目录
堆的性质:
堆的实现
堆向下调整算法
堆的创建
堆的插入
堆的删除
堆的应用
堆排序
对比冒泡的优势:
代码
头文件
源文件
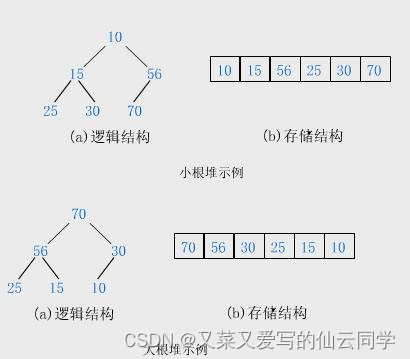
如果有一个关键码的集合K = { , , ,…, },把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储 在一个一维数组中,并满足: 且 = 且 >= ) i = 0,1, 2…,则称为小堆(或大堆)。将根结点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根结点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
堆的性质:
堆中某个结点的值总是不大于或不小于其父结点的值; 堆总是一棵完全二叉树。
堆的实现
堆向下调整算法
现在我们给出一个数组,逻辑上看做一颗完全二叉树。我们通过从根结点开始的向下调整算法可以把它调整 成一个小堆。向下调整算法有一个前提:左右子树必须是一个堆,才能调整。
int array[] = {27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37};

堆的创建
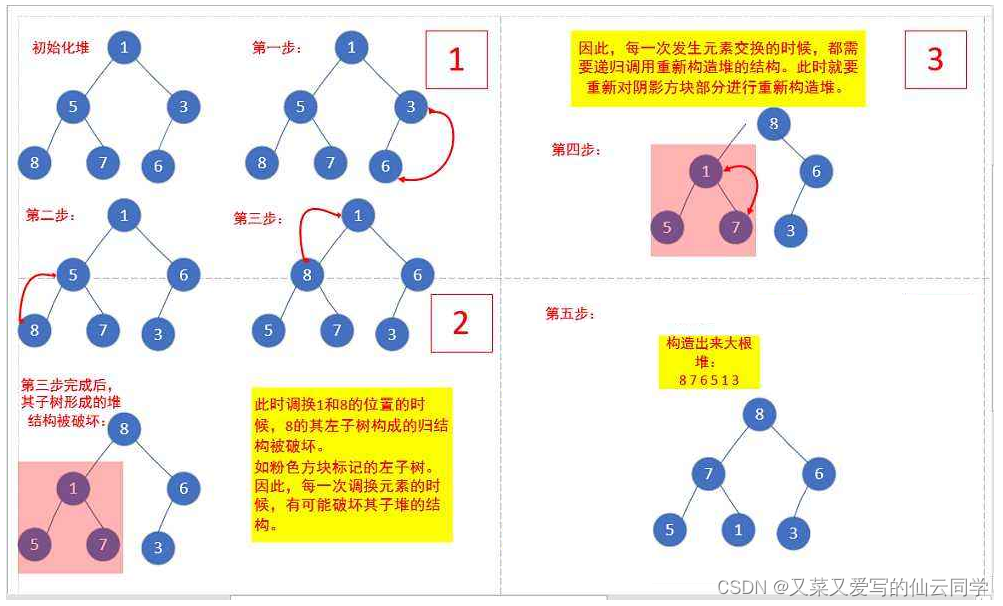
下面我们给出一个数组,这个数组逻辑上可以看做一颗完全二叉树,但是还不是一个堆,现在我们通过算 法,把它构建成一个堆。根结点左右子树不是堆,我们怎么调整呢?这里我们从倒数的第一个非叶子结点的 子树开始调整,一直调整到根结点的树,就可以调整成堆。
int a[] = {1,5,3,8,7,6};
堆的插入
先插入一个10到数组的尾上,再进行向上调整算法,直到满足堆。

堆的删除
删除堆是删除堆顶的数据,将堆顶的数据根最后一个数据一换,然后删除数组最后一个数据,再进行向下调 整算法。

堆的应用
堆排序
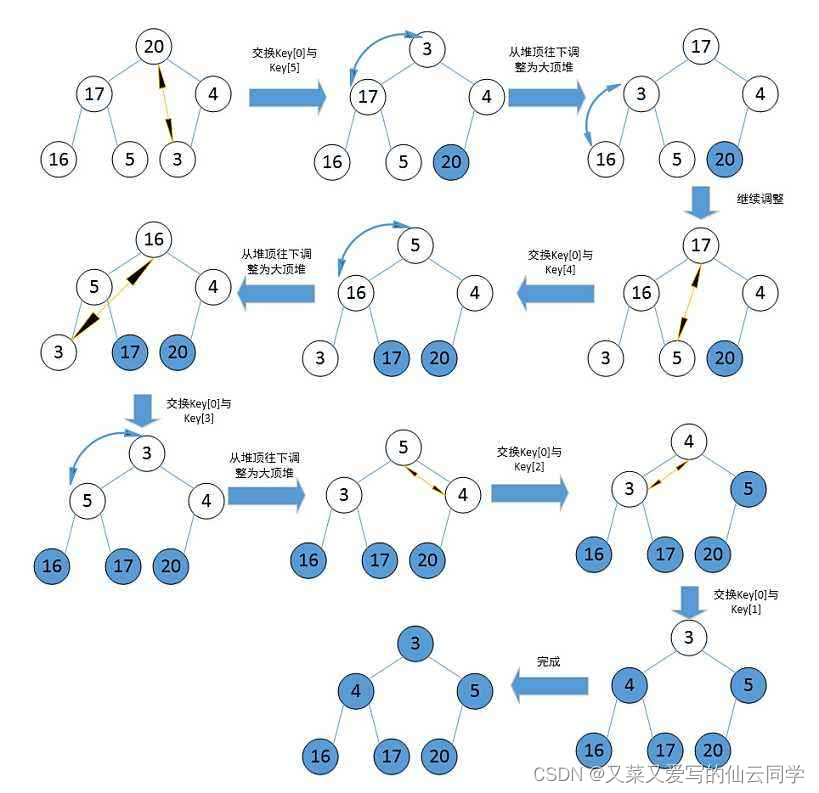
堆排序即利用堆的思想来进行排序,总共分为两个步骤:
1. 建堆
升序:建大堆
降序:建小堆
2. 利用堆删除思想来进行排序
建堆和堆删除中都用到了向下调整,因此掌握了向下调整,就可以完成堆排序。
对比冒泡的优势:
堆排序时间复杂度为nlogn
而冒泡则为n^2,效率大大提高
代码
头文件
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int HPDataType; //大根堆
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* _a;
int _size;
int _capacity;
}Heap;
void HeapInit(Heap* php);
// 堆的销毁
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp);
// 堆的插入
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x);
// 堆的删除
void HeapPop(Heap* hp);
// 取堆顶的数据
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp);
// 堆的数据个数
int HeapSize(Heap* hp);
// 堆的判空
int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp);
//堆排序1(向上与向下堆)
void HeapSort1(int* a, int n);
//堆排序2(纯向下)
void HeapSort2(int* a, int n);源文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"heap.h"
void HeapInit(Heap* php) {
assert(php);
php->_a = NULL;
php->_capacity = php->_size = 0;
}
void extendcapacity(Heap* php){
assert(php);
HPDataType* mn;
if (php->_capacity == 0) {
mn = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * 4);
php->_capacity = 4;
php->_a = mn;
return;
}
else {
mn = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->_a,sizeof(HPDataType) * (2*php->_capacity));
php->_capacity *= 2;
php->_a = mn;
return;
}
}
void HeapDestory(Heap* hp) {
free(hp->_a);
hp->_a = NULL;
hp->_capacity = hp->_size = 0;
}
void swap(HPDataType* a, HPDataType* b) {
int tmp;
tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
void adjustup(HPDataType* x, HPDataType now) {
int parent = (now - 1) / 2, child = now;
while (child > 0) {
if (x[child] > x[parent]) {
swap(&x[child], &x[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
break;
}
}
void HeapPush(Heap* hp, HPDataType x) {
assert(hp);
if (hp->_capacity == hp->_size)
extendcapacity(hp);
hp->_a[hp->_size] = x;
adjustup(hp->_a,hp->_size);
hp->_size++;
}
void adjustdown(HPDataType* x, HPDataType size) {
int parent=0, child=1;
while (child < size) {
if (x[parent * 2 + 2] > x[child])
child = parent * 2 + 2;
if (x[child] > x[parent]) {
swap(&x[child], &x[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
break;
}
}
void HeapPop(Heap* hp) {
assert(hp);
hp->_a[0] = hp->_a[hp->_size - 1];
hp->_size--;
adjustdown(hp->_a, hp->_size);
}
HPDataType HeapTop(Heap* hp) {
return hp->_a[0];
}
int HeapSize(Heap* hp) {
return hp->_size;
}
int HeapEmpty(Heap* hp) {
return hp->_size == 0;
}
void HeapSort1(int* a, int n) { //由下往上使用向上堆
int i;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
adjustup(a, i);
for (i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
swap(&a[0], &a[i]);
adjustdown(a, i-1);
}
}
void HeapSort2(int* a, int n) { //由最后一个父节点往上使用向下堆
int i;
for (i =(n-2)/2; i > 1; i--)
adjustdown(a, i);
for (i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
swap(&a[0], &a[i]);
adjustdown(a, i - 1);
}
}