根据曲线tag,返回曲线相关信息:弦宽容、弧度、最大步长、点数组的点。
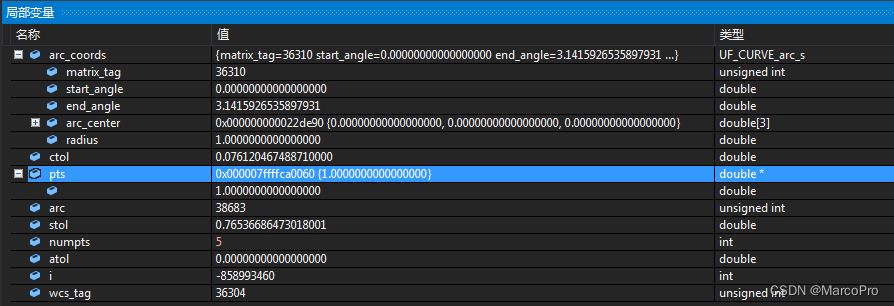
实例返回结果截图如下:
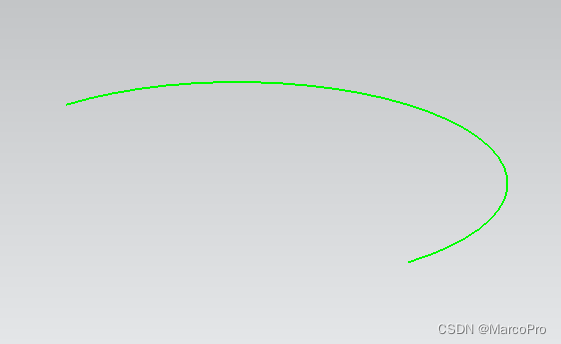
实例创建曲线截图如下:
1、函数结构
int UF_MODL_ask_curve_points
(tag_t curve_id,
double ctol,
double atol,
double stol,
int * numpts,
double * * pts)
2、实例源码
/*
The following example uses a semi-circle as the input curve. The ctol
and stol parameters were chosen so that five coordinates (located at 0,
45, 90, 135, and 180 degrees on the arc) are outputted.
*/
#include <uf.h>
#include <uf_modl.h>
#include <uf_curve.h>
#include <uf_csys.h>
#include <uf_obj.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define UF_CALL(X) (report( __FILE__, __LINE__, #X, (X)))
static int report( char *file, int line, char *call, int irc)
{
if (irc)
{
char messg[133];
printf("%s, line %d: %s\n", file, line, call);
(UF_get_fail_message(irc, messg)) ?
printf(" returned a %d\n", irc) :
printf(" returned error %d: %s\n", irc, messg);
}
return(irc);
}
static void do_ugopen_api(void)
{
double ctol = 0.07612046748871;
double atol = 0.0;
double stol = 0.76536686473018;
double *pts;
int numpts, i;
tag_t arc, wcs_tag;
UF_CURVE_arc_t arc_coords;
UF_CALL(UF_CSYS_ask_wcs(&wcs_tag));
UF_CALL(UF_CSYS_ask_matrix_of_object(wcs_tag,
&arc_coords.matrix_tag));
arc_coords.start_angle = 0.0;
arc_coords.end_angle = PI;
arc_coords.arc_center[0] = 0.0;
arc_coords.arc_center[1] = 0.0;
arc_coords.arc_center[2] = 0.0;
arc_coords.radius = 1.0;
UF_CALL(UF_CURVE_create_arc(&arc_coords, &arc));
if(UF_CALL(UF_MODL_ask_curve_points(arc,ctol,atol,stol,
&numpts, &pts)))
{
/* Print the error message from UF_CALL macro */
}
else
{
printf("The number of points are: %d\n",numpts);
for(i = 0; i < 3 * numpts; i++)
printf("The points are: %f\n",pts[i]);
}
UF_free(pts);
}
/*ARGSUSED*/
void ufusr(char *param, int *retcode, int param_len)
{
if (!UF_CALL(UF_initialize()))
{
do_ugopen_api();
UF_CALL(UF_terminate());
}
}
int ufusr_ask_unload(void)
{
return (UF_UNLOAD_IMMEDIATELY);
}1、创建曲线UF_CURVE_create_arc
2、获取曲线信息UF_MODL_ask_curve_points