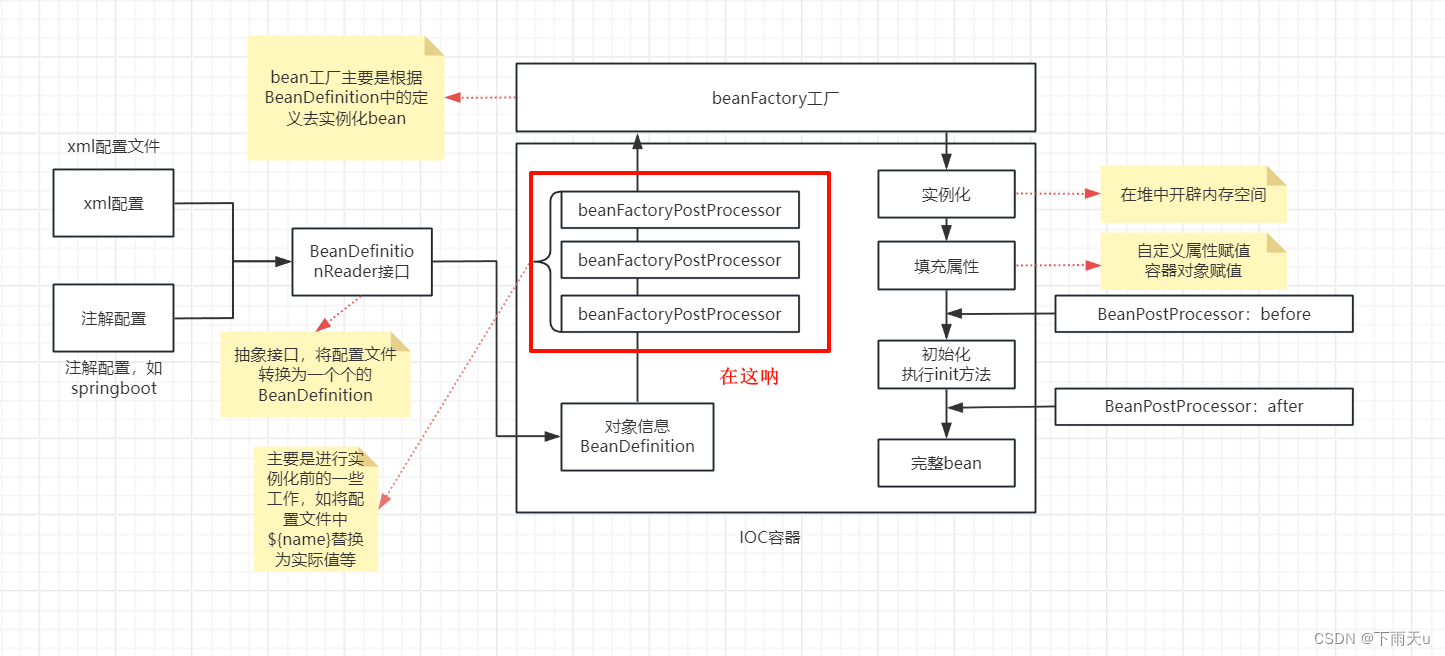
介绍
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是spring中一个很重要的接口,位于spring流程中的获取BeanDefinition之后,实例化之前(点击spring流程),我们可以实现该接口并注入spring容器中进行拓展(对BeanDefinition进行自定义修改),我们知道容器中的Bean都是根据BeanDefinition信息去是实例化的,BeanDefinition中存储了bean的信息,我们这儿可以修改BeanDefinition,所以相当于修改bean。
spring官方解释
解释
修改 Bean 定义:
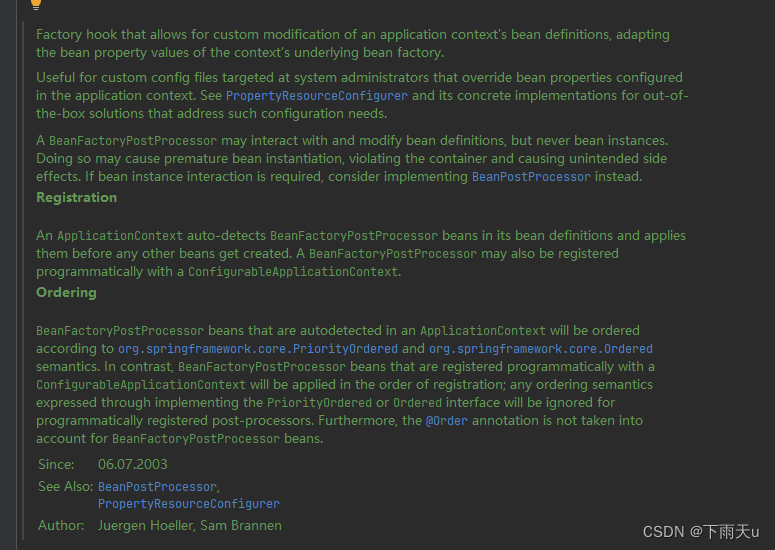
允许在 Bean 实例化之前自定义修改应用上下文中的 Bean 定义,适用于系统管理员通过自定义配置文件覆盖 Bean 属性配置。
配置文件支持:
支持使用 PropertyResourceConfigurer 等解决方案处理配置文件中的 Bean 属性覆盖需求。
操作限制:
只能与 Bean 定义交互,不能与 Bean 实例交互,以避免 Bean 过早实例化和意外副作用。如果需要与 Bean 实例交互,应使用 BeanPostProcessor。
自动检测与注册:
ApplicationContext 会自动检测并应用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
也可以通过 ConfigurableApplicationContext 编程方式注册。
排序机制:
-
自动检测的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 会根据 PriorityOrdered 和 Ordered 接口排序。
自动检测是指 ApplicationContext 在启动时会自动检测其 Bean 定义中是否存在 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的实现类。 -
编程注册的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 按注册顺序应用,忽略排序接口和 @Order 注解。
编程注册是指通过编码的方式在应用程序启动时显式地向 ApplicationContext 注册 BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
源码
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
*获取到beanFactory之后可获取所有BeanDefinition,可以对BeanDefinition进行更改
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
例子
光描述起来可能有点苍白无力,其实我们也见过,比如我们配置数据库是写的${jdbc.userName}就是实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口去替换的,我这儿也写个类似的功能,看一下代码。
package com.lp.entity;
public class Student {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.lp;
public class Constants {
public static String userName = "root";
}
package com.lp;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.TypedStringValue;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
@Component
public class TestBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
String[] beanDefinitionNames = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanDefinitionName);
MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValues.getPropertyValues()) {
Object value = propertyValue.getValue();
if (value != null && value instanceof TypedStringValue){
String input = ((TypedStringValue) value).getValue();
String regex = "\\^\\{([^}]*)\\}";
// 编译正则表达式
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(input);
// 查找匹配项并提取捕获组
if (matcher.find()) {
String extracted = matcher.group(1); // 捕获组1的内容
// 获取 Constants 类的所有字段
Field[] fields = Constants.class.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (field.getName().equals(extracted)){
Object object = null;
try {
object = field.get(null);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
propertyValues.addPropertyValue(propertyValue.getName(), object);
break;
}else {
propertyValues.addPropertyValue(propertyValue.getName(), "");
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lp"/>
<bean id="student" class="com.lp.entity.Student">
<property name="name" value="^{userName}"/>
</bean>
</beans>
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Student student = (Student)context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("-----------"+student.getName());
}
}

简单说一下,我有个Student类,有name属性,我配置的name=^{userName},我的匹配规则就是当匹配到的时候就把userName拿出来匹配常量的属性,如果匹配上就将属性值给name,这儿注意的就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor 执行时机,操作BeanDefinition就完成,如果了解spring流程这个功能就变为异常简单了。