什么是堆排序:
堆排序(Heapsort)是指利用堆(完全二叉树)这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法,它是选择排序的一种。需要注意的是排升序要建大堆,排降序建小堆。
堆排序排序的特性总结:
1. 堆排序使用堆来选数,效率就高了很多。
2. 时间复杂度:O(N*logN)
3. 空间复杂度:O(1)
4. 稳定性:不稳定
在开始堆排序之前有两个重要的概念:
大堆:父节点>=子节点的堆。
小堆:父节点<=子节点的堆。
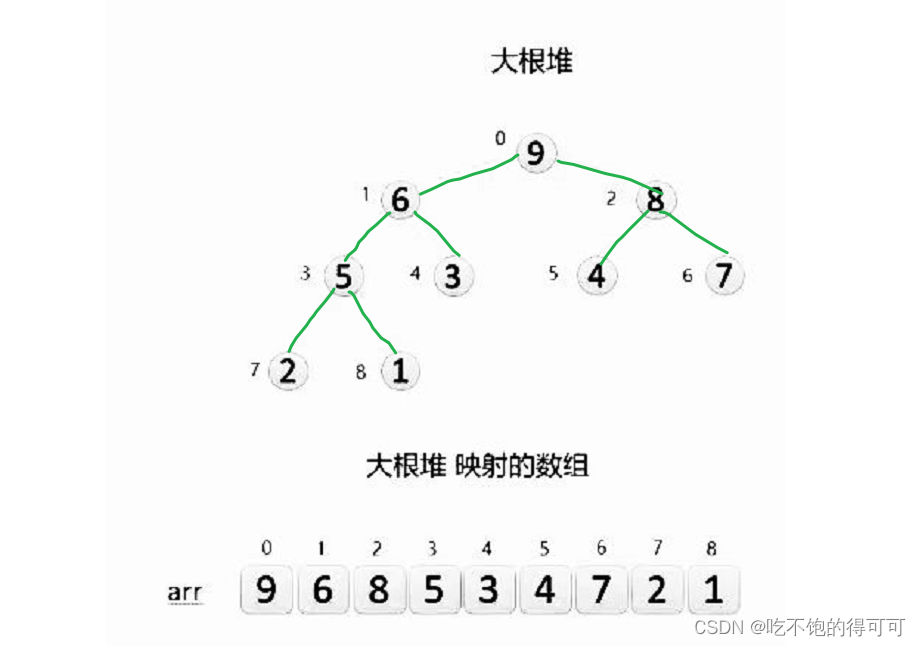
堆是什么:堆是完全二叉树。
在逻辑结构方面我们可以将一个数组想象成一个堆。
在物理结构方面看堆其实是一个数组。
如下:
在我看来,堆排序中最重要的是向上调整和向下调整算法。
堆排序是基于这两个算法来进行的。
向上调整算法:
目的:
当向堆中插入新元素时,为了维护堆的性质,需要对该元素进行向上调整。向上调整法就是从新插入的节点开始,通过与其父节点的比较和交换,确保该节点的值不大于(对于大根堆)或不小于(对于小根堆)其父节点的值。
//以大堆为例
void Adjustup(int* a, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[child] > a[parent])
swap(a[child], a[parent]);
else
break;
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
}向下调整算法:
目的:
当向堆中插入新元素时,为了维护堆的性质,需要对该元素进行向上调整。向上调整法就是从新插入的节点开始,通过与其父节点的比较和交换,确保该节点的值不大于(对于大根堆)或不小于(对于小根堆)其父节点的值。
//向下调整算法
//大堆为例
void Adjustdown(int* a, int parent, int n)//n是数组a的元素个数
{
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1])
{
++child;
}
if (a[child] > a[parent])
{
swap(a[child], a[parent]);
}
else
break;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
}需要注意的是对堆进行向上向下调整算法是要确保堆左子树和右子树是大堆/小堆。
下面我们来实现一下堆排序的完整代码:
void swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//以大堆为例
void Adjustup(int* a, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[child] > a[parent])
swap(a[child], a[parent]);
else
break;
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
}
//向下调整算法
//大堆为例
void Adjustdown(int* a, int parent, int n)//n是数组a的元素个数
{
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1])
{
++child;
}
if (a[child] > a[parent])
{
swap(a[child], a[parent]);
}
else
break;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
}
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
{
//首先利用向上调整算法建一个大堆(即父节点>=子节点的完全二叉树二叉树)
for (int i = 1;i < n;i++)
{
Adjustup(a, i);
}
int end = n - 1;
while (end > 0)
{
swap(a[0], a[end]);
Adjustdown(a, 0, end);
--end;
}
}上述堆排序代码是针对数组升序编写的,这里就不写降序的代码了,降序的堆排序和升序的如出一辙。
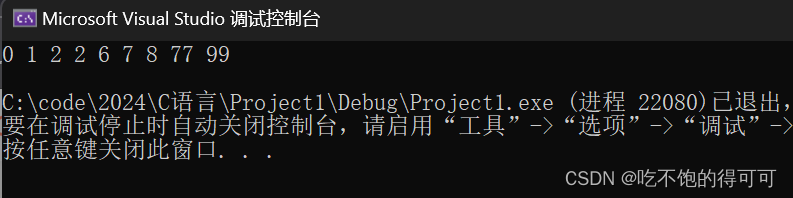
试验结果如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 77,99,2,1,2,8,6,7,0 };
HeapSort(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
for (auto e : arr)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}










![[香橙派 AIpro] 性能强劲的昇腾AI开发板,应用广泛,性能出众,遥遥领先!](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8643aa18f0fb47c2ba992de9a9e03eee.png)