文章目录
- 一:相机坐标系,像素平面坐标系,世界坐标系,归一化坐标系介绍
- 1:概述
- 公式
- 二:实现
- 1:整体流程
- 4:求出每张图像的单应性矩阵并用LMA优化
- 5:求解理想无畸变情况下的摄像机的内参数和外参数
- 6:应用最小二乘求出实际的畸变系数
- 五:总结
原文链接:http://t.csdn.cn/Qvvjv
个人笔记:
本次介绍针对于单目相机标定,实现方法:张正友标定法。
一:相机坐标系,像素平面坐标系,世界坐标系,归一化坐标系介绍
1:概述
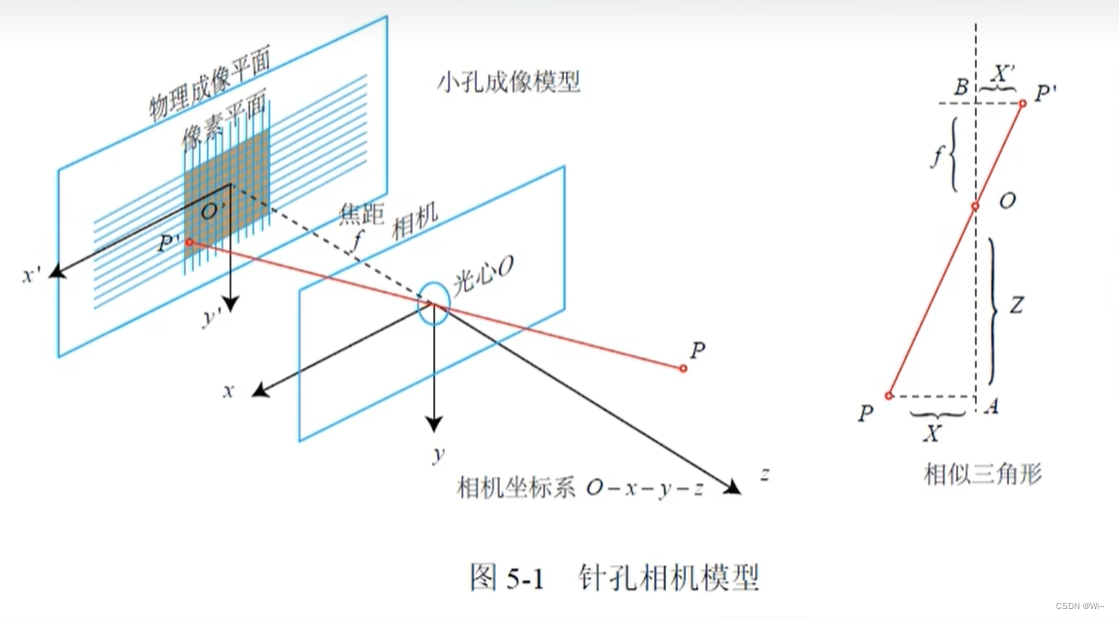
如图,现实世界中有一个P点和一个相机(光心),描述这个P点的空间坐标首先得有一个坐标系,那么以光心为原点O建一个坐标系,叫相机坐标系。
那么就可以在相机坐标系下,设
P
坐标
(
X
,
Y
,
Z
)
P坐标(X,Y,Z)
P坐标(X,Y,Z)和P的投影点
P
′
(
x
′
,
y
′
,
z
′
)
P'(x',y',z')
P′(x′,y′,z′)。值得一提的是,
P
′
(
x
′
,
y
′
,
z
′
)
P'(x',y',z')
P′(x′,y′,z′)坐落在物理成像平面和像素平面。
物理成像平面,像素平面是二维的,他们的坐标系并不一样:
物理成像平面在
O
′
(
x
′
,
y
′
)
O'(x',y')
O′(x′,y′)平面上;
像素平面的原点在那个黑灰色图的左上角(图片的左上角),横轴向右称为
u
u
u轴,纵轴向下称为
v
v
v轴。
这样就得到了
P
′
P'
P′的像素坐标
P
(
u
,
v
)
P(u,v)
P(u,v),称为
P
u
v
Puv
Puv。
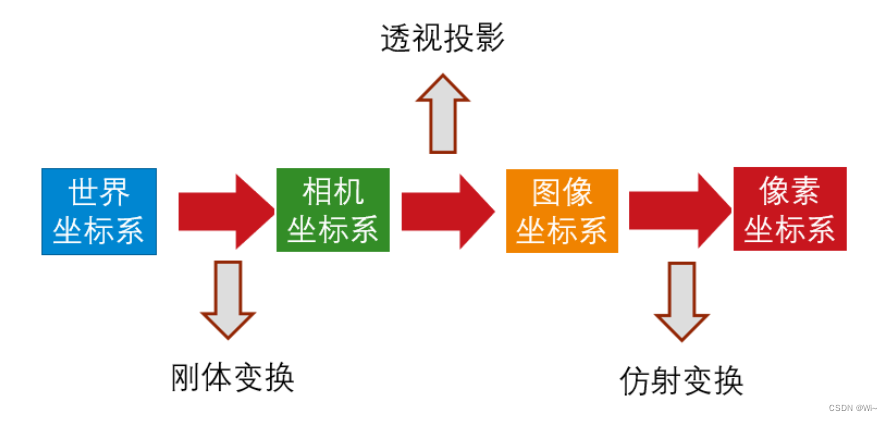
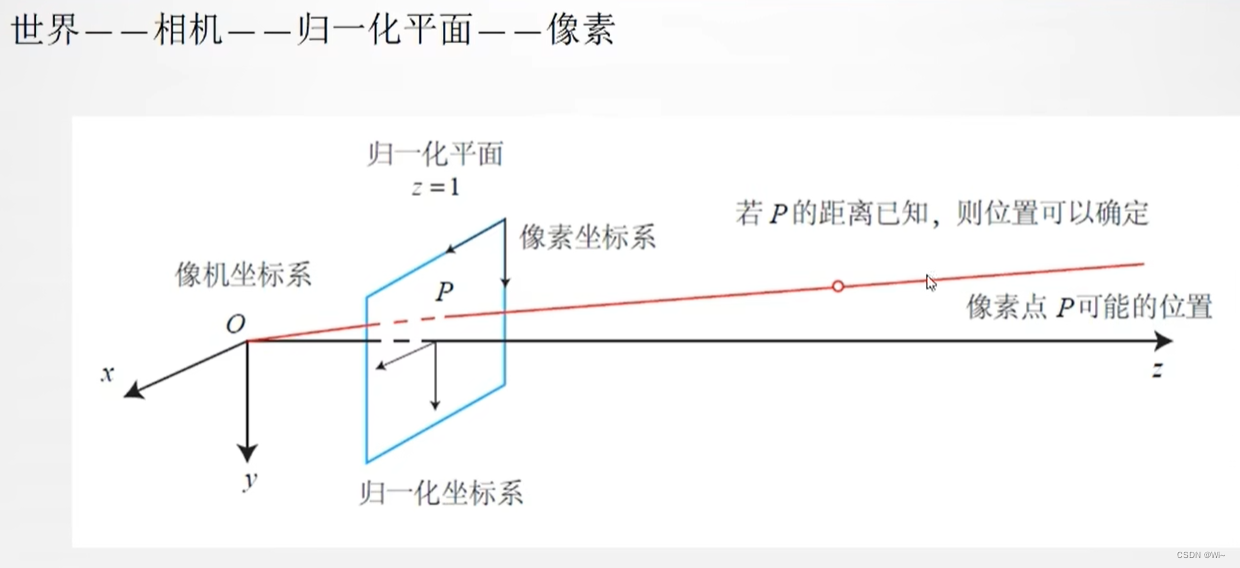 所谓的归一化的成像平面,就是将三维空间点的坐标都除以Z,在相机坐标系下,P有X, Y, Z 三个量,如果把它们投影到归一化平面 Z = 1 上,就会得到P的归一化坐标P(X/Z, Y/Z, 1)。
所谓的归一化的成像平面,就是将三维空间点的坐标都除以Z,在相机坐标系下,P有X, Y, Z 三个量,如果把它们投影到归一化平面 Z = 1 上,就会得到P的归一化坐标P(X/Z, Y/Z, 1)。
公式

[
X
Y
Z
1
]
−
>
\left[\begin{array}{c} X \\ Y \\ Z \\ 1 \end{array}\right]->
XYZ1
−>物体坐标.
[ R T 0 1 ] − > \left[\begin{array}{cc} R & T \\ 0 & 1 \end{array}\right]-> [R0T1]−>外参
[ α γ u 0 0 0 β v 0 0 0 0 1 0 ] − > \left[\begin{array}{cccc} \alpha & \gamma & u_{0} & 0 \\ 0 & \beta & v_{0} & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array}\right]-> α00γβ0u0v01000 −>内参
[ u v 1 ] − > \left[\begin{array}{l} u \\ v \\ 1 \end{array}\right]-> uv1 −>像素坐标
其中外参
T
T
T是平移向量
(
t
1
,
t
2
,
t
3
)
T
(t1,t2,t3)^T
(t1,t2,t3)T.
R
R
R旋转矩阵如下图:
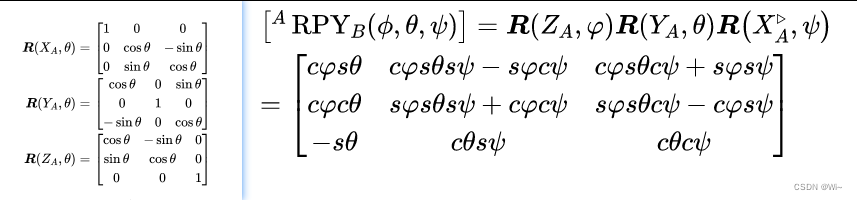
二:实现
1:整体流程
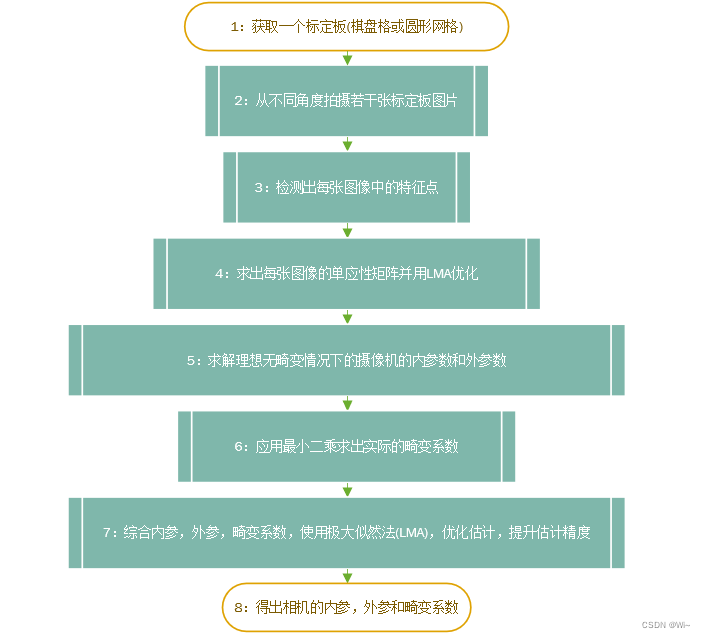
第1步,第2步,第3步 暂不介绍了,主要介绍获取到特征点以后,优化获取参数部分。
4:求出每张图像的单应性矩阵并用LMA优化
如何计算单应性矩阵:
[
x
b
y
b
w
b
]
=
[
h
1
h
2
h
3
h
4
h
5
h
6
h
7
h
8
h
9
]
[
x
a
y
a
w
a
]
x
b
w
b
=
h
1
x
a
+
h
2
y
a
+
h
3
w
a
h
7
x
a
+
h
8
y
a
+
h
9
w
a
=
h
1
x
a
/
w
a
+
h
2
y
a
/
w
a
+
h
3
h
7
x
a
/
w
a
+
h
8
y
a
/
w
a
+
h
9
y
b
w
b
=
h
4
x
a
+
h
5
y
a
+
h
6
w
a
h
7
x
a
+
h
8
y
a
+
h
9
w
a
=
h
4
x
a
/
w
a
+
h
5
y
a
/
w
a
+
h
6
h
7
x
a
/
w
a
+
h
8
y
a
/
w
a
+
h
9
\begin{array}{c} \left[\begin{array}{l} x_{b} \\ y_{b} \\ w_{b} \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc} \mathrm{h}_{1} & \mathrm{~h}_{2} & \mathrm{~h}_{3} \\ \mathrm{~h}_{4} & \mathrm{~h}_{5} & \mathrm{~h}_{6} \\ \mathrm{~h}_{7} & \mathrm{~h}_{8} & \mathrm{~h}_{9} \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l} x_{a} \\ y_{a} \\ w_{a} \end{array}\right] \\\\ \frac{x_{b}}{w_{b}}=\frac{h_{1} x_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{2} y_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{3} w_{a}}{h_{7} x_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} y_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9} w_{a}}=\frac{h_{1} x_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{2} y_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{3}}{h_{7} x_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} y_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \\ \frac{y_{b}}{w_{b}}=\frac{h_{4} x_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{5} y_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{6} w_{a}}{h_{7} x_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} y_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9} w_{a}}=\frac{h_{4} x_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{5} y_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{6}}{h_{7} x_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} y_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \end{array}
xbybwb
=
h1 h4 h7 h2 h5 h8 h3 h6 h9
xayawa
wbxb=h7xa+h8ya+h9wah1xa+h2ya+h3wa=h7xa/wa+h8ya/wa+h9h1xa/wa+h2ya/wa+h3wbyb=h7xa+h8ya+h9wah4xa+h5ya+h6wa=h7xa/wa+h8ya/wa+h9h4xa/wa+h5ya/wa+h6
令
u
a
=
x
a
w
a
,
v
a
=
y
a
w
a
,
u
b
=
x
b
w
b
,
v
b
=
y
b
w
b
, 上式化简为
\text { 令 } u_{a}=\frac{x_{a}}{w_{a}}, v_{a}=\frac{y_{a}}{w_{a}}, u_{b}=\frac{x_{b}}{w_{b}}, v_{b}=\frac{y_{b}}{w_{b}} \text {, 上式化简为 }
令 ua=waxa,va=waya,ub=wbxb,vb=wbyb, 上式化简为
u
b
=
h
1
u
a
+
h
2
v
a
+
h
3
h
7
u
a
+
h
8
v
a
+
h
9
v
b
=
h
4
u
a
+
h
5
v
a
+
h
6
h
7
u
a
+
h
8
v
a
+
h
9
\begin{array}{l} u_{b}=\frac{h_{1} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{2} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{3}}{h_{7} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \\ v_{b}=\frac{h_{4} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{5} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{6}}{h_{7} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \end{array}
ub=h7ua+h8va+h9h1ua+h2va+h3vb=h7ua+h8va+h9h4ua+h5va+h6
h 1 u a + h 2 v a + h 3 − h 7 u a u b − h 8 v a u b − h 9 u b = 0 h 4 u a + h 5 v a + h 6 − h 7 u a v b − h 8 v a v b − h 9 v b = 0 \begin{array}{c} h_{1} u_{a}+h_{2} v_{a}+h_{3}-h_{7} u_{a} u_{b}-h_{8} v_{a} u_{b}-h_{9} u_{b}=0 \\ h_{4} u_{a}+h_{5} v_{a}+h_{6}-h_{7} u_{a} v_{b}-h_{8} v_{a} v_{b}-h_{9} v_{b}=0 \end{array} h1ua+h2va+h3−h7uaub−h8vaub−h9ub=0h4ua+h5va+h6−h7uavb−h8vavb−h9vb=0
可以直接设
∥
h
∥
2
2
=
1
,此时仍然可以固定住尺度,且有:
\text { 可以直接设 }\|h\|_{2}^{2}=1 \text { ,此时仍然可以固定住尺度,且有: }
可以直接设 ∥h∥22=1 ,此时仍然可以固定住尺度,且有:
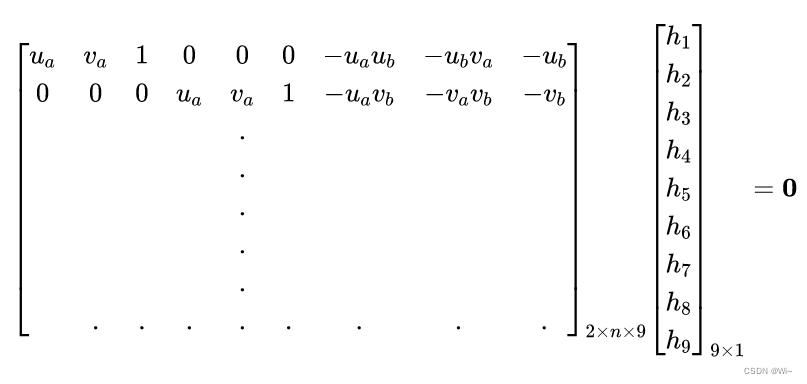
此时系数矩阵秩为8,有线性空间解,解的自由度为1,满足齐次性,又由于限制单位长度,有唯一解,此时仍可以通过SVD分解求解出 h,从而得到单应矩阵。
代码实现:
//获取标准差
double CameraCalibration::StdDiffer(const Eigen::VectorXd& data)
{
//获取平均值
double mean = data.mean();
//std::sqrt((Σ(x-_x)²) / n)
return std::sqrt((data.array() - mean).pow(2).sum() / data.rows());
}
// 归一化
Eigen::Matrix3d CameraCalibration::Normalization (const Eigen::MatrixXd& P)
{
Eigen::Matrix3d T;
double cx = P.col ( 0 ).mean();
double cy = P.col ( 1 ).mean();
double stdx = StdDiffer(P.col(0));
double stdy = StdDiffer(P.col(1));;
double sqrt_2 = std::sqrt ( 2 );
double scalex = sqrt_2 / stdx;
double scaley = sqrt_2 / stdy;
T << scalex, 0, -scalex*cx,
0, scaley, -scaley*cy,
0, 0, 1;
return T;
}
//获取初始矩阵H
Eigen::VectorXd CameraCalibration::GetInitialH (const Eigen::MatrixXd& srcNormal,const Eigen::MatrixXd& dstNormal )
{
Eigen::Matrix3d realNormMat = Normalization(srcNormal);
Eigen::Matrix3d picNormMat = Normalization(dstNormal);
int n = srcNormal.rows();
// 2. DLT
Eigen::MatrixXd input ( 2*n, 9 );
for ( int i=0; i<n; ++i )
{
//转换齐次坐标
Eigen::MatrixXd singleSrcCoor(3,1),singleDstCoor(3,1);
singleSrcCoor(0,0) = srcNormal(i,0);
singleSrcCoor(1,0) = srcNormal(i,1);
singleSrcCoor(2,0) = 1;
singleDstCoor(0,0) = dstNormal(i,0);
singleDstCoor(1,0) = dstNormal(i,1);
singleDstCoor(2,0) = 1;
//坐标归一化
Eigen::MatrixXd realNorm(3,1),picNorm(3,1);
realNorm = realNormMat * singleSrcCoor;
picNorm = picNormMat * singleDstCoor;
input ( 2*i, 0 ) = realNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i, 1 ) = realNorm ( 1, 0 );
input ( 2*i, 2 ) = 1.;
input ( 2*i, 3 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i, 4 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i, 5 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i, 6 ) = -picNorm ( 0, 0 ) * realNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i, 7 ) = -picNorm ( 0, 0 ) * realNorm ( 1, 0 );
input ( 2*i, 8 ) = -picNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 0 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i+1, 1 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i+1, 2 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i+1, 3 ) = realNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 4 ) = realNorm ( 1, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 5 ) = 1.;
input ( 2*i+1, 6 ) = -picNorm ( 1, 0 ) * realNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 7 ) = -picNorm ( 1, 0 ) * realNorm ( 1, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 8 ) = -picNorm ( 1, 0 );
}
// 3. SVD分解
JacobiSVD<Eigen::MatrixXd> svdSolver ( input, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV );
Eigen::MatrixXd V = svdSolver.matrixV();
Eigen::Matrix3d H = V.rightCols(1).reshaped<RowMajor>(3,3);
//去归一化
H = (picNormMat.inverse() * H) * realNormMat;
H /= H(2,2);
return H.reshaped<RowMajor>(9,1);
}
求出初始单应性矩阵
h
h
h,然后用
L
M
A
LMA
LMA优化,得到具有实际意义的单应性矩阵。
优化代码:
//单应性残差值向量
class HomographyResidualsVector
{
public:
Eigen::VectorXd operator()(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> &otherArgs)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd inValue = otherArgs.at(0);
Eigen::MatrixXd outValue = otherArgs.at(1);
int dataCount = inValue.rows();
//保存残差值
Eigen::VectorXd residual(dataCount*2) ,residualNew(dataCount*2);
Eigen::Matrix3d HH = parameter.reshaped<RowMajor>(3,3);
//获取预测偏差值 r= ^y(预测值) - y(实际值)
for(int i=0;i<dataCount;++i)
{
//转换齐次坐标
Eigen::VectorXd singleRealCoor(3),U(3);
singleRealCoor(0,0) = inValue(i,0);
singleRealCoor(1,0) = inValue(i,1);
singleRealCoor(2,0) = 1;
U = HH * singleRealCoor;
U /= U(2);
residual(i*2) = U(0);
residual(i*2+1) = U(1);
residualNew(i*2) = outValue(i,0);
residualNew(i*2+1) = outValue(i,1);
}
residual -= residualNew;
return residual;
}
};
//求单应性雅克比矩阵
class HomographyJacobi
{
//求偏导1
double PartialDeriv_1(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,int paraIndex,const Eigen::MatrixXd &inValue,int objIndex)
{
Eigen::VectorXd para1 = parameter;
Eigen::VectorXd para2 = parameter;
para1(paraIndex) -= DERIV_STEP;
para2(paraIndex) += DERIV_STEP;
//逻辑
double obj1 = ((para1(0))*inValue(objIndex,0) + para1(1)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para1(2)) / (para1(6)*inValue(objIndex,0) + para1(7)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para1(8));
double obj2 = ((para2(0))*inValue(objIndex,0) + para2(1)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para2(2)) / (para2(6)*inValue(objIndex,0) + para2(7)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para2(8));;
return (obj2 - obj1) / (2 * DERIV_STEP);
}
//求偏导2
double PartialDeriv_2(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,int paraIndex,const Eigen::MatrixXd &inValue,int objIndex)
{
Eigen::VectorXd para1 = parameter;
Eigen::VectorXd para2 = parameter;
para1(paraIndex) -= DERIV_STEP;
para2(paraIndex) += DERIV_STEP;
//逻辑
double obj1 = ((para1(3))*inValue(objIndex,0) + para1(4)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para1(5)) / (para1(6)*inValue(objIndex,0) + para1(7)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para1(8));
double obj2 = ((para2(3))*inValue(objIndex,0) + para2(4)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para2(5)) / (para2(6)*inValue(objIndex,0) + para2(7)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para2(8));;
return (obj2 - obj1) / (2 * DERIV_STEP);
}
public:
Eigen::MatrixXd operator()(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> &otherArgs)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd inValue = otherArgs.at(0);
int rowNum = inValue.rows();
Eigen::MatrixXd Jac(rowNum*2, parameter.rows());
for (int i = 0; i < rowNum; i++)
{
// //第一种方法:直接求偏导
// double sx = parameter(0)*inValue(i,0) + parameter(1)*inValue(i,1) + parameter(2);
// double sy = parameter(3)*inValue(i,0) + parameter(4)*inValue(i,1) + parameter(5);
// double w = parameter(6)*inValue(i,0) + parameter(7)*inValue(i,1) + parameter(8);
// double w2 = w*w;
// Jac(i*2,0) = inValue(i,0)/w;
// Jac(i*2,1) = inValue(i,1)/w;
// Jac(i*2,2) = 1/w;
// Jac(i*2,3) = 0;
// Jac(i*2,4) = 0;
// Jac(i*2,5) = 0;
// Jac(i*2,6) = -sx*inValue(i,0)/w2;
// Jac(i*2,7) = -sx*inValue(i,1)/w2;
// Jac(i*2,8) = -sx/w2;
// Jac(i*2+1,0) = 0;
// Jac(i*2+1,1) = 0;
// Jac(i*2+1,2) = 0;
// Jac(i*2+1,3) = inValue(i,0)/w;
// Jac(i*2+1,4) = inValue(i,1)/w;
// Jac(i*2+1,5) = 1/w;
// Jac(i*2+1,6) = -sy*inValue(i,0)/w2;
// Jac(i*2+1,7) = -sy*inValue(i,1)/w2;
// Jac(i*2+1,8) = -sy/w2;
//第二种方法: 计算求偏导
Jac(i*2,0) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,0,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,1) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,1,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,2) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,2,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,3) = 0;
Jac(i*2,4) = 0;
Jac(i*2,5) = 0;
Jac(i*2,6) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,6,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,7) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,7,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,8) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,8,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,0) = 0;
Jac(i*2+1,1) = 0;
Jac(i*2+1,2) = 0;
Jac(i*2+1,3) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,3,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,4) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,4,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,5) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,5,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,6) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,6,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,7) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,7,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,8) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,8,inValue,i);
}
return Jac;
}
};
//求单应性矩阵H
Eigen::Matrix3d CameraCalibration::GetHomography(const Eigen::MatrixXd& src,const Eigen::MatrixXd& dst)
{
//获取初始单应性矩阵 -- svd
Eigen::VectorXd H = GetInitialH(src,dst);
QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> otherValue{src,dst};
//非线性优化 H 参数 -- LM算法
H =GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->LevenbergMarquardtAlgorithm(H,otherValue,HomographyResidualsVector(),HomographyJacobi());
H /= H(8);
// std::cout<<"H:"<<std::endl<<H<<std::endl;
return H.reshaped<RowMajor>(3,3);
}
5:求解理想无畸变情况下的摄像机的内参数和外参数
在求取了单应性矩阵后, 还要进一步求出摄像机的内参数。首先令
h
i
h_{i}
hi
表示
H
H
H 的 每一列向量, 于是有:
[ h 1 h 2 h 3 ] = λ K [ r 1 r 2 t ] \left[\begin{array}{lll} h_{1} & h_{2} & h_{3} \end{array}\right]=\lambda K\left[\begin{array}{lll} r_{1} & r_{2} & t \end{array}\right] [h1h2h3]=λK[r1r2t]
又因为 r 1 r_{1} r1 和 r 2 r_{2} r2 是单位正交向量, 所以有 :
h
1
T
K
−
T
K
−
1
h
2
=
0
h
1
T
K
−
T
K
−
1
h
1
=
h
2
T
K
−
T
K
−
1
h
2
\begin{aligned} h_{1}^{T} K^{-T} K^{-1} h_{2} & =0 \\ h_{1}^{T} K^{-T} K^{-1} h_{1} & =h_{2}^{T} K^{-T} K^{-1} h_{2} \end{aligned}
h1TK−TK−1h2h1TK−TK−1h1=0=h2TK−TK−1h2

则:
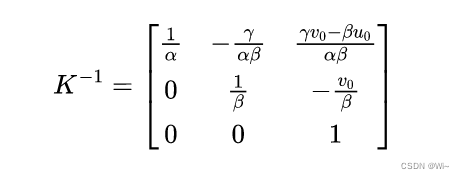
这样就为内参数的求解提供了两个约束方程,令:
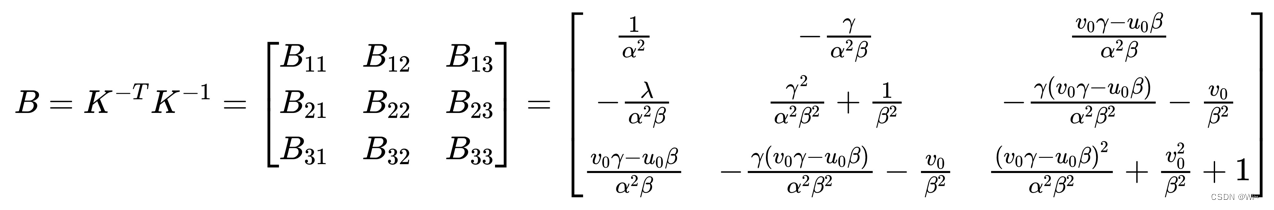 由于
B
B
B 为对称矩阵, 所以它可以由一个 6 维向量来定义, 即:
由于
B
B
B 为对称矩阵, 所以它可以由一个 6 维向量来定义, 即:
b
=
[
B
11
B
12
B
22
B
13
B
23
B
33
]
T
b=\left[\begin{array}{llllll} B_{11} & B_{12} & B_{22} & B_{13} & B_{23} & B_{33} \end{array}\right]^{T}
b=[B11B12B22B13B23B33]T
令
H
的第
i
列向量为
h
i
=
[
h
i
1
h
i
2
h
i
3
]
T
,
则
:
令 H 的第 i 列向量为 h_{i}=\left[\begin{array}{lll}h_{i 1} & h_{i 2} & h_{i 3}\end{array}\right]^{T} , 则:
令H的第i列向量为hi=[hi1hi2hi3]T,则:
h
i
T
B
h
j
=
V
i
j
T
b
h_{i}^{T} B h_{j}=V_{i j}^{T} b
hiTBhj=VijTb
其中:
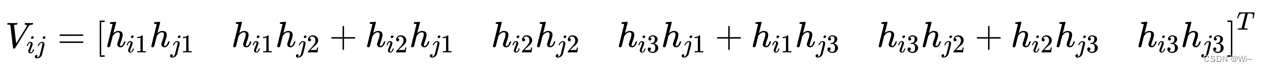
所以组成一个方程组为:
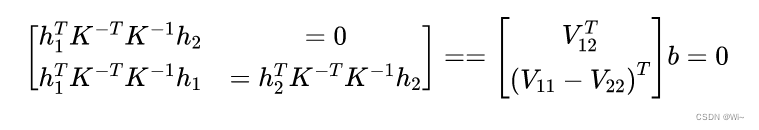 V
为
2
n
∗
6
矩阵
V为2n*6矩阵
V为2n∗6矩阵。如果
n
>
=
3
n>=3
n>=3,则可以列出6个方程,从而解出6个内参数。这6个解出的内部参数不是唯一的,而是通过了一个比例因子缩放。求出内参:
V
为
2
n
∗
6
矩阵
V为2n*6矩阵
V为2n∗6矩阵。如果
n
>
=
3
n>=3
n>=3,则可以列出6个方程,从而解出6个内参数。这6个解出的内部参数不是唯一的,而是通过了一个比例因子缩放。求出内参:
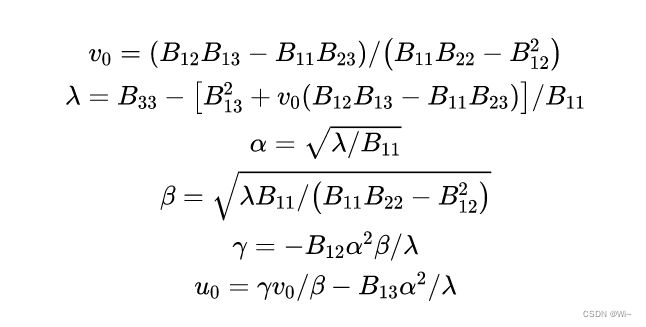
即可求出相机内参矩阵:
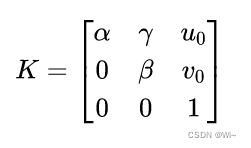
内参求出后,求外参:
再根据
[
h
1
h
2
h
3
]
=
λ
A
[
r
1
r
2
t
]
\left[\begin{array}{lll} \mathbf{h}_{1} & \mathbf{h}_{2} & \mathbf{h}_{3} \end{array}\right]=\lambda \mathbf{A}\left[\begin{array}{lll} \mathbf{r}_{1} & \mathbf{r}_{2} & \mathbf{t} \end{array}\right]
[h1h2h3]=λA[r1r2t]化简可得外部参数,即:
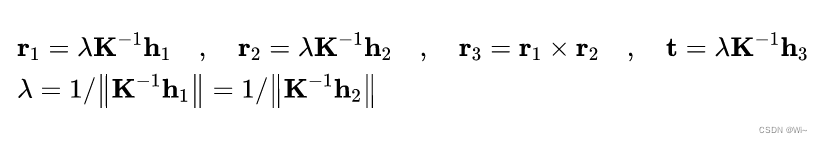
代码实现:
//根据单应性矩阵H返回pq位置对应的v向量
Eigen::VectorXd CameraCalibration::CreateV(int p, int q,const Eigen::Matrix3d& H)
{
Eigen::VectorXd v(6,1);
v << H(0, p) * H(0, q),
H(0, p) * H(1, q) + H(1, p) * H(0, q),
H(1, p) * H(1, q),
H(2, p) * H(0, q) + H(0, p) * H(2, q),
H(2, p) * H(1, q) + H(1, p) * H(2, q),
H(2, p) * H(2, q);
return v;
}
//求相机内参
Eigen::Matrix3d CameraCalibration::GetIntrinsicParameter(const QList<Eigen::Matrix3d>& HList)
{
int HCount = HList.count();
//构建V矩阵
Eigen::MatrixXd V(HCount*2,6);
for(int i=0;i<HCount;++i)
{
V.row(i*2) = CreateV(0, 1, HList.at(i)).transpose();
V.row(i*2+1) = (CreateV(0, 0, HList.at(i)) - CreateV(1, 1, HList.at(i))).transpose();
}
//Vb = 0
//svd分解求x
JacobiSVD<Eigen::MatrixXd> svd(V, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);
//获取V矩阵最后一列就是b的值
Eigen::VectorXd b = svd.matrixV().rightCols(1);
double B11 = b(0);
double B12 = b(1);
double B22 = b(2);
double B13 = b(3);
double B23 = b(4);
double B33 = b(5);
double v0 = (B12*B13 - B11*B23) / (B11*B22 - B12*B12);
double lambda = B33 - (B13*B13 + v0*(B12*B13 - B11*B23))/B11;
//double lambda = 1.0;
double alpha = qSqrt(lambda / B11);
double beta = qSqrt(lambda*B11 / (B11*B22 - B12 *B12));
double gamma = (- B12*alpha*alpha*beta) / lambda;
double u0 = (gamma*v0 / beta) - (B13 * alpha * alpha / lambda);
Eigen::Matrix3d K;
if(m_intrinsicCount == 5)
{
K<<alpha,gamma,u0,
0,beta,v0,
0,0,1;
}
else if(m_intrinsicCount == 4)
{
K<<alpha,0,u0,
0,beta,v0,
0,0,1;
}
return K;
}
//求相机外参
QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> CameraCalibration::GetExternalParameter(const QList<Eigen::Matrix3d>& HList,const Eigen::Matrix3d& intrinsicParam)
{
QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> exterParame;
//内参逆矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3d intrinsicParamInv = intrinsicParam.inverse();
int HCount = HList.count();
for(int i=0;i<HCount;++i)
{
Eigen::Matrix3d H = HList.at(i);
Eigen::Vector3d h0,h1,h2;
h0 = H.col(0);
h1 = H.col(1);
h2 = H.col(2);
Eigen::Vector3d r0,r1,r2,t;
//比例因子λ
double scaleFactor = 1 / (intrinsicParamInv * h0).lpNorm<2>();
r0 = scaleFactor * (intrinsicParamInv * h0);
r1 = scaleFactor * (intrinsicParamInv * h1);
r2 = r0.cross(r1);
t = scaleFactor * (intrinsicParamInv * h2);
Eigen::MatrixXd Rt(3,4);
Rt.col(0) = r0;
Rt.col(1) = r1;
Rt.col(2) = r2;
Rt.col(3) = t;
exterParame.append(Rt);
// std::cout<<"Rt"<<i<<":"<<std::endl<<Rt<<std::endl;
}
return exterParame;
}
//无畸变优化
Eigen::VectorXd disCoeff1(0);
//GetDistortionCoeff(srcL,dstL,A,W,disCoeff);
OptimizeParameter(srcL,dstL,A,disCoeff1,W);
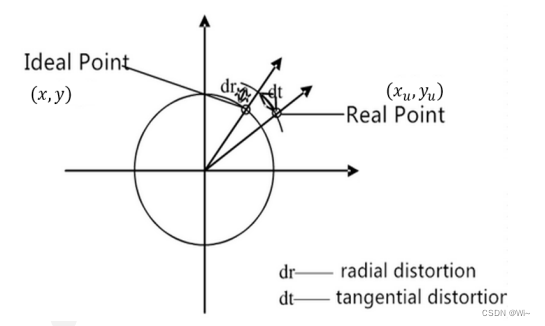
6:应用最小二乘求出实际的畸变系数
相机主要包括径向畸变和切向畸变
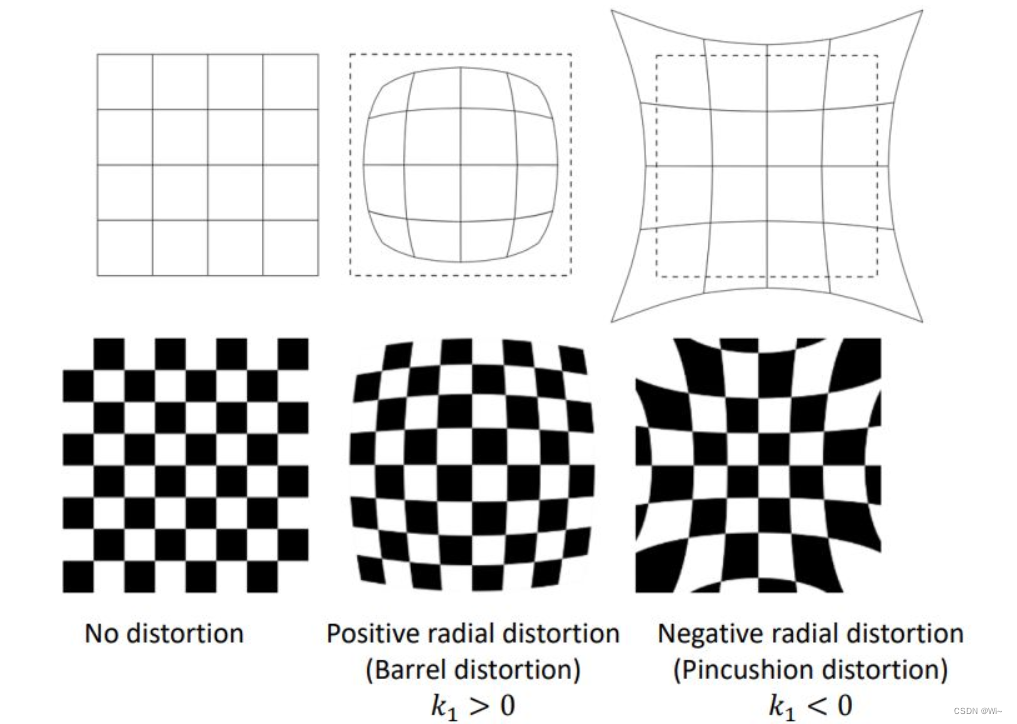
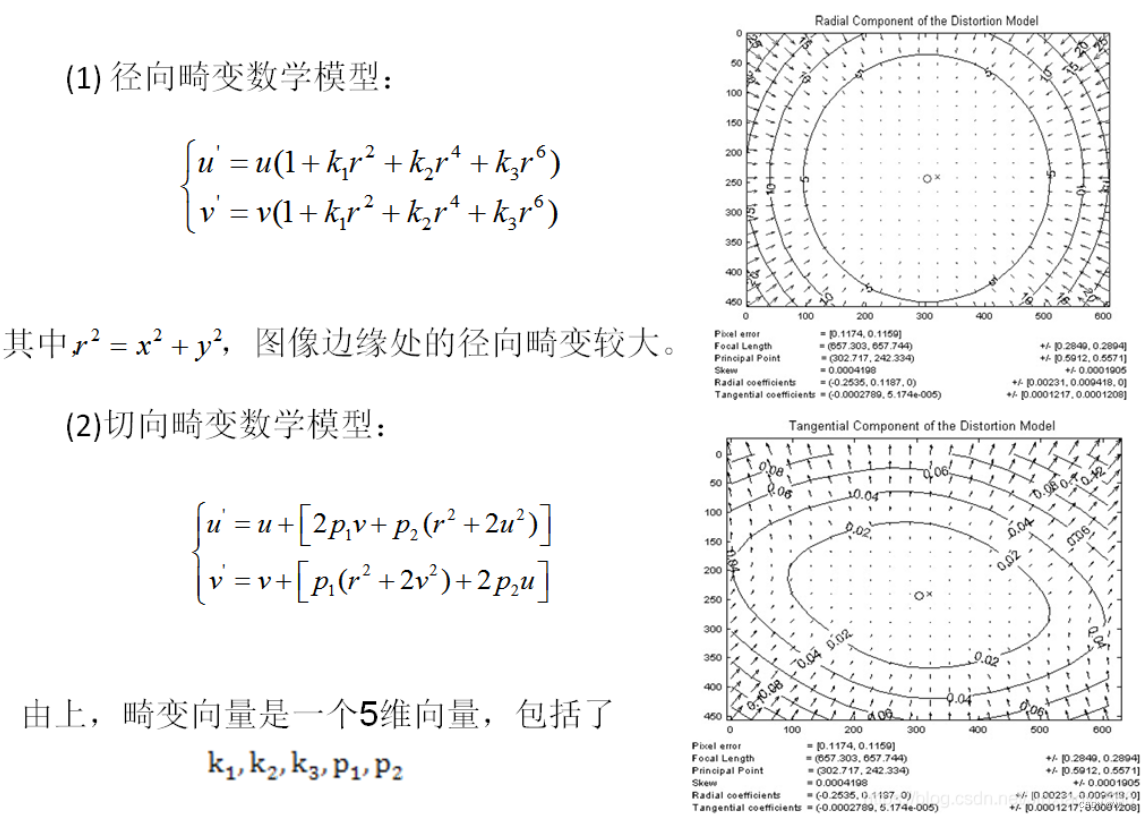
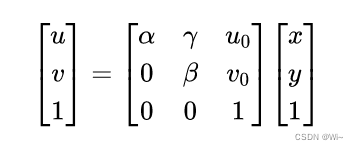 代码实现:
代码实现:
//获取畸变系数 k1,k2,[p1,p2,[k3]]
void CameraCalibration::GetDistortionCoeff(const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& srcL,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& dstL,const Eigen::Matrix3d& intrinsicParam ,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& externalParams,Eigen::VectorXd & disCoeff)
{
//按照畸变个数获取参数
int disCount = disCoeff.rows();
if(!(disCount == 2 || disCount == 4 || disCount == 5))
{
qDebug()<<QString("畸变参数个数按照数组大小为2或者4或者5,请重新设置数组大小!");
return;
}
int count = srcL.count();
double u0 = intrinsicParam(0,2);
double v0 = intrinsicParam(1,2);
int rowS = 0;
int k = 0;
//获取数据个数
for(int i=0;i<count;++i)
{
rowS += srcL.at(i).rows();
}
//初始化数据大小
Eigen::MatrixXd D(rowS*2,disCount),d(rowS*2,1);
for(int i=0;i<count;++i)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd src = srcL.at(i);
int dataCount = src.rows();
Eigen::MatrixXd dst = dstL.at(i);
Eigen::MatrixXd externalParam = externalParams.at(i);
for(int j=0;j<dataCount;++j)
{
//转换齐次坐标
Eigen::VectorXd singleCoor(4);
singleCoor(0) = src(j,0);
singleCoor(1) = src(j,1);
singleCoor(2) = 0.0;
singleCoor(3) = 1.0;
//用现有的内参及外参求估计图像坐标
Eigen::VectorXd imageCoorEstimate = intrinsicParam * externalParam * singleCoor;
//归一化图像坐标
double u_estimate = imageCoorEstimate(0)/imageCoorEstimate(2);
double v_estimate = imageCoorEstimate(1)/imageCoorEstimate(2);
//相机坐标系下的坐标
Eigen::VectorXd normCoor = externalParam * singleCoor;
//归一化坐标
normCoor /= normCoor(2);
double r = std::sqrt(std::pow(normCoor(0),2) + std::pow(normCoor(1),2));
//k1,k2
if(disCount >= 2)
{
D(k,0) = (u_estimate - u0)*std::pow(r,2);
D(k,1) = (u_estimate - u0)*std::pow(r,4);
D(k+1,0) = (v_estimate - v0)*std::pow(r,2);
D(k+1,1) = (v_estimate - v0)*std::pow(r,4);
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2
if(disCount >= 4)
{
D(k,2) = (u_estimate - u0)*(v_estimate - v0)*2;
D(k,3) = 2 * std::pow((u_estimate - u0),2) + std::pow(r,2);
D(k+1,2) = 2 * std::pow((v_estimate - v0),2) + std::pow(r,2);
D(k+1,3) = (u_estimate - u0)*(v_estimate - v0)*2;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3
if(disCount >= 5)
{
D(k,4) = (u_estimate - u0)*std::pow(r,6);
D(k+1,4) = (v_estimate - v0)*std::pow(r,6);
}
d(k,0) = dst(j,0) - u_estimate;
d(k+1,0) = dst(j,1) - v_estimate;
k += 2;
}
}
// 最小二乘求解畸变系数
disCoeff = GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->LeastSquares(D,d);
}
待续:
五:总结