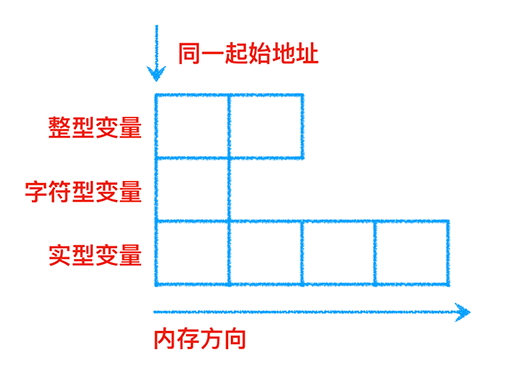
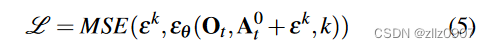Spirng Bean 元信息配置阶段
1 面向资源
- xml配置(很熟悉了不做讨论)
- Properties配置
public class BeanMetaDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader reader = new PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("/meta-info/person.properties");
// 解决乱码的问题
EncodedResource encodedResource = new EncodedResource(resource, "UTF-8");
int i = reader.loadBeanDefinitions(encodedResource);
Object person = factory.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
}
person.(class)=pojo.Person
person.id=10010
person.name=李勇
2 面向注解
3 面向API
Bean 元信息解析
1 面向资源BeanDefiniton 解析
- BeanDefinitonReader
- xml 解析器 BeanDefinitionParser
2 面向注解BeanDefiniton - AnnotatedBeanDefinitonReader
// 基于注解的APIBean注册
public class AnnotatedBeanDefinitionParsingDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
int beforeCount = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionCount();
reader.register(AnnotatedBeanDefinitionParsingDemo.class);
int afterCount = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionCount();
System.out.println(afterCount - beforeCount);
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionParsingDemo bean = beanFactory.getBean(AnnotatedBeanDefinitionParsingDemo.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
Bean注册阶段
BeanDefinitionregistery
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
// 线程安全
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
// 保证顺序
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}
BeanDefinition 合并阶段
BeanDefinition#getParentName
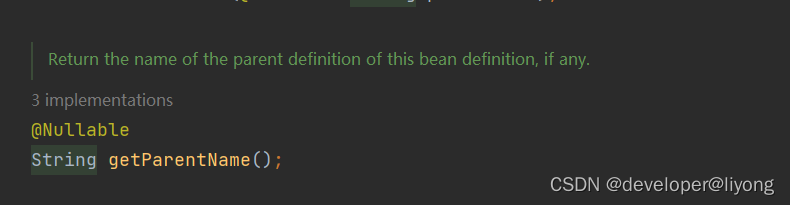
在xml里面是通过这个属性来配置的,所以需要classloader的参与:

在注解其实本身就包含了继承关系,可以直接拿到父类信息。
1 没有父类了已经RootBeanDefinition 不需要合并
2 普通的BeanDefinition为GenericBeanDefinition需要合并
合并过程中GenericBeanDefinition->RootBeanDefinition
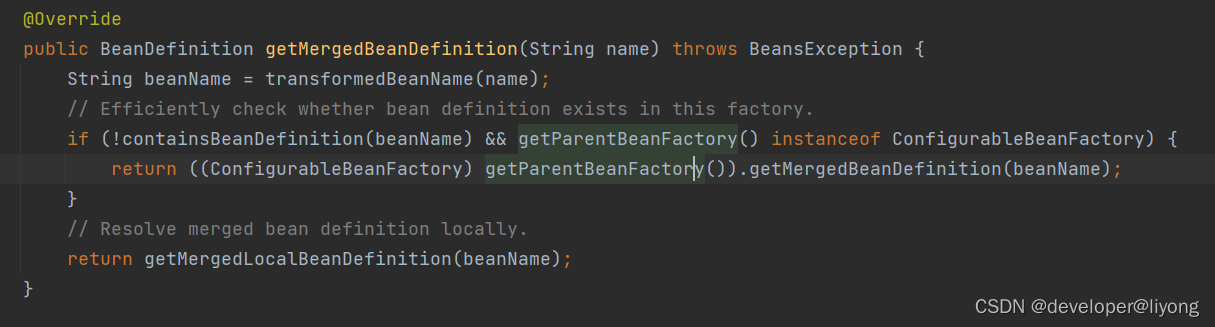
代码贴士:ConcurrentHashMap虽然是线程安全的但是只针对于单个操作,get和put,如果有多个get,put操作一起也不能保证是线程安全的。
Bean Class 加载
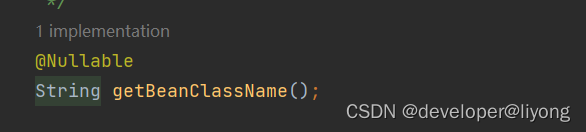
这里返回的是一个文本BeanDefinition#getBeanClassName
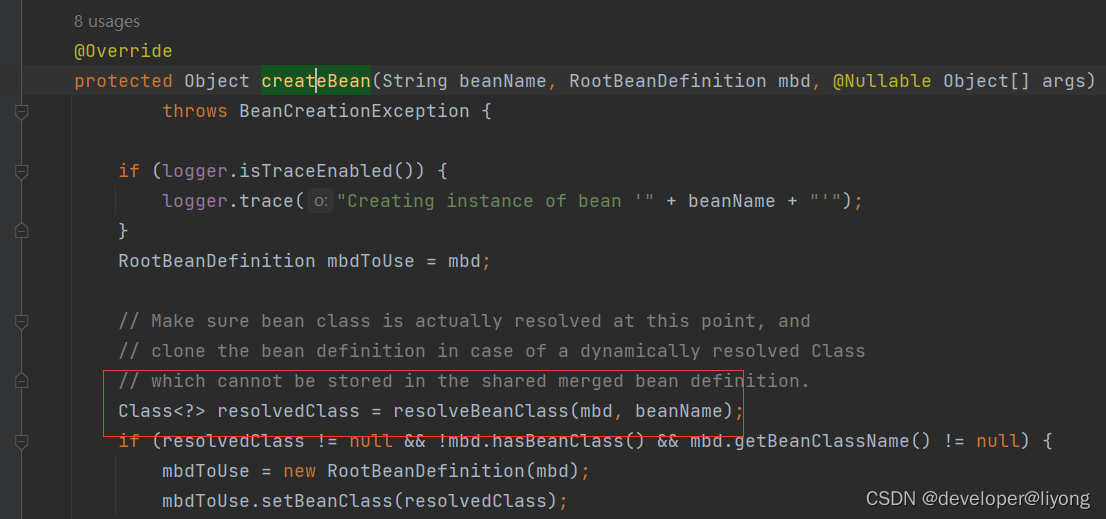
 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#resolveBeanClass
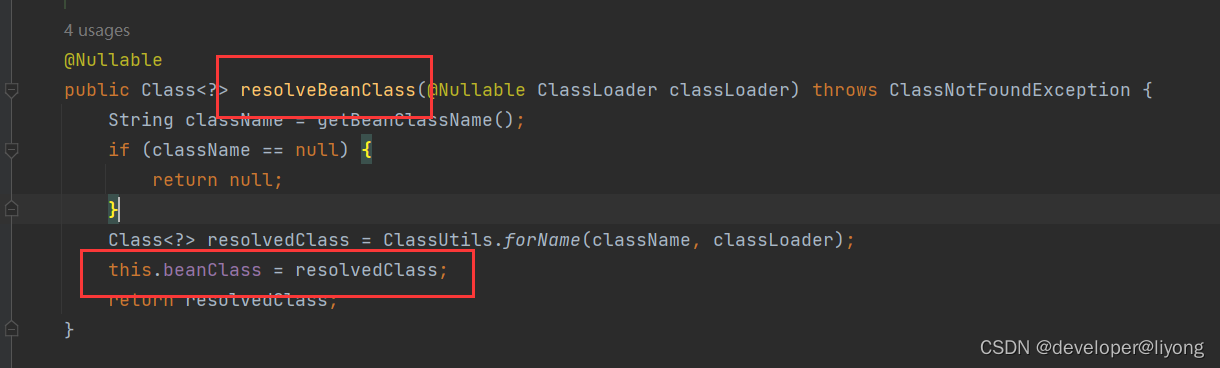
this.beanClass 之前是字符串类型,在处理完毕以后是Class类型。
Bean实例化前阶段
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
通常用于替换之前的实现类,绕开Spring的实例化。
public class BeanInstantiationLifeCycleDemo {
@Bean
public Person person() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("liyong");
person.setId(11L);
return person;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(BeanInstantiationLifeCycleDemo.class);
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new MyPostProcessBeforeInstantiation());
context.refresh();
Object person = context.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
static class MyPostProcessBeforeInstantiation implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 实例化之前执行 如果说满足条件直接替换之前的实现
if (ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals("person", beanName) && Person.class.equals(beanClass)) {
Person person = new Person();
person.setId(11L);
person.setName("person");
return person;
}
return null;
}
}
}
在这里我们返回了我们创建的对象,所以后面的操作不再进行了:
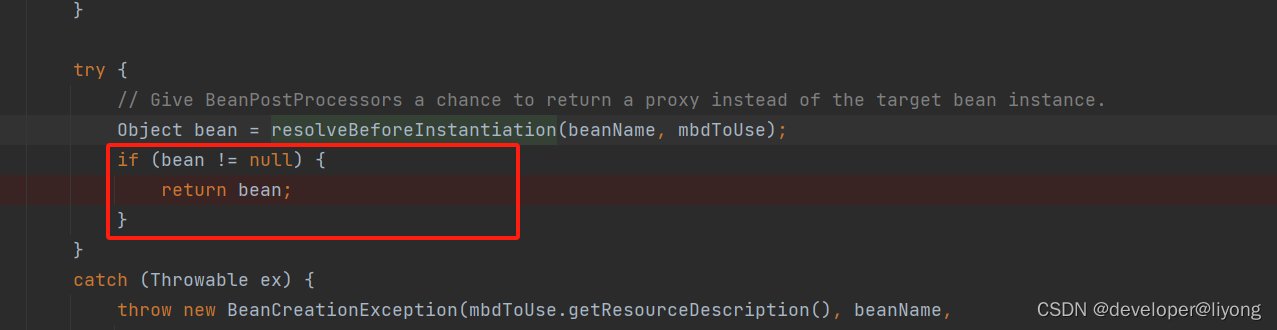
Spring Bean 实例化阶段
实例化方式
- 传统方式
- 实例化策略InstantitaionStrategy
构造器依赖注入
InstantitaionStrategy有两种实现方法
1 传统的实现方法
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance
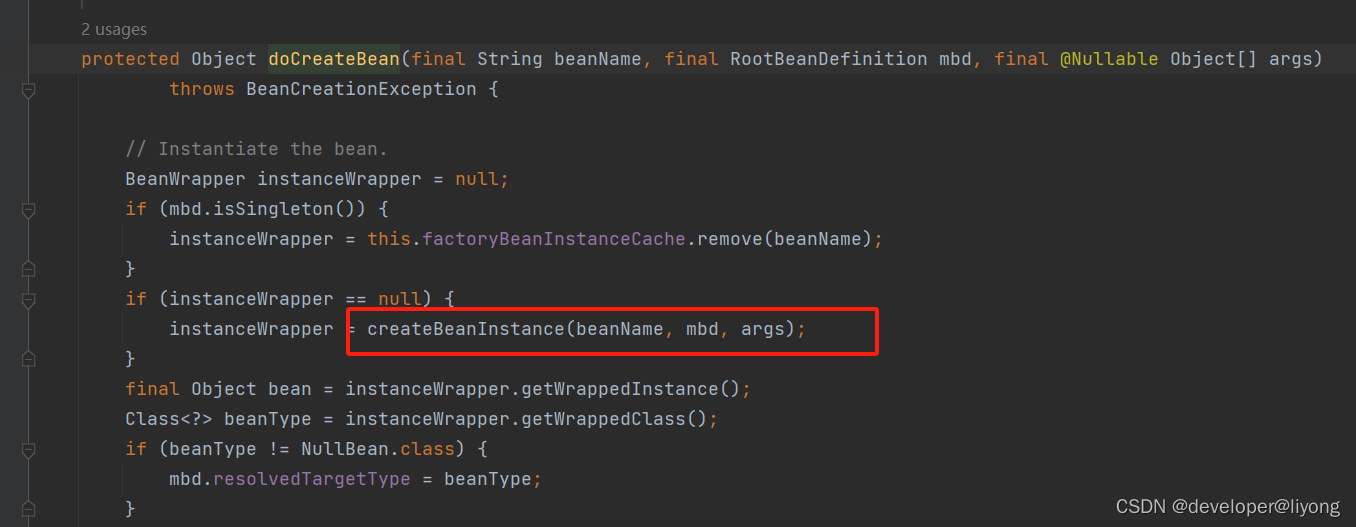
2 特殊的实现方法
Spring Bean 实例化后阶段
这里控制了对象实例化以后是否对属性进行赋值:
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 这里就可以注入我们自己的值,这里和前面before的区别就是 这里我们对象已经被创建了,我们是在已经创建好的对象给它改变属性值
if (ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals("person", beanName) && Person.class.equals(bean.getClass())) {
Person person = (Person) bean;
person.setId(11L);
person.setName("person");
return false;
}
return true;
}
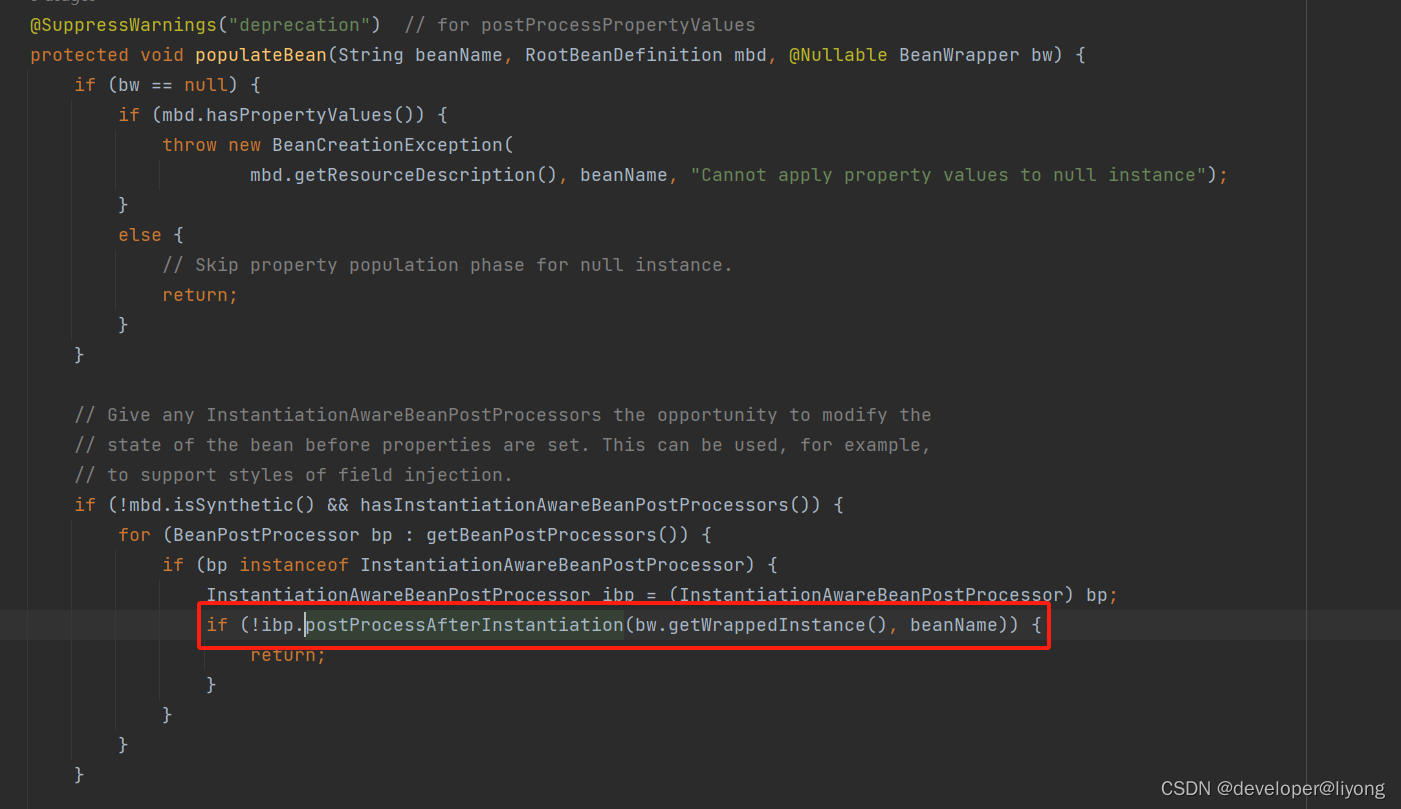
在这里我们返回了false,所以后面操作不会执行了,而后面的操作也就是赋值属性。
Spring Bean 属性赋值前阶段
Bean 属性值元信息
- PropertyValues
Bean属性值前回调
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues 注意到在高版本的Spring 这个方法已经被打上了过时的标签
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties (5.1及以后)
如果我们希望拦截属性赋值操作
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 这里就可以注入我们自己的值 需要注意如果我们postProcessAfterInstantiation 已经返回了false这里就不会执行
if (ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals("person", beanName) && Person.class.equals(bean.getClass())) {
MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = new MutablePropertyValues();
propertyValues.add("number", "1111");
return propertyValues;
}
return pvs;
}
Spring 生命周期 Aware 接口的顺序
其实顺序就是下面这个顺序:

我们可以看到源码中的调用顺序:
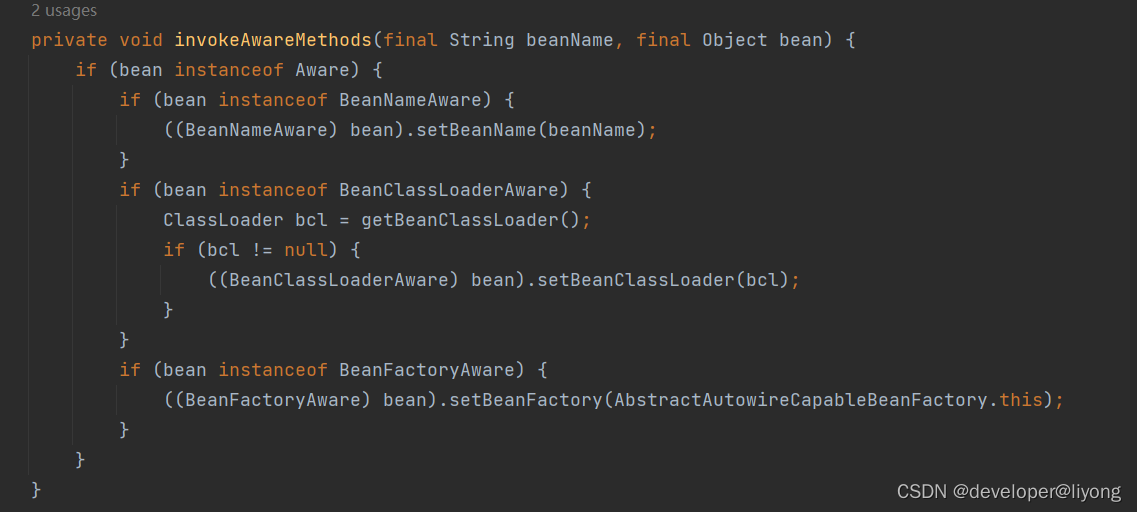
EnvironmentAware 以及后面的接口都是属于ApplicationContext的生命周期,普通的BeanFactory 并不会回调这些Aware接口,在操作ApplicationContext的时候才会回调这些接口,因为在ApplicationContext初始化阶段,会添加一个AwarePostProcessor但是这个类是内置类,所以只有与ApplicationContext打交道才会有更多的Aware接口方法回调。
SpirngBean初始化 前阶段
在前面的讨论,已经完成了以下工作,这些工作也是属于前阶段

InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
}
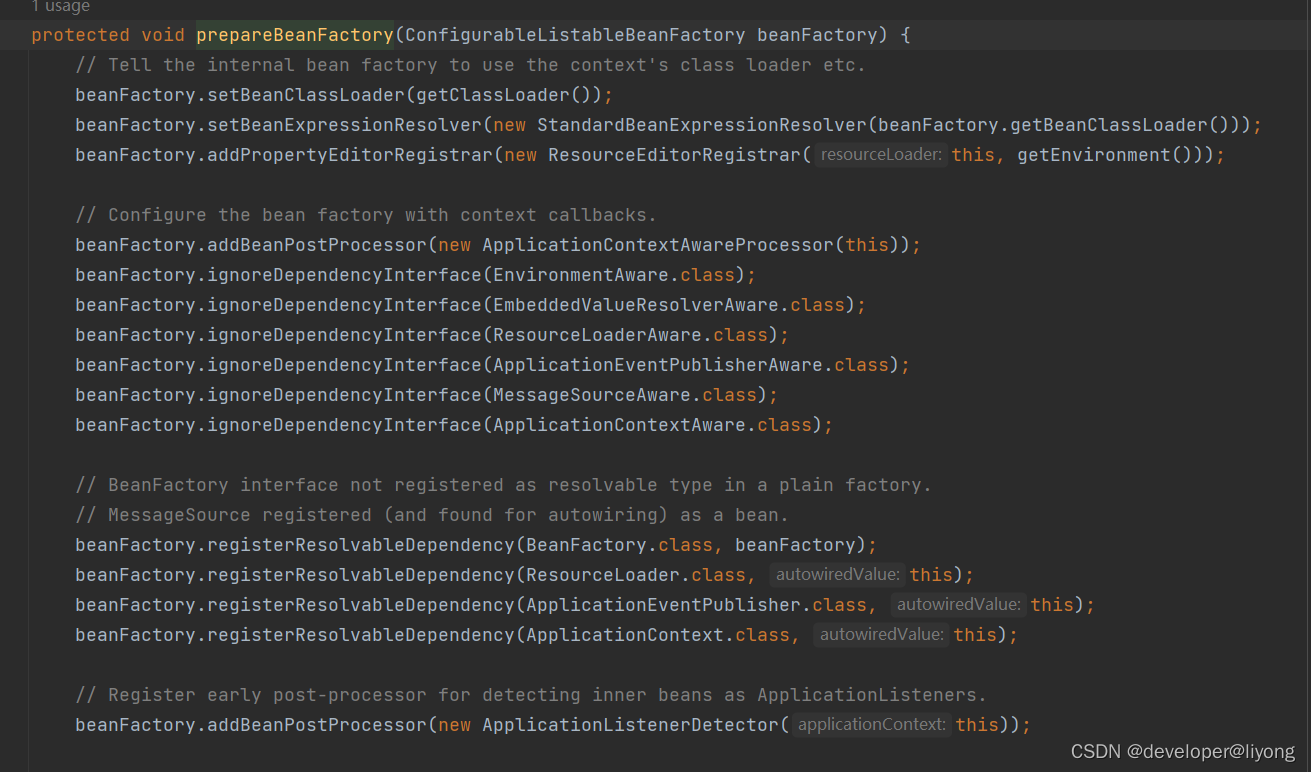
源码是在这里进行应用的:
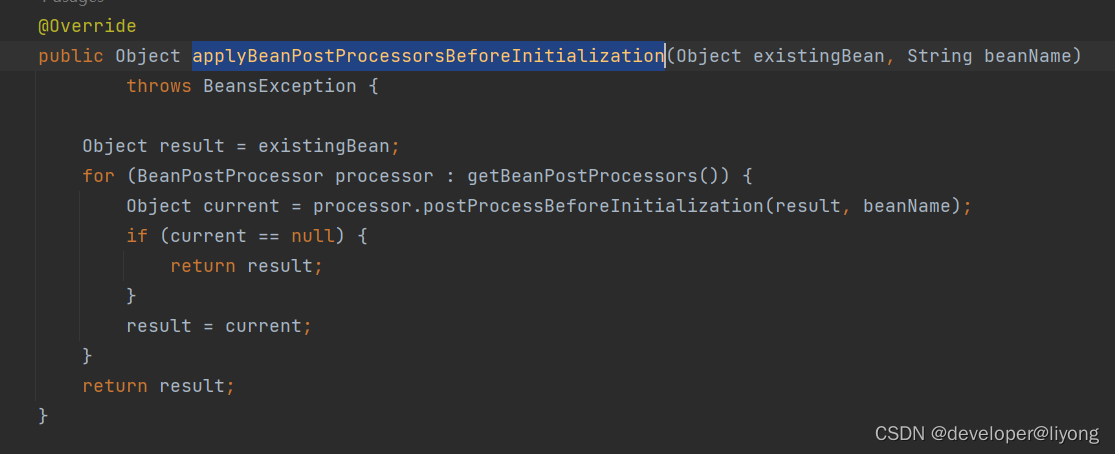
AbstractApplicationContext#prepareBeanFactory
SpringBean 初始化阶段
他们的执行顺序就是下面的执行顺序

@PostConstruct 是依赖于注解驱动的,如果通过xml的方式是不会触发的,因为没有对应的PostProcessor。如果我们需要这个生效
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new CommonAnnotationPostProcessor());
自定义方法是通过xml init-method来进行配置。
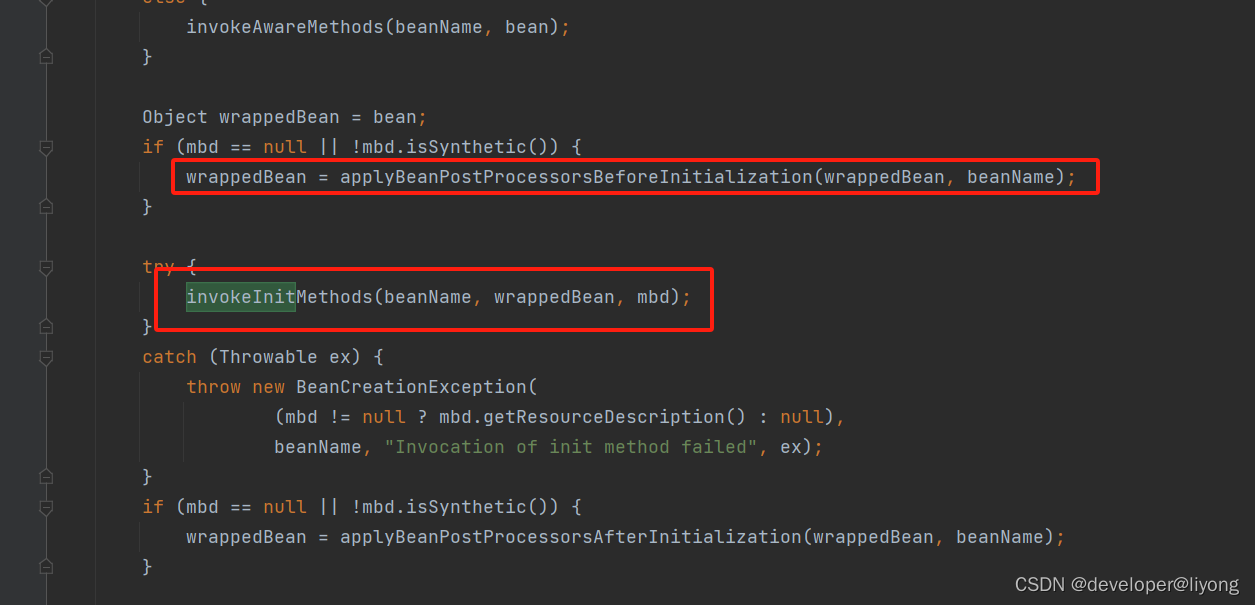
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean
实际上PostConstruct是在这个方法applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization进行触发的
初始化后阶段
BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
初始化完成阶段
通过下面这个接口来实现
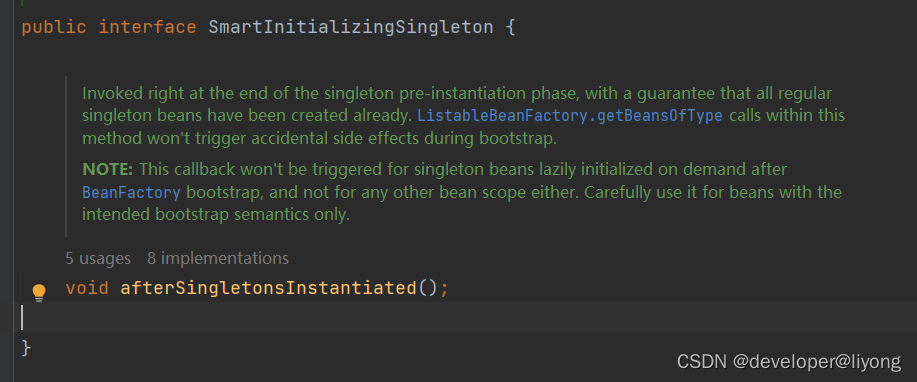
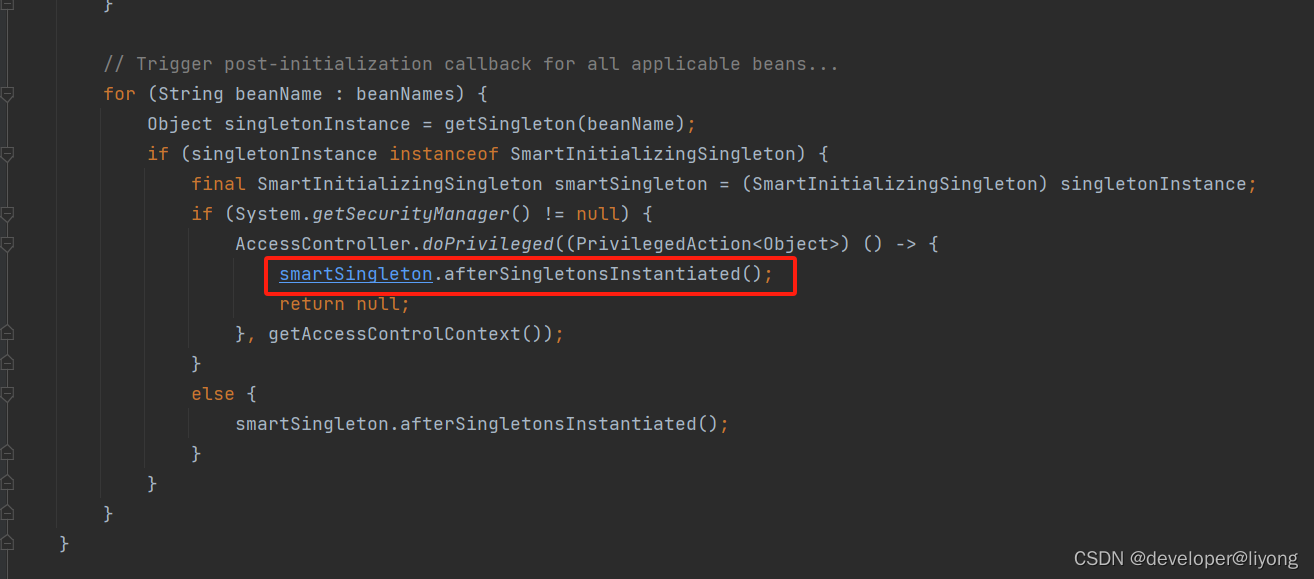
preInstantiateSingletons在这个方法里面被调用,他通常需要在ApplicationContext来进行使用,需要显式的调用。确保Bean已经被完全初始化。
Spring Bean销毁阶段

DisposableBeanAdapter#destroy()
销毁前:
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
@Override
public void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
}
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new MyDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor());
// 这个销毁是在容器中销毁 而不是在Java 中销毁
beanFactory.destoryBean("person", person);
Spring销毁阶段
有这样几种方式

Spirng Bean垃圾回收