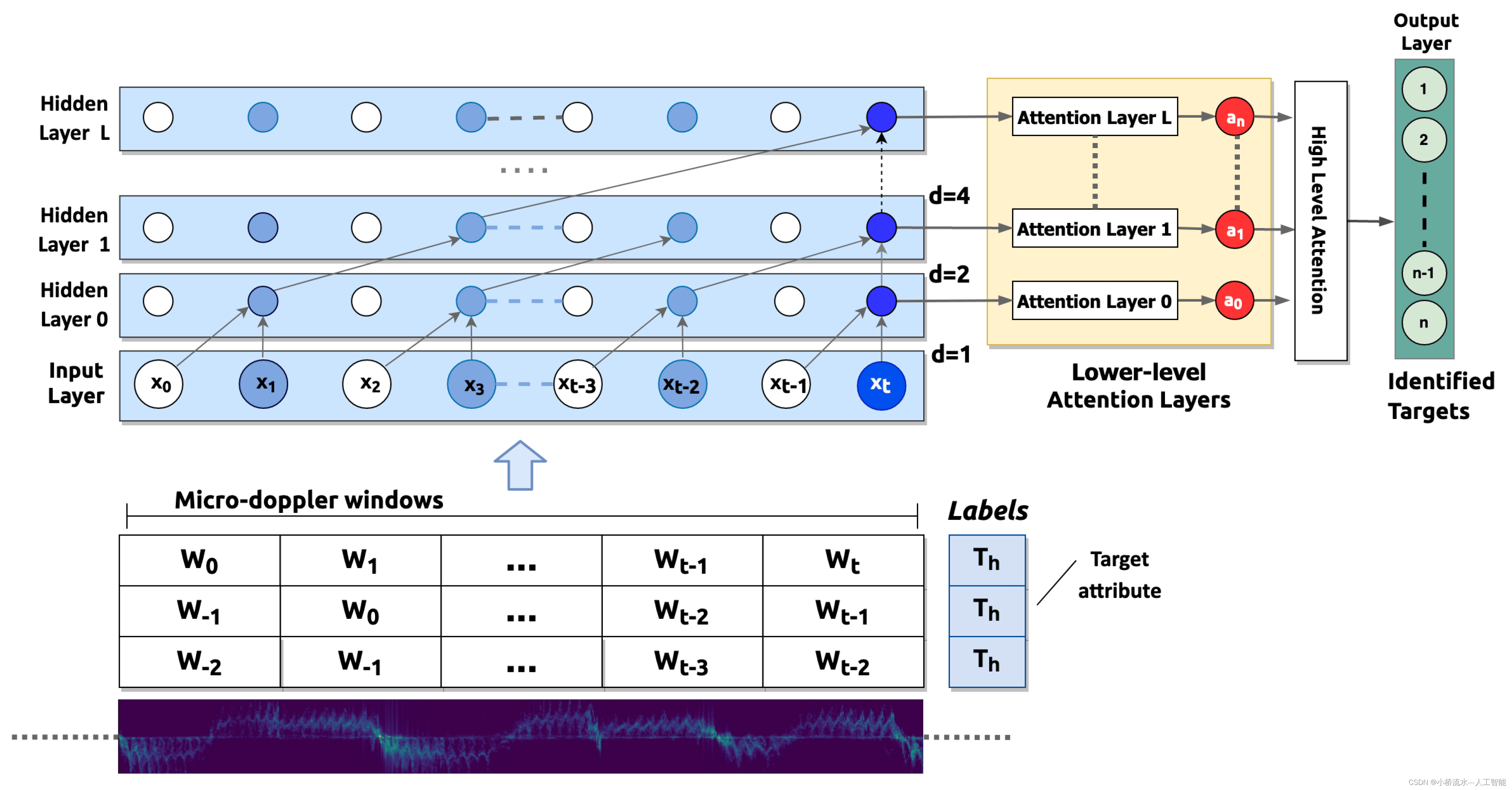
采用8领域搜索方式,红色箭头为可行走8个方向:
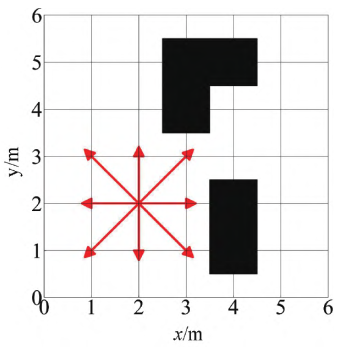
函数child_nodes_cal.m得到父结点的可行子结点列表,可行子结点需要判断是否在地图内,通过代码进行判断:
inpolygon(child_node(1), child_node(2), field(:,1), field(:,2))
另一方面,可行子结点不能为障碍物:
~ismember(child_node, obs, 'rows')
起点预处理
% 初始化closeList
closeList = start_node;
closeList_path = {start_node,start_node};
closeList_cost = 0;
child_nodes = child_nodes_cal(start_node, m,n,obs,closeList);
% 初始化openList
openList = child_nodes;
for i = 1:size(openList,1)
openList_path{i,1} = openList(i,:);
openList_path{i,2} = [start_node;openList(i,:)];
end
for i = 1:size(openList, 1)
g = norm(start_node - openList(i,1:2)); %欧氏距离
h = abs(target_node(1) - openList(i,1)) + abs(target_node(2) - openList(i,2)); %曼哈顿距离
f=g+h;
openList_cost(i,:) = [g, h, f];
end
这里g(n)采用欧式距离(表示结点n到起点实际距离),h(n)采用曼哈顿距离(表示结点n到终点估计值)。
计算迭代
% 从openList开始搜索移动代价最小的节点
[~, min_idx] = min(openList_cost(:,3));
parent_node = openList(min_idx,:);
%% 进入循环
flag = 1;
while flag
% 找出父节点的忽略closeList的子节点
child_nodes = child_nodes_cal(parent_node, m, n, obs, closeList);
% 判断这些子节点是否在openList中,若在,则比较更新;没在则追加到openList中
for i = 1:size(child_nodes,1)
child_node = child_nodes(i,:);
[in_flag,openList_idx] = ismember(child_node, openList, 'rows'); %in_flag=1则该child_node节点在openList中,openList_idx保存openList中第几位与child_node节点相同
g = openList_cost(min_idx, 1) + norm(parent_node - child_node);
h = abs(child_node(1) - target_node(1)) + abs(child_node(2) - target_node(2));
f=g+h;
if in_flag % 若在,更新路径和成本
if g < openList_cost(openList_idx,1)
openList_cost(openList_idx, 1) = g;
openList_cost(openList_idx, 3) = f;
openList_path{openList_idx,2} = [openList_path{min_idx,2}; child_node];
end
else % 若不在,加入openList
openList(end+1,:) = child_node;
openList_cost(end+1, :) = [g, h, f];
openList_path{end+1, 1} = child_node;
openList_path{end, 2} = [openList_path{min_idx,2}; child_node];
end
end
% 从openList移除移动代价最小的节点到 closeList
closeList(end+1,: ) = openList(min_idx,:);
closeList_cost(end+1,1) = openList_cost(min_idx,3);
closeList_path(end+1,:) = openList_path(min_idx,:);
openList(min_idx,:) = [];
openList_cost(min_idx,:) = [];
openList_path(min_idx,:) = [];
% 重新搜索:从openList搜索移动代价最小的节点
[~, min_idx] = min(openList_cost(:,3));
parent_node = openList(min_idx,:);
% 判断是否搜索到终点
if parent_node == target_node
closeList(end+1,: ) = openList(min_idx,:);
closeList_cost(end+1,1) = openList_cost(min_idx,1);
closeList_path(end+1,:) = openList_path(min_idx,:);
flag = 0;
end
end
3.结果展示
4.代码获取
完整代码公众号回复:A*,免费获取