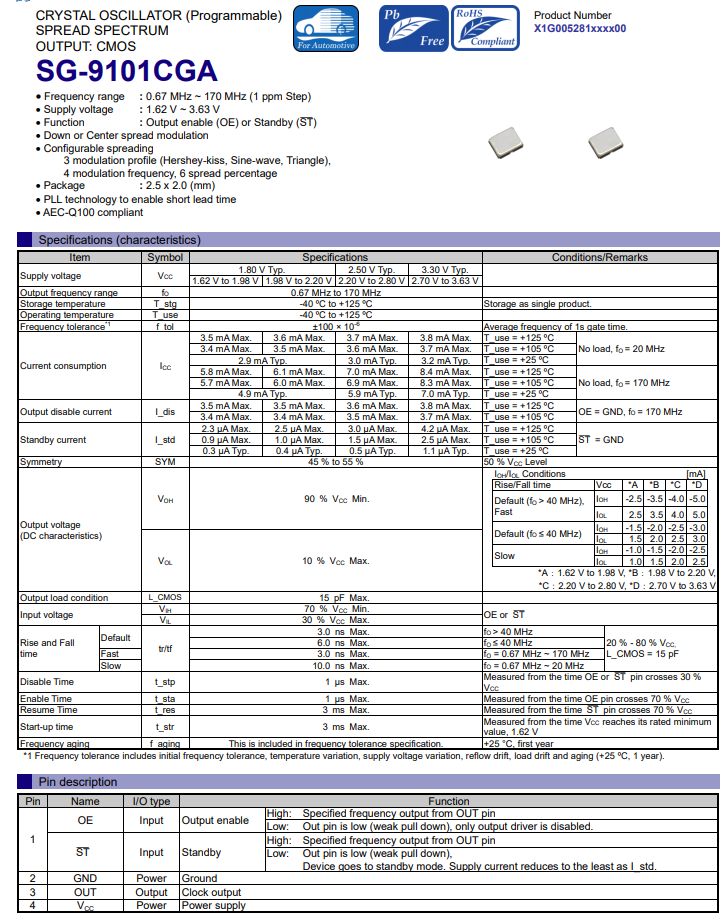
目录
实验要求
子网划分
配置IP地址
AS2内使用ospf协议配置全网通
配置
查看建邻情况
配置BGP协议
配置
测试
配置BGP反射器
宣告网段达成全网通
宣告
测试
构建VPN隧道
配置
测试
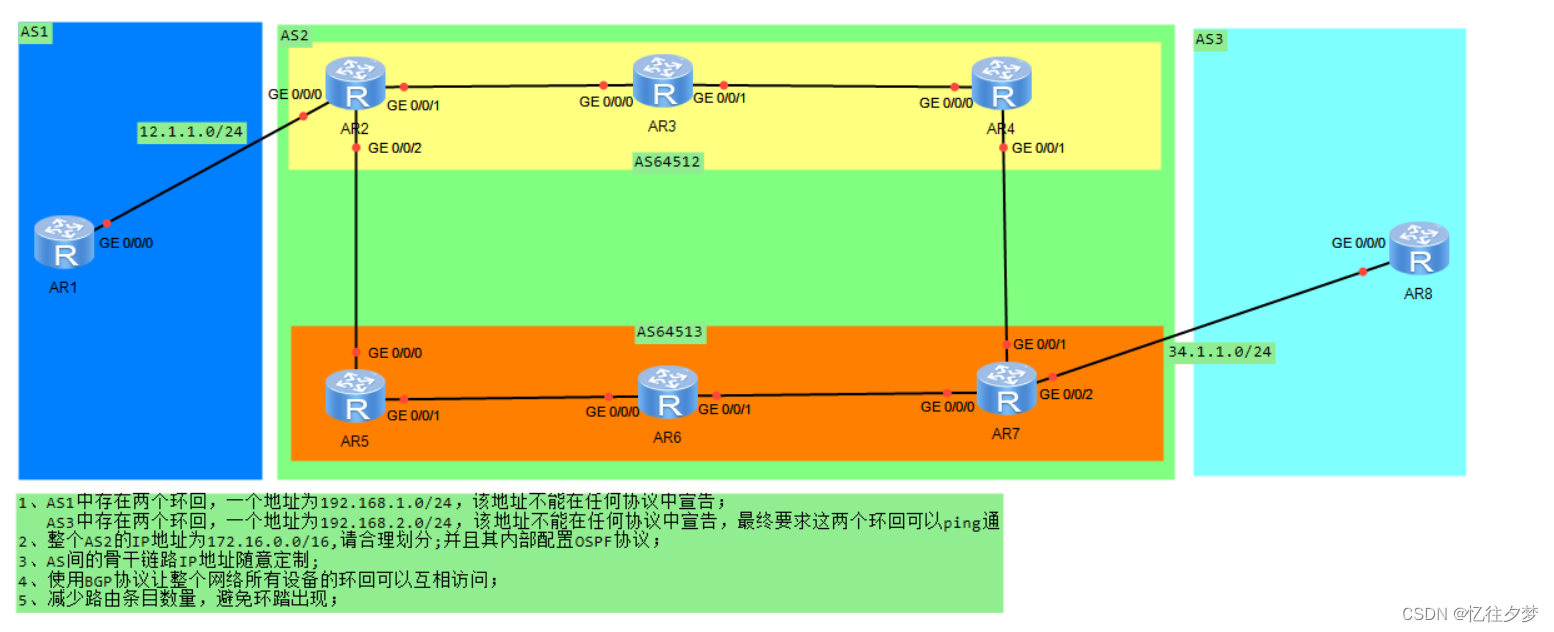
实验要求
1、AS 1中存在两个环回,一个地址为192.168.1.0/24,该地址不能在任何协议中宣告;
AS 3中存在两个环回,一个地址为192.168.2.0/24,该地址不能在任何协议中宣告,最终要求这两个环回可以ping通
2、整个AS 2的IP地址为172.16.0.0/16,请合理划分;并且其内部配置OSPF协议;
3、AS间的骨干链路IP地址随意定制;
4、使用BGP协议让整个网络所有设备的环回可以互相访问;
5、减少路由条目数量,避免环踏出现;
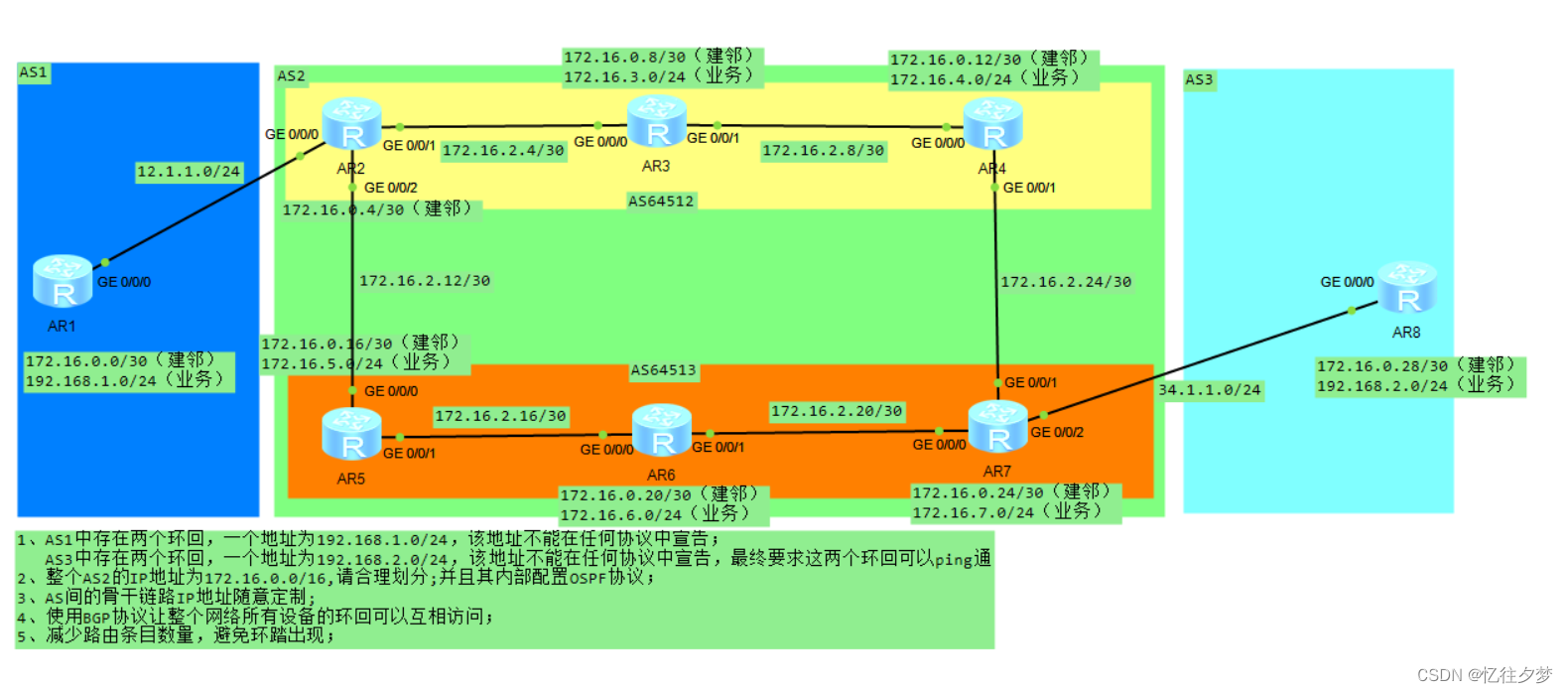
子网划分
在172.16.0.0/16网段进行子网的划分。
我们将骨干链路划分在一个网段,建邻地址划分在一个网段。需要两个网段。
业务网段各给一个网段。需要5个网段
直接将其划分到24位的掩码,需要7个网段:
172.16.0000 0000.0000 0000:
172.16.0000 0001.0 --- 建邻网段:172.16.1.0/24
建邻网段只需要一个IP,故直接使用30位掩码
172.16.1.0000 0000 --- 172.16.0.0/30:R1
172.16.1.0000 0100 --- 172.16.0.4/30:R2
172.16.1.0000 1000 --- 172.16.0.8/30:R3
172.16.1.0000 1100 --- 172.16.0.12/30:R4
172.16.1.0001 0000 --- 172.16.0.16/30:R5
172.16.1.0001 0100 --- 172.16.0.20/30:R6
172.16.1.0001 1000 --- 172.16.0.24/30:R7
172.16.1.0001 1100 --- 172.16.0.28/30:R8
172.16.0000 00010.0 --- 骨干链路:172.16.2.0/24
骨干链路也仅需要2个IP,故试用版30位的 掩码。
172.16.2.0000 0000 --- 172.16.2.0/30
172.16.2.0000 0100 --- 172.16.2.4/30:R2-R3
172.16.2.0000 1000 --- 172.16.2.8/30:R3-R4
172.16.2.0000 1100 --- 172.16.2.12/30:R2-R5
172.16.2.0001 0000 --- 172.16.2.16/30:R5-R6
172.16.2.0001 0100 --- 172.16.2.20/30:R6-R7
172.16.2.0001 1000 --- 172.16.2.24/30:R7-R8
172.16.0000 0011.0 --- R3业务网段:172.16.3.0/24
172.16.0000 0100.0 --- R4业务网段:172.16.4.0/24
172.16.0000 0101.0 --- R5业务网段:172.16.5.0/24
172.16.0000 0110.0 --- R6业务网段:172.16.6.0/24
172.16.0000 0111.0 --- R7业务网段:172.16.7.0/24
综上:
配置IP地址
R1:
<Huawei>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]sysname R1
[R1]int g0/0/0
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 12.1.1.1 24
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]
May 12 2024 16:52:28-08:00 R1 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[0]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 has entered the UP state.
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R1-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.0.1 30
[R1-LoopBack0]int l1
[R1-LoopBack1]ip add 192.168.1.1 24
[R1-LoopBack1]q
[R1]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 2
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 12.1.1.1/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.0.1/30 up up(s)
LoopBack1 192.168.1.1/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R1]R2:
<Huawei>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]sysname R2
[R2]int g0/0/0
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 12.1.1.2 24
May 12 2024 16:54:46-08:00 R2 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[0]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 has entered the UP state.
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g0/0/1
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.2.5 30
May 12 2024 16:55:09-08:00 R2 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[1]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 has entered the UP state.
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int l0
[R2-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.0.5 30
[R2-LoopBack0]q
[R2]int g 0/0/2
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]ip add 172.16.2.13 30
May 12 2024 17:47:19-08:00 R2 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[0]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 has entered the UP state.
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]q
[R2]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 0
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 0
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 12.1.1.2/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.2.5/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 172.16.2.13/30 up up
LoopBack0 172.16.0.5/30 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R2]R3:
<Huawei>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]sysname R3
[R3]int g0/0/0
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.2.6 30
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]
May 12 2024 16:56:57-08:00 R3 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[0]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 has entered the UP state.
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g0/0/1
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.2.9 30
May 12 2024 16:57:16-08:00 R3 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[1]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 has entered the UP state.
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int l0
[R3-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.0.9 30
[R3-LoopBack0]int l1
[R3-LoopBack1]ip add 172.16.3.3 24
[R3-LoopBack1]q
[R3]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 1
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 1
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.2.6/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.2.9/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.0.9/30 up up(s)
LoopBack1 172.16.3.3/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R3]R4:
<Huawei>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]sysname R4
[R4]int g0/0/0
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.2.10 30
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]
May 12 2024 16:59:17-08:00 R4 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[0]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 has entered the UP state.
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g0/0/1
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.2.25 30
May 12 2024 16:59:37-08:00 R4 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[1]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 has entered the UP state.
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int l0
[R4-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.0.13 30
[R4-LoopBack0]int l1
[R4-LoopBack1]ip add 172.16.4.4 24
[R4-LoopBack1]q
[R4]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 1
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 1
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.2.10/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.2.25/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.0.13/30 up up(s)
LoopBack1 172.16.4.4/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R4]R5:
<Huawei>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]sysname
May 12 2024 17:41:54-08:00 Huawei %%01IFPDT/4/IF_STATE(l)[0]:Interface GigabitEt
hernet0/0/0 has turned into UP state.
[Huawei]sysname R5
[R5]int g0/0/0
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.2.14 30
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]
May 12 2024 17:42:31-08:00 R5 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[1]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 has entered the UP state.
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g0/0/1
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.2.17 30
May 12 2024 17:42:49-08:00 R5 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[2]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 has entered the UP state.
[R5-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int l0
[R5-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.0.17 30
[R5-LoopBack0]int l1
[R5-LoopBack1]ip add 172.16.5.5 24
[R5-LoopBack1]q
[R5]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 1
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 1
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.2.14/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.2.17/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.0.17/30 up up(s)
LoopBack1 172.16.5.5/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R5]R6:
<Huawei>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]sysname R6
[R6]int g0/0/0
[R6-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.2.18 30
May 12 2024 17:44:36-08:00 R6 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[0]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 has entered the UP state.
[R6-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g0/0/1
[R6-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.2.21 30
May 12 2024 17:44:59-08:00 R6 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[1]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 has entered the UP state.
[R6-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int l0
[R6-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.0.21 30
[R6-LoopBack0]int l1
[R6-LoopBack1]ip add 172.16.6.6 24
[R6-LoopBack1]q
[R6]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 1
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 1
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.2.18/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.2.21/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.0.21/30 up up(s)
LoopBack1 172.16.6.6/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R6]R7:
<Huawei>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]sysname R7
[R7]int g0/0/0
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.2.22 30
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]
May 12 2024 17:49:46-08:00 R7 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[0]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 has entered the UP state.
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g0/0/1
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.2.26 30
May 12 2024 17:50:07-08:00 R7 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[1]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 has entered the UP state.
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int g0/0/2
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]ip add 34.1.1.7 24
May 12 2024 17:50:29-08:00 R7 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[2]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 has entered the UP state.
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/2]int l0
[R7-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.0.25 30
[R7-LoopBack0]int l1
[R7-LoopBack1]ip add 172.16.7.7 24
[R7-LoopBack1]q
[R7]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 6
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 0
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 6
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 0
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.2.22/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.2.26/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 34.1.1.7/24 up up
LoopBack0 172.16.0.25/30 up up(s)
LoopBack1 172.16.7.7/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R7]R8:
<Huawei>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[Huawei]sysname R8
[R8]int g0/0/0
[R8-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 34.1.1.8 24
May 12 2024 17:52:36-08:00 R8 %%01IFNET/4/LINK_STATE(l)[0]:The line protocol IP
on the interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 has entered the UP state.
[R8-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R8-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.0.29 30
[R8-LoopBack0]int l1
[R8-LoopBack1]ip add 192.168.2.8 24
[R8-LoopBack1]q
[R8]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 2
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 34.1.1.8/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.0.29/30 up up(s)
LoopBack1 192.168.2.8/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
[R8]AS2内使用ospf协议配置全网通
因为该区域内网段全为172.16.0.0/16网段内的,且与AS1和AS3间没有该网段内的网段连接,故直接使用172.16.0.0/16网段宣告即可。
配置
R2:
<R2>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[R2]ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2
[R2-ospf-1]a 0
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]net 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255R3:
<R3>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[R3]ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3
[R3-ospf-1]a 0
[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]net 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255R4:
<R4>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[R4]ospf 1 router-id 4.4.4.4
[R4-ospf-1]a 0
[R4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]net 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255R5:
<R5>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[R5]ospf 1 router-id 5.5.5.5
[R5-ospf-1]a 0
[R5-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]net 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255R6:
<R6>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[R6]ospf 1 router-id 6.6.6.6
[R6-ospf-1]a 0
[R6-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]net 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255R7:
<R7>sys
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[R7]ospf 1 router-id 7.7.7.7
[R7-ospf-1]a 0
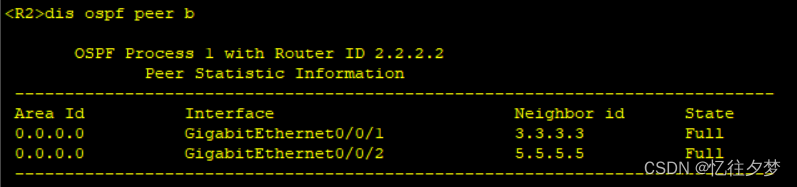
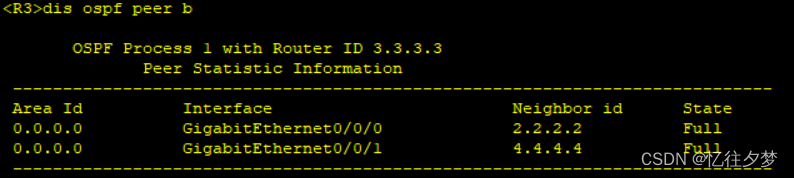
[R7-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]net 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255查看建邻情况
R2:
R3:
R4:
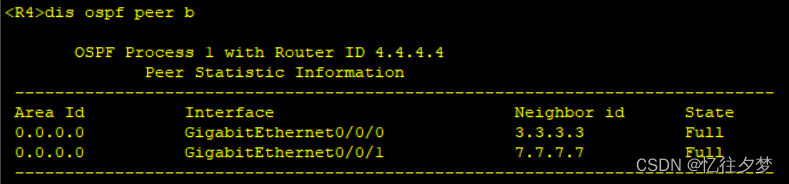
R5:
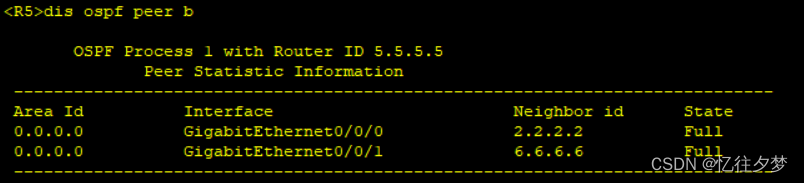
R6:
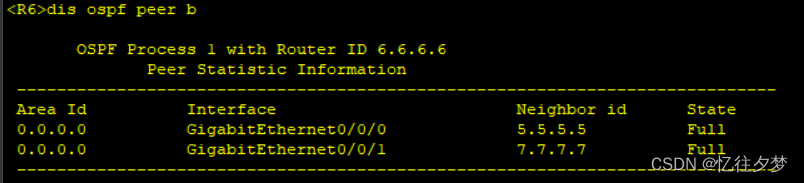
R7:
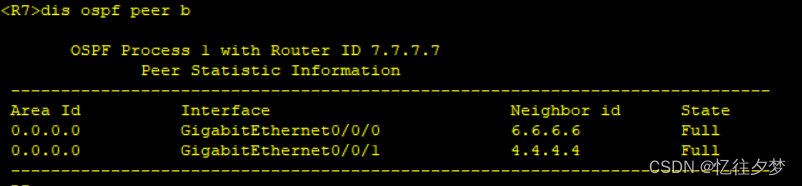
查看R2路由表:
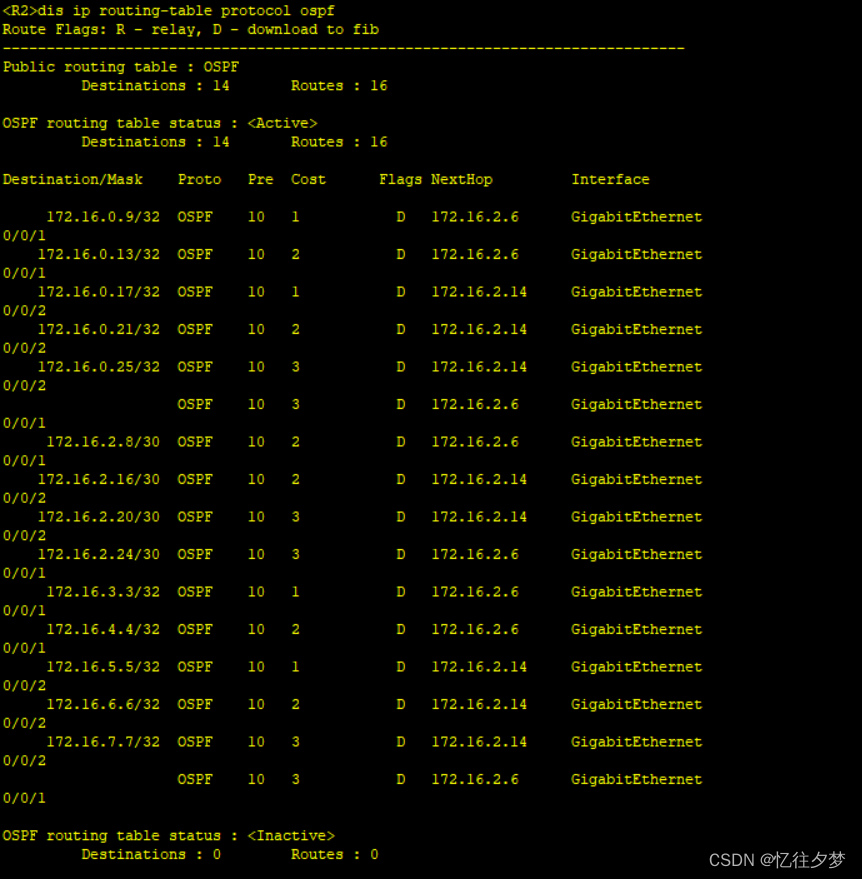
查看R7路由表:
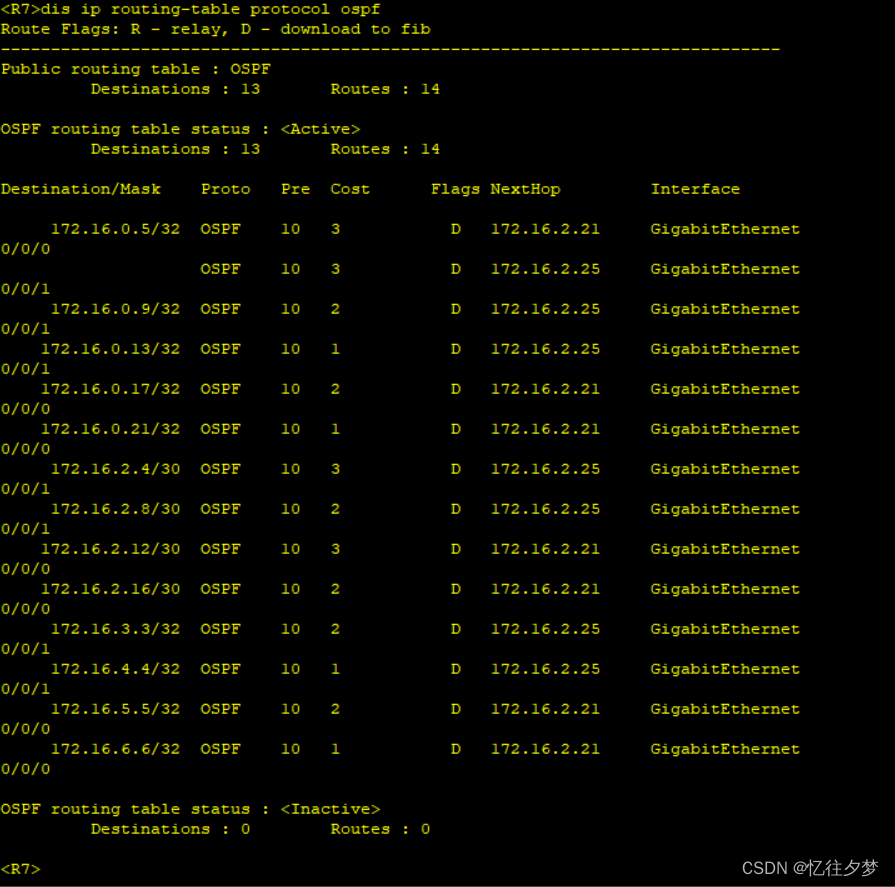
可以判定ospf内部通了。
配置BGP协议
配置
R1:
[R1]bgp 1
[R1-bgp]peer 12.1.1.2 as-number 2R2:
[R2]bgp 64512
[R2-bgp]confederation id 2
[R2-bgp]confederation peer-as 64513
[R2-bgp]peer 12.1.1.1 as 1
[R2-bgp]peer 172.16.0.9 as-number 64512
[R2-bgp]peer 172.16.0.9 connect-interface l0
[R2-bgp]peer 172.16.0.9 next-hop-local
[R2-bgp]peer 172.16.2.14 as 64513
[R2-bgp]peer 172.16.2.14 next-hop-localR3:
[R3]bgp 64512
[R3-bgp]confederation id 2
[R3-bgp]confederation peer-as 64513
[R3-bgp]peer 172.16.0.5 as 64512
[R3-bgp]peer 172.16.0.5 connect-interface l0
[R3-bgp]peer 172.16.0.13 as 64512
[R3-bgp]peer 172.16.0.13 connect-interface l0R4:
[R4]bgp 64512
[R4-bgp]confederation id 2
[R4-bgp]confederation peer-as 64513
[R4-bgp]peer 172.16.0.9 as 64512
[R4-bgp]peer 172.16.0.9 connect-interface l0
[R4-bgp]peer 172.16.0.9 next-hop-localR5:
[R5]bgp 64513
[R5-bgp]confederation id 2
[R5-bgp]confederation peer-as 64512
[R5-bgp]peer 172.16.2.13 as 64512
[R5-bgp]peer 172.16.2.13 next-hop-local
[R5-bgp]peer 172.16.0.21 as 64513
[R5-bgp]peer 172.16.0.21 connect-interface l0
[R5-bgp]peer 172.16.0.21 next-hop-localR6:
[R6]bgp 64513
[R6-bgp]confederation id 2
[R6-bgp]confederation peer-as 64512
[R6-bgp]peer 172.16.0.17 as 64513
[R6-bgp]peer 172.16.0.17 connect-interface l0
[R6-bgp]peer 172.16.0.25 as 64513
[R6-bgp]peer 172.16.0.25 connect-interface l0R7:
[R7]bgp 64513
[R7-bgp]confederation id 2
[R7-bgp]confederation peer-as 64512
[R7-bgp]peer 172.16.0.21 as 64513
[R7-bgp]peer 172.16.0.21 connect-interface l0
[R7-bgp]peer 172.16.0.21 next-hop-local
[R7-bgp]peer 34.1.1.8 as 3R8:
[R8]bgp 3
[R8-bgp]peer 34.1.1.7 as 2查看建邻情况:
R1:
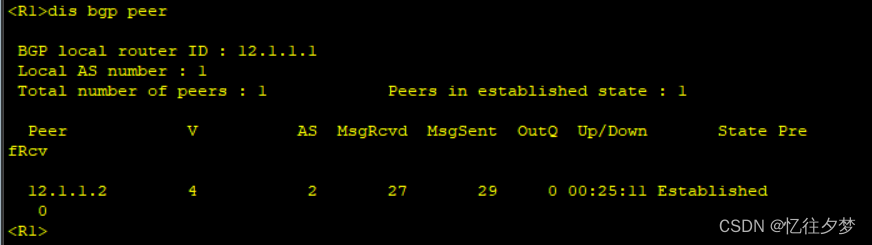
R2:
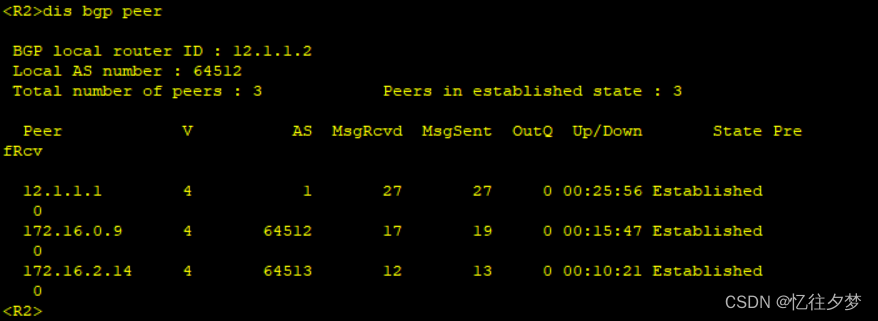
R3:
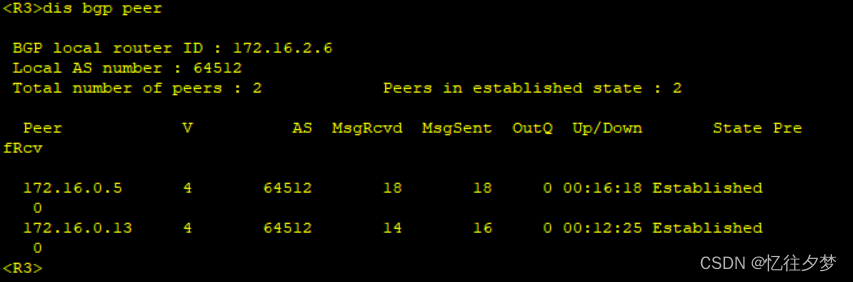
R4:
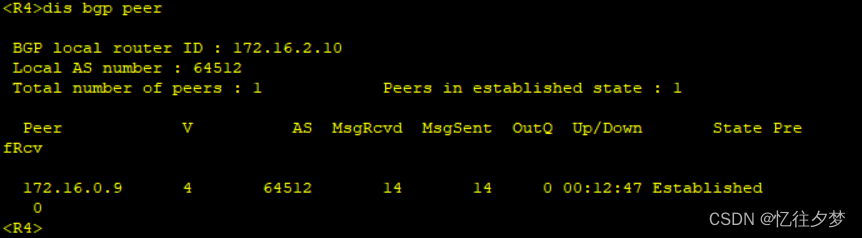
R5:
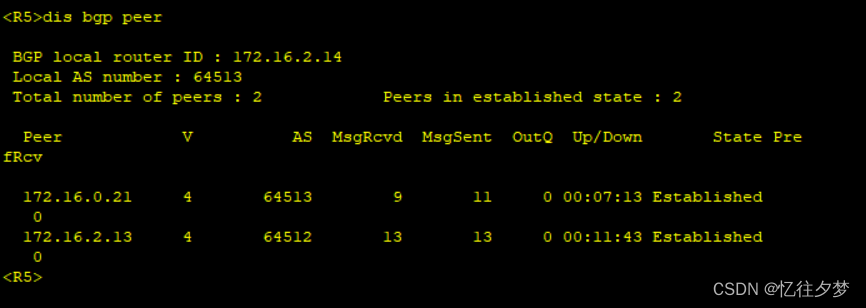
R6:
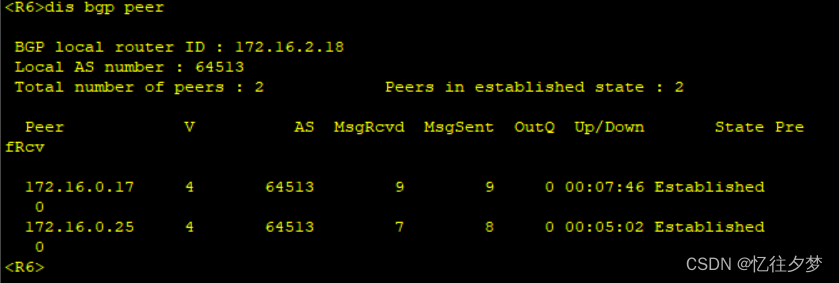
R7:
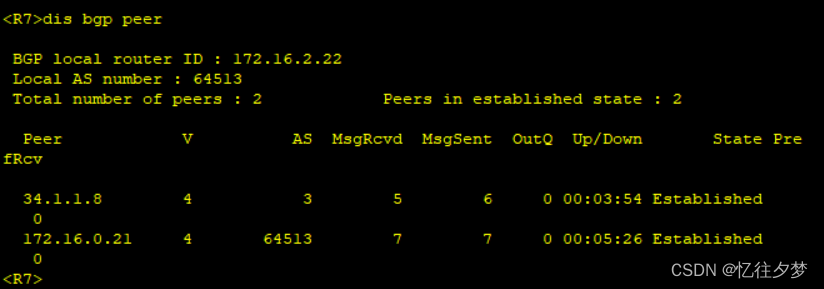
R8:
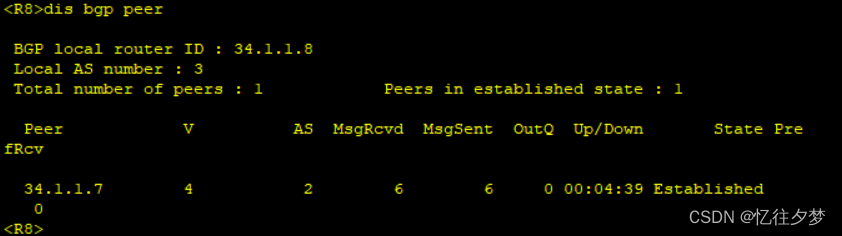
测试
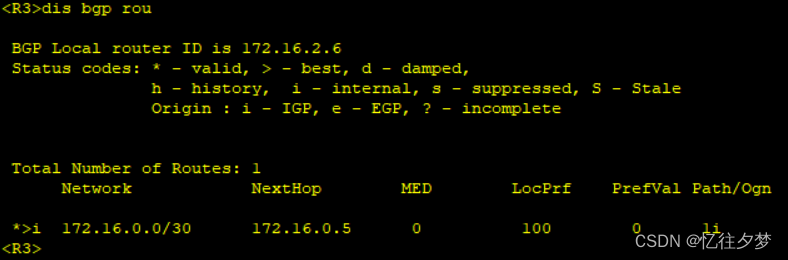
将R1中的172.16.0.0/30网段宣告进入bgp协议中,看其他路由器能否收到该条路由:
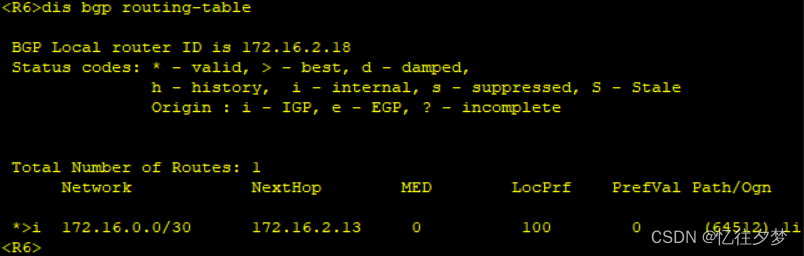
R3:
R6:
R4:
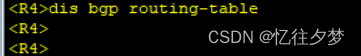
经测试,R4、R7、R8接收不到该条路由,这是由于bgp水平分割造成的。故接下来配置bgp反射器。
配置BGP反射器
经分析,在R3和R6上面进行反射器的配置:
R3:
[R3]bgp 64512
[R3-bgp]peer 172.16.0.13 reflect-clientR6:
[R6]bgp 64513
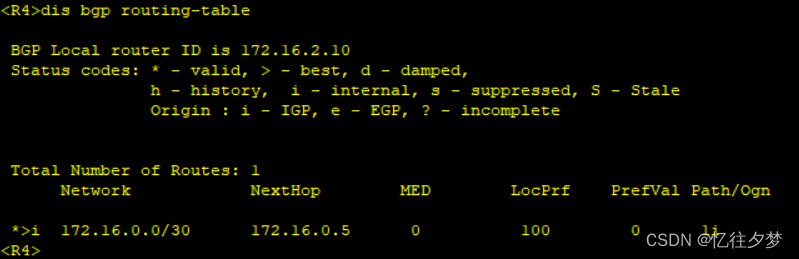
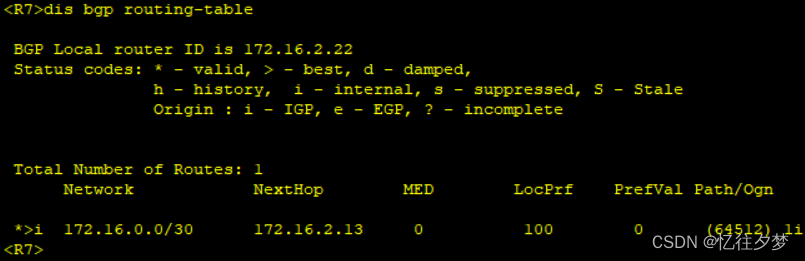
[R6-bgp]peer 172.16.0.25 reflect-client 再次查看:
R4:
R7:
R8:
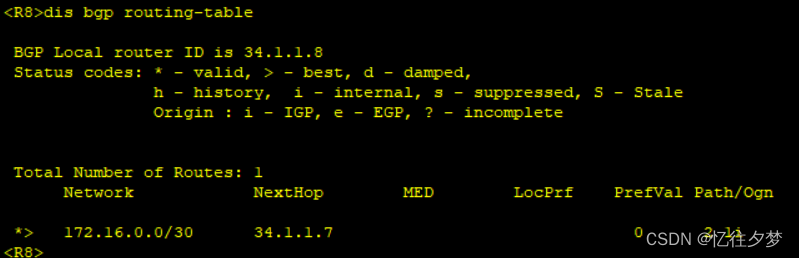
由此达成bgp配置
宣告网段达成全网通
宣告
由题意知R1和R8上的业务网段不宣告进入协议中。
R1:
[R1]bgp 1
[R1-bgp]net 172.16.0.0 30R2:
[R2]ip route-static 172.16.0.0 16 NULL 0
[R2]bgp 64512
[R2-bgp]net 172.16.0.0 16R7:
[R7]ip route-static 172.16.0.0 16 NULL 0
[R7]bgp 64513
[R7-bgp]net 172.16.0.0 16
R8:
[R8]bgp 3
[R8-bgp]net 172.16.0.28 30直接使用这个IP可以实现路由聚合的功能,简单易行。
测试
R1pingR4业务:
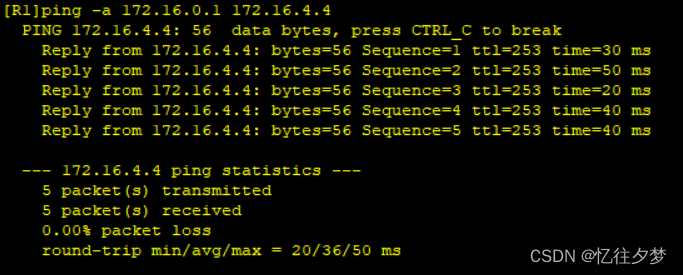
R1pingR8:
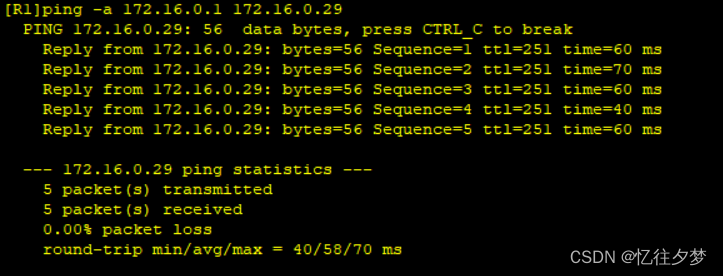
R8pingR3业务:
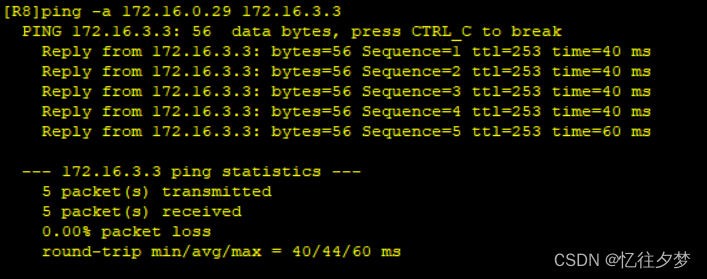
达成全网通。
构建VPN隧道
因为需要让R1的业务网段仅能与R8的业务网段沟通,故构建一条VPN隧道。
这里使用10.1.1.0/24网段来给隧道IP:
配置
R1:
[R1]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 10.1.1.1 24
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 3
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 12.1.1.1/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.0.1/30 up up(s)
LoopBack1 192.168.1.1/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
Tunnel0/0/0 10.1.1.1/24 up down
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]source 172.16.0.1
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]destination 172.16.0.29
[R1-Tunnel0/0/0]q
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 Tunnel0/0/0R8:
[R8]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R8-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 10.1.1.8 24
[R8-Tunnel0/0/0]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 5
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 3
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 34.1.1.8/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.0.29/30 up up(s)
LoopBack1 192.168.2.8/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
Tunnel0/0/0 10.1.1.8/24 up down
[R8-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre
[R8-Tunnel0/0/0]source 172.16.0.29
[R8-Tunnel0/0/0]destination 172.16.0.1
[R8-Tunnel0/0/0]q
[R8]ip route-static 192.168.1.0 24 Tunnel0/0/0测试
R1业务pingR8业务:
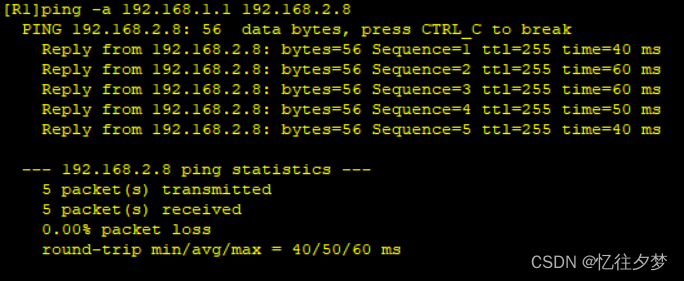
R8业务pingR1业务:
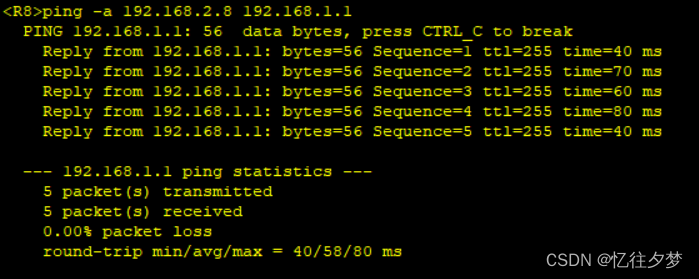
至此,配置完成