psychtoolbox 是 MATLAB 中的一个工具包,对于科研人员设计实验范式来说是不二之选,因为它可以操作计算机的底层硬件,精度可以达到帧的级别。
文章目录
- 一、实验目的
- 二、psychtoolbox 的下载安装
- 三、Psychtoolbox 的基本使用
- 四、完整代码
一、实验目的
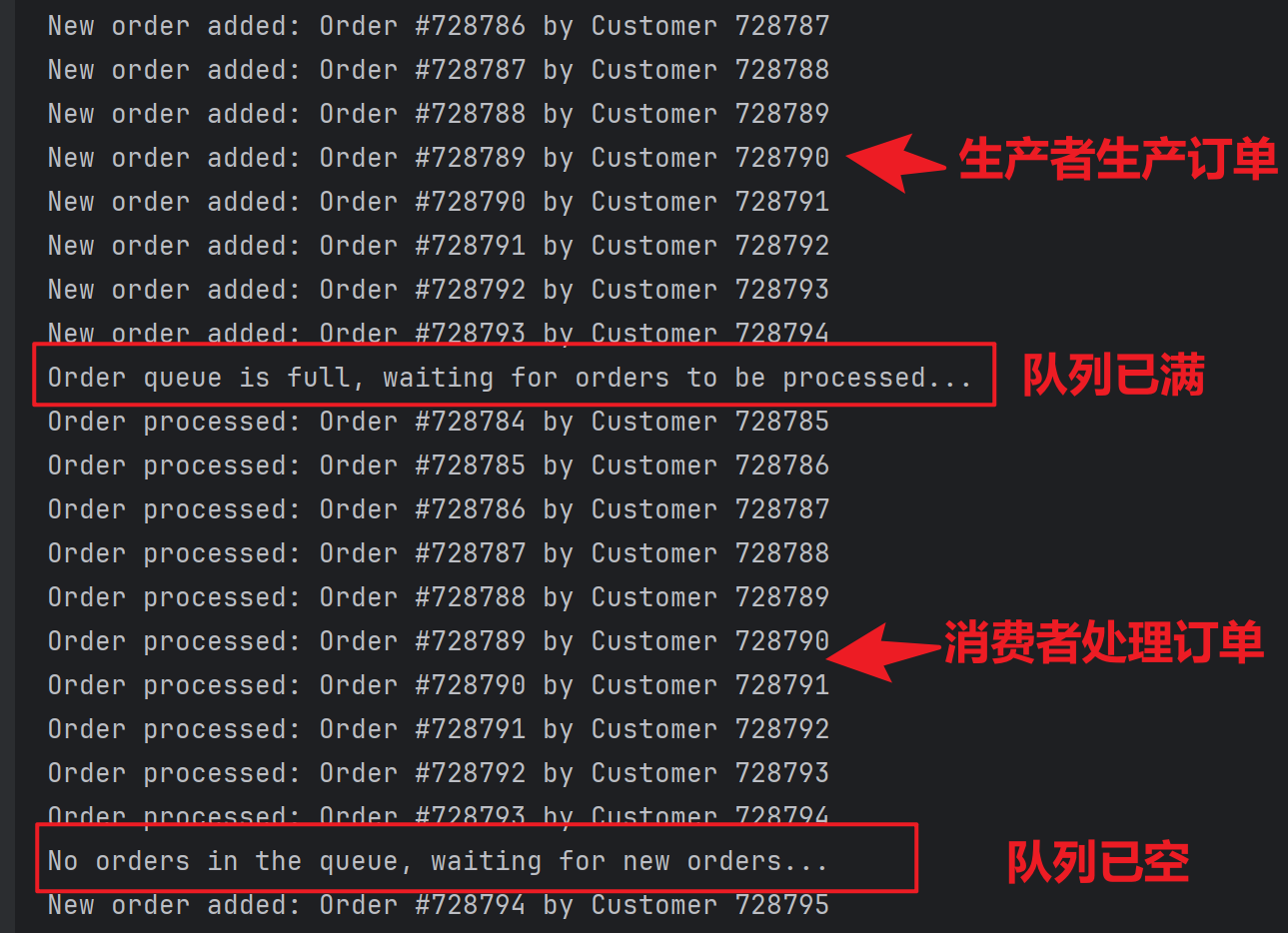
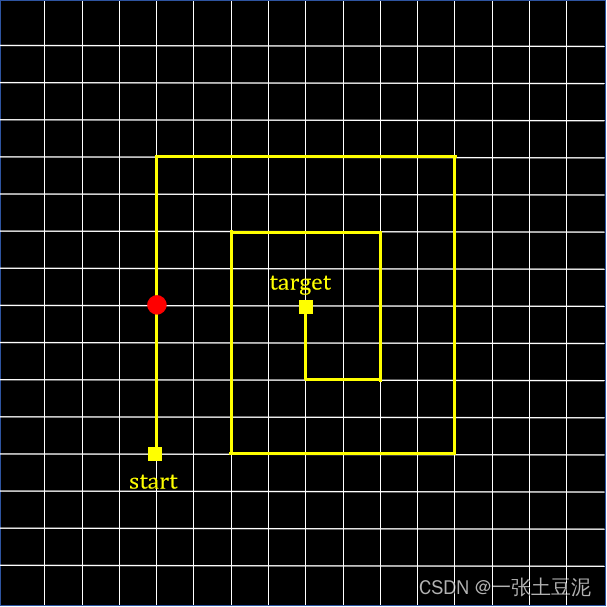
我们的目的是设计出一个迷宫(网格线上的一条路径),使得小球每隔3s就移动一格,当然每次小球移动的对错概率都是我们自己实现设定好的。
二、psychtoolbox 的下载安装
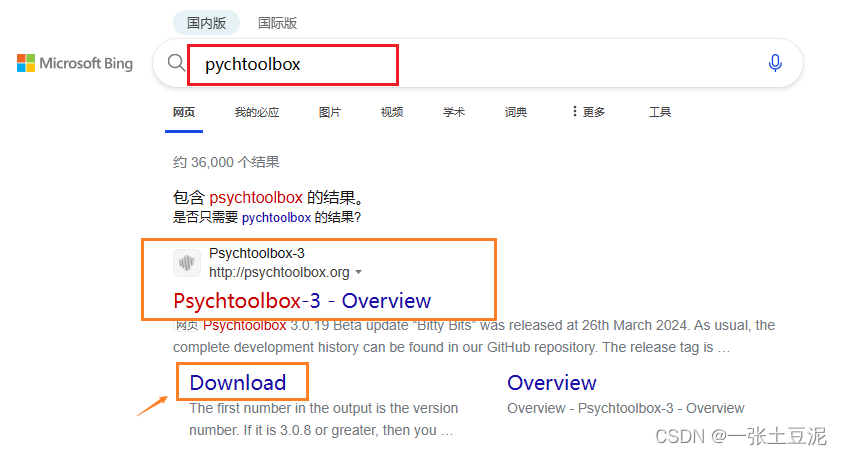
- 首先在BING搜索,认准第一个org结尾的官网,可以进入官网,也可以直接点击下方的“Download”,跳转到下载界面。
- 进入到下载界面后,按照下图中的三个步骤(第一步可不做,如果是第一次安装)。
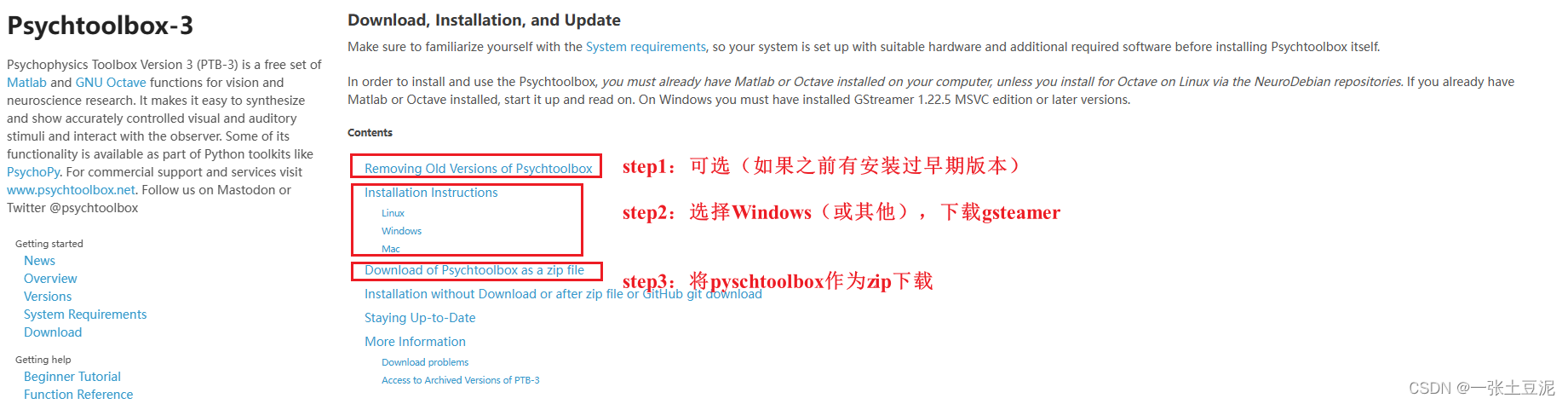
(1)下面是第二步,点击这里可下载gstreamer,按照指引一步步安装即可。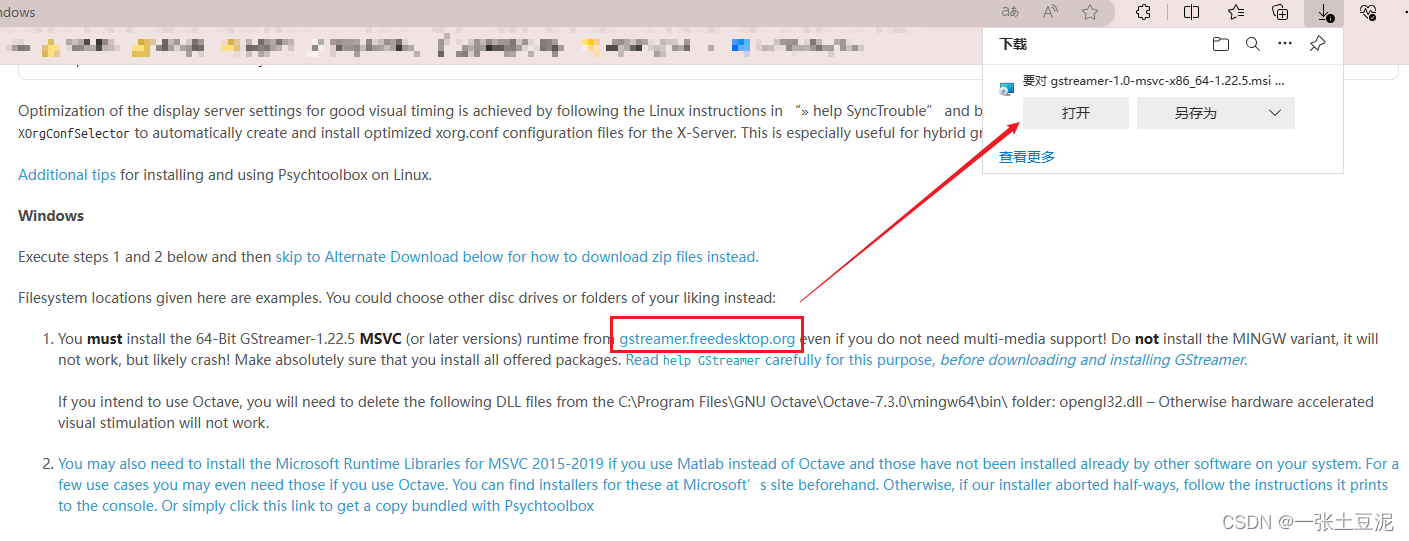
(2)下载zip,将压缩包的子文件夹里的所有文件都拖入到一个新建的“toolbox”文件夹里。
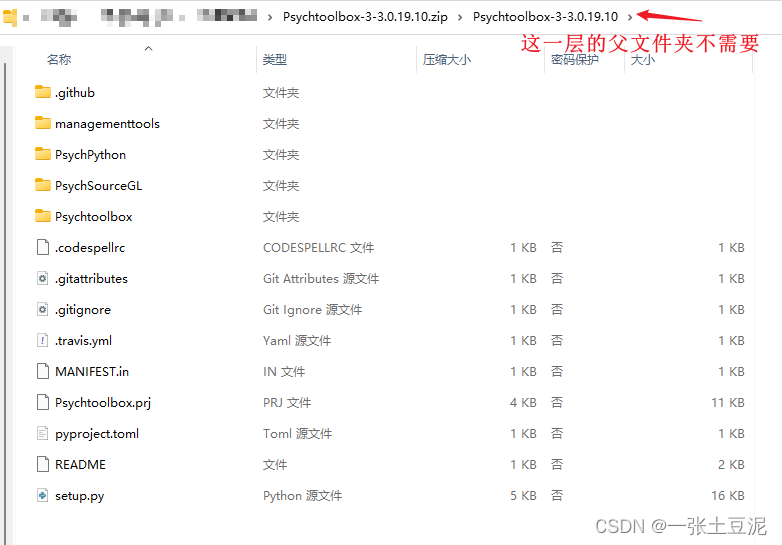
处理完之后像下图一样就对了。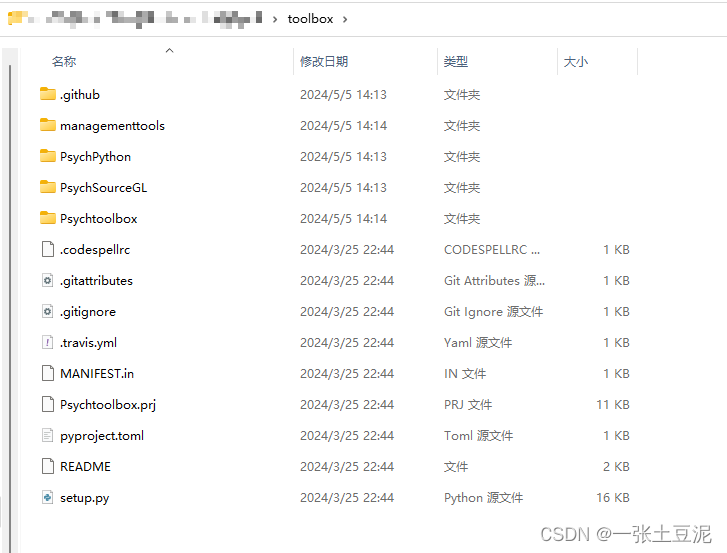
- 进入MATLAB,打开到刚才的toolbox->Psychtoolbox 路径。
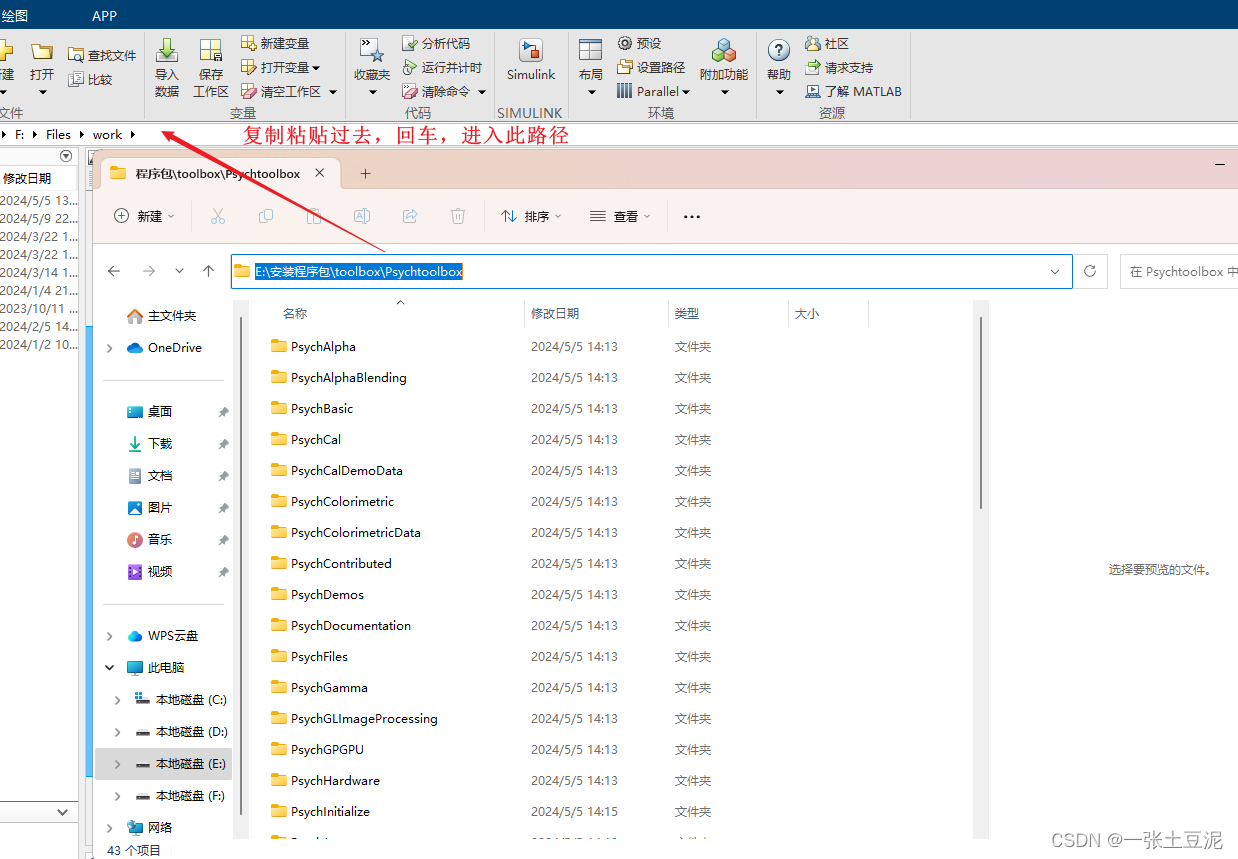
- 在命令行中输入
SetupPsychtoolbox,回车,等待即可,中间需要一路回车进行。最后出现“Success,Enjoy”等字样即安装成功。可以继续在命令行使用Screen来测试是否安装成功。
三、Psychtoolbox 的基本使用
-
基本原理
首先它是通过一帧一帧翻转窗口来实现所谓的动态效果,所以我们的逻辑基本就是先在画布上绘制下一帧的画面,然后翻转。
可以自行到官网找到参考文档,网络上所有文章基本都是从那里复制出来的,并且还可以看到官网提供的Demos。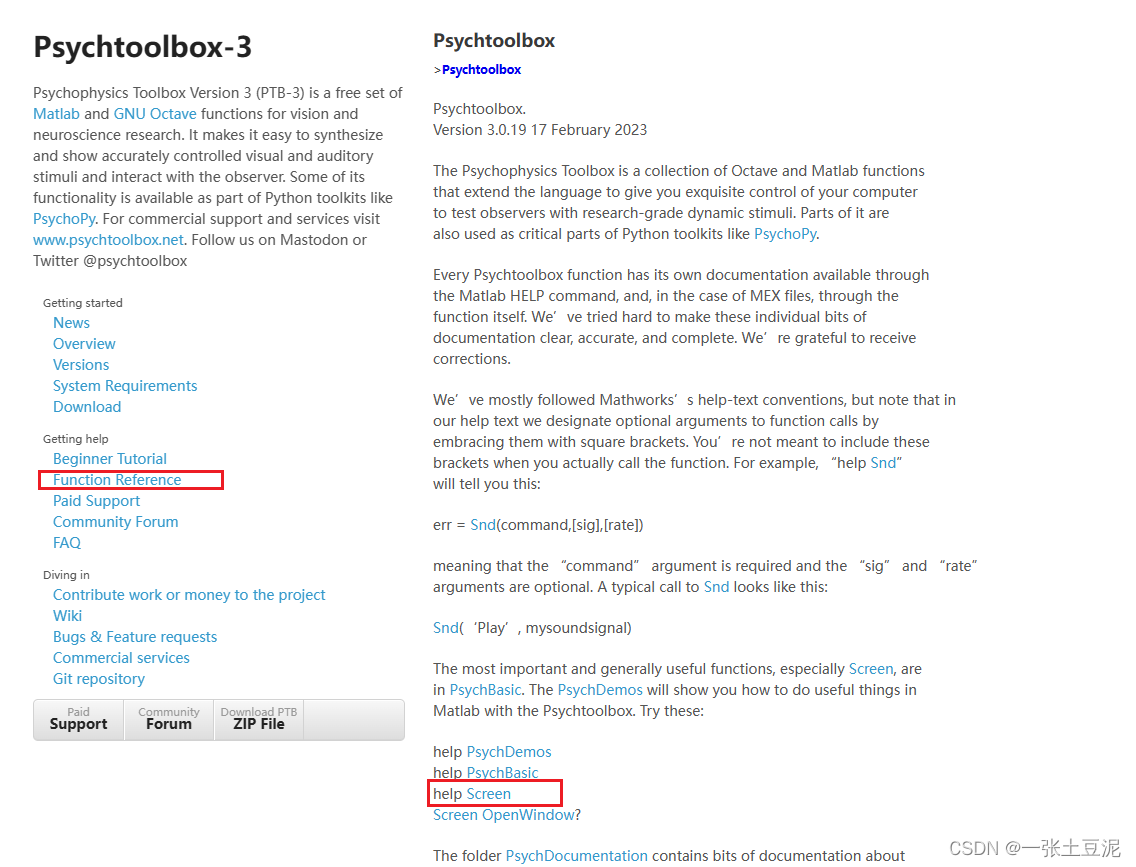
-
这里提供几个常使用到的函数:
/* 开头需要加的。 */
Screen('Preference', 'SkipSyncTests', 1);
Screen('Preference','SkipSyncTests',2);
/* 隐藏鼠标。 */
HideCursor;
/* 函数功能:新建一个窗口。
* 返回值:w,窗口的句柄;
* 返回值:wrect,主要用来获取屏幕的长宽。
* 参数:命令,可在命令行“help Screen”获取帮助文档或者直接到官网。
* 参数:第n个屏幕,一般无扩展屏的话直接默认0.
* 参数:颜色,窗口的RGB数组。这里是黑色。
*/
[w, wrect] = Screen('OpenWindow', 0, [0, 0, 0]);
/* 写文本。一般进行心理实验之前需要一段引导语。
* 参数:imread后面为图片的路径。
*/
instruction=Screen('MakeTexture',w,imread('xxx\xxx\xx.tif'));
Screen('DrawTexture',w,instruction,[]);%显示提示语
/* 函数功能:画直线。
* 返回值:无
* 参数:命令,画直线、画圆等等。
* 参数:窗口的句柄,按之前来讲就是w。
* 参数:颜色。
* 参数:后面四个参数依次为x轴起点坐标、y轴起点坐标、x轴终点坐标、y轴终点坐标。
* 参数:线宽。
*/
Screen(‘DrawLine’, windowPtr [,color], fromH, fromV, toH, toV [,penWidth]);
/* 函数功能:画实心圆。
* 返回值:无
* 参数:命令。
* 参数:窗口的句柄。
* 参数:颜色。
* 参数:后面四个参数依次为圆的左、上、右、下边界坐标。
*/
Screen(‘FillOval’, windowPtr [,color] [,rect] [,perfectUpToMaxDiameter]);
/* 翻转。每次绘制完画布都要进行一次翻转,这样新绘制的场景才能显示出来。重要!!! */
Screen('Flip',w)
/* 延时函数,单位:秒。*/
WaitSecs();
/* 按键检测。以下是一个退出机制,按下Esc键退出。27对应Esc键的ASCII值。*/
while true
[keyIsDown,~,keyCode]=KbCheck;
if keyCode(27)
break;
end
end
/* 关闭窗口,搭配上面的退出机制使用。*/
Screen('CloseAll');
/* 常用的颜色RGB值。*/
color_red = [255,0,0];
color_white = [255, 255, 255];
color_black = [0, 0, 0];
color_yellow = [255, 255, 0];
四、完整代码
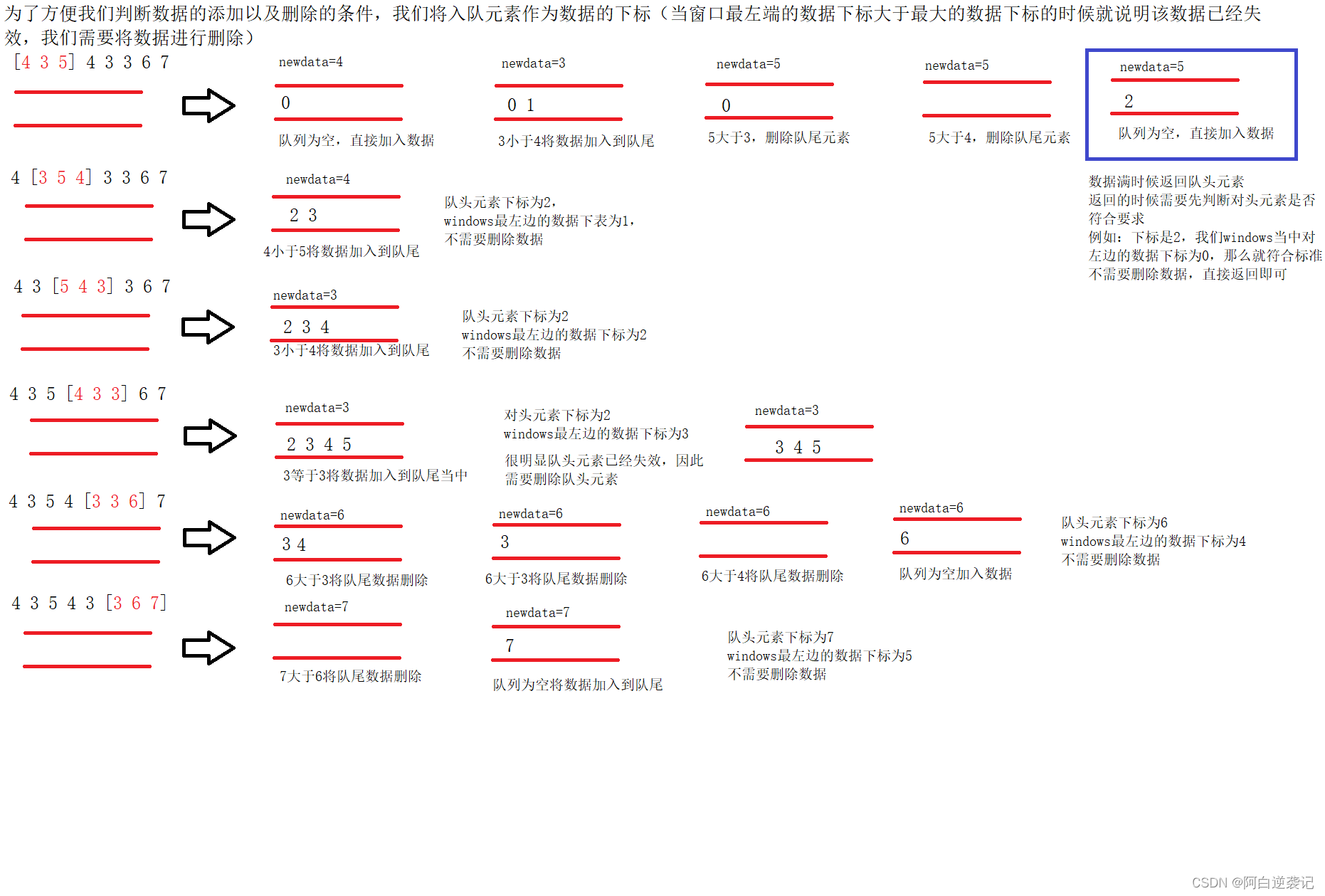
- 功能逻辑通过一个哈希表来一一映射小球每一步的正确、错误情况。
decision_hashmap = zeros(1, 100);
decision_hashmap(1, [3,7,13,18,23,27,32,37, 42,46,50, 54,58, 63,67, 72,76, 79, 83]) = 1; % 第i个元素置一表示第i步为小球错误运动方向
step_up_right = 8 + 2 * 2; % 由up转向right的第x步
step_right_down = step_up_right + 8 + 2 * 3;
step_down_left = step_right_down + 8 + 2 * 3;
step_left_up = step_down_left + 6 + 2 * 3;
step_up_right_2 = step_left_up + 6 + 2 * 2;
step_right_down_2 = step_up_right_2 + 4 + 2 * 2;
step_down_left_2 = step_right_down_2 + 4 + 2 * 2;
step_left_up_2 = step_down_left_2 + 2 + 2 * 1;
step_up_end = step_left_up_2 + 2 + 2 * 1;
在for循环里实现小球的转向和正误判断,下面只张贴正确情况的转向逻辑代码,完整代码可移步gitee仓库Psychtoolbox绘制小球走迷宫下载。
for step = 1 : step_up_end
% 通过中间变量,记录上一步小球的位置
if(step == 1)
previous_y_index_up = xy_4_trace_start(2);
previous_y_index_down = xy_4_trace_start(4);
previous_x_index_left = xy_4_trace_start(1);
previous_x_index_right = xy_4_trace_start(3);
else
previous_y_index_up = current_y_index_up;
previous_y_index_down = current_y_index_down;
previous_x_index_left = current_x_index_left;
previous_x_index_right = current_x_index_right;
end
% 小球动态路径
if ~decision_hashmap(step) % 正确
if step <= step_up_right
current_y_index_up = previous_y_index_up - length_chessboard;
current_y_index_down = previous_y_index_down - length_chessboard;
current_x_index_left = previous_x_index_left;
current_x_index_right = previous_x_index_right;
Screen('FillOval', w, color_ball, [current_x_index_left current_y_index_up ...
current_x_index_right current_y_index_down]);
elseif step <= step_right_down
current_y_index_up = previous_y_index_up ;
current_y_index_down = previous_y_index_down ;
current_x_index_left = previous_x_index_left + length_chessboard;
current_x_index_right = previous_x_index_right + length_chessboard;
Screen('FillOval', w, color_ball, [current_x_index_left current_y_index_up ...
current_x_index_right current_y_index_down]);
...
end