文章目录
- 前言:Java常见的单元测试框架
- 一.Junit5基础
- 二.SpringBoot项目单元测试
- 1.添加依赖
- 2.SpringBoot单元测试标准结构
- 3.SpringBoot单元测试常用注解
- 三.单元测试中如何注入依赖对象
- 1.真实注入(@AutoWired、 @Resource)
- 2.Mock注入
- 2.1.前言
- 2.2.Mock的概念
- 2.3.实现原理和优点
- 3.mock方法驱动
- 4.Mock注解驱动
- 1.@Spy
- 2.@InjectMocks
- 3. @MockBean
- 4.thenReturn
- 5.thenThrow
- 6.doThrow
- 7.行为验证
- 5.非spring环境和spring环境注解驱动
- @MockBean+@SpyBean+@Autowired
- 使用mock
- 使用Spy
- 6. mock静态方法
- 7.统计覆盖率
- 四.拓展
- 1.springboot设置虚拟属性
- 2.模拟Web层(控制器)(GET请求/POST请求)
- 五.私有方法的模拟
- 六.总结
前言:Java常见的单元测试框架
JUnit:
- JUnit是最早也是最著名的Java单元测试框架。它提供了丰富的断言方法,支持注解驱动测试,并与许多IDE(如IntelliJ IDEA和Eclipse)和构建工具(如Maven和Gradle)集成良好。
JUnit 5是JUnit的最新版本,它引入了全新的编程模型和扩展模型,使得编写和扩展测试更加灵活和强大。
TestNG:
- TestNG是一个强大的Java测试框架,它允许你组织测试方法成组,并支持依赖测试(即一个测试依赖于另一个测试的结果)。
- TestNG也提供了参数化测试的功能,允许你使用不同的数据集来运行相同的测试逻辑。
Mockito:
- Mockito是目前Java社区中最受欢迎的Mock框架之一。
通常与JUnit一起使用。它提供了一个简单且灵活的API来创建和配置模拟对象。 - Mockito支持创建模拟对象、定义模拟对象的行为、验证方法调用等。它还提供了许多高级功能,如参数匹配、部分模拟、验证调用顺序等。
PowerMock:
- PowerMock
扩展了EasyMock和Mockito的功能,支持对静态方法、构造函数、私有方法等进行模拟。 - PowerMock特别适用于那些难以使用传统Mock框架进行模拟的场景,例如使用了静态方法或私有方法的代码。
AssertJ:
- AssertJ是一个流式的
Java断言库,它提供了更自然和富有表达力的方式来编写断言代码。与JUnit等测试框架结合使用,可以使测试代码更加清晰和易于理解。
Hamcrest:
- Hamcrest是一个
匹配器库,它提供了丰富的匹配器来构建复杂的断言条件。Hamcrest与JUnit等测试框架配合使用,可以使断言更加灵活和强大。
一.Junit5基础
学习单元测试和断言前请先了解 【Java基础】使用Junit5进行单元测试 基础

二.SpringBoot项目单元测试
1.添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
spring-boot-starter-test中包含了junit和mockito等依赖
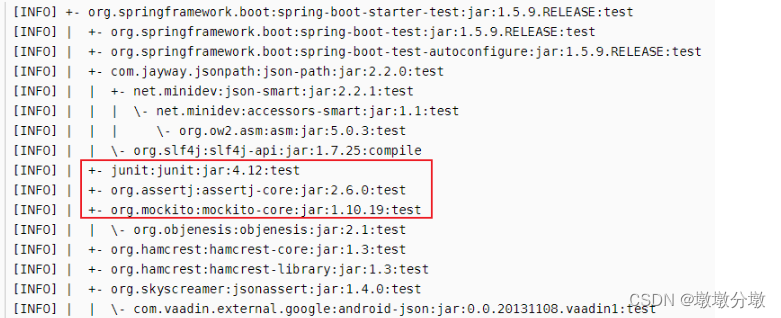
相关依赖
- junit:标准的单元测试Java应用程序
- Spring Test & Spring Boot Test : 对Spring Boot应用程序的单元测试提供支持
- Mockito:Java mocking框架,用于模拟任何Spring管理的Bean,比如在单元测试中模拟一个第三方系统Service接口返回的数据,而不会去真正调用第三方系统;
- assertj:断言库,提供多种比较期望值与测试返回值的方法;
- JSONassert:对JSON对象或者JSON字符串断言的库。
- Hamcrest:它提供了
丰富的匹配器来构建复杂的断言条件。Hamcrest与JUnit等测试框架配合使用,可以使断言更加灵活和强大。 - …
2.SpringBoot单元测试标准结构
@DisplayName("TestDemo测试类") //起别名
@SpringBootTest //1.类上添加注解,加载ApplicationContext,启动spring容器。
@AutoConfigureMockMvc //2.启动mockMVC测试
@Transactional //3.开启事务管理
@TestMethodOrder(MethodOrderer.OrderAnnotation.class)//开启测试类的执行顺序按@order配置的优先级执行
public class TestDemo {
@Test
@Order(3)//第3个执行
public void test1() {
int a = 1;
Assertions.assertNotEquals(1, a);//判断二者是否不相等
}
@Test
@Order(2)//第2个执行
public void test2() {
int a = 1;
Assertions.assertNotEquals(1, a);//判断二者是否不相等
}
@Test
@Order(1)//第一个执行
public void test3() {
int a = 1;
Assertions.assertNotEquals(1, a);//判断二者是否不相等
}
}
执行结果
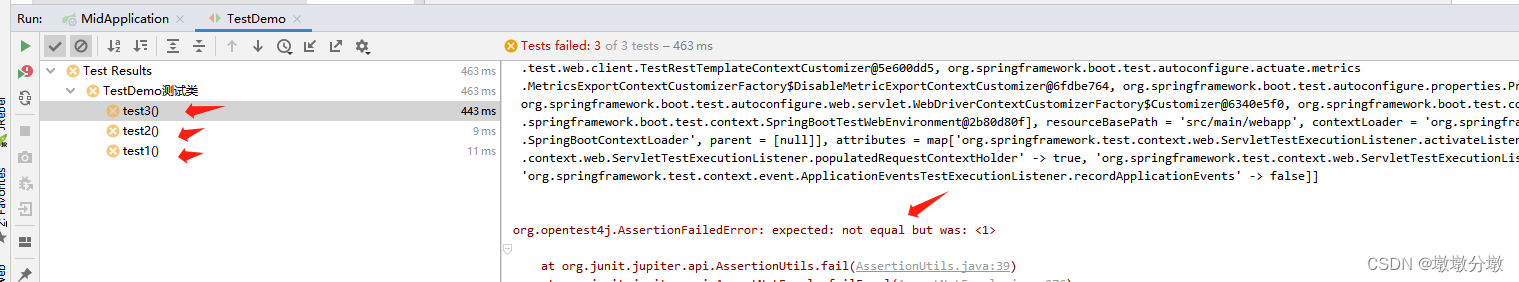
一 般情况下,使用@SpringBootTest后,Spring将加载所有被管理的bean,基本等同于启动了整个springboot服务,此时便可以开始功能测试。
-
可以通过webEnvironment参数启动的Web环境对应的端口,springboot提供了4种设置如下:
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)- MOCK:
默认值,该类型提供一个mock环境,可以和@AutoConfigureMockMvc或@AutoConfigureWebTestClient搭配使用,开启Mock相关的功能。注意此时内嵌的服务(servlet容器)并没有真正启动,也不会监听web服务端口。 - RANDOM_PORT:启动一个真实的web服务,监听一个随机端口。(
建议) - DEFINED_PORT:启动一个真实的web服务,监听一个定义好的端口(从
application.properties读取)。 - NONE:启动一个非web的ApplicationContext,既不提供mock环境,也不提供真实的web服务。
- MOCK:
3.SpringBoot单元测试常用注解

-
@Mock :是
Mockito.mock()方法的简写。创建的是全部mock的对象,即在对具体的方法打桩(即创建模拟对象)之前,mock对象的所有属性和方法全被置空(0或null)。- @mock注解需要搭配
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(testClass)方法一起使用.
- @mock注解需要搭配
-
@Spy:是Mockito.Spy()方法的简写。被 spy 的对象,调用其方法时默认会走真实方法。,有返回值的调用真实方法并返回真实值- 如果发现修饰的变量是 null,会自动调用类的无参构造函数来初始化。定义了mock方法的则执行mock(即
虚假函数);默认生成后所有依赖的对象都会null,且要一个无参构造。
- 如果发现修饰的变量是 null,会自动调用类的无参构造函数来初始化。定义了mock方法的则执行mock(即
-
@InjectMocks :将 @Mock、@Spy 修饰的对象自动注入到 @InjectMocks 修饰的对象中。
注入方式有多种,mockito 会按照下面的顺序尝试注入:- 构造函数注入
- 设值函数注入(set函数)
- 属性注入
//类1 public class HttpService { public int queryStatus() { // 发起网络请求,提取返回结果 // 这里用随机数模拟结果 return new Random().nextInt(2); } } //类2 public class ExampleService { private HttpService httpService; public String hello() { int status = httpService.queryStatus(); if (status == 0) { return "你好"; } else if (status == 1) { return "Hello"; } else { return "未知状态"; } } }public class ExampleServiceTest { @InjectMocks // 将@Mock httpService主动注入ExampleService private ExampleService exampleService = new ExampleService(); @Mock private HttpService httpService; @Test public void test01() { MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this); when(httpService.queryStatus()).thenReturn(0); Assert.assertEquals("你好", exampleService.hello()); } } -
@MockBean : Spring Boot 中的注解。我们可以使用
@MockBean将mock 对象添加到 Spring 应用程序上下文中。该 mock 对象将替换应用程序上下文中任何现有的相同类型的 bean。如果应用程序上下文中没有相同类型的 bean,它将使用 mock 的对象作为 bean 添加到上下文中。 -
@SpyBean:同上。
三.单元测试中如何注入依赖对象
1.真实注入(@AutoWired、 @Resource)
- 对DAO层(Service层同理)
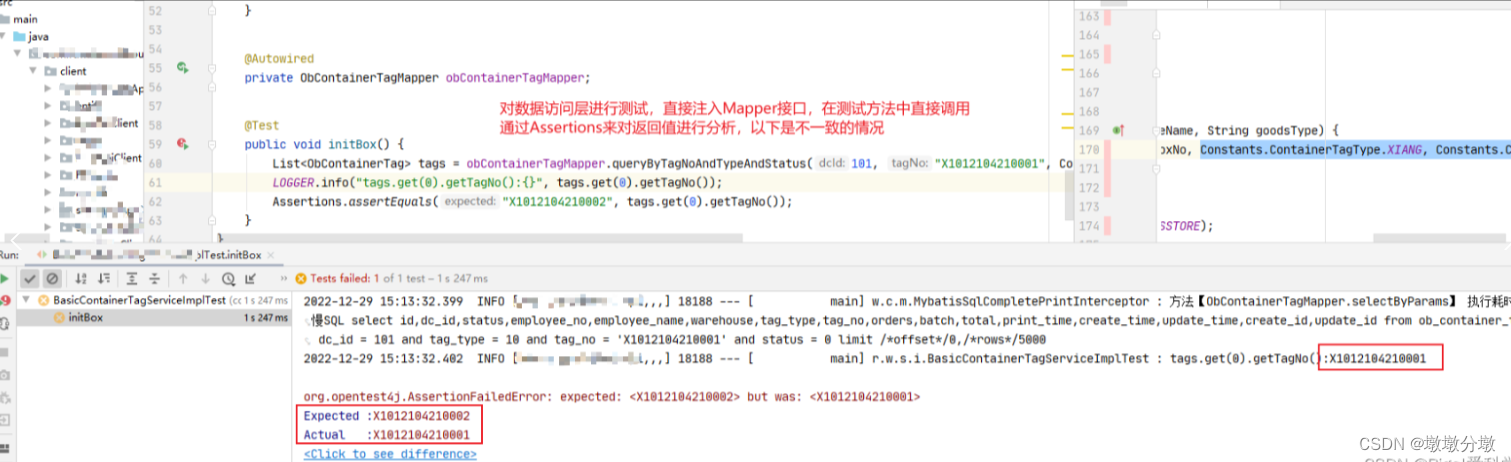
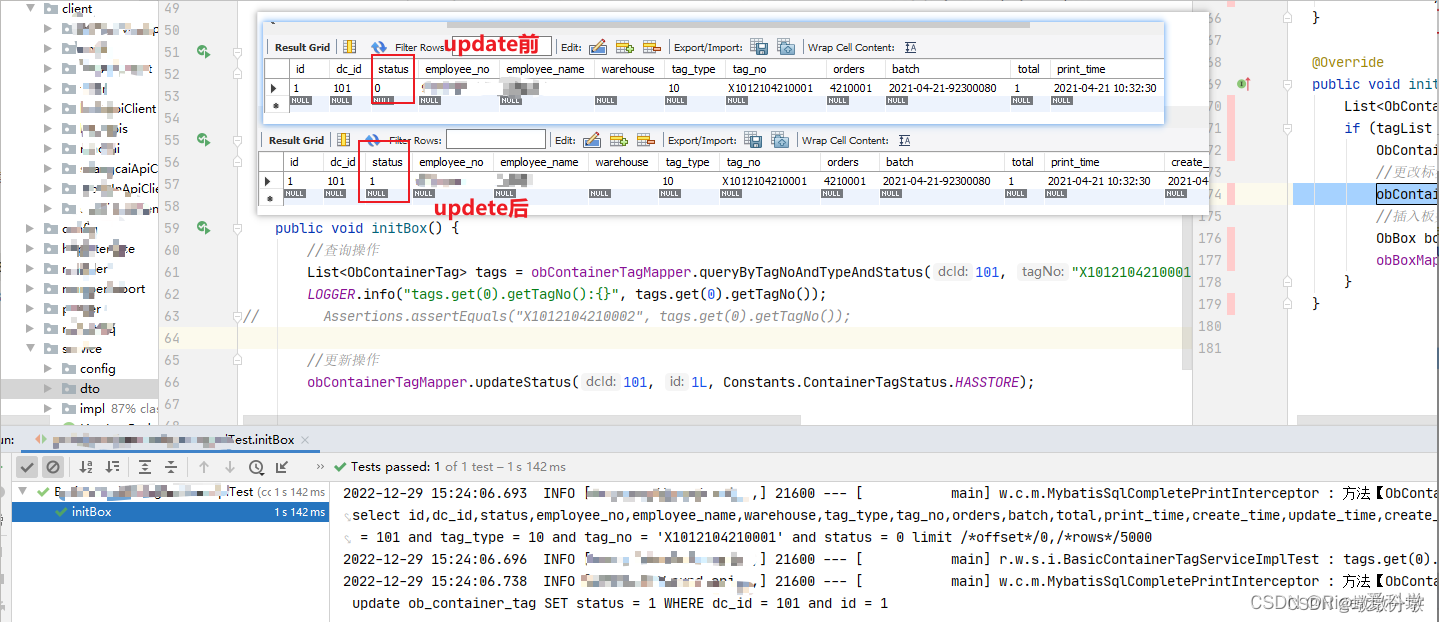
- @Autowired直接注入的方式是基于真实环境的,
会真实操作数据库,如果在单元测试中不想改变数据数据库中的值,不能使用直接注入的方法
可以在类上再添加这两个注解,通过
@Transactional+@Rollback(true)可以知道调用了数据库,对其操作进行回滚
但是如果项目中使用了@Component注解(在SpringBoot项目启动的时候就会跟着实例化/启动),@Component注解的类里有多线程方法,那么在执行单元测试的时候,由于多线程任务的影响,就可能对数据库造成了数据修改,
- 即使使用了事务回滚注解@Transactional。(我在百度上看到的,没找到具体的测试方法,所以没试)
@Transactional
@Rollback(true) // 事务自动回滚,默认是true。可以不写
2.Mock注入
2.1.前言
2.2.Mock的概念
-
所谓的mock就是创建一个
类的虚拟对象,在测试环境中,用来替换掉真实的对象,以达到2个目的:- 验证这个对象的某些方法的调用情况,调用了多少次,参数是什么等等
- 指定这个对象的某些方法的行为,返回特定的值,或者是执行特定的动作
-
使用Mock之前,需要在
@Before或@BeforeClass对应的方法中添加如下,表示 添加mock注解初始化。MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this); -
另外需要补充以下几个常用的测试注解:
-
@InjectMocks:通过创建一个实例,它可以调用真实代码的方法,其余用@Mock(或@Spy)注解创建的mock将被注入到用该实例中。
-
@Mock:该对象下对函数的调用均执行
mock(即虚假函数),不执行真正具体操作。 -
@Spy:对函数的调用均执行真正部分。
-
-
Mockito中的@Mock和@Spy都可用于拦截那些尚未实现或不期望被真实调用的对象和方法,并为其设置自定义行为。- 二者的区别在
于Mock不真实调用,Spy会真实调用。
- 二者的区别在
Mockito 默认是“不支持静态方法,可使用 PowerMock 让 Mockito 支持静态方法(新增依赖)
2.3.实现原理和优点
实现原理:使用Stub(桩)技术动态的替换原程序的功能。
- 直接跑Java代码,不需要启用Spring容器及连接数据库,模拟一切操作数据库的步骤,不执行任何SQL,也可以模拟任何返回值
- Stub(桩)技术:在单元测试中中用于替代实际对象或方法的技术,主要是提供一个预定义的、固定的返回值或调用,以便在测试中
模拟实际对象或方法的调用。
- Stub(桩)技术:在单元测试中中用于替代实际对象或方法的技术,主要是提供一个预定义的、固定的返回值或调用,以便在测试中
使用Mock的优点:
- 可以完全脱离数据库
- 只针对某一个小方法(一个小的单元)来测试,测试过程中,不需要启动其他的东西,不免其他因素可能产生的干扰
3.mock方法驱动
-
Mockito.mock(xxx.class) 创建mock对象
-
Mockito.mock(classToMock,defaultAnswer) 使用默认Answer模拟对象
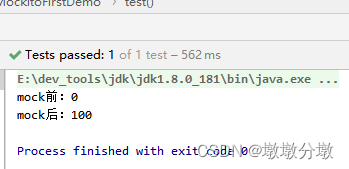
import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Test; import org.mockito.Mockito; import java.util.Random; public class MockitoFirstDemo { @Test public void test() { //mock了一个Random对象 Random mockRandom = Mockito.mock(Random.class); System.out.println("mock前:"+mockRandom.nextInt()); Assert.assertEquals(0, mockRandom.nextInt());//未进行打桩,每次返回值都是0 //设置random.nextInt()虚拟值为100 Mockito.when(mockRandom.nextInt()).thenReturn(100); // 进行打桩操作,指定调用 nextInt 方法时,永远返回 100 System.out.println("mock后:"+mockRandom.nextInt()); Assert.assertEquals(100, mockRandom.nextInt()); } }·
-
Mockito.doThrow(toBeThrown).when(mock).[method] 模拟抛出异常
//如果mockRandom对象调用nextInt()方法 抛出空指针异常 Mockito.doThrow(new NullPointerException()).when(mockRandom).nextInt(); mockRandom.nextInt(); -
Mockito.when(methodCall).thenReturn(value) 模拟方法调用返回值
-
Mockito.doReturn(toBeReturned).when(mock).[method] 模拟方法调用返回值(直接执行不判断)
-
Mockito.when(methodCall).thenReturn(value1).thenReturn(value2) 模拟多次方法调用返回值,触发时第一次返回value1,第n次都返回value2
//1.模拟nextInt方法调用返回100 Mockito.when(mockRandom.nextInt()).thenReturn(100); //2.触发时方法调用nextInt第一次返回101,nextInt的第n次都返回102(可以一直设置值) Mockito.when(mockRandom.nextInt()).thenReturn(101).thenReturn(102); //3.模拟nextInt方法调用返回100 (同第一种) Mockito.doReturn(100).when(mockRandom).nextInt(); System.out.println(mockRandom.nextInt());//返回100 -
Mockito.when(methodCall).thenAnswer(answer)) 自定义模拟方法的返回值,可以根据方法的传参定义方法的返回
-
Mockito.doAnswer(answer).when(methodCall).[method] 自定义模拟方法的返回值,可以根据方法的传参定义方法的返回
@Test public void test() { // mock一个对象 HashMap mockMap = Mockito.mock(HashMap.class); mockMap.put("key1", "value1"); mockMap.put("key2", "value2"); Mockito.when(mockMap.get(ArgumentMatchers.anyString())).thenAnswer( new Answer() { public Object answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) { Object[] args = invocation.getArguments(); Object mock = invocation.getMock(); String key = (String) args[0]; //修改key=key1的返回值 if (key.equals("key1")) { return "called with arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args); } //修改key=key2的返回值 if (key.equals("key2")) { return "called with arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args); } return "error key"; } }); System.out.println(mockMap.get("key1")); // called with arguments: [key1] System.out.println(mockMap.get("key2")); // called with arguments: [key2] System.out.println(mockMap.get("key3")); //error key } -
Mockito.verify(mock) 验证对象的方法调用是否发生
//创建mock对象 ArrayList list = Mockito.mock(ArrayList.class); list.add(1); list.add(2); Mockito.verify(list).add(1);//验证通过 Mockito.verify(list).add(5);//验证未通过,因为没有执行过该操作 -
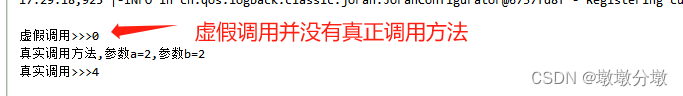
Mockito.spy(Object) 用spy监控真实对象,设置真实对象行为
//虚假调用 ExampleService mockExample = Mockito.mock(ExampleService.class); int num = mockExample.add(1, 1); System.out.println("虚假调用>>>"+num); //返回虚假调用>>>0 ExampleService spyExample = Mockito.spy(ExampleService.class); num = spyExample.add(2, 2); System.out.println("真实调用>>>"+num); //真实调用方法,参数a=2,参数b=2 //真实调用>>>4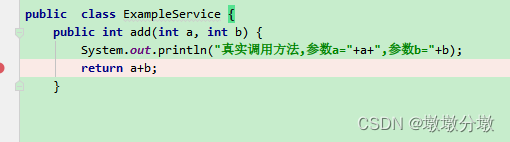
-
when().Return() 与 doReturn() 设置方法的返回值
Mockito.when(mock.someMethod("some args")).Return("result"); Mockito.doReturn("result").when(mock).someMethod("some arg"); -
when().thenthrow() 与 doThrow() 让方法抛出异常
// 只针对返回值非void的函数 Mockito.when(mock.someMethod("some args")).thenthrow(new Exception("自定义异常")); // 通用 Mockito.doThrow(new Exception("自定义异常")) .when(mock) .someMethod("some arg"); -
doNothing() 让void函数什么都不做
Mockito.doNothing().when(mock).someMethod("some args"); -
doAnswer()自定义方法处理逻辑
// 自定义返回值thenAnswer() when(mock.someMethod(anyString())).thenAnswer( new Answer() { public Object answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) { Object[] args = invocation.getArguments(); Object mock = invocation.getMock(); return "called with arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args); } }); //Following prints "called with arguments: [foo]" System.out.println(mock.someMethod("foo")); -
thenCallRealMethod()调用 spy 对象的真实方法
Mockito.when(spy.someMethod("some args")).thenCallRealMethod(); Mockito.doCallRealMethod().when(spy).someMethod("some arg"); -
使用then、thenAnswer 自定义方法处理逻辑
- 实现 Answer 接口的对象,在该对象中可以获取调用参数,自定义返回值
// 自定义返回值thenAnswer() when(mock.someMethod(anyString())).thenAnswer( new Answer() { public Object answer(InvocationOnMock invocation) { Object[] args = invocation.getArguments(); Object mock = invocation.getMock(); return "called with arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args); } }); //Following prints "called with arguments: [foo]" System.out.println(mock.someMethod("foo")); @Test void testDemo02() { Mockito.when(studentService.getStudentByUserName("张三")).thenAnswer( (Answer<Student>) invocationOnMock -> new Student("赵六","13215522144","河南省") ); Student student = studentService.getStudentByUserName("张三"); // prints: Student{username='赵六', phone='13215522144', address='河南省'} System.out.println(student.toString()); } -
reset()方法,可以重置之前自定义的返回值和异常
import org.junit.Assert; import org.junit.Test; import static org.mockito.Mockito.*; public class MockitoDemo { static class ExampleService { public int add(int a, int b) { return a+b; } } @Test public void test() { ExampleService exampleService = mock(ExampleService.class); // mock 对象方法的默认返回值是返回类型的默认值 Assert.assertEquals(0, exampleService.add(1, 2)); // 设置让 add(1,2) 返回 100 when(exampleService.add(1, 2)).thenReturn(100); Assert.assertEquals(100, exampleService.add(1, 2)); // 重置 mock 对象,add(1,2) 返回 0 reset(exampleService); Assert.assertEquals(0, exampleService.add(1, 2)); }
4.Mock注解驱动
- @Mock 注解可以理解为对
Mockito.mock()的一个替代 - 使用该注解时,
要使用MockitoAnnotations.initMocks 方法,让注解生效。- 旧版的是initMocks,新版的是openMocks
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.MockitoAnnotations;
import java.util.Random;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
public class MockitoTwoDemo {
@Mock
private Random random;
@Before
public void before() {
// 初始化mock,让注解生效(新版)
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
}
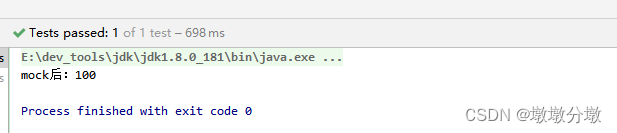
@Test
public void test() {
//设置random.nextInt()虚拟值为100
when(random.nextInt()).thenReturn(100);
System.out.println("mock后:"+random.nextInt());
Assert.assertEquals(100, random.nextInt());
}
}
也可以用MockitoJUnitRunner来代替MockitoAnnotations.openMocks
1.@Spy
mock()方法与spy()方法的不同:
- 被spy的对象会走真实的方法,而mock对象不会
- spy方法的参数是
对象实例,mock的参数是class
2.@InjectMocks
-
@InjectMocks由mock框架管理,只能将
@Mock、@Spy修饰的对象自动注入到@InjectMocks修饰的对象中@Mock AService aService; @InjectMocks AController aController; //这里会注aService @Autowired AController aController;//这里不会注aService class BController{ AService aService; } -
如果想一个spring对象注入mock框架的对象,可通过@InjectMocks桥接。
@Mock AService aService; @Autowired @InjectMocks AController aController;//这里会注入aService
3. @MockBean
-
@MockBean和
@SpyBean由spring管理,会替换上下文相同对象。@MockBean AService aService; @Autowired AController aController; //这里会注入aService
4.thenReturn
thenReturn 用来指定特定函数和参数调用的返回值;
- thenReturn 中可以
指定多个返回值。在调用时返回值依次返回。 若调用次数超过返回值的数量,再次调用时返回最后一个返回值。
doReturn 的作用和 thenReturn 相同,但使用方式不同:
//mockRandom.nextInt()返回虚拟值1
Mockito.when(mockRandom.nextInt()).thenReturn(1);//返回值为1
//mockRandom.nextInt()依次返回虚拟值1 2 3
Mockito.when(mockRandom.nextInt()).thenReturn(1, 2, 3);
//mockRandom.nextInt()的返回值设置为1
Mockito.doReturn(1).when(random).nextInt();
5.thenThrow
-
thenThrow 用来让函数调用抛出异常。(可搭配try catch使用)
可以指定多个异常。在调用时异常依次返回。若调用次数超过异常的数量,再次调用时抛出最后一个异常。
//调用mockRandom.nextInt()抛出RuntimeException异常
Mockito.when(mockRandom.nextInt()).thenThrow(new RuntimeException("异常"));
//调用mockRandom.nextInt()依次抛出RuntimeException异常
Mockito.when(mockRandom.nextInt()).thenThrow(new RuntimeException("异常1"), new RuntimeException("异常2"));
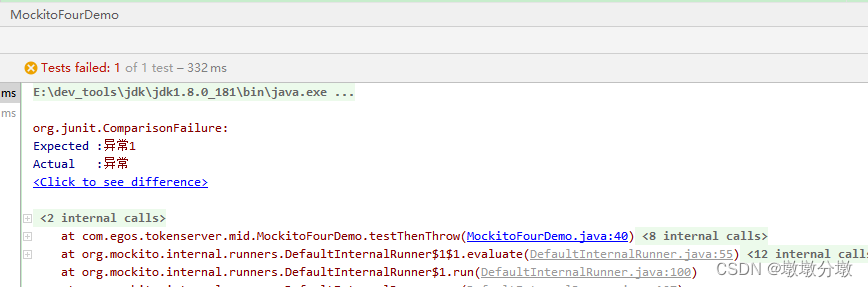
@Test
public void testThenThrow() {
Random mockRandom = mock(Random.class);
//调用mockRandom.nextInt()抛出RuntimeException异常
Mockito.when(mockRandom.nextInt()).thenThrow(new RuntimeException("异常"));
try {
mockRandom.nextInt();
Assert.fail();//上一行会抛出异常,到catch中去,走不到这里
} catch (Exception ex) {
Assert.assertTrue(ex instanceof RuntimeException);
Assert.assertEquals("异常1", ex.getMessage());
}
try {
mockRandom.nextInt();
Assert.fail();
} catch (Exception ex) {
Assert.assertTrue(ex instanceof RuntimeException);
Assert.assertEquals("异常2", ex.getMessage());
}
}
6.doThrow
- 对应返回类型是
void 的函数,thenThrow 是无效的,要使用doThrow。也可以用 doThrow让返回非void的函数抛出异常
doThrow(new RuntimeException("异常")).when(exampleService).hello();
// 下面这句等同于 when(random.nextInt()).thenThrow(new RuntimeException("异常"));
doThrow(new RuntimeException("异常")).when(random).nextInt();
7.行为验证
- 使用 verify 可以校验 mock 对象是否发生过某些操作,配合 time 方法,可以校验某些操作发生的次数
//是否调用过一次
Mockito.verify(spy).hasReturnAndArgs(Mockito.anyString());
//是否调用过N次
Mockito.verify(spy,times(1)).hasReturnAndArgs(Mockito.anyString());
//没有被调用,相当于 times(0)
Mockito.verify(spy,never()).hasReturnAndArgs(Mockito.anyString());
//atLeast(N) 至少被调用 N 次
//atLeastOnce() 相当于 atLeast(1)
//atMost(N) 最多被调用 N 次
5.非spring环境和spring环境注解驱动
- 非spring环境:@Mock+@Spy+@InjectMocks
- spring环境:@MockBean+@SpyBean+@Autowired
@MockBean+@SpyBean+@Autowired
spring环境使用@MockBean+@SpyBean+@Autowired,为测试主体类部分打桩考虑使用@SpyBean, 为外部依赖打桩,考虑使用@MockBean
//业务层
@Service
public class AService {
public String hasReturnAndArgs(String str){
return "10";
}
public String hasReturn(){
return "10";
}
public void hasArgs(String str){
System.out.println(1000);
}
public void noArgs(){
System.out.println(1000);
}
}
//控制层
@RestController
public class AController {
@Autowired //注入aService
private AService aService;
public String hasReturnAndArgs(String str){
return aService.hasReturnAndArgs(str);
}
public String hasReturn(){
return aService.hasReturn();
}
public void hasArgs(String str){
aService.hasArgs(str);
}
public void noArgs(){
aService.noArgs();
}
}
使用mock
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class ServiceTest {
@Before
public void before() {
// 启用 Mockito 注解
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);
}
@Mock //mock AService
AService aService;
@InjectMocks //将 @Mock、@Spy 修饰的对象自动注入到@InjectMocks修饰的对象中
AController aController;
@Test
public void test() {
//1.不调用真实方法,默认返回null
String value = aService.hasReturnAndArgs("10");
Assert.assertEquals(value, null);
//2.打桩
//当传参是10L时,返回 30
Mockito.when(aService.hasReturnAndArgs("10")).thenReturn("30");
//当传参是20L时,真实调用
Mockito.when(aService.hasReturnAndArgs("20")).thenCallRealMethod();
//当传参是30L时,抛出异常
Mockito.when(aService.hasReturnAndArgs("30")).thenThrow(new Exception("test error"));
//断言方法传参为10时是否等于 30,
Assert.assertEquals(aService.hasReturnAndArgs("10"), "30");
//当传参是20L时,真实调用方法,内部mock对象调用的也是mock方法
Assert.assertNotEquals(aService.hasReturnAndArgs("20"), "30");
try {
Assert.assertNotEquals(aService.hasReturnAndArgs("30"), "30");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
//3.注入对象
Assert.assertEquals(aController.hasReturnAndArgs("10"), "30");
}
}
使用Spy
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class ServiceTest {
@Before
public void before() {
// 启用 Mockito 注解
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);
}
@Spy
AService spy;
@Test
public void test() {
//AService spyTemp = new AService();
//AService spy = Mockito.spy(spyTemp);
//1.调用真实方法
Assert.assertEquals(spy.hasReturnAndArgs("20"), "10");
//2.打桩
Mockito.doReturn("30").when(spy).hasReturnAndArgs("20");
Assert.assertEquals(spy.hasReturnAndArgs("20"), "30");
//验证是否被调用了一次
Mockito.verify(spy,times(1)).hasReturnAndArgs("20");
//设置任何hasReturnAndArgs调用都返回30
Mockito.doReturn("30").when(spy).hasReturnAndArgs(Mockito.anyString());
Assert.assertEquals( spy.hasReturnAndArgs("-2"), "30");
Mockito.verify(spy,times(2)).hasReturnAndArgs(Mockito.anyString());
//不支持这样
Mockito.when(spy.hasReturnAndArgs("20")).thenReturn("10");
Assert.assertEquals(spy.hasReturnAndArgs("20"), "10");
}
}
使用spring集成
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = Application.class)
public class ServiceTest {
@Before
public void before() {
// 启用 Mockito 注解
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);
}
@SpyBean
private AService spy;
@Autowired
AController aController;
@Test
public void test() {
//调用真实方法
Assert.assertEquals(spy.hasReturnAndArgs("20"), "10");
Mockito.doReturn("30").when(spy).hasReturnAndArgs(Mockito.anyString());
Assert.assertEquals(spy.hasReturnAndArgs("20"), "30");
Mockito.verify(spy,times(1)).hasReturnAndArgs(Mockito.anyString());
Assert.assertEquals(aController.hasReturnAndArgs("20"), "30");
}
}
6. mock静态方法
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-inline</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);
Mockito.mockStatic(XXX.class).when(XXX::getXXX)
.thenReturn("xxx");
//如果用多次需要关闭
try(MockedStatic<XXX> xx= Mockito.mockStatic(XXX.class)) {
xx.when(() -> A.b(params)).thenReturn(null);
}
7.统计覆盖率
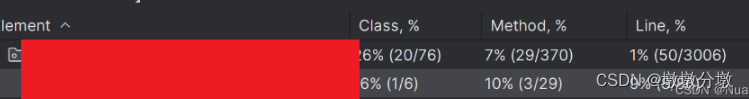
红色为尚未覆盖的行,绿色为覆盖的行。class,method,line分别表示类/方法/行代码测试覆盖率
四.拓展
1.springboot设置虚拟属性
假如我springboot项目有一个application.yml文件
test:
prop: testValue1
当编写单元测试测试的时候,在不修改源码的情况下,想改变prop属性为testValue2,该怎么办呢?
加载测试临时属性可以通过注解@SpringBootTest的properties和args属性进行设定,作用域仅限于当前测试用例@Slf4j @SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue2"}) class PropertiesAndArgsTest { @Value("${test.prop}") private String msg; @Test void test01() { log.info(msg); } }
2.模拟Web层(控制器)(GET请求/POST请求)
springMVC框架的测试中,一般采用mockMvc+Mockito的组合来进行mock模拟测试,即:Mockito模拟服务层的方法, MockMvc 来模拟发起HTTP请求
- 切片测试:指用mockmvc测试controller层,模拟返回service层的值,将层与层间的联系断开。
- 集成测试:指用mockmvc测试controller层,但不间隔service层。将controller层和service层集合起来测试。
在单元测试中对controller层功能进行测试,必须模拟一个真实的web环境,具体步骤如下:
-
测试类中启动web环境
-
每一个springboot的测试类都
需@SpringBootTest注解,通过webEnvironment属性设置在测试用例中启动web环境,具体如下:@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) public class WebTest { }
-
-
测试类中发送请求
- 先提前写一个controller,用于后面的get和post测试
@RestController @RequestMapping("/user") @Slf4j public class TestController { /** * post请求 * @param param json数据 * @return json数据 */ @PostMapping("/post") public Map<String, Object> post(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> param) { log.info(">>>>>>>>>post user:{}", param); Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>(); data.put("id", 2); data.put("username", "post"); return data; } /** * get请求,接收json以及 地址栏参数 * @param param json数据 * @param id 地址栏参数 * @return json数据 */ @GetMapping("/get") public Map<String, Object> get(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> param,@RequestParam("id") Integer id) { log.info(">>>>>>>>>get user:{},id={}", param,id); Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>(); data.put("id", 1); data.put("username", "get"); return data; } }
- 先提前写一个controller,用于后面的get和post测试
-
在测试类中通过
@AutoConfigureMockMvc开启web虚拟调用功能- 注入MockMvc对象,通过MockMvc对象可以发送虚拟请求,模拟web请求调用过程
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MvcResult; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers; //1.测试类中启动web环境 @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) //日志调用 @Slf4j //2.开启虚拟MVC调用 @AutoConfigureMockMvc public class WebTest { //3.注入MockMVC @Autowired MockMvc mockMvc; /** * 测试post请求 * * @throws Exception */ @Test void testUserPost() throws Exception { MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/user/post") //g请求参数为json .content("{\"username\":\"oyang\",\"password\":\"123456\"}") .header("Authorization", "Bearer ...") .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) ) //预期响应状态为200 .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()) // 可以取出 json的字段值,判断code是否为0 响应结果: .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.code").value("0")) .andReturn(); //{"code":0,"msg":"success","time":"20240327150240","data":{"id":2,"username":"post"},"requestId":null} log.info(">>>>>mock响应结果:{}", mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString()); } /** * 测试get请求 * * @throws Exception */ @Test void testUserGet() throws Exception { int id = 111; MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/user/get") //get请求参数在url上 .param("id", "" + id) //get请求参数为json .content("{\"username\":\"oyang\",\"password\":\"123456\"}") .header("Authorization", "Bearer ...") .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) ) .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()) .andReturn() ; //预期响应状态为200 //{"code":0,"msg":"success","time":"20240327150240","data":{"id":1,"username":"get"},"requestId":null} log.info(">>>>>mock响应结果:{}", mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString()); }- 最终web测试需要将预计值与真实值的比对才能确认测试结果是否通过
五.私有方法的模拟
-
对
待类中私有方法,可以用反射的方式进行测试-
spring框架中使用封装的反射API,来设置private的属性:
ReflectionTestUtils.setField(Object targetObject, String name, @Nullable Object value); //或者 Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(targetClass, name, type); if (field == null) { } ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field); ReflectionUtils.setField(field, targetObject, value); -
如果是非spring框架,也可以直接使用Java原生反射API:
Field field = target.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true); //改成可访问,不管现有修饰 field.set(target, value);
-
-
maven打包时使用命令打包时跳过testmvn deploy -f pom_http.xml-jar -Dmaven.test.skip=true -
Mockito 默认是
不支持静态方法,可使用PowerMock 让 Mockito 支持静态方法(新增依赖)
六.总结
- Mockito可以轻松集成到现有的Spring Boot项目中,无论是对于简单的单元测试还是更复杂的集成测试。
- 通过使用Mockito,可以模拟
服务层、存储库、REST客户端等组件,而无需依赖实际的实现。来减少测试对外部系统的依赖,模拟异常情况和边缘用例,从而确保代码在各种环境下的稳健性。