data模块
- overview布局
- \_\_init__.py
- from .base import BaseDataset
- \_\_all__
- annotator.py
- augment.py
- `class BaseTransform`
- `class Compose`
- `class BaseMixTransform`
- `class Mosaic`
- 静态方法更新label
- `class MixUp`
- `RandomPerspective`
- `class RandomHSV`
- `class RandomFlip`
- `class LetterBox`
- `class CopyPaste`
- `class Albumtation`
- `class Format `
- `class `
- `v8_transforms`
- `classify_transforms`
- `class ClassifyLetterBox`
- `class CenterCrop`
- `class ToTensor`
- base.py
- `class BaseDataset`
- bulid.py
- `class InfiniteDataLoader`
- `class _RepeatSampler`
- dataset.py
- `class YOLODataset`
- 未完待续
overview布局
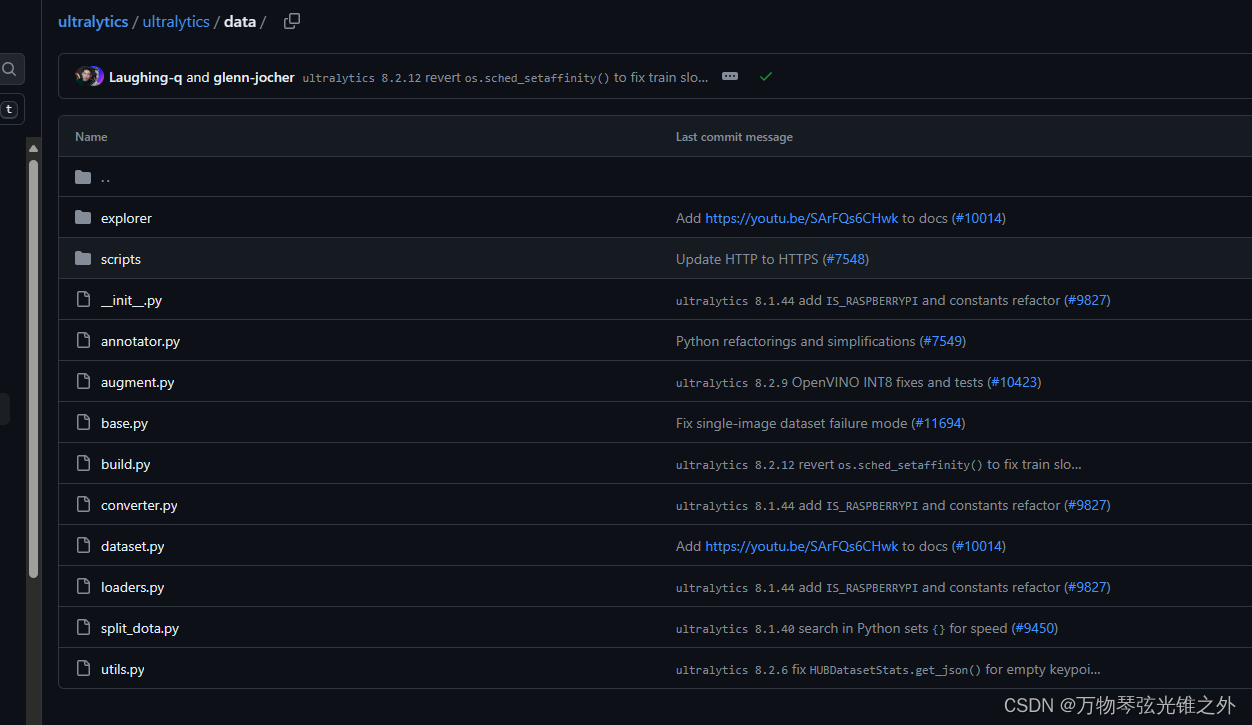
从上往下解析
__init__.py
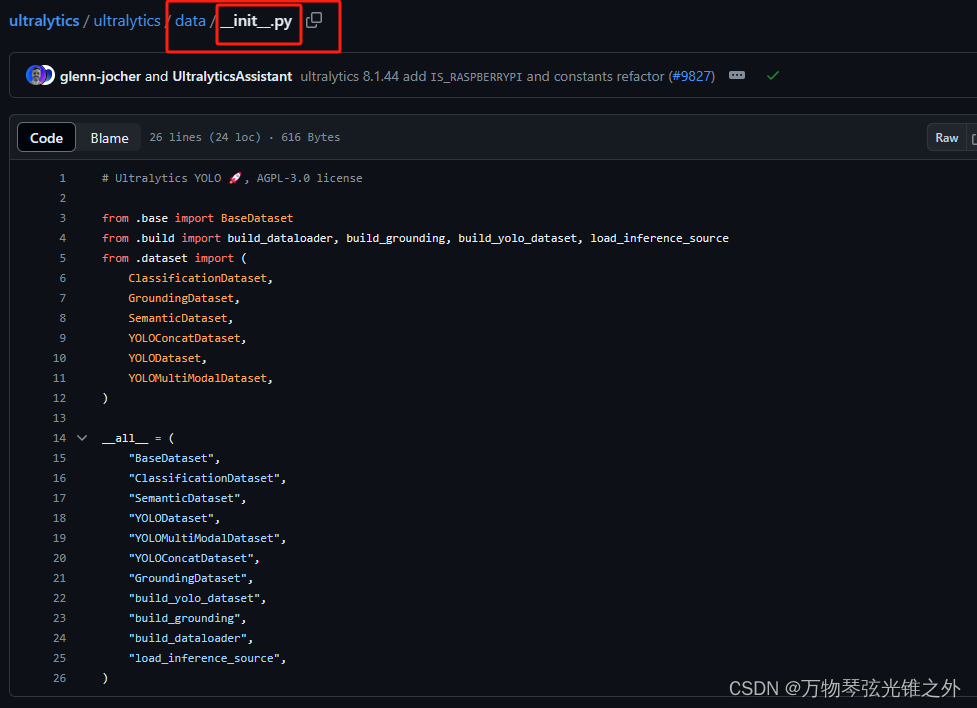
from .base import BaseDataset
__init__.py 文件在 Python 中扮演着重要的角色,它是 Python 包结构的一部分。
当一个目录包含 __init__.py 文件时,Python 会将这个目录视为一个包,允许你导入其中的模块和类。这个文件的目的是告诉 Python 解释器,目录内的内容是一个可导入的模块集合,也就是一个包。
在这个特定的例子中,__init__.py 文件是 ultralytics 库(假设是 ultralytics 包)的一部分,它导出了 base.py、build.py 和 dataset.py 中的一些关键类和函数。通过这种方式,用户可以直接从 ultralytics 包中导入这些导出的类和函数,而不需要知道它们在哪个具体的模块里。
例如,用户可以这样导入和使用这些类和函数:
from ultralytics import BaseDataset, YOLODataset, build_yolo_dataset
dataset = BaseDataset()
yolo_dataset = YOLODataset()
dataloader = build_yolo_dataset(dataset)
这种组织方式提高了代码的可读性和可维护性,因为用户只需要记住在包级别上可用的接口,而不是每个单独模块的细节。同时,__init__.py 也可以用来执行一些初始化逻辑,比如设置配置、注册自定义类型等。
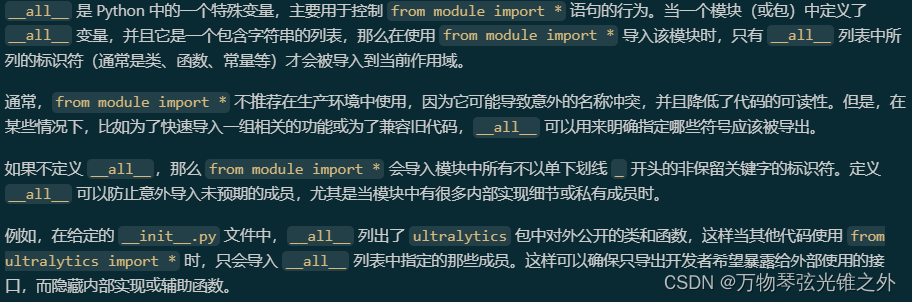
__all__
annotator.py
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
from pathlib import Path
from ultralytics import SAM, YOLO
def auto_annotate(data, det_model="yolov8x.pt", sam_model="sam_b.pt", device="", output_dir=None):
"""
Automatically annotates images using a YOLO object detection model and a SAM segmentation model.
Args:
data (str): Path to a folder containing images to be annotated.
det_model (str, optional): Pre-trained YOLO detection model. Defaults to 'yolov8x.pt'.
sam_model (str, optional): Pre-trained SAM segmentation model. Defaults to 'sam_b.pt'.
device (str, optional): Device to run the models on. Defaults to an empty string (CPU or GPU, if available).
output_dir (str | None | optional): Directory to save the annotated results.
Defaults to a 'labels' folder in the same directory as 'data'.
Example:
```python
from ultralytics.data.annotator import auto_annotate
auto_annotate(data='ultralytics/assets', det_model='yolov8n.pt', sam_model='mobile_sam.pt')
```
"""
det_model = YOLO(det_model)
sam_model = SAM(sam_model)
data = Path(data)
if not output_dir:
output_dir = data.parent / f"{data.stem}_auto_annotate_labels"
Path(output_dir).mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
det_results = det_model(data, stream=True, device=device)
for result in det_results:
class_ids = result.boxes.cls.int().tolist() # noqa
if len(class_ids):
boxes = result.boxes.xyxy # Boxes object for bbox outputs
sam_results = sam_model(result.orig_img, bboxes=boxes, verbose=False, save=False, device=device)
segments = sam_results[0].masks.xyn # noqa
with open(f"{Path(output_dir) / Path(result.path).stem}.txt", "w") as f:
for i in range(len(segments)):
s = segments[i]
if len(s) == 0:
continue
segment = map(str, segments[i].reshape(-1).tolist())
f.write(f"{class_ids[i]} " + " ".join(segment) + "\n")

augment.py
数据增强
class BaseTransform
# TODO: we might need a BaseTransform to make all these augments be compatible with both classification and semantic
class BaseTransform:
"""
Base class for image transformations.
This is a generic transformation class that can be extended for specific image processing needs.
The class is designed to be compatible with both classification and semantic segmentation tasks.
Methods:
__init__: Initializes the BaseTransform object.
apply_image: Applies image transformation to labels.
apply_instances: Applies transformations to object instances in labels.
apply_semantic: Applies semantic segmentation to an image.
__call__: Applies all label transformations to an image, instances, and semantic masks.
"""
def __init__(self) -> None:
"""Initializes the BaseTransform object."""
pass
def apply_image(self, labels):
"""Applies image transformations to labels."""
pass
def apply_instances(self, labels):
"""Applies transformations to object instances in labels."""
pass
def apply_semantic(self, labels):
"""Applies semantic segmentation to an image."""
pass
def __call__(self, labels):
"""Applies all label transformations to an image, instances, and semantic masks."""
self.apply_image(labels)
self.apply_instances(labels)
self.apply_semantic(labels)

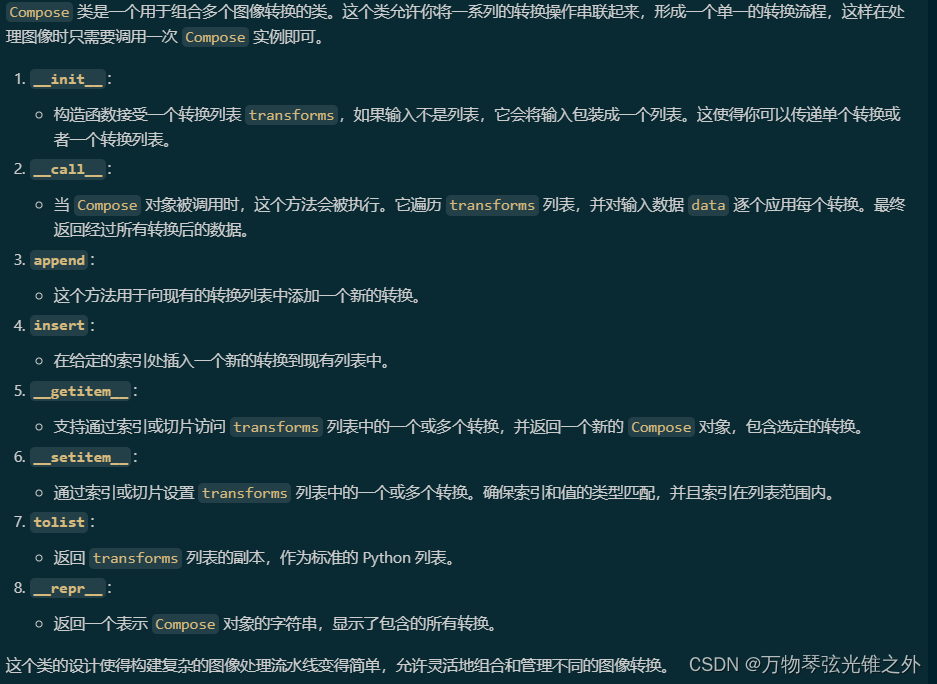
class Compose
class Compose:
"""Class for composing multiple image transformations."""
def __init__(self, transforms):
"""Initializes the Compose object with a list of transforms."""
self.transforms = transforms if isinstance(transforms, list) else [transforms]
def __call__(self, data):
"""Applies a series of transformations to input data."""
for t in self.transforms:
data = t(data)
return data
def append(self, transform):
"""Appends a new transform to the existing list of transforms."""
self.transforms.append(transform)
def insert(self, index, transform):
"""Inserts a new transform to the existing list of transforms."""
self.transforms.insert(index, transform)
def __getitem__(self, index: Union[list, int]) -> "Compose":
"""Retrieve a specific transform or a set of transforms using indexing."""
assert isinstance(index, (int, list)), f"The indices should be either list or int type but got {type(index)}"
index = [index] if isinstance(index, int) else index
return Compose([self.transforms[i] for i in index])
def __setitem__(self, index: Union[list, int], value: Union[list, int]) -> None:
"""Retrieve a specific transform or a set of transforms using indexing."""
assert isinstance(index, (int, list)), f"The indices should be either list or int type but got {type(index)}"
if isinstance(index, list):
assert isinstance(
value, list
), f"The indices should be the same type as values, but got {type(index)} and {type(value)}"
if isinstance(index, int):
index, value = [index], [value]
for i, v in zip(index, value):
assert i < len(self.transforms), f"list index {i} out of range {len(self.transforms)}."
self.transforms[i] = v
def tolist(self):
"""Converts the list of transforms to a standard Python list."""
return self.transforms
def __repr__(self):
"""Returns a string representation of the object."""
return f"{self.__class__.__name__}({', '.join([f'{t}' for t in self.transforms])})"
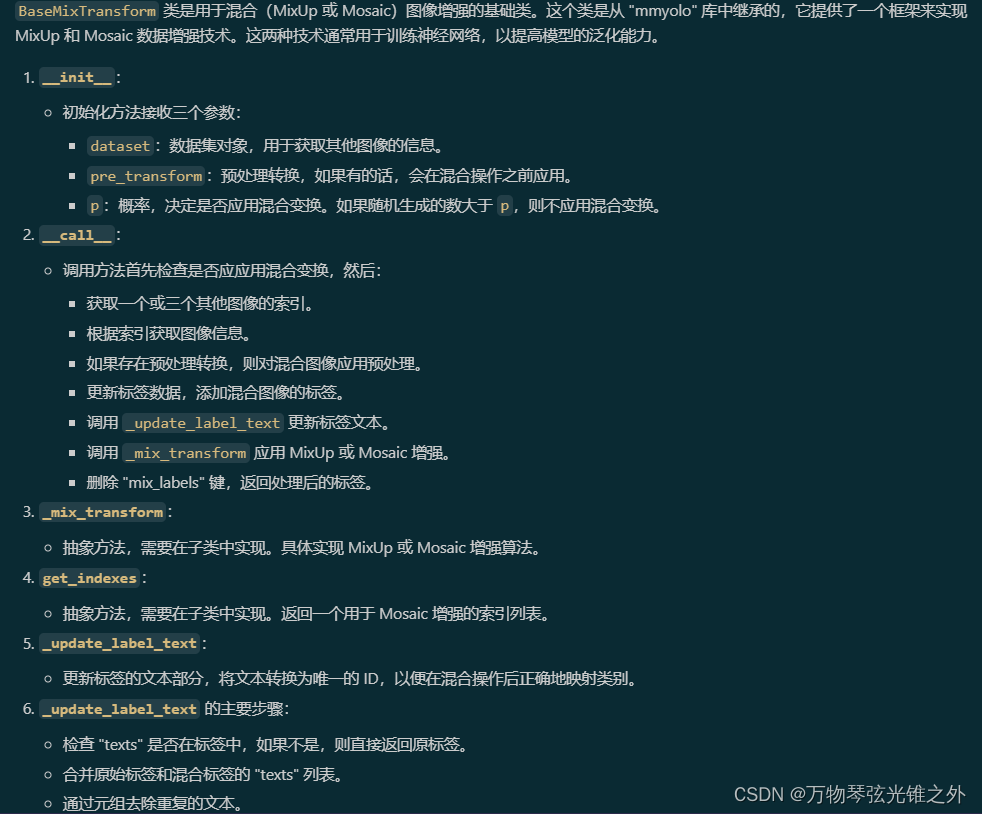
class BaseMixTransform
class BaseMixTransform:
"""
Class for base mix (MixUp/Mosaic) transformations.
This implementation is from mmyolo.
"""
def __init__(self, dataset, pre_transform=None, p=0.0) -> None:
"""Initializes the BaseMixTransform object with dataset, pre_transform, and probability."""
self.dataset = dataset
self.pre_transform = pre_transform
self.p = p
def __call__(self, labels):
"""Applies pre-processing transforms and mixup/mosaic transforms to labels data."""
if random.uniform(0, 1) > self.p:
return labels
# Get index of one or three other images
indexes = self.get_indexes()
if isinstance(indexes, int):
indexes = [indexes]
# Get images information will be used for Mosaic or MixUp
mix_labels = [self.dataset.get_image_and_label(i) for i in indexes]
if self.pre_transform is not None:
for i, data in enumerate(mix_labels):
mix_labels[i] = self.pre_transform(data)
labels["mix_labels"] = mix_labels
# Update cls and texts
labels = self._update_label_text(labels)
# Mosaic or MixUp
labels = self._mix_transform(labels)
labels.pop("mix_labels", None)
return labels
def _mix_transform(self, labels):
"""Applies MixUp or Mosaic augmentation to the label dictionary."""
raise NotImplementedError
def get_indexes(self):
"""Gets a list of shuffled indexes for mosaic augmentation."""
raise NotImplementedError
def _update_label_text(self, labels):
"""Update label text."""
if "texts" not in labels:
return labels
mix_texts = sum([labels["texts"]] + [x["texts"] for x in labels["mix_labels"]], [])
mix_texts = list({tuple(x) for x in mix_texts})
text2id = {text: i for i, text in enumerate(mix_texts)}
for label in [labels] + labels["mix_labels"]:
for i, cls in enumerate(label["cls"].squeeze(-1).tolist()):
text = label["texts"][int(cls)]
label["cls"][i] = text2id[tuple(text)]
label["texts"] = mix_texts
return labels
class Mosaic
class Mosaic(BaseMixTransform):
"""
Mosaic augmentation.
This class performs mosaic augmentation by combining multiple (4 or 9) images into a single mosaic image.
The augmentation is applied to a dataset with a given probability.
Attributes:
dataset: The dataset on which the mosaic augmentation is applied.
imgsz (int, optional): Image size (height and width) after mosaic pipeline of a single image. Default to 640.
p (float, optional): Probability of applying the mosaic augmentation. Must be in the range 0-1. Default to 1.0.
n (int, optional): The grid size, either 4 (for 2x2) or 9 (for 3x3).
"""
def __init__(self, dataset, imgsz=640, p=1.0, n=4):
"""Initializes the object with a dataset, image size, probability, and border."""
assert 0 <= p <= 1.0, f"The probability should be in range [0, 1], but got {p}."
assert n in {4, 9}, "grid must be equal to 4 or 9."
super().__init__(dataset=dataset, p=p)
self.dataset = dataset
self.imgsz = imgsz
self.border = (-imgsz // 2, -imgsz // 2) # width, height
self.n = n
def get_indexes(self, buffer=True):
"""Return a list of random indexes from the dataset."""
if buffer: # select images from buffer
return random.choices(list(self.dataset.buffer), k=self.n - 1)
else: # select any images
return [random.randint(0, len(self.dataset) - 1) for _ in range(self.n - 1)]
def _mix_transform(self, labels):
"""Apply mixup transformation to the input image and labels."""
assert labels.get("rect_shape", None) is None, "rect and mosaic are mutually exclusive."
assert len(labels.get("mix_labels", [])), "There are no other images for mosaic augment."
return (
self._mosaic3(labels) if self.n == 3 else self._mosaic4(labels) if self.n == 4 else self._mosaic9(labels)
) # This code is modified for mosaic3 method.
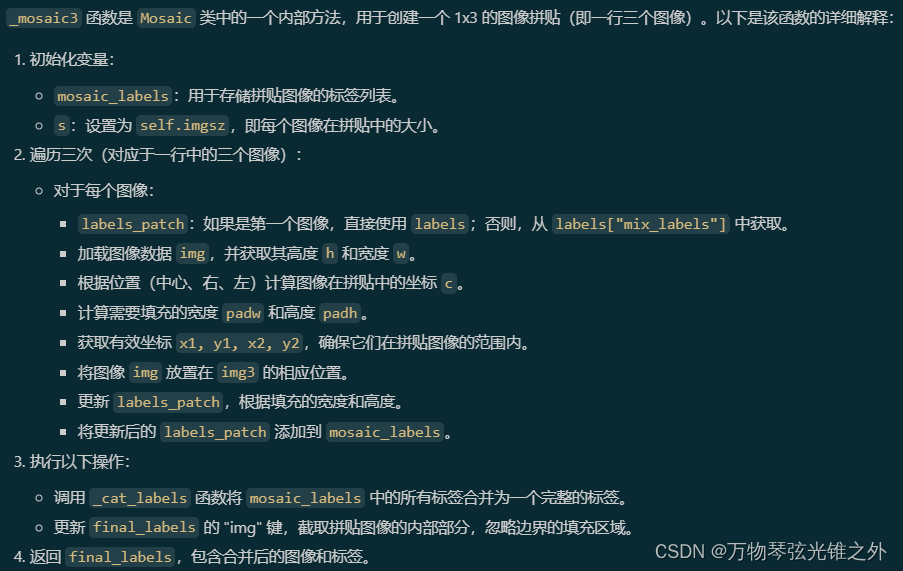
def _mosaic3(self, labels):
"""Create a 1x3 image mosaic."""
mosaic_labels = []
s = self.imgsz
for i in range(3):
labels_patch = labels if i == 0 else labels["mix_labels"][i - 1]
# Load image
img = labels_patch["img"]
h, w = labels_patch.pop("resized_shape")
# Place img in img3
if i == 0: # center
img3 = np.full((s * 3, s * 3, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 3 tiles
h0, w0 = h, w
c = s, s, s + w, s + h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (base) coordinates
elif i == 1: # right
c = s + w0, s, s + w0 + w, s + h
elif i == 2: # left
c = s - w, s + h0 - h, s, s + h0
padw, padh = c[:2]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = (max(x, 0) for x in c) # allocate coords
img3[y1:y2, x1:x2] = img[y1 - padh :, x1 - padw :] # img3[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
# hp, wp = h, w # height, width previous for next iteration
# Labels assuming imgsz*2 mosaic size
labels_patch = self._update_labels(labels_patch, padw + self.border[0], padh + self.border[1])
mosaic_labels.append(labels_patch)
final_labels = self._cat_labels(mosaic_labels)
final_labels["img"] = img3[-self.border[0] : self.border[0], -self.border[1] : self.border[1]]
return final_labels
def _mosaic4(self, labels):
"""Create a 2x2 image mosaic."""
mosaic_labels = []
s = self.imgsz
yc, xc = (int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.border) # mosaic center x, y
for i in range(4):
labels_patch = labels if i == 0 else labels["mix_labels"][i - 1]
# Load image
img = labels_patch["img"]
h, w = labels_patch.pop("resized_shape")
# Place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image)
elif i == 1: # top right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
padw = x1a - x1b
padh = y1a - y1b
labels_patch = self._update_labels(labels_patch, padw, padh)
mosaic_labels.append(labels_patch)
final_labels = self._cat_labels(mosaic_labels)
final_labels["img"] = img4
return final_labels
def _mosaic9(self, labels):
"""Create a 3x3 image mosaic."""
mosaic_labels = []
s = self.imgsz
hp, wp = -1, -1 # height, width previous
for i in range(9):
labels_patch = labels if i == 0 else labels["mix_labels"][i - 1]
# Load image
img = labels_patch["img"]
h, w = labels_patch.pop("resized_shape")
# Place img in img9
if i == 0: # center
img9 = np.full((s * 3, s * 3, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
h0, w0 = h, w
c = s, s, s + w, s + h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (base) coordinates
elif i == 1: # top
c = s, s - h, s + w, s
elif i == 2: # top right
c = s + wp, s - h, s + wp + w, s
elif i == 3: # right
c = s + w0, s, s + w0 + w, s + h
elif i == 4: # bottom right
c = s + w0, s + hp, s + w0 + w, s + hp + h
elif i == 5: # bottom
c = s + w0 - w, s + h0, s + w0, s + h0 + h
elif i == 6: # bottom left
c = s + w0 - wp - w, s + h0, s + w0 - wp, s + h0 + h
elif i == 7: # left
c = s - w, s + h0 - h, s, s + h0
elif i == 8: # top left
c = s - w, s + h0 - hp - h, s, s + h0 - hp
padw, padh = c[:2]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = (max(x, 0) for x in c) # allocate coords
# Image
img9[y1:y2, x1:x2] = img[y1 - padh :, x1 - padw :] # img9[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
hp, wp = h, w # height, width previous for next iteration
# Labels assuming imgsz*2 mosaic size
labels_patch = self._update_labels(labels_patch, padw + self.border[0], padh + self.border[1])
mosaic_labels.append(labels_patch)
final_labels = self._cat_labels(mosaic_labels)
final_labels["img"] = img9[-self.border[0] : self.border[0], -self.border[1] : self.border[1]]
return final_labels
@staticmethod
def _update_labels(labels, padw, padh):
"""Update labels."""
nh, nw = labels["img"].shape[:2]
labels["instances"].convert_bbox(format="xyxy")
labels["instances"].denormalize(nw, nh)
labels["instances"].add_padding(padw, padh)
return labels
def _cat_labels(self, mosaic_labels):
"""Return labels with mosaic border instances clipped."""
if len(mosaic_labels) == 0:
return {}
cls = []
instances = []
imgsz = self.imgsz * 2 # mosaic imgsz
for labels in mosaic_labels:
cls.append(labels["cls"])
instances.append(labels["instances"])
# Final labels
final_labels = {
"im_file": mosaic_labels[0]["im_file"],
"ori_shape": mosaic_labels[0]["ori_shape"],
"resized_shape": (imgsz, imgsz),
"cls": np.concatenate(cls, 0),
"instances": Instances.concatenate(instances, axis=0),
"mosaic_border": self.border,
}
final_labels["instances"].clip(imgsz, imgsz)
good = final_labels["instances"].remove_zero_area_boxes()
final_labels["cls"] = final_labels["cls"][good]
if "texts" in mosaic_labels[0]:
final_labels["texts"] = mosaic_labels[0]["texts"]
return final_labels

具体介绍一下_mosaic3
静态方法更新label
# 静态方法,用于更新单个图像的标签
@staticmethod
def _update_labels(labels, padw, padh):
# 获取图像的高度和宽度
nh, nw = labels["img"].shape[:2]
# 将实例(boxes)转换为xyxy格式
labels["instances"].convert_bbox(format="xyxy")
# 反标准化实例坐标,基于图像的实际尺寸
labels["instances"].denormalize(nw, nh)
# 添加填充到实例坐标
labels["instances"].add_padding(padw, padh)
# 返回更新后的标签
return labels
# 静态方法,用于将多个图像的标签组合成一个拼贴图像的标签
@staticmethod
def _cat_labels(mosaic_labels):
# 检查输入列表是否为空
if len(mosaic_labels) == 0:
return {}
# 初始化类别列表和实例列表
cls = []
instances = []
# 拼贴图像的大小是原始图像大小的两倍
imgsz = self.imgsz * 2
# 遍历每个图像的标签
for labels in mosaic_labels:
# 收集类别
cls.append(labels["cls"])
# 收集实例
instances.append(labels["instances"])
# 创建最终的标签字典
final_labels = {
"im_file": mosaic_labels[0]["im_file"], # 图像的文件名
"ori_shape": mosaic_labels[0]["ori_shape"], # 图像的原始形状
"resized_shape": (imgsz, imgsz), # 拼贴图像的尺寸
"cls": np.concatenate(cls, 0), # 合并所有图像的类别
"instances": Instances.concatenate(instances, axis=0), # 合并所有图像的实例
"mosaic_border": self.border, # 拼贴图像的边框信息
}
# 裁剪超出拼贴图像边界的实例
final_labels["instances"].clip(imgsz, imgsz)
# 移除面积为零的实例
good = final_labels["instances"].remove_zero_area_boxes()
# 根据有效的实例更新类别
final_labels["cls"] = final_labels["cls"][good]
# 如果原始标签中有"texts"字段,将其添加到最终标签中
if "texts" in mosaic_labels[0]:
final_labels["texts"] = mosaic_labels[0]["texts"]
# 返回组合后的标签
return final_labels
class MixUp
class MixUp(BaseMixTransform):
"""Class for applying MixUp augmentation to the dataset."""
def __init__(self, dataset, pre_transform=None, p=0.0) -> None:
"""初始化MixUp对象,传入数据集、预处理变换和应用MixUp的概率。
参数:
- dataset: 数据集对象
- pre_transform: 可选的预处理变换
- p: 应用MixUp的概率,默认为0.0,表示默认不应用MixUp
"""
super().__init__(dataset=dataset, pre_transform=pre_transform, p=p)
def get_indexes(self):
"""从数据集中随机获取一个索引。
返回:
- 一个随机生成的整数索引,范围在0到数据集长度减1之间。
"""
return random.randint(0, len(self.dataset) - 1)
def _mix_transform(self, labels):
"""根据https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09412.pdf中的描述应用MixUp数据增强。
参数:
- labels: 包含图像和对应标签的字典,如{'img': 图像, 'instances': 实例, 'cls': 类别}
返回:
- 应用MixUp后的混合标签字典。
"""
# 生成MixUp的混合比例,这里使用alpha=beta=32.0
r = np.random.beta(32.0, 32.0)
# 获取第二个图像及其标签
labels2 = labels["mix_labels"][0]
# 混合两个图像
mixed_img = (labels["img"] * r + labels2["img"] * (1 - r)).astype(np.uint8)
# 混合两个实例(如边界框)
mixed_instances = Instances.concatenate([labels["instances"], labels2["instances"]], axis=0)
# 混合两个类别
mixed_cls = np.concatenate([labels["cls"], labels2["cls"]], 0)
# 返回混合后的标签字典
return {"img": mixed_img, "instances": mixed_instances, "cls": mixed_cls}
RandomPerspective
class RandomPerspective:
"""
Implements random perspective and affine transformations on images and corresponding bounding boxes, segments, and
keypoints. These transformations include rotation, translation, scaling, and shearing. The class also offers the
option to apply these transformations conditionally with a specified probability.
Attributes:
degrees (float): Degree range for random rotations.
translate (float): Fraction of total width and height for random translation.
scale (float): Scaling factor interval, e.g., a scale factor of 0.1 allows a resize between 90%-110%.
shear (float): Shear intensity (angle in degrees).
perspective (float): Perspective distortion factor.
border (tuple): Tuple specifying mosaic border.
pre_transform (callable): A function/transform to apply to the image before starting the random transformation.
Methods:
affine_transform(img, border): Applies a series of affine transformations to the image.
apply_bboxes(bboxes, M): Transforms bounding boxes using the calculated affine matrix.
apply_segments(segments, M): Transforms segments and generates new bounding boxes.
apply_keypoints(keypoints, M): Transforms keypoints.
__call__(labels): Main method to apply transformations to both images and their corresponding annotations.
box_candidates(box1, box2): Filters out bounding boxes that don't meet certain criteria post-transformation.
"""
def __init__(
self, degrees=0.0, translate=0.1, scale=0.5, shear=0.0, perspective=0.0, border=(0, 0), pre_transform=None
):
"""Initializes RandomPerspective object with transformation parameters."""
self.degrees = degrees
self.translate = translate
self.scale = scale
self.shear = shear
self.perspective = perspective
self.border = border # mosaic border
self.pre_transform = pre_transform
def affine_transform(self, img, border):
"""
Applies a sequence of affine transformations centered around the image center.
Args:
img (ndarray): Input image.
border (tuple): Border dimensions.
Returns:
img (ndarray): Transformed image.
M (ndarray): Transformation matrix.
s (float): Scale factor.
"""
# Center
C = np.eye(3, dtype=np.float32)
C[0, 2] = -img.shape[1] / 2 # x translation (pixels)
C[1, 2] = -img.shape[0] / 2 # y translation (pixels)
# Perspective
P = np.eye(3, dtype=np.float32)
P[2, 0] = random.uniform(-self.perspective, self.perspective) # x perspective (about y)
P[2, 1] = random.uniform(-self.perspective, self.perspective) # y perspective (about x)
# Rotation and Scale
R = np.eye(3, dtype=np.float32)
a = random.uniform(-self.degrees, self.degrees)
# a += random.choice([-180, -90, 0, 90]) # add 90deg rotations to small rotations
s = random.uniform(1 - self.scale, 1 + self.scale)
# s = 2 ** random.uniform(-scale, scale)
R[:2] = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(angle=a, center=(0, 0), scale=s)
# Shear
S = np.eye(3, dtype=np.float32)
S[0, 1] = math.tan(random.uniform(-self.shear, self.shear) * math.pi / 180) # x shear (deg)
S[1, 0] = math.tan(random.uniform(-self.shear, self.shear) * math.pi / 180) # y shear (deg)
# Translation
T = np.eye(3, dtype=np.float32)
T[0, 2] = random.uniform(0.5 - self.translate, 0.5 + self.translate) * self.size[0] # x translation (pixels)
T[1, 2] = random.uniform(0.5 - self.translate, 0.5 + self.translate) * self.size[1] # y translation (pixels)
# Combined rotation matrix
M = T @ S @ R @ P @ C # order of operations (right to left) is IMPORTANT
# Affine image
if (border[0] != 0) or (border[1] != 0) or (M != np.eye(3)).any(): # image changed
if self.perspective:
img = cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, dsize=self.size, borderValue=(114, 114, 114))
else: # affine
img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M[:2], dsize=self.size, borderValue=(114, 114, 114))
return img, M, s
def apply_bboxes(self, bboxes, M):
"""
Apply affine to bboxes only.
Args:
bboxes (ndarray): list of bboxes, xyxy format, with shape (num_bboxes, 4).
M (ndarray): affine matrix.
Returns:
new_bboxes (ndarray): bboxes after affine, [num_bboxes, 4].
"""
n = len(bboxes)
if n == 0:
return bboxes
xy = np.ones((n * 4, 3), dtype=bboxes.dtype)
xy[:, :2] = bboxes[:, [0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 3, 2, 1]].reshape(n * 4, 2) # x1y1, x2y2, x1y2, x2y1
xy = xy @ M.T # transform
xy = (xy[:, :2] / xy[:, 2:3] if self.perspective else xy[:, :2]).reshape(n, 8) # perspective rescale or affine
# Create new boxes
x = xy[:, [0, 2, 4, 6]]
y = xy[:, [1, 3, 5, 7]]
return np.concatenate((x.min(1), y.min(1), x.max(1), y.max(1)), dtype=bboxes.dtype).reshape(4, n).T
def apply_segments(self, segments, M):
"""
Apply affine to segments and generate new bboxes from segments.
Args:
segments (ndarray): list of segments, [num_samples, 500, 2].
M (ndarray): affine matrix.
Returns:
new_segments (ndarray): list of segments after affine, [num_samples, 500, 2].
new_bboxes (ndarray): bboxes after affine, [N, 4].
"""
n, num = segments.shape[:2]
if n == 0:
return [], segments
xy = np.ones((n * num, 3), dtype=segments.dtype)
segments = segments.reshape(-1, 2)
xy[:, :2] = segments
xy = xy @ M.T # transform
xy = xy[:, :2] / xy[:, 2:3]
segments = xy.reshape(n, -1, 2)
bboxes = np.stack([segment2box(xy, self.size[0], self.size[1]) for xy in segments], 0)
segments[..., 0] = segments[..., 0].clip(bboxes[:, 0:1], bboxes[:, 2:3])
segments[..., 1] = segments[..., 1].clip(bboxes[:, 1:2], bboxes[:, 3:4])
return bboxes, segments
def apply_keypoints(self, keypoints, M):
"""
Apply affine to keypoints.
Args:
keypoints (ndarray): keypoints, [N, 17, 3].
M (ndarray): affine matrix.
Returns:
new_keypoints (ndarray): keypoints after affine, [N, 17, 3].
"""
n, nkpt = keypoints.shape[:2]
if n == 0:
return keypoints
xy = np.ones((n * nkpt, 3), dtype=keypoints.dtype)
visible = keypoints[..., 2].reshape(n * nkpt, 1)
xy[:, :2] = keypoints[..., :2].reshape(n * nkpt, 2)
xy = xy @ M.T # transform
xy = xy[:, :2] / xy[:, 2:3] # perspective rescale or affine
out_mask = (xy[:, 0] < 0) | (xy[:, 1] < 0) | (xy[:, 0] > self.size[0]) | (xy[:, 1] > self.size[1])
visible[out_mask] = 0
return np.concatenate([xy, visible], axis=-1).reshape(n, nkpt, 3)
def __call__(self, labels):
"""
Affine images and targets.
Args:
labels (dict): a dict of `bboxes`, `segments`, `keypoints`.
"""
if self.pre_transform and "mosaic_border" not in labels:
labels = self.pre_transform(labels)
labels.pop("ratio_pad", None) # do not need ratio pad
img = labels["img"]
cls = labels["cls"]
instances = labels.pop("instances")
# Make sure the coord formats are right
instances.convert_bbox(format="xyxy")
instances.denormalize(*img.shape[:2][::-1])
border = labels.pop("mosaic_border", self.border)
self.size = img.shape[1] + border[1] * 2, img.shape[0] + border[0] * 2 # w, h
# M is affine matrix
# Scale for func:`box_candidates`
img, M, scale = self.affine_transform(img, border)
bboxes = self.apply_bboxes(instances.bboxes, M)
segments = instances.segments
keypoints = instances.keypoints
# Update bboxes if there are segments.
if len(segments):
bboxes, segments = self.apply_segments(segments, M)
if keypoints is not None:
keypoints = self.apply_keypoints(keypoints, M)
new_instances = Instances(bboxes, segments, keypoints, bbox_format="xyxy", normalized=False)
# Clip
new_instances.clip(*self.size)
# Filter instances
instances.scale(scale_w=scale, scale_h=scale, bbox_only=True)
# Make the bboxes have the same scale with new_bboxes
i = self.box_candidates(
box1=instances.bboxes.T, box2=new_instances.bboxes.T, area_thr=0.01 if len(segments) else 0.10
)
labels["instances"] = new_instances[i]
labels["cls"] = cls[i]
labels["img"] = img
labels["resized_shape"] = img.shape[:2]
return labels
def box_candidates(self, box1, box2, wh_thr=2, ar_thr=100, area_thr=0.1, eps=1e-16):
"""
Compute box candidates based on a set of thresholds. This method compares the characteristics of the boxes
before and after augmentation to decide whether a box is a candidate for further processing.
Args:
box1 (numpy.ndarray): The 4,n bounding box before augmentation, represented as [x1, y1, x2, y2].
box2 (numpy.ndarray): The 4,n bounding box after augmentation, represented as [x1, y1, x2, y2].
wh_thr (float, optional): The width and height threshold in pixels. Default is 2.
ar_thr (float, optional): The aspect ratio threshold. Default is 100.
area_thr (float, optional): The area ratio threshold. Default is 0.1.
eps (float, optional): A small epsilon value to prevent division by zero. Default is 1e-16.
Returns:
(numpy.ndarray): A boolean array indicating which boxes are candidates based on the given thresholds.
"""
w1, h1 = box1[2] - box1[0], box1[3] - box1[1]
w2, h2 = box2[2] - box2[0], box2[3] - box2[1]
ar = np.maximum(w2 / (h2 + eps), h2 / (w2 + eps)) # aspect ratio
return (w2 > wh_thr) & (h2 > wh_thr) & (w2 * h2 / (w1 * h1 + eps) > area_thr) & (ar < ar_thr) # candidates
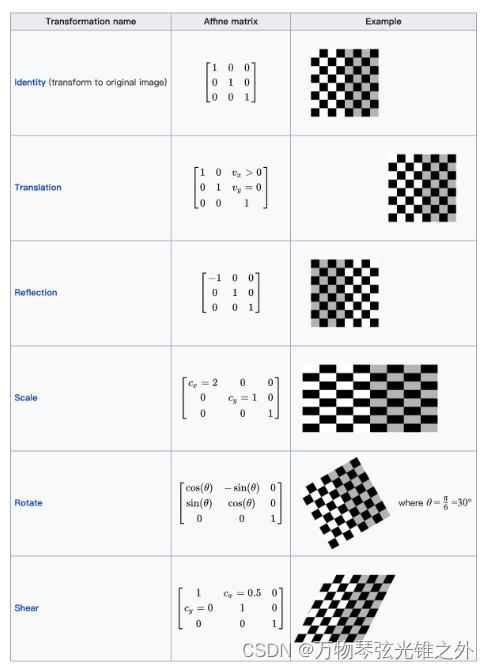
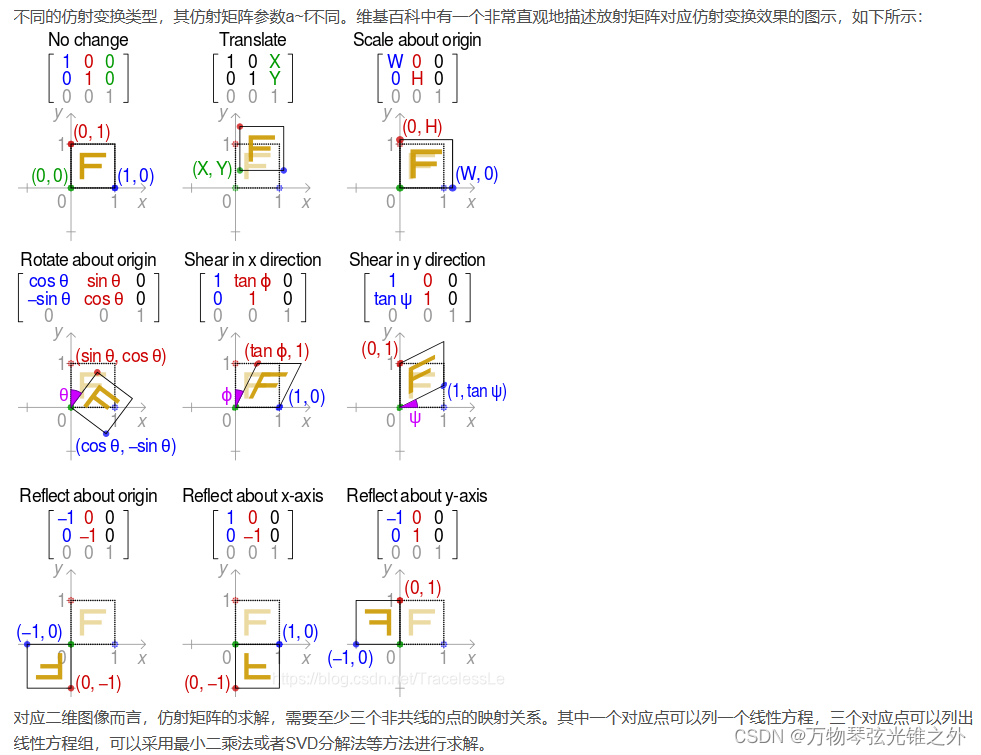
M = T @ S @ R @ P @ C

关于这种矩阵变换可以看下面这个网址:
矩阵变换

class RandomHSV
class RandomHSV:
"""
This class is responsible for performing random adjustments to the Hue, Saturation, and Value (HSV) channels of an
image.
The adjustments are random but within limits set by hgain, sgain, and vgain.
"""
def __init__(self, hgain=0.5, sgain=0.5, vgain=0.5) -> None:
"""
Initialize RandomHSV class with gains for each HSV channel.
Args:
hgain (float, optional): Maximum variation for hue. Default is 0.5.
sgain (float, optional): Maximum variation for saturation. Default is 0.5.
vgain (float, optional): Maximum variation for value. Default is 0.5.
"""
self.hgain = hgain
self.sgain = sgain
self.vgain = vgain
def __call__(self, labels):
"""
Applies random HSV augmentation to an image within the predefined limits.
The modified image replaces the original image in the input 'labels' dict.
"""
img = labels["img"]
if self.hgain or self.sgain or self.vgain:
r = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 3) * [self.hgain, self.sgain, self.vgain] + 1 # random gains
hue, sat, val = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV))
dtype = img.dtype # uint8
x = np.arange(0, 256, dtype=r.dtype)
lut_hue = ((x * r[0]) % 180).astype(dtype)
lut_sat = np.clip(x * r[1], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
lut_val = np.clip(x * r[2], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
im_hsv = cv2.merge((cv2.LUT(hue, lut_hue), cv2.LUT(sat, lut_sat), cv2.LUT(val, lut_val)))
cv2.cvtColor(im_hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR, dst=img) # no return needed
return labels
class RandomFlip
class RandomFlip:
"""
Applies a random horizontal or vertical flip to an image with a given probability.
Also updates any instances (bounding boxes, keypoints, etc.) accordingly.
"""
def __init__(self, p=0.5, direction="horizontal", flip_idx=None) -> None:
"""
Initializes the RandomFlip class with probability and direction.
Args:
p (float, optional): The probability of applying the flip. Must be between 0 and 1. Default is 0.5.
direction (str, optional): The direction to apply the flip. Must be 'horizontal' or 'vertical'.
Default is 'horizontal'.
flip_idx (array-like, optional): Index mapping for flipping keypoints, if any.
"""
assert direction in {"horizontal", "vertical"}, f"Support direction `horizontal` or `vertical`, got {direction}"
assert 0 <= p <= 1.0
self.p = p
self.direction = direction
self.flip_idx = flip_idx
def __call__(self, labels):
"""
Applies random flip to an image and updates any instances like bounding boxes or keypoints accordingly.
Args:
labels (dict): A dictionary containing the keys 'img' and 'instances'. 'img' is the image to be flipped.
'instances' is an object containing bounding boxes and optionally keypoints.
Returns:
(dict): The same dict with the flipped image and updated instances under the 'img' and 'instances' keys.
"""
img = labels["img"]
instances = labels.pop("instances")
instances.convert_bbox(format="xywh")
h, w = img.shape[:2]
h = 1 if instances.normalized else h
w = 1 if instances.normalized else w
# Flip up-down
if self.direction == "vertical" and random.random() < self.p:
img = np.flipud(img)
instances.flipud(h)
if self.direction == "horizontal" and random.random() < self.p:
img = np.fliplr(img)
instances.fliplr(w)
# For keypoints
if self.flip_idx is not None and instances.keypoints is not None:
instances.keypoints = np.ascontiguousarray(instances.keypoints[:, self.flip_idx, :])
labels["img"] = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
labels["instances"] = instances
return labels
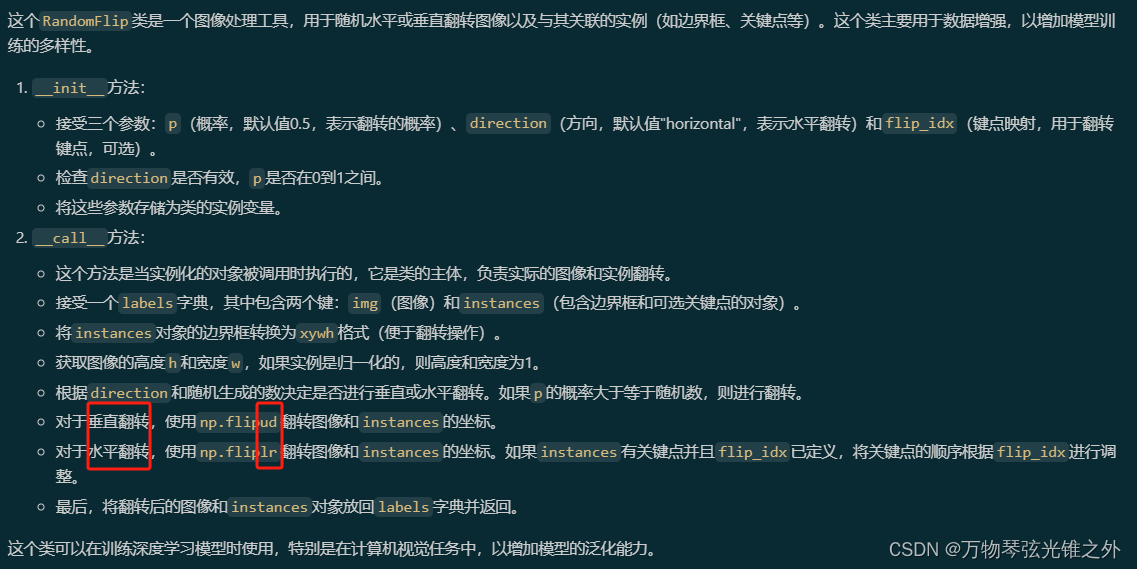
class LetterBox
class LetterBox:
"""Resize image and padding for detection, instance segmentation, pose."""
def __init__(self, new_shape=(640, 640), auto=False, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, center=True, stride=32):
"""Initialize LetterBox object with specific parameters."""
self.new_shape = new_shape
self.auto = auto
self.scaleFill = scaleFill
self.scaleup = scaleup
self.stride = stride
self.center = center # Put the image in the middle or top-left
def __call__(self, labels=None, image=None):
"""Return updated labels and image with added border."""
if labels is None:
labels = {}
img = labels.get("img") if image is None else image
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
new_shape = labels.pop("rect_shape", self.new_shape)
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not self.scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better val mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if self.auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, self.stride), np.mod(dh, self.stride) # wh padding
elif self.scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
if self.center:
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)) if self.center else 0, int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)) if self.center else 0, int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(
img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=(114, 114, 114)
) # add border
if labels.get("ratio_pad"):
labels["ratio_pad"] = (labels["ratio_pad"], (left, top)) # for evaluation
if len(labels):
labels = self._update_labels(labels, ratio, dw, dh)
labels["img"] = img
labels["resized_shape"] = new_shape
return labels
else:
return img
def _update_labels(self, labels, ratio, padw, padh):
"""Update labels."""
labels["instances"].convert_bbox(format="xyxy")
labels["instances"].denormalize(*labels["img"].shape[:2][::-1])
labels["instances"].scale(*ratio)
labels["instances"].add_padding(padw, padh)
return labels
class CopyPaste
class CopyPaste:
"""
Implements the Copy-Paste augmentation as described in the paper https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.07177. This class is
responsible for applying the Copy-Paste augmentation on images and their corresponding instances.
"""
def __init__(self, p=0.5) -> None:
"""
Initializes the CopyPaste class with a given probability.
Args:
p (float, optional): The probability of applying the Copy-Paste augmentation. Must be between 0 and 1.
Default is 0.5.
"""
self.p = p
def __call__(self, labels):
"""
Applies the Copy-Paste augmentation to the given image and instances.
Args:
labels (dict): A dictionary containing:
- 'img': The image to augment.
- 'cls': Class labels associated with the instances.
- 'instances': Object containing bounding boxes, and optionally, keypoints and segments.
Returns:
(dict): Dict with augmented image and updated instances under the 'img', 'cls', and 'instances' keys.
Notes:
1. Instances are expected to have 'segments' as one of their attributes for this augmentation to work.
2. This method modifies the input dictionary 'labels' in place.
"""
im = labels["img"]
cls = labels["cls"]
h, w = im.shape[:2]
instances = labels.pop("instances")
instances.convert_bbox(format="xyxy")
instances.denormalize(w, h)
if self.p and len(instances.segments):
n = len(instances)
_, w, _ = im.shape # height, width, channels
im_new = np.zeros(im.shape, np.uint8)
# Calculate ioa first then select indexes randomly
ins_flip = deepcopy(instances)
ins_flip.fliplr(w)
ioa = bbox_ioa(ins_flip.bboxes, instances.bboxes) # intersection over area, (N, M)
indexes = np.nonzero((ioa < 0.30).all(1))[0] # (N, )
n = len(indexes)
for j in random.sample(list(indexes), k=round(self.p * n)):
cls = np.concatenate((cls, cls[[j]]), axis=0)
instances = Instances.concatenate((instances, ins_flip[[j]]), axis=0)
cv2.drawContours(im_new, instances.segments[[j]].astype(np.int32), -1, (1, 1, 1), cv2.FILLED)
result = cv2.flip(im, 1) # augment segments (flip left-right)
i = cv2.flip(im_new, 1).astype(bool)
im[i] = result[i]
labels["img"] = im
labels["cls"] = cls
labels["instances"] = instances
return labels

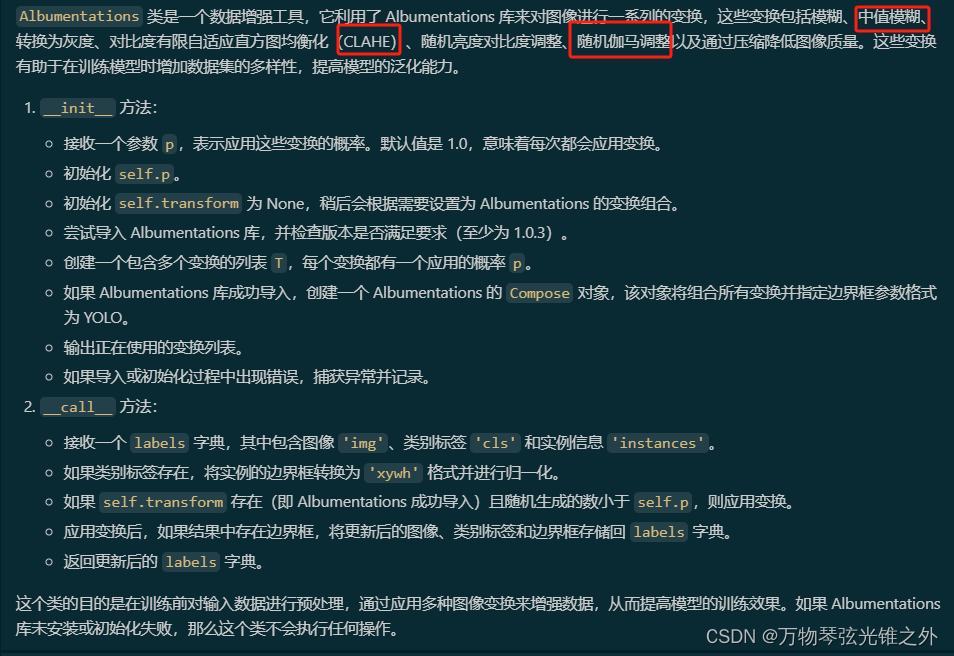
class Albumtation
class Albumentations:
"""
Albumentations transformations.
Optional, uninstall package to disable. Applies Blur, Median Blur, convert to grayscale, Contrast Limited Adaptive
Histogram Equalization, random change of brightness and contrast, RandomGamma and lowering of image quality by
compression.
"""
def __init__(self, p=1.0):
"""Initialize the transform object for YOLO bbox formatted params."""
self.p = p
self.transform = None
prefix = colorstr("albumentations: ")
try:
import albumentations as A
check_version(A.__version__, "1.0.3", hard=True) # version requirement
# Transforms
T = [
A.Blur(p=0.01),
A.MedianBlur(p=0.01),
A.ToGray(p=0.01),
A.CLAHE(p=0.01),
A.RandomBrightnessContrast(p=0.0),
A.RandomGamma(p=0.0),
A.ImageCompression(quality_lower=75, p=0.0),
]
self.transform = A.Compose(T, bbox_params=A.BboxParams(format="yolo", label_fields=["class_labels"]))
LOGGER.info(prefix + ", ".join(f"{x}".replace("always_apply=False, ", "") for x in T if x.p))
except ImportError: # package not installed, skip
pass
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.info(f"{prefix}{e}")
def __call__(self, labels):
"""Generates object detections and returns a dictionary with detection results."""
im = labels["img"]
cls = labels["cls"]
if len(cls):
labels["instances"].convert_bbox("xywh")
labels["instances"].normalize(*im.shape[:2][::-1])
bboxes = labels["instances"].bboxes
# TODO: add supports of segments and keypoints
if self.transform and random.random() < self.p:
new = self.transform(image=im, bboxes=bboxes, class_labels=cls) # transformed
if len(new["class_labels"]) > 0: # skip update if no bbox in new im
labels["img"] = new["image"]
labels["cls"] = np.array(new["class_labels"])
bboxes = np.array(new["bboxes"], dtype=np.float32)
labels["instances"].update(bboxes=bboxes)
return labels
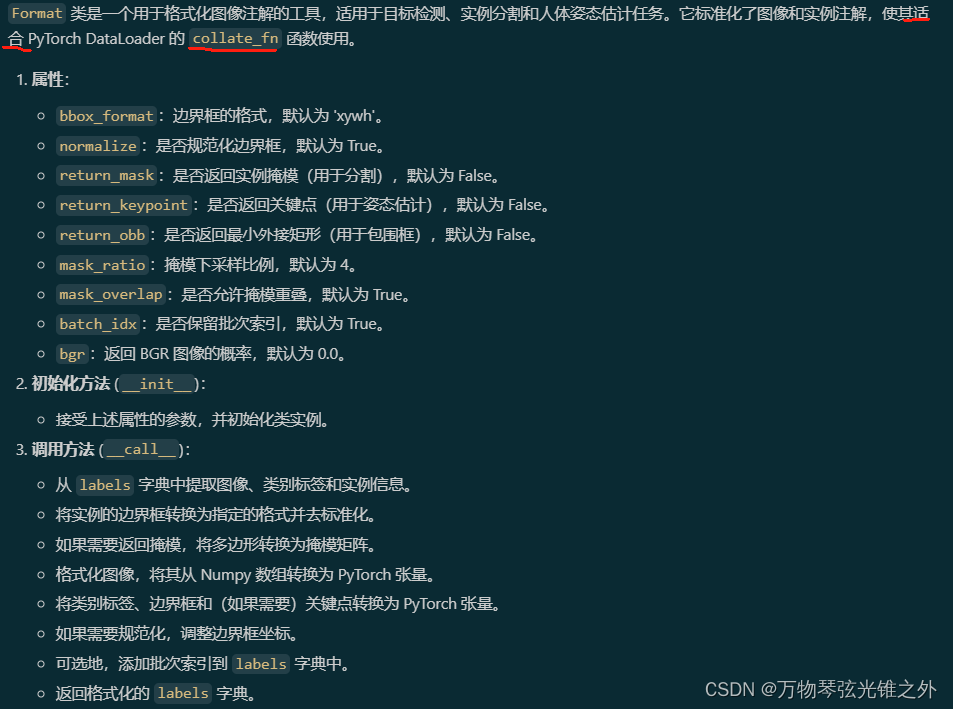
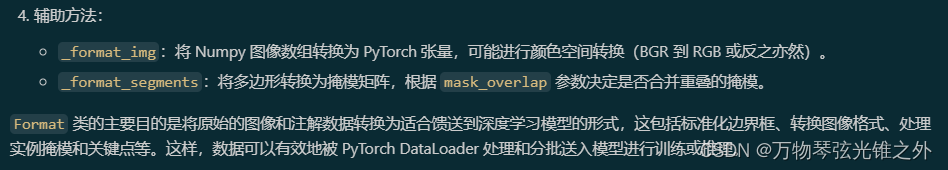
class Format
class Format:
"""
Formats image annotations for object detection, instance segmentation, and pose estimation tasks. The class
standardizes the image and instance annotations to be used by the `collate_fn` in PyTorch DataLoader.
Attributes:
bbox_format (str): Format for bounding boxes. Default is 'xywh'.
normalize (bool): Whether to normalize bounding boxes. Default is True.
return_mask (bool): Return instance masks for segmentation. Default is False.
return_keypoint (bool): Return keypoints for pose estimation. Default is False.
mask_ratio (int): Downsample ratio for masks. Default is 4.
mask_overlap (bool): Whether to overlap masks. Default is True.
batch_idx (bool): Keep batch indexes. Default is True.
bgr (float): The probability to return BGR images. Default is 0.0.
"""
def __init__(
self,
bbox_format="xywh",
normalize=True,
return_mask=False,
return_keypoint=False,
return_obb=False,
mask_ratio=4,
mask_overlap=True,
batch_idx=True,
bgr=0.0,
):
"""Initializes the Format class with given parameters."""
self.bbox_format = bbox_format
self.normalize = normalize
self.return_mask = return_mask # set False when training detection only
self.return_keypoint = return_keypoint
self.return_obb = return_obb
self.mask_ratio = mask_ratio
self.mask_overlap = mask_overlap
self.batch_idx = batch_idx # keep the batch indexes
self.bgr = bgr
def __call__(self, labels):
"""Return formatted image, classes, bounding boxes & keypoints to be used by 'collate_fn'."""
img = labels.pop("img")
h, w = img.shape[:2]
cls = labels.pop("cls")
instances = labels.pop("instances")
instances.convert_bbox(format=self.bbox_format)
instances.denormalize(w, h)
nl = len(instances)
if self.return_mask:
if nl:
masks, instances, cls = self._format_segments(instances, cls, w, h)
masks = torch.from_numpy(masks)
else:
masks = torch.zeros(
1 if self.mask_overlap else nl, img.shape[0] // self.mask_ratio, img.shape[1] // self.mask_ratio
)
labels["masks"] = masks
labels["img"] = self._format_img(img)
labels["cls"] = torch.from_numpy(cls) if nl else torch.zeros(nl)
labels["bboxes"] = torch.from_numpy(instances.bboxes) if nl else torch.zeros((nl, 4))
if self.return_keypoint:
labels["keypoints"] = torch.from_numpy(instances.keypoints)
if self.normalize:
labels["keypoints"][..., 0] /= w
labels["keypoints"][..., 1] /= h
if self.return_obb:
labels["bboxes"] = (
xyxyxyxy2xywhr(torch.from_numpy(instances.segments)) if len(instances.segments) else torch.zeros((0, 5))
)
# NOTE: need to normalize obb in xywhr format for width-height consistency
if self.normalize:
labels["bboxes"][:, [0, 2]] /= w
labels["bboxes"][:, [1, 3]] /= h
# Then we can use collate_fn
if self.batch_idx:
labels["batch_idx"] = torch.zeros(nl)
return labels
def _format_img(self, img):
"""Format the image for YOLO from Numpy array to PyTorch tensor."""
if len(img.shape) < 3:
img = np.expand_dims(img, -1)
img = img.transpose(2, 0, 1)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img[::-1] if random.uniform(0, 1) > self.bgr else img)
img = torch.from_numpy(img)
return img
def _format_segments(self, instances, cls, w, h):
"""Convert polygon points to bitmap."""
segments = instances.segments
if self.mask_overlap:
masks, sorted_idx = polygons2masks_overlap((h, w), segments, downsample_ratio=self.mask_ratio)
masks = masks[None] # (640, 640) -> (1, 640, 640)
instances = instances[sorted_idx]
cls = cls[sorted_idx]
else:
masks = polygons2masks((h, w), segments, color=1, downsample_ratio=self.mask_ratio)
return masks, instances, cls
class
class RandomLoadText:
"""
Randomly sample positive texts and negative texts and update the class indices accordingly to the number of samples.
Attributes:
prompt_format (str): Format for prompt. Default is '{}'.
neg_samples (tuple[int]): A ranger to randomly sample negative texts, Default is (80, 80).
max_samples (int): The max number of different text samples in one image, Default is 80.
padding (bool): Whether to pad texts to max_samples. Default is False.
padding_value (str): The padding text. Default is "".
"""
def __init__(
self,
prompt_format: str = "{}",
neg_samples: Tuple[int, int] = (80, 80),
max_samples: int = 80,
padding: bool = False,
padding_value: str = "",
) -> None:
"""Initializes the RandomLoadText class with given parameters."""
self.prompt_format = prompt_format
self.neg_samples = neg_samples
self.max_samples = max_samples
self.padding = padding
self.padding_value = padding_value
def __call__(self, labels: dict) -> dict:
"""Return updated classes and texts."""
assert "texts" in labels, "No texts found in labels."
class_texts = labels["texts"]
num_classes = len(class_texts)
cls = np.asarray(labels.pop("cls"), dtype=int)
pos_labels = np.unique(cls).tolist()
if len(pos_labels) > self.max_samples:
pos_labels = set(random.sample(pos_labels, k=self.max_samples))
neg_samples = min(min(num_classes, self.max_samples) - len(pos_labels), random.randint(*self.neg_samples))
neg_labels = []
for i in range(num_classes):
if i not in pos_labels:
neg_labels.append(i)
neg_labels = random.sample(neg_labels, k=neg_samples)
sampled_labels = pos_labels + neg_labels
random.shuffle(sampled_labels)
label2ids = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(sampled_labels)}
valid_idx = np.zeros(len(labels["instances"]), dtype=bool)
new_cls = []
for i, label in enumerate(cls.squeeze(-1).tolist()):
if label not in label2ids:
continue
valid_idx[i] = True
new_cls.append([label2ids[label]])
labels["instances"] = labels["instances"][valid_idx]
labels["cls"] = np.array(new_cls)
# Randomly select one prompt when there's more than one prompts
texts = []
for label in sampled_labels:
prompts = class_texts[label]
assert len(prompts) > 0
prompt = self.prompt_format.format(prompts[random.randrange(len(prompts))])
texts.append(prompt)
if self.padding:
valid_labels = len(pos_labels) + len(neg_labels)
num_padding = self.max_samples - valid_labels
if num_padding > 0:
texts += [self.padding_value] * num_padding
labels["texts"] = texts
return labels

v8_transforms
def v8_transforms(dataset, imgsz, hyp, stretch=False):
"""Convert images to a size suitable for YOLOv8 training."""
pre_transform = Compose(
[
Mosaic(dataset, imgsz=imgsz, p=hyp.mosaic),
CopyPaste(p=hyp.copy_paste),
RandomPerspective(
degrees=hyp.degrees,
translate=hyp.translate,
scale=hyp.scale,
shear=hyp.shear,
perspective=hyp.perspective,
pre_transform=None if stretch else LetterBox(new_shape=(imgsz, imgsz)),
),
]
)
flip_idx = dataset.data.get("flip_idx", []) # for keypoints augmentation
if dataset.use_keypoints:
kpt_shape = dataset.data.get("kpt_shape", None)
if len(flip_idx) == 0 and hyp.fliplr > 0.0:
hyp.fliplr = 0.0
LOGGER.warning("WARNING ⚠️ No 'flip_idx' array defined in data.yaml, setting augmentation 'fliplr=0.0'")
elif flip_idx and (len(flip_idx) != kpt_shape[0]):
raise ValueError(f"data.yaml flip_idx={flip_idx} length must be equal to kpt_shape[0]={kpt_shape[0]}")
return Compose(
[
pre_transform,
MixUp(dataset, pre_transform=pre_transform, p=hyp.mixup),
Albumentations(p=1.0),
RandomHSV(hgain=hyp.hsv_h, sgain=hyp.hsv_s, vgain=hyp.hsv_v),
RandomFlip(direction="vertical", p=hyp.flipud),
RandomFlip(direction="horizontal", p=hyp.fliplr, flip_idx=flip_idx),
]
) # transforms


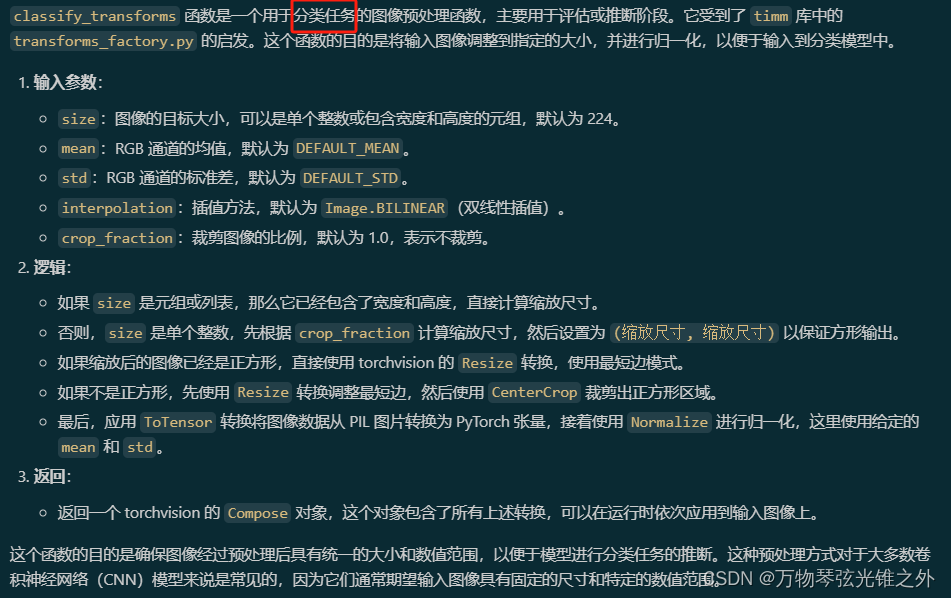
classify_transforms
# Classification augmentations -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def classify_transforms(
size=224,
mean=DEFAULT_MEAN,
std=DEFAULT_STD,
interpolation=Image.BILINEAR,
crop_fraction: float = DEFAULT_CROP_FRACTION,
):
"""
Classification transforms for evaluation/inference. Inspired by timm/data/transforms_factory.py.
Args:
size (int): image size
mean (tuple): mean values of RGB channels
std (tuple): std values of RGB channels
interpolation (T.InterpolationMode): interpolation mode. default is T.InterpolationMode.BILINEAR.
crop_fraction (float): fraction of image to crop. default is 1.0.
Returns:
(T.Compose): torchvision transforms
"""
import torchvision.transforms as T # scope for faster 'import ultralytics'
if isinstance(size, (tuple, list)):
assert len(size) == 2
scale_size = tuple(math.floor(x / crop_fraction) for x in size)
else:
scale_size = math.floor(size / crop_fraction)
scale_size = (scale_size, scale_size)
# Aspect ratio is preserved, crops center within image, no borders are added, image is lost
if scale_size[0] == scale_size[1]:
# Simple case, use torchvision built-in Resize with the shortest edge mode (scalar size arg)
tfl = [T.Resize(scale_size[0], interpolation=interpolation)]
else:
# Resize the shortest edge to matching target dim for non-square target
tfl = [T.Resize(scale_size)]
tfl += [T.CenterCrop(size)]
tfl += [
T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize(
mean=torch.tensor(mean),
std=torch.tensor(std),
),
]
return T.Compose(tfl)
# Classification training augmentations --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def classify_augmentations(
size=224,
mean=DEFAULT_MEAN,
std=DEFAULT_STD,
scale=None,
ratio=None,
hflip=0.5,
vflip=0.0,
auto_augment=None,
hsv_h=0.015, # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
hsv_s=0.4, # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
hsv_v=0.4, # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
force_color_jitter=False,
erasing=0.0,
interpolation=Image.BILINEAR,
):
"""
Classification transforms with augmentation for training. Inspired by timm/data/transforms_factory.py.
Args:
size (int): image size
scale (tuple): scale range of the image. default is (0.08, 1.0)
ratio (tuple): aspect ratio range of the image. default is (3./4., 4./3.)
mean (tuple): mean values of RGB channels
std (tuple): std values of RGB channels
hflip (float): probability of horizontal flip
vflip (float): probability of vertical flip
auto_augment (str): auto augmentation policy. can be 'randaugment', 'augmix', 'autoaugment' or None.
hsv_h (float): image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
hsv_s (float): image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
hsv_v (float): image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
force_color_jitter (bool): force to apply color jitter even if auto augment is enabled
erasing (float): probability of random erasing
interpolation (T.InterpolationMode): interpolation mode. default is T.InterpolationMode.BILINEAR.
Returns:
(T.Compose): torchvision transforms
"""
# Transforms to apply if Albumentations not installed
import torchvision.transforms as T # scope for faster 'import ultralytics'
if not isinstance(size, int):
raise TypeError(f"classify_transforms() size {size} must be integer, not (list, tuple)")
scale = tuple(scale or (0.08, 1.0)) # default imagenet scale range
ratio = tuple(ratio or (3.0 / 4.0, 4.0 / 3.0)) # default imagenet ratio range
primary_tfl = [T.RandomResizedCrop(size, scale=scale, ratio=ratio, interpolation=interpolation)]
if hflip > 0.0:
primary_tfl += [T.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=hflip)]
if vflip > 0.0:
primary_tfl += [T.RandomVerticalFlip(p=vflip)]
secondary_tfl = []
disable_color_jitter = False
if auto_augment:
assert isinstance(auto_augment, str)
# color jitter is typically disabled if AA/RA on,
# this allows override without breaking old hparm cfgs
disable_color_jitter = not force_color_jitter
if auto_augment == "randaugment":
if TORCHVISION_0_11:
secondary_tfl += [T.RandAugment(interpolation=interpolation)]
else:
LOGGER.warning('"auto_augment=randaugment" requires torchvision >= 0.11.0. Disabling it.')
elif auto_augment == "augmix":
if TORCHVISION_0_13:
secondary_tfl += [T.AugMix(interpolation=interpolation)]
else:
LOGGER.warning('"auto_augment=augmix" requires torchvision >= 0.13.0. Disabling it.')
elif auto_augment == "autoaugment":
if TORCHVISION_0_10:
secondary_tfl += [T.AutoAugment(interpolation=interpolation)]
else:
LOGGER.warning('"auto_augment=autoaugment" requires torchvision >= 0.10.0. Disabling it.')
else:
raise ValueError(
f'Invalid auto_augment policy: {auto_augment}. Should be one of "randaugment", '
f'"augmix", "autoaugment" or None'
)
if not disable_color_jitter:
secondary_tfl += [T.ColorJitter(brightness=hsv_v, contrast=hsv_v, saturation=hsv_s, hue=hsv_h)]
final_tfl = [
T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize(mean=torch.tensor(mean), std=torch.tensor(std)),
T.RandomErasing(p=erasing, inplace=True),
]
return T.Compose(primary_tfl + secondary_tfl + final_tfl)

class ClassifyLetterBox
# NOTE: keep this class for backward compatibility
class ClassifyLetterBox:
"""
YOLOv8 LetterBox class for image preprocessing, designed to be part of a transformation pipeline, e.g.,
T.Compose([LetterBox(size), ToTensor()]).
Attributes:
h (int): Target height of the image.
w (int): Target width of the image.
auto (bool): If True, automatically solves for short side using stride.
stride (int): The stride value, used when 'auto' is True.
"""
def __init__(self, size=(640, 640), auto=False, stride=32):
"""
Initializes the ClassifyLetterBox class with a target size, auto-flag, and stride.
Args:
size (Union[int, Tuple[int, int]]): The target dimensions (height, width) for the letterbox.
auto (bool): If True, automatically calculates the short side based on stride.
stride (int): The stride value, used when 'auto' is True.
"""
super().__init__()
self.h, self.w = (size, size) if isinstance(size, int) else size
self.auto = auto # pass max size integer, automatically solve for short side using stride
self.stride = stride # used with auto
def __call__(self, im):
"""
Resizes the image and pads it with a letterbox method.
Args:
im (numpy.ndarray): The input image as a numpy array of shape HWC.
Returns:
(numpy.ndarray): The letterboxed and resized image as a numpy array.
"""
imh, imw = im.shape[:2]
r = min(self.h / imh, self.w / imw) # ratio of new/old dimensions
h, w = round(imh * r), round(imw * r) # resized image dimensions
# Calculate padding dimensions
hs, ws = (math.ceil(x / self.stride) * self.stride for x in (h, w)) if self.auto else (self.h, self.w)
top, left = round((hs - h) / 2 - 0.1), round((ws - w) / 2 - 0.1)
# Create padded image
im_out = np.full((hs, ws, 3), 114, dtype=im.dtype)
im_out[top : top + h, left : left + w] = cv2.resize(im, (w, h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
return im_out

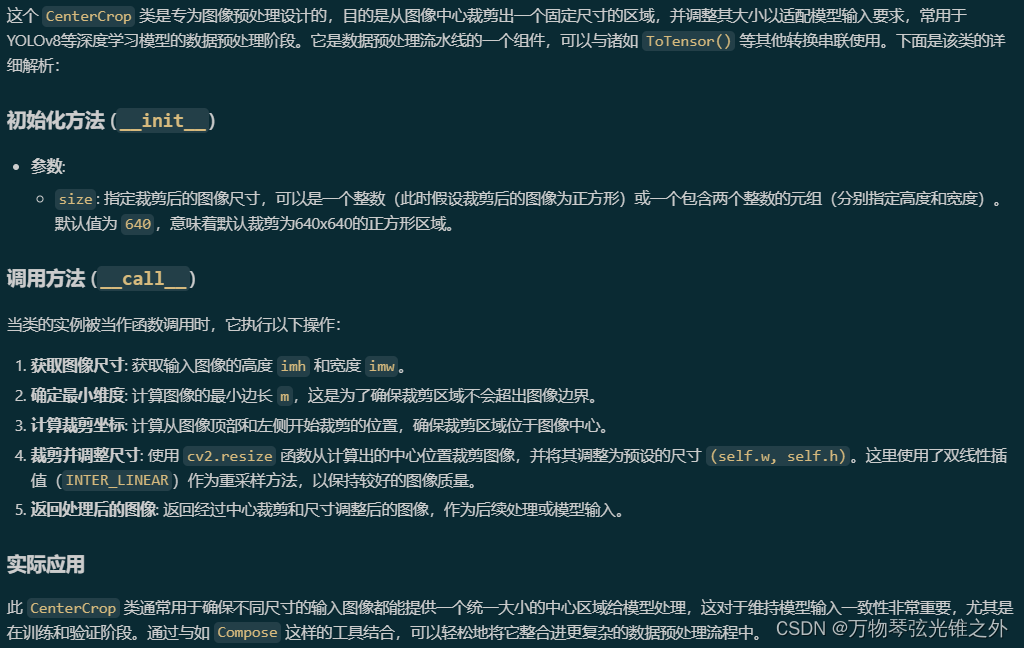
class CenterCrop
# NOTE: keep this class for backward compatibility
class CenterCrop:
"""YOLOv8 CenterCrop class for image preprocessing, designed to be part of a transformation pipeline, e.g.,
T.Compose([CenterCrop(size), ToTensor()]).
"""
def __init__(self, size=640):
"""Converts an image from numpy array to PyTorch tensor."""
super().__init__()
self.h, self.w = (size, size) if isinstance(size, int) else size
def __call__(self, im):
"""
Resizes and crops the center of the image using a letterbox method.
Args:
im (numpy.ndarray): The input image as a numpy array of shape HWC.
Returns:
(numpy.ndarray): The center-cropped and resized image as a numpy array.
"""
imh, imw = im.shape[:2]
m = min(imh, imw) # min dimension
top, left = (imh - m) // 2, (imw - m) // 2
return cv2.resize(im[top : top + m, left : left + m], (self.w, self.h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
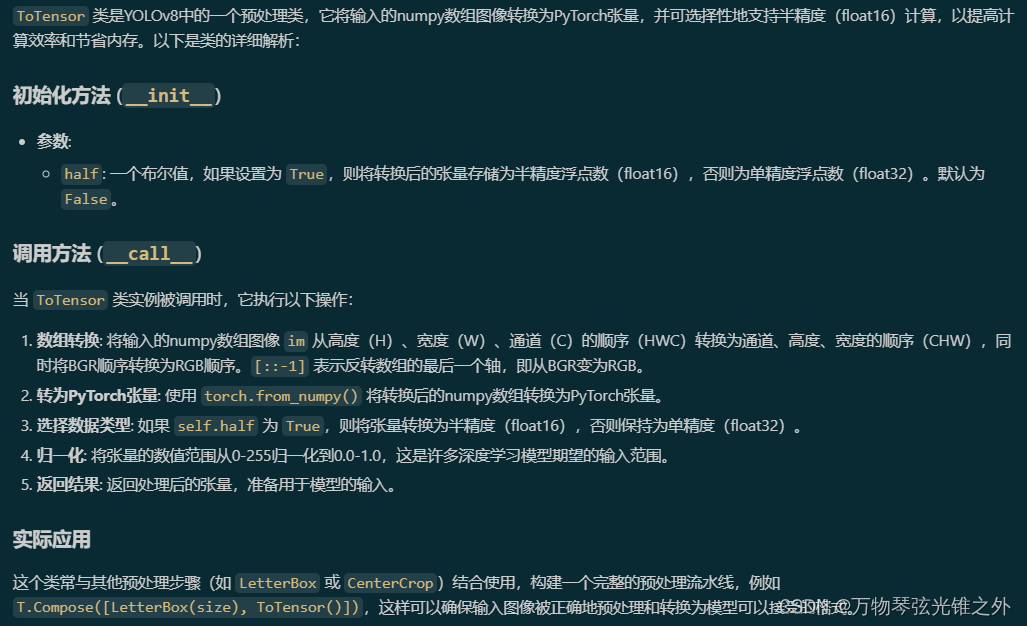
class ToTensor
# NOTE: keep this class for backward compatibility
class ToTensor:
"""YOLOv8 ToTensor class for image preprocessing, i.e., T.Compose([LetterBox(size), ToTensor()])."""
def __init__(self, half=False):
"""Initialize YOLOv8 ToTensor object with optional half-precision support."""
super().__init__()
self.half = half
def __call__(self, im):
"""
Transforms an image from a numpy array to a PyTorch tensor, applying optional half-precision and normalization.
Args:
im (numpy.ndarray): Input image as a numpy array with shape (H, W, C) in BGR order.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The transformed image as a PyTorch tensor in float32 or float16, normalized to [0, 1].
"""
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1]) # HWC to CHW -> BGR to RGB -> contiguous
im = torch.from_numpy(im) # to torch
im = im.half() if self.half else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
im /= 255.0 # 0-255 to 0.0-1.0
return im
base.py
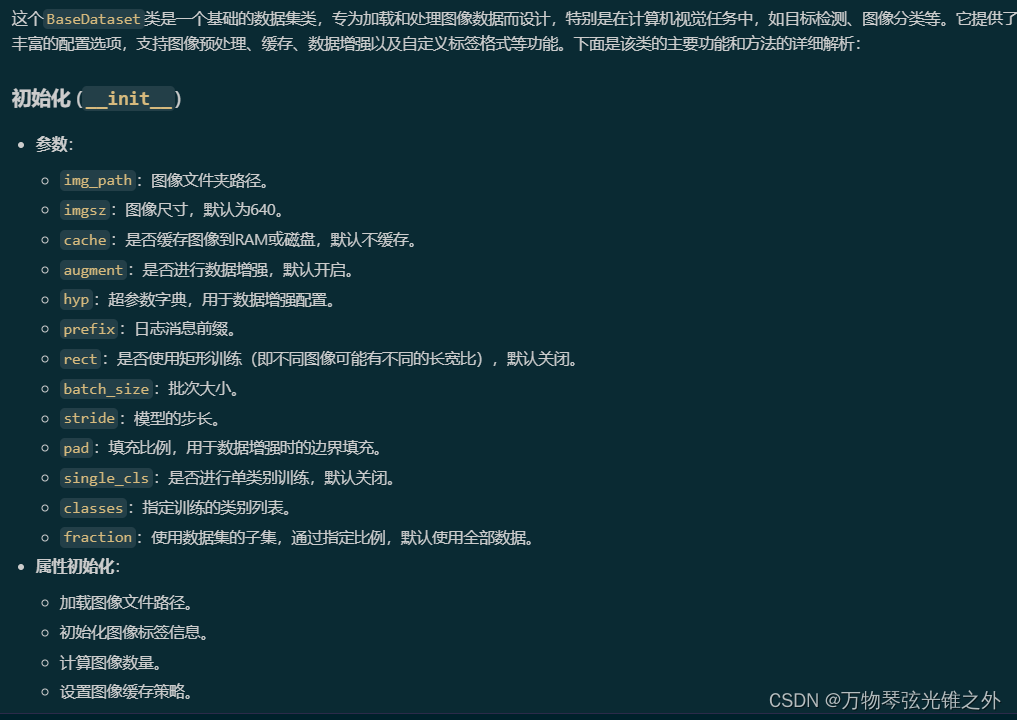
class BaseDataset
class BaseDataset(Dataset):
"""
Base dataset class for loading and processing image data.
Args:
img_path (str): Path to the folder containing images.
imgsz (int, optional): Image size. Defaults to 640.
cache (bool, optional): Cache images to RAM or disk during training. Defaults to False.
augment (bool, optional): If True, data augmentation is applied. Defaults to True.
hyp (dict, optional): Hyperparameters to apply data augmentation. Defaults to None.
prefix (str, optional): Prefix to print in log messages. Defaults to ''.
rect (bool, optional): If True, rectangular training is used. Defaults to False.
batch_size (int, optional): Size of batches. Defaults to None.
stride (int, optional): Stride. Defaults to 32.
pad (float, optional): Padding. Defaults to 0.0.
single_cls (bool, optional): If True, single class training is used. Defaults to False.
classes (list): List of included classes. Default is None.
fraction (float): Fraction of dataset to utilize. Default is 1.0 (use all data).
Attributes:
im_files (list): List of image file paths.
labels (list): List of label data dictionaries.
ni (int): Number of images in the dataset.
ims (list): List of loaded images.
npy_files (list): List of numpy file paths.
transforms (callable): Image transformation function.
"""
def __init__(
self,
img_path,
imgsz=640,
cache=False,
augment=True,
hyp=DEFAULT_CFG,
prefix="",
rect=False,
batch_size=16,
stride=32,
pad=0.5,
single_cls=False,
classes=None,
fraction=1.0,
):
"""Initialize BaseDataset with given configuration and options."""
super().__init__()
self.img_path = img_path
self.imgsz = imgsz
self.augment = augment
self.single_cls = single_cls
self.prefix = prefix
self.fraction = fraction
self.im_files = self.get_img_files(self.img_path)
self.labels = self.get_labels()
self.update_labels(include_class=classes) # single_cls and include_class
self.ni = len(self.labels) # number of images
self.rect = rect
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.stride = stride
self.pad = pad
if self.rect:
assert self.batch_size is not None
self.set_rectangle()
# Buffer thread for mosaic images
self.buffer = [] # buffer size = batch size
self.max_buffer_length = min((self.ni, self.batch_size * 8, 1000)) if self.augment else 0
# Cache images (options are cache = True, False, None, "ram", "disk")
self.ims, self.im_hw0, self.im_hw = [None] * self.ni, [None] * self.ni, [None] * self.ni
self.npy_files = [Path(f).with_suffix(".npy") for f in self.im_files]
self.cache = cache.lower() if isinstance(cache, str) else "ram" if cache is True else None
if (self.cache == "ram" and self.check_cache_ram()) or self.cache == "disk":
self.cache_images()
# Transforms
self.transforms = self.build_transforms(hyp=hyp)
def get_img_files(self, img_path):
"""Read image files."""
try:
f = [] # image files
for p in img_path if isinstance(img_path, list) else [img_path]:
p = Path(p) # os-agnostic
if p.is_dir(): # dir
f += glob.glob(str(p / "**" / "*.*"), recursive=True)
# F = list(p.rglob('*.*')) # pathlib
elif p.is_file(): # file
with open(p) as t:
t = t.read().strip().splitlines()
parent = str(p.parent) + os.sep
f += [x.replace("./", parent) if x.startswith("./") else x for x in t] # local to global path
# F += [p.parent / x.lstrip(os.sep) for x in t] # local to global path (pathlib)
else:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"{self.prefix}{p} does not exist")
im_files = sorted(x.replace("/", os.sep) for x in f if x.split(".")[-1].lower() in IMG_FORMATS)
# self.img_files = sorted([x for x in f if x.suffix[1:].lower() in IMG_FORMATS]) # pathlib
assert im_files, f"{self.prefix}No images found in {img_path}. {FORMATS_HELP_MSG}"
except Exception as e:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"{self.prefix}Error loading data from {img_path}\n{HELP_URL}") from e
if self.fraction < 1:
im_files = im_files[: round(len(im_files) * self.fraction)] # retain a fraction of the dataset
return im_files
def update_labels(self, include_class: Optional[list]):
"""Update labels to include only these classes (optional)."""
include_class_array = np.array(include_class).reshape(1, -1)
for i in range(len(self.labels)):
if include_class is not None:
cls = self.labels[i]["cls"]
bboxes = self.labels[i]["bboxes"]
segments = self.labels[i]["segments"]
keypoints = self.labels[i]["keypoints"]
j = (cls == include_class_array).any(1)
self.labels[i]["cls"] = cls[j]
self.labels[i]["bboxes"] = bboxes[j]
if segments:
self.labels[i]["segments"] = [segments[si] for si, idx in enumerate(j) if idx]
if keypoints is not None:
self.labels[i]["keypoints"] = keypoints[j]
if self.single_cls:
self.labels[i]["cls"][:, 0] = 0
def load_image(self, i, rect_mode=True):
"""Loads 1 image from dataset index 'i', returns (im, resized hw)."""
im, f, fn = self.ims[i], self.im_files[i], self.npy_files[i]
if im is None: # not cached in RAM
if fn.exists(): # load npy
try:
im = np.load(fn)
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.warning(f"{self.prefix}WARNING ⚠️ Removing corrupt *.npy image file {fn} due to: {e}")
Path(fn).unlink(missing_ok=True)
im = cv2.imread(f) # BGR
else: # read image
im = cv2.imread(f) # BGR
if im is None:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Image Not Found {f}")
h0, w0 = im.shape[:2] # orig hw
if rect_mode: # resize long side to imgsz while maintaining aspect ratio
r = self.imgsz / max(h0, w0) # ratio
if r != 1: # if sizes are not equal
w, h = (min(math.ceil(w0 * r), self.imgsz), min(math.ceil(h0 * r), self.imgsz))
im = cv2.resize(im, (w, h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
elif not (h0 == w0 == self.imgsz): # resize by stretching image to square imgsz
im = cv2.resize(im, (self.imgsz, self.imgsz), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# Add to buffer if training with augmentations
if self.augment:
self.ims[i], self.im_hw0[i], self.im_hw[i] = im, (h0, w0), im.shape[:2] # im, hw_original, hw_resized
self.buffer.append(i)
if 1 < len(self.buffer) >= self.max_buffer_length: # prevent empty buffer
j = self.buffer.pop(0)
if self.cache != "ram":
self.ims[j], self.im_hw0[j], self.im_hw[j] = None, None, None
return im, (h0, w0), im.shape[:2]
return self.ims[i], self.im_hw0[i], self.im_hw[i]
def cache_images(self):
"""Cache images to memory or disk."""
b, gb = 0, 1 << 30 # bytes of cached images, bytes per gigabytes
fcn, storage = (self.cache_images_to_disk, "Disk") if self.cache == "disk" else (self.load_image, "RAM")
with ThreadPool(NUM_THREADS) as pool:
results = pool.imap(fcn, range(self.ni))
pbar = TQDM(enumerate(results), total=self.ni, disable=LOCAL_RANK > 0)
for i, x in pbar:
if self.cache == "disk":
b += self.npy_files[i].stat().st_size
else: # 'ram'
self.ims[i], self.im_hw0[i], self.im_hw[i] = x # im, hw_orig, hw_resized = load_image(self, i)
b += self.ims[i].nbytes
pbar.desc = f"{self.prefix}Caching images ({b / gb:.1f}GB {storage})"
pbar.close()
def cache_images_to_disk(self, i):
"""Saves an image as an *.npy file for faster loading."""
f = self.npy_files[i]
if not f.exists():
np.save(f.as_posix(), cv2.imread(self.im_files[i]), allow_pickle=False)
def check_cache_ram(self, safety_margin=0.5):
"""Check image caching requirements vs available memory."""
b, gb = 0, 1 << 30 # bytes of cached images, bytes per gigabytes
n = min(self.ni, 30) # extrapolate from 30 random images
for _ in range(n):
im = cv2.imread(random.choice(self.im_files)) # sample image
ratio = self.imgsz / max(im.shape[0], im.shape[1]) # max(h, w) # ratio
b += im.nbytes * ratio**2
mem_required = b * self.ni / n * (1 + safety_margin) # GB required to cache dataset into RAM
mem = psutil.virtual_memory()
success = mem_required < mem.available # to cache or not to cache, that is the question
if not success:
self.cache = None
LOGGER.info(
f"{self.prefix}{mem_required / gb:.1f}GB RAM required to cache images "
f"with {int(safety_margin * 100)}% safety margin but only "
f"{mem.available / gb:.1f}/{mem.total / gb:.1f}GB available, not caching images ⚠️"
)
return success
def set_rectangle(self):
"""Sets the shape of bounding boxes for YOLO detections as rectangles."""
bi = np.floor(np.arange(self.ni) / self.batch_size).astype(int) # batch index
nb = bi[-1] + 1 # number of batches
s = np.array([x.pop("shape") for x in self.labels]) # hw
ar = s[:, 0] / s[:, 1] # aspect ratio
irect = ar.argsort()
self.im_files = [self.im_files[i] for i in irect]
self.labels = [self.labels[i] for i in irect]
ar = ar[irect]
# Set training image shapes
shapes = [[1, 1]] * nb
for i in range(nb):
ari = ar[bi == i]
mini, maxi = ari.min(), ari.max()
if maxi < 1:
shapes[i] = [maxi, 1]
elif mini > 1:
shapes[i] = [1, 1 / mini]
self.batch_shapes = np.ceil(np.array(shapes) * self.imgsz / self.stride + self.pad).astype(int) * self.stride
self.batch = bi # batch index of image
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""Returns transformed label information for given index."""
return self.transforms(self.get_image_and_label(index))
def get_image_and_label(self, index):
"""Get and return label information from the dataset."""
label = deepcopy(self.labels[index]) # requires deepcopy() https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/pull/1948
label.pop("shape", None) # shape is for rect, remove it
label["img"], label["ori_shape"], label["resized_shape"] = self.load_image(index)
label["ratio_pad"] = (
label["resized_shape"][0] / label["ori_shape"][0],
label["resized_shape"][1] / label["ori_shape"][1],
) # for evaluation
if self.rect:
label["rect_shape"] = self.batch_shapes[self.batch[index]]
return self.update_labels_info(label)
def __len__(self):
"""Returns the length of the labels list for the dataset."""
return len(self.labels)
def update_labels_info(self, label):
"""Custom your label format here."""
return label
def build_transforms(self, hyp=None):
"""
Users can customize augmentations here.
Example:
```python
if self.augment:
# Training transforms
return Compose([])
else:
# Val transforms
return Compose([])
```
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def get_labels(self):
"""
Users can customize their own format here.
Note:
Ensure output is a dictionary with the following keys:
```python
dict(
im_file=im_file,
shape=shape, # format: (height, width)
cls=cls,
bboxes=bboxes, # xywh
segments=segments, # xy
keypoints=keypoints, # xy
normalized=True, # or False
bbox_format="xyxy", # or xywh, ltwh
)
```
"""
raise NotImplementedError

bulid.py
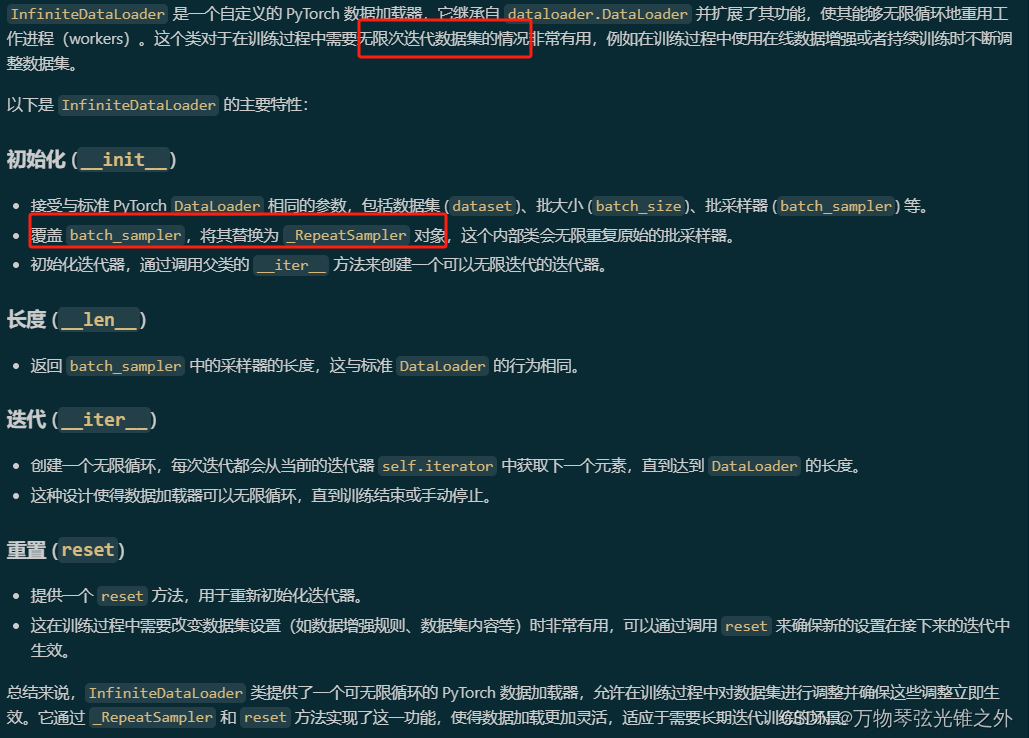
class InfiniteDataLoader
class InfiniteDataLoader(dataloader.DataLoader):
"""
Dataloader that reuses workers.
Uses same syntax as vanilla DataLoader.
"""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""Dataloader that infinitely recycles workers, inherits from DataLoader."""
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
object.__setattr__(self, "batch_sampler", _RepeatSampler(self.batch_sampler))
self.iterator = super().__iter__()
def __len__(self):
"""Returns the length of the batch sampler's sampler."""
return len(self.batch_sampler.sampler)
def __iter__(self):
"""Creates a sampler that repeats indefinitely."""
for _ in range(len(self)):
yield next(self.iterator)
def reset(self):
"""
Reset iterator.
This is useful when we want to modify settings of dataset while training.
"""
self.iterator = self._get_iterator()
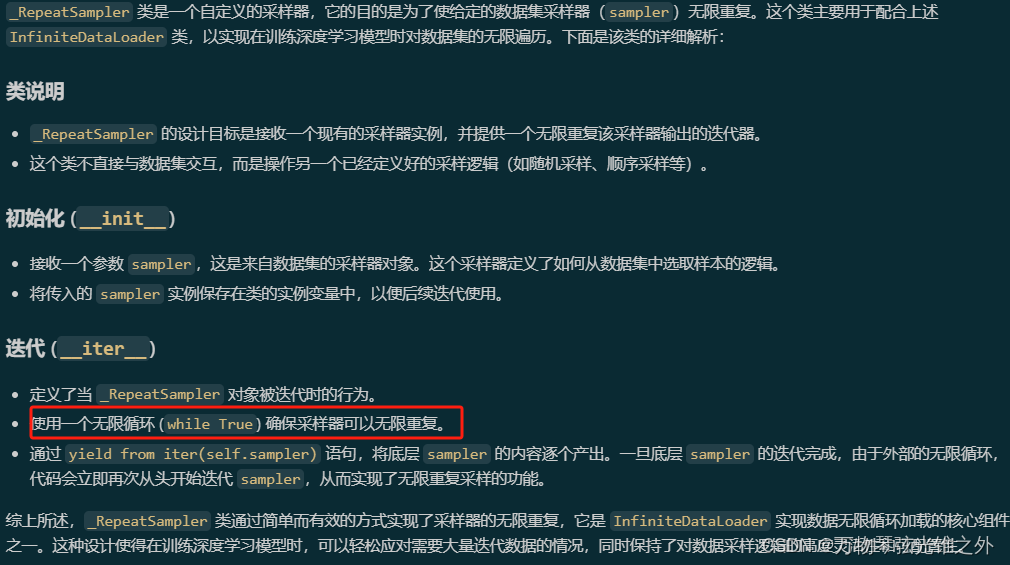
class _RepeatSampler
class _RepeatSampler:
"""
Sampler that repeats forever.
Args:
sampler (Dataset.sampler): The sampler to repeat.
"""
def __init__(self, sampler):
"""Initializes an object that repeats a given sampler indefinitely."""
self.sampler = sampler
def __iter__(self):
"""Iterates over the 'sampler' and yields its contents."""
while True:
yield from iter(self.sampler)
def seed_worker(worker_id): # noqa
"""Set dataloader worker seed https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#dataloader."""
worker_seed = torch.initial_seed() % 2**32
np.random.seed(worker_seed)
random.seed(worker_seed)
def build_yolo_dataset(cfg, img_path, batch, data, mode="train", rect=False, stride=32, multi_modal=False):
"""Build YOLO Dataset."""
dataset = YOLOMultiModalDataset if multi_modal else YOLODataset
return dataset(
img_path=img_path,
imgsz=cfg.imgsz,
batch_size=batch,
augment=mode == "train", # augmentation
hyp=cfg, # TODO: probably add a get_hyps_from_cfg function
rect=cfg.rect or rect, # rectangular batches
cache=cfg.cache or None,
single_cls=cfg.single_cls or False,
stride=int(stride),
pad=0.0 if mode == "train" else 0.5,
prefix=colorstr(f"{mode}: "),
task=cfg.task,
classes=cfg.classes,
data=data,
fraction=cfg.fraction if mode == "train" else 1.0,
)
def build_grounding(cfg, img_path, json_file, batch, mode="train", rect=False, stride=32):
"""Build YOLO Dataset."""
return GroundingDataset(
img_path=img_path,
json_file=json_file,
imgsz=cfg.imgsz,
batch_size=batch,
augment=mode == "train", # augmentation
hyp=cfg, # TODO: probably add a get_hyps_from_cfg function
rect=cfg.rect or rect, # rectangular batches
cache=cfg.cache or None,
single_cls=cfg.single_cls or False,
stride=int(stride),
pad=0.0 if mode == "train" else 0.5,
prefix=colorstr(f"{mode}: "),
task=cfg.task,
classes=cfg.classes,
fraction=cfg.fraction if mode == "train" else 1.0,
)
def build_dataloader(dataset, batch, workers, shuffle=True, rank=-1):
"""Return an InfiniteDataLoader or DataLoader for training or validation set."""
batch = min(batch, len(dataset))
nd = torch.cuda.device_count() # number of CUDA devices
nw = min([os.cpu_count() // max(nd, 1), workers]) # number of workers
sampler = None if rank == -1 else distributed.DistributedSampler(dataset, shuffle=shuffle)
generator = torch.Generator()
generator.manual_seed(6148914691236517205 + RANK)
return InfiniteDataLoader(
dataset=dataset,
batch_size=batch,
shuffle=shuffle and sampler is None,
num_workers=nw,
sampler=sampler,
pin_memory=PIN_MEMORY,
collate_fn=getattr(dataset, "collate_fn", None),
worker_init_fn=seed_worker,
generator=generator,
)
def check_source(source):
"""Check source type and return corresponding flag values."""
webcam, screenshot, from_img, in_memory, tensor = False, False, False, False, False
if isinstance(source, (str, int, Path)): # int for local usb camera
source = str(source)
is_file = Path(source).suffix[1:] in (IMG_FORMATS | VID_FORMATS)
is_url = source.lower().startswith(("https://", "http://", "rtsp://", "rtmp://", "tcp://"))
webcam = source.isnumeric() or source.endswith(".streams") or (is_url and not is_file)
screenshot = source.lower() == "screen"
if is_url and is_file:
source = check_file(source) # download
elif isinstance(source, LOADERS):
in_memory = True
elif isinstance(source, (list, tuple)):
source = autocast_list(source) # convert all list elements to PIL or np arrays
from_img = True
elif isinstance(source, (Image.Image, np.ndarray)):
from_img = True
elif isinstance(source, torch.Tensor):
tensor = True
else:
raise TypeError("Unsupported image type. For supported types see https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/predict")
return source, webcam, screenshot, from_img, in_memory, tensor
def load_inference_source(source=None, batch=1, vid_stride=1, buffer=False):
"""
Loads an inference source for object detection and applies necessary transformations.
Args:
source (str, Path, Tensor, PIL.Image, np.ndarray): The input source for inference.
batch (int, optional): Batch size for dataloaders. Default is 1.
vid_stride (int, optional): The frame interval for video sources. Default is 1.
buffer (bool, optional): Determined whether stream frames will be buffered. Default is False.
Returns:
dataset (Dataset): A dataset object for the specified input source.
"""
source, stream, screenshot, from_img, in_memory, tensor = check_source(source)
source_type = source.source_type if in_memory else SourceTypes(stream, screenshot, from_img, tensor)
# Dataloader
if tensor:
dataset = LoadTensor(source)
elif in_memory:
dataset = source
elif stream:
dataset = LoadStreams(source, vid_stride=vid_stride, buffer=buffer)
elif screenshot:
dataset = LoadScreenshots(source)
elif from_img:
dataset = LoadPilAndNumpy(source)
else:
dataset = LoadImagesAndVideos(source, batch=batch, vid_stride=vid_stride)
# Attach source types to the dataset
setattr(dataset, "source_type", source_type)
return dataset

dataset.py
class YOLODataset
class YOLODataset(BaseDataset):
"""
Dataset class for loading object detection and/or segmentation labels in YOLO format.
Args:
data (dict, optional): A dataset YAML dictionary. Defaults to None.
task (str): An explicit arg to point current task, Defaults to 'detect'.
Returns:
(torch.utils.data.Dataset): A PyTorch dataset object that can be used for training an object detection model.
"""
def __init__(self, *args, data=None, task="detect", **kwargs):
"""Initializes the YOLODataset with optional configurations for segments and keypoints."""
self.use_segments = task == "segment"
self.use_keypoints = task == "pose"
self.use_obb = task == "obb"
self.data = data
assert not (self.use_segments and self.use_keypoints), "Can not use both segments and keypoints."
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
def cache_labels(self, path=Path("./labels.cache")):
"""
Cache dataset labels, check images and read shapes.
Args:
path (Path): Path where to save the cache file. Default is Path('./labels.cache').
Returns:
(dict): labels.
"""
x = {"labels": []}
nm, nf, ne, nc, msgs = 0, 0, 0, 0, [] # number missing, found, empty, corrupt, messages
desc = f"{self.prefix}Scanning {path.parent / path.stem}..."
total = len(self.im_files)
nkpt, ndim = self.data.get("kpt_shape", (0, 0))
if self.use_keypoints and (nkpt <= 0 or ndim not in {2, 3}):
raise ValueError(
"'kpt_shape' in data.yaml missing or incorrect. Should be a list with [number of "
"keypoints, number of dims (2 for x,y or 3 for x,y,visible)], i.e. 'kpt_shape: [17, 3]'"
)
with ThreadPool(NUM_THREADS) as pool:
results = pool.imap(
func=verify_image_label,
iterable=zip(
self.im_files,
self.label_files,
repeat(self.prefix),
repeat(self.use_keypoints),
repeat(len(self.data["names"])),
repeat(nkpt),
repeat(ndim),
),
)
pbar = TQDM(results, desc=desc, total=total)
for im_file, lb, shape, segments, keypoint, nm_f, nf_f, ne_f, nc_f, msg in pbar:
nm += nm_f
nf += nf_f
ne += ne_f
nc += nc_f
if im_file:
x["labels"].append(
{
"im_file": im_file,
"shape": shape,
"cls": lb[:, 0:1], # n, 1
"bboxes": lb[:, 1:], # n, 4
"segments": segments,
"keypoints": keypoint,
"normalized": True,
"bbox_format": "xywh",
}
)
if msg:
msgs.append(msg)
pbar.desc = f"{desc} {nf} images, {nm + ne} backgrounds, {nc} corrupt"
pbar.close()
if msgs:
LOGGER.info("\n".join(msgs))
if nf == 0:
LOGGER.warning(f"{self.prefix}WARNING ⚠️ No labels found in {path}. {HELP_URL}")
x["hash"] = get_hash(self.label_files + self.im_files)
x["results"] = nf, nm, ne, nc, len(self.im_files)
x["msgs"] = msgs # warnings
save_dataset_cache_file(self.prefix, path, x, DATASET_CACHE_VERSION)
return x
def get_labels(self):
"""Returns dictionary of labels for YOLO training."""
self.label_files = img2label_paths(self.im_files)
cache_path = Path(self.label_files[0]).parent.with_suffix(".cache")
try:
cache, exists = load_dataset_cache_file(cache_path), True # attempt to load a *.cache file
assert cache["version"] == DATASET_CACHE_VERSION # matches current version
assert cache["hash"] == get_hash(self.label_files + self.im_files) # identical hash
except (FileNotFoundError, AssertionError, AttributeError):
cache, exists = self.cache_labels(cache_path), False # run cache ops
# Display cache
nf, nm, ne, nc, n = cache.pop("results") # found, missing, empty, corrupt, total
if exists and LOCAL_RANK in {-1, 0}:
d = f"Scanning {cache_path}... {nf} images, {nm + ne} backgrounds, {nc} corrupt"
TQDM(None, desc=self.prefix + d, total=n, initial=n) # display results
if cache["msgs"]:
LOGGER.info("\n".join(cache["msgs"])) # display warnings
# Read cache
[cache.pop(k) for k in ("hash", "version", "msgs")] # remove items
labels = cache["labels"]
if not labels:
LOGGER.warning(f"WARNING ⚠️ No images found in {cache_path}, training may not work correctly. {HELP_URL}")
self.im_files = [lb["im_file"] for lb in labels] # update im_files
# Check if the dataset is all boxes or all segments
lengths = ((len(lb["cls"]), len(lb["bboxes"]), len(lb["segments"])) for lb in labels)
len_cls, len_boxes, len_segments = (sum(x) for x in zip(*lengths))
if len_segments and len_boxes != len_segments:
LOGGER.warning(
f"WARNING ⚠️ Box and segment counts should be equal, but got len(segments) = {len_segments}, "
f"len(boxes) = {len_boxes}. To resolve this only boxes will be used and all segments will be removed. "
"To avoid this please supply either a detect or segment dataset, not a detect-segment mixed dataset."
)
for lb in labels:
lb["segments"] = []
if len_cls == 0:
LOGGER.warning(f"WARNING ⚠️ No labels found in {cache_path}, training may not work correctly. {HELP_URL}")
return labels
def build_transforms(self, hyp=None):
"""Builds and appends transforms to the list."""
if self.augment:
hyp.mosaic = hyp.mosaic if self.augment and not self.rect else 0.0
hyp.mixup = hyp.mixup if self.augment and not self.rect else 0.0
transforms = v8_transforms(self, self.imgsz, hyp)
else:
transforms = Compose([LetterBox(new_shape=(self.imgsz, self.imgsz), scaleup=False)])
transforms.append(
Format(
bbox_format="xywh",
normalize=True,
return_mask=self.use_segments,
return_keypoint=self.use_keypoints,
return_obb=self.use_obb,
batch_idx=True,
mask_ratio=hyp.mask_ratio,
mask_overlap=hyp.overlap_mask,
bgr=hyp.bgr if self.augment else 0.0, # only affect training.
)
)
return transforms
def close_mosaic(self, hyp):
"""Sets mosaic, copy_paste and mixup options to 0.0 and builds transformations."""
hyp.mosaic = 0.0 # set mosaic ratio=0.0
hyp.copy_paste = 0.0 # keep the same behavior as previous v8 close-mosaic
hyp.mixup = 0.0 # keep the same behavior as previous v8 close-mosaic
self.transforms = self.build_transforms(hyp)
def update_labels_info(self, label):
"""
Custom your label format here.
Note:
cls is not with bboxes now, classification and semantic segmentation need an independent cls label
Can also support classification and semantic segmentation by adding or removing dict keys there.
"""
bboxes = label.pop("bboxes")
segments = label.pop("segments", [])
keypoints = label.pop("keypoints", None)
bbox_format = label.pop("bbox_format")
normalized = label.pop("normalized")
# NOTE: do NOT resample oriented boxes
segment_resamples = 100 if self.use_obb else 1000
if len(segments) > 0:
# list[np.array(1000, 2)] * num_samples
# (N, 1000, 2)
segments = np.stack(resample_segments(segments, n=segment_resamples), axis=0)
else:
segments = np.zeros((0, segment_resamples, 2), dtype=np.float32)
label["instances"] = Instances(bboxes, segments, keypoints, bbox_format=bbox_format, normalized=normalized)
return label
@staticmethod
def collate_fn(batch):
"""Collates data samples into batches."""
new_batch = {}
keys = batch[0].keys()
values = list(zip(*[list(b.values()) for b in batch]))
for i, k in enumerate(keys):
value = values[i]
if k == "img":
value = torch.stack(value, 0)
if k in {"masks", "keypoints", "bboxes", "cls", "segments", "obb"}:
value = torch.cat(value, 0)
new_batch[k] = value
new_batch["batch_idx"] = list(new_batch["batch_idx"])
for i in range(len(new_batch["batch_idx"])):
new_batch["batch_idx"][i] += i # add target image index for build_targets()
new_batch["batch_idx"] = torch.cat(new_batch["batch_idx"], 0)
return new_batch
class YOLOMultiModalDataset(YOLODataset):
"""
Dataset class for loading object detection and/or segmentation labels in YOLO format.
Args:
data (dict, optional): A dataset YAML dictionary. Defaults to None.
task (str): An explicit arg to point current task, Defaults to 'detect'.
Returns:
(torch.utils.data.Dataset): A PyTorch dataset object that can be used for training an object detection model.
"""
def __init__(self, *args, data=None, task="detect", **kwargs):
"""Initializes a dataset object for object detection tasks with optional specifications."""
super().__init__(*args, data=data, task=task, **kwargs)
def update_labels_info(self, label):
"""Add texts information for multi modal model training."""
labels = super().update_labels_info(label)
# NOTE: some categories are concatenated with its synonyms by `/`.
labels["texts"] = [v.split("/") for _, v in self.data["names"].items()]
return labels
def build_transforms(self, hyp=None):
"""Enhances data transformations with optional text augmentation for multi-modal training."""
transforms = super().build_transforms(hyp)
if self.augment:
# NOTE: hard-coded the args for now.
transforms.insert(-1, RandomLoadText(max_samples=min(self.data["nc"], 80), padding=True))
return transforms


tips:
pool.imap