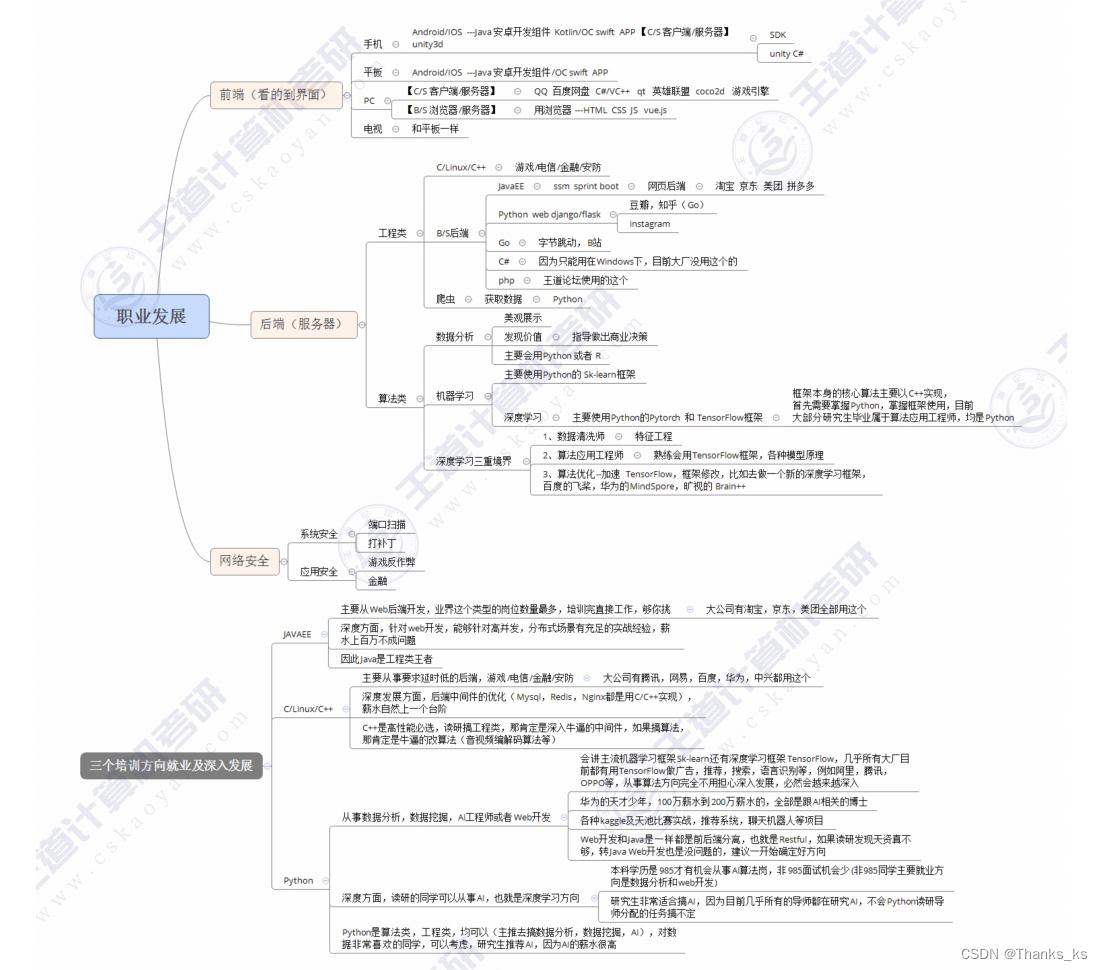
目录
- 实时同步是什么
- 定时同步的缺陷
- 实时同步简介
- Sersync简介
- rsync+inotify-tools与rsync+sersync架构的区别?
- SerSync工作流程
- SerSync同步架构
- Sersync配置详解
- 执行文件
- 配置文件
- NFS+Sersync+Rsync实时同步服务实验
- 0. 实验简介
- 1. 实验架构
- 2. 实验环境
- 3. 实验步骤
- front主机
- 1. 安装nfs-utils
- 2. 挂载目录
- storage主机
- 0. 测试rsync服务是否正常
- 1. 安装sersync服务
- 2. 安装nfs-utils和rpc-bind
- 3. 修改sersync配置文件
- 4. 启动sersync
- backup主机
- 1. 安装rsync服务
- 2. 创建并修改rsync配置文件
- 3. 创建密码文件
- 4. 创建备份目录并设置权限
- 5. 启动rsync服务
- 4. 实验测试
实时同步是什么
定时同步的缺陷
之前的文章我有写过远程同步Rsync——Linux下的Rsync简介,也做过Rsync的实验——Linux(openEuler22.03) 定时备份任务 解决方案。
尤其是实验文章,用到的实际是Rsync + Crontab的定时备份方式。
备份涉及到一个RPO和RTO的相关概念,简单来说,前者指的是灾难发生后能恢复到的数据点,后者指的是灾难发生后恢复服务的时间。
既然是定时备份,那么对于RPO,就有可能出现距离下一次备份前出现了灾难,但未备份导致的数据丢失。
实时同步可以很好的解决上面的问题。
实时同步简介
当然,备份是一个很复杂的工程,本文介绍的实时同步只是最简单的一种。
实时同步需要两部分:一是实时检测文件变化;二是变化发生后进行同步
常见的实时同步方式有:
- notify-tools: inotify 是 Linux 内核提供的一种机制,用于监视文件系统事件。inotify-tools 是一个用户空间的工具集,它利用 inotify 来监视文件系统的变化,并可以触发自定义的脚本或命令。
- lsyncd: lsyncd(Live Syncing Daemon)是一个轻量级的同步守护进程,它使用 inotify 来监视文件系统的变化,并将这些变化实时同步到远程服务器。
- Sersync:这是一个和lsync类似的服务,基于inotify开发的,类似于inotify-tools的工具。
本文采用的是实时同步是SerSync服务。
Sersync简介
Sersync是一个国人开发的同步工具,以二进制包的方式提供服务。
sersync是基于inotify开发的,类似于inotify-tools的工具。(但并不是inotify+rsync的解决方案)
sersync可以记录下被监听目录中发生变化的(包括增加、删除、修改)具体某一个文件或者某一个目录的名字,然后使用rsync同步的时候,只同步发生变化的文件或者目录。
Sersync是利用inotify和rsync两种软件技术来实现数据实时同步功能的。
- inotify是用于监听sersync所在服务器上的文件变化
- rsync软件来进行数据同步,将数据实时同步给客户端服务器
rsync+inotify-tools与rsync+sersync架构的区别?
-
rsync+inotify-tools
inotify只能记录下被监听的目录发生了变化(增,删,改)并没有把具体是哪个文件或者哪个目录发生了变化记录下来;
rsync在同步的时候,并不知道具体是哪个文件或目录发生了变化,每次都是对整个目录进行同步,当数据量很大时,整个目录同步非常耗时(rsync要对整个目录遍历查找对比文件),因此效率很低 -
rsync+sersync
sersync可以记录被监听目录中发生变化的(增,删,改)具体某个文件或目录的名字;
rsync在同步时,只同步发生变化的文件或目录(每次发生变化的数据相对整个同步目录数据来说很小,rsync在遍历查找对比文件时,速度很快),因此效率很高。
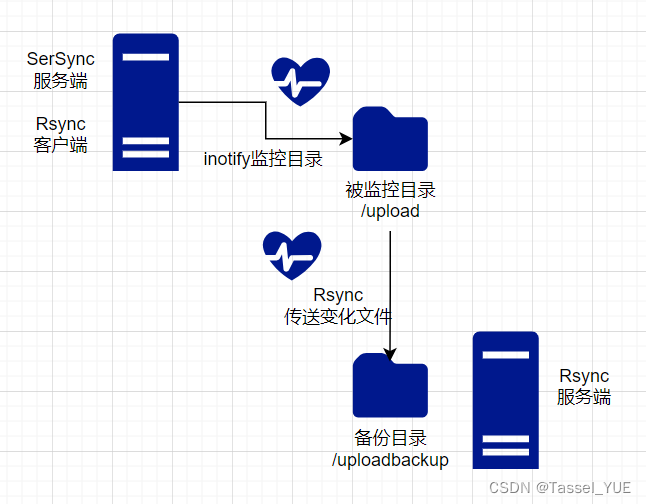
SerSync工作流程
- 通过inotify监控目录
- 通过rsync把变化文件同步
- 同步到rsync服务端
SerSync同步架构
在被监控目录的主机上安装Sersync服务
Sersync配置详解
https://github.com/wsgzao/sersync
执行文件
可以直接通过命令 -h查看命令的选项
/opt/sersync/bin/sersync2 -h
set the system param
execute:echo 50000000 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
execute:echo 327679 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
parse the command param
_______________________________________________________
参数-d:启用守护进程模式
参数-r:在监控前,将监控目录与远程主机用rsync命令推送一遍
c参数-n: 指定开启守护线程的数量,默认为10个
参数-o:指定配置文件,默认使用confxml.xml文件
参数-m:单独启用其他模块,使用 -m refreshCDN 开启刷新CDN模块
参数-m:单独启用其他模块,使用 -m socket 开启socket模块
参数-m:单独启用其他模块,使用 -m http 开启http模块
不加-m参数,则默认执行同步程序
________________________________________________________________
一般来说,常用的参数为rdo,要注意o放在最后面用于指定配置文件
配置文件
一般来说只要修改其中五条。
1.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<head version="2.5">
<host hostip="localhost" port="8008"></host>
<debug start="true"/>
<fileSystem xfs="false"/>
<filter start="false">
<exclude expression="(.*)\.php"></exclude>
<exclude expression="^data/*"></exclude>
</filter>
<inotify>
<delete start="true"/>
<createFolder start="true"/>
<createFile start="false"/>
<closeWrite start="true"/>
<moveFrom start="true"/>
<moveTo start="true"/>
<attrib start="false"/>
<modify start="false"/>
</inotify>
<sersync>
<!-- 这里填写服务器A要同步的文件夹路径-->
<localpath watch="/home/">
<!-- 这里填写服务器B的IP地址和模块名-->
<remote ip="8.8.8.8" name="rsync"/>
<!--<remote ip="192.168.28.39" name="tongbu"/>-->
<!--<remote ip="192.168.28.40" name="tongbu"/>-->
</localpath>
<rsync>
<!-- rsync选项 这里填写rsync命令使用的选项,一般az即可-->
<commonParams params="-artuz"/>
<!-- rsync+密码文件 这里填写服务器B的认证信息-->
<auth start="true" users="rsync" passwordfile="/app/local/sersync/user.pass"/>
<userDefinedPort start="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 -->
<timeout start="false" time="100"/><!-- timeout=100 -->
<ssh start="false"/>
</rsync>
<!-- 修改失败日志记录(可选)-->
<failLog path="/tmp/rsync_fail_log.sh" timeToExecute="60"/><!--default every 60mins execute once-->
<crontab start="false" schedule="600"><!--600mins-->
<crontabfilter start="false">
<exclude expression="*.php"></exclude>
<exclude expression="info/*"></exclude>
</crontabfilter>
</crontab>
<plugin start="false" name="command"/>
</sersync>
<!-- 下面这些有关于插件你可以忽略了 -->
<plugin name="command">
<param prefix="/bin/sh" suffix="" ignoreError="true"/> <!--prefix /opt/tongbu/mmm.sh suffix-->
<filter start="false">
<include expression="(.*)\.php"/>
<include expression="(.*)\.sh"/>
</filter>
</plugin>
<plugin name="socket">
<localpath watch="/home/demo">
<deshost ip="210.36.158.xxx" port="8009"/>
</localpath>
</plugin>
<plugin name="refreshCDN">
<localpath watch="/data0/htdocs/cdn.markdream.com/site/">
<cdninfo domainname="cdn.chinacache.com" port="80" username="xxxx" passwd="xxxx"/>
<sendurl base="http://cdn.markdream.com/cms"/>
<regexurl regex="false" match="cdn.markdream.com/site([/a-zA-Z0-9]*).cdn.markdream.com/images"/>
</localpath>
</plugin>
</head>
具体的配置文件解释可以看:
https://www.cnblogs.com/bill2014/p/7417077.html
NFS+Sersync+Rsync实时同步服务实验
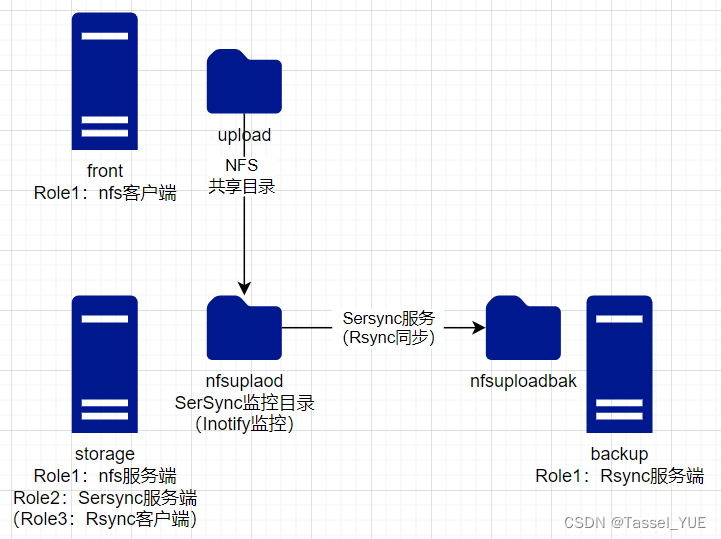
0. 实验简介
本实验是模拟front主机挂载nfs共享目录,在storage主机上通过sersync监控与实时同步nfs共享目录,同步目的地为backup主机。
1. 实验架构
2. 实验环境
宿主机: Win11
Server1-front:CentOS8
Server2-storage:CentOS8
Server3-backup:CentOS8
均一张网卡,同一网段
3. 实验步骤
配置顺序:backup主机->storage主机->front主机
front主机
1. 安装nfs-utils
#安装nfs-utils
yum install -y nfs-utils
2. 挂载目录
mkdir -p /upload
#测试
mount -t nfs 192.168.100.150:/nfsupload /upload
storage主机
0. 测试rsync服务是否正常
#rsync客户端密码文件配置,可以不配置
echo "backupuser" > /etc/rsyncpwd
chmod 600 rsyncpwd
#安装rsync,若没有需要安装
yum install -y rsync
#测试
rsync -avz /etc/hostname backupuser@192.168.100.149::nfsuploadbak --password-file=rsyncpwd
sending incremental file list
hostname
sent 99 bytes received 35 bytes 268.00 bytes/sec
total size is 8 speedup is 0.06
1. 安装sersync服务
# 这是一个国人开发的服务,以二进制包的方式提供服务
wget --no-check-certificate https://raw.githubusercontent.com/orangle/sersync/master/release/sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz
tar -zxvf sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz
cp -r /root/GNU-Linux-x86/ /opt/sersync/
#最终设计后的目录位置,bin放执行文件,conf放配置文件
tree
/opt/sersync
├── bin
│ └── sersync2
└── conf
└── confxml.xml
原连接:https://code.google.com/archive/p/sersync/
github镜像:https://github.com/orangle/sersync
2. 安装nfs-utils和rpc-bind
#安装
yum install -y nfs-utils rpc-bind
#启动rpc服务
systemctl enable rpcbind --now
#创建目录
mkdir -p /nfsupload
chown -R nobody.nobody /nfsupload/
#编写/etc/exports并启动服务
echo "/nfsupload 192.168.100.0/24(rw)" >> /etc/exports
systemctl start nfs-server #centos8 启动nfs服务端命令
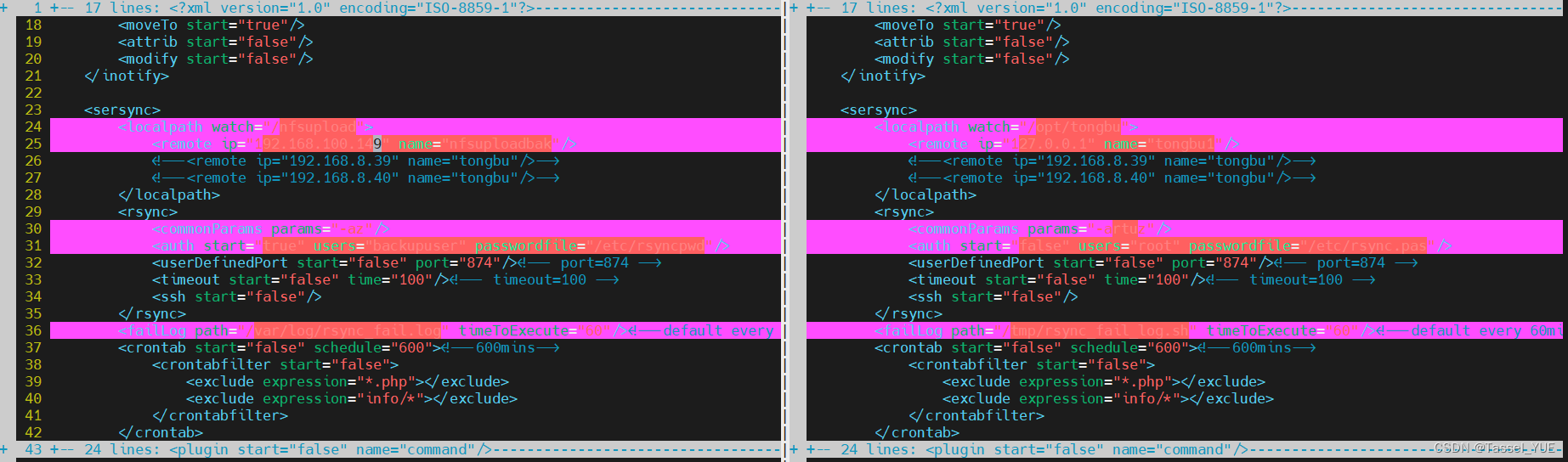
3. 修改sersync配置文件
vim conf/conf.xml
#修改为本机(storage主机)需要监控的目录
24 <localpath watch="/nfsupload">
#修改为rsync服务端(backup主机)的ip和对应的备份目录名
25 <remote ip="192.168.100.149" name="nfsuploadbak"/>
#修改需要的rsync参数
30 <commonParams params="-az"/>
# 修改认证方式为true,user为服务端设置的,密码文件目录对应修改
31 <auth start="true" users="backupuser" passwordfile="/etc/rsyncpwd"/>
# 修改错误日志存放位置
36 <failLog path="/var/log/rsync_fail.log" timeToExecute="60"/><!--default every 60min s execute once-->
4. 启动sersync
#启动服务
/opt/sersync/bin/sersync2 -rdo /opt/sersync/conf/confxml.xml
#查看进程号
ps -ef | grep sersync
root 13907 1 0 23:47 ? 00:00:00 /opt/sersync/bin/sersync2 -rdo /opt/sersync/conf/confxml.xml
backup主机
1. 安装rsync服务
yum install -y rsync
2. 创建并修改rsync配置文件
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
# 全局配置
fake super = yes
uid = rsync
gid = rsync
use chroot = no
max connections = 4
ignore errors
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
lock file = /var/run/rsyncd.lock
# 模块配置
[nfsuploadbak]
path = /nfsuploadbak
comment = NFS Backup Directory
read only = no
list = yes
auth users = backupuser
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd.secrets
3. 创建密码文件
echo "backupuser:backupuser" >> /etc/rsyncd.secrets
4. 创建备份目录并设置权限
useradd -s /sbin/nologin -M rsync
mkdir -p /nfsuploadbak
chown rsync.rsync /nfsuploadbak/
chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.secrets
5. 启动rsync服务
systemctl enable rsyncd --now
systemctl restart rsyncd
Centos8 yum安装rsync没有rsyncd服务解决方案:
https://blog.csdn.net/Tassel_YUE/article/details/139131074
4. 实验测试
在front主机上创建文件,在storage和backup主机上使用watch持续查看命令查看目录变化情况
# front
[root@front ~]# ll /upload/
total 0
[root@front ~]# touch /upload/hello{1..10}.txt
[root@front ~]# ll /upload/
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello10.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello1.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello3.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello4.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello5.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello6.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello7.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello8.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello9.txt
# storage
[root@storage sersync]# watch ls -l /nfsupload/
Every 2.0s: ls -l /nfsupload/ storage: Wed May 22 23:55:36 2024
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello10.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello1.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello3.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello4.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello5.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello6.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello7.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello8.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nobody nobody 0 May 22 23:54 hello9.txt
# backup
[root@backup ~]# watch ls -l /nfsuploadbak/
Every 2.0s: ls -l /nfsuploadbak/ backup: Wed May 22 23:57:37 2024
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello10.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello1.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello3.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello4.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello5.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello6.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello7.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello8.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsync rsync 0 May 22 23:54 hello9.txt

![[数组查找]2.图解二分查找及其代码实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5def84a21d1243c59e98e9e927668726.png)