OpenCV | 入门
安装
参考教程
基础知识
V
G
A
=
640
×
480
VGA = 640 \times 480
VGA=640×480
H
D
=
1280
×
720
HD = 1280 \times 720
HD=1280×720
F
H
D
=
1920
×
1080
FHD = 1920 \times 1080
FHD=1920×1080
4
K
=
3840
×
2160
4K = 3840 \times 2160
4K=3840×2160
这些都表示了固定的像素,例如 VGA,代表在宽度上 640 像素(px),在高度上 480 像素。我们可以把这些像素看成一个一个框。
对于黑白图像 Binary Image, 用 0 代表黑色,用 1 代表白色。
对于 8 位,可以表示
2
8
=
256
2^8 = 256
28=256 个级别,也就是 0 ~ 255。一个灰度图像(Gray Scale Image) 也就是 8 Bit or 256 Level 的。
OpenCV学习笔记——HSV颜色空间超极详解&inRange函数用法及实战
显示图像
图片与代码放在同个目录下。
#include <opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
/* Importing Images */
string path = "../dog.jpeg";
Mat img = imread(path);
imshow("Image", img);
waitKey(0);
}

播放视频
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string path = "../Megamind.avi";
VideoCapture cap(path);
Mat img;
while(1)
{
cap.read(img);
imshow("Image", img);
waitKey(3); // 添加延时
}
return 0;
}
将图片转换为灰度图像
string path = "../dog.jpeg";
Mat img = imread(path);
Mat imgGray;
/* 转换图像颜色 */
cvtColor(img, imgGray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
imshow("Image", img);
imshow("Image Gray", imgGray);
waitKey(0);

模糊图像
Mat imgBlur;
GaussianBlur(img, imgBlur, Size(7, 7), 5, 0);
imshow("Image Blur", imgBlur);

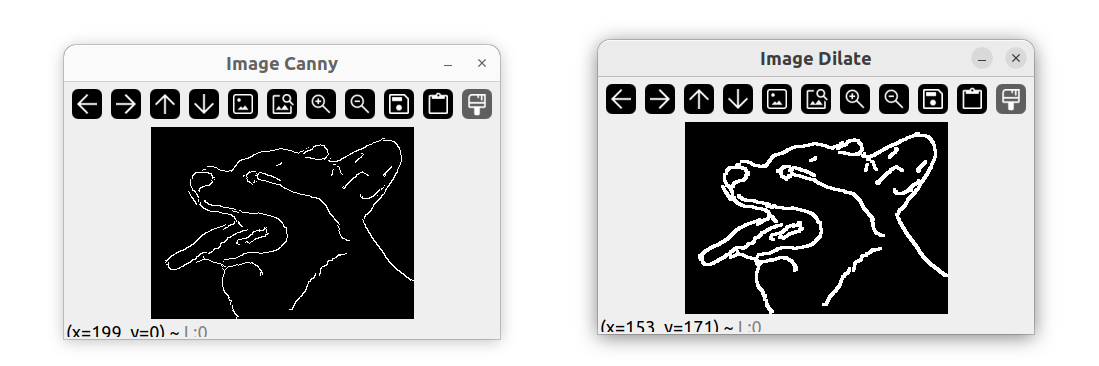
边缘检测
Mat imgCanny;
Canny(imgBlur, imgCanny, 50, 150);
imshow("Image Canny", imgCanny);

对于 Canny 函数
void cv::Canny(InputArray image, OutputArray edges, double lowThreshold, double highThreshold, int apertureSize = 3);
/*
image:输入图像,应该是灰度图像。
edges:输出图像,即检测到的边缘图像。
lowThreshold:低阈值,用于双阈值检测。
highThreshold:高阈值,用于双阈值检测。
apertureSize:指定Sobel算子的大小,默认为3。
*/
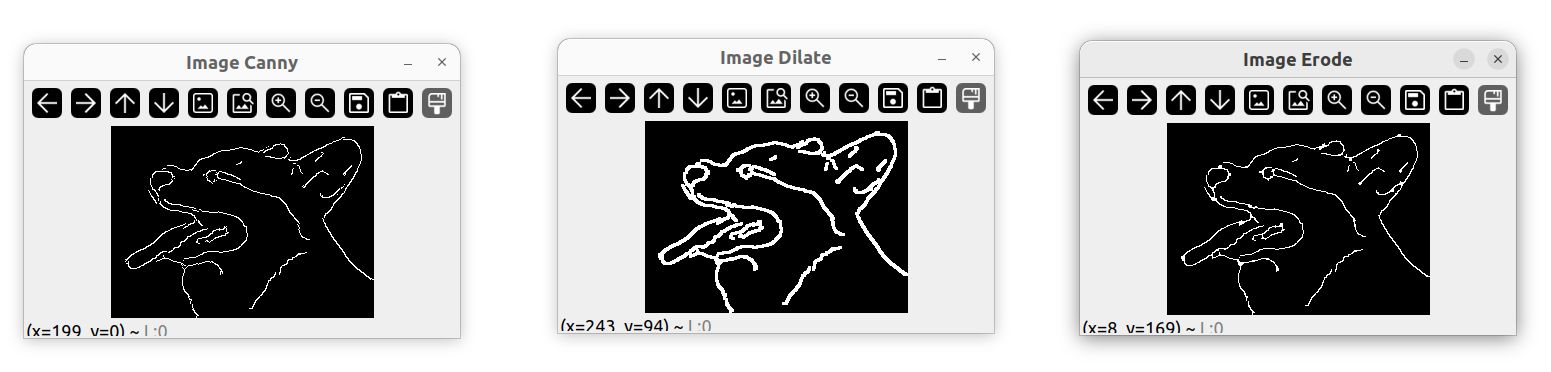
图像膨胀
Mat imgDil;
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3));
dilate(imgCanny, imgDil, kernel);
imshow("Image Dilate", imgDil);
getStructuringElement 函数返回一个结构元素(卷积核)。
Mat kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(a,b,c);
/*
a 设定卷积核的形状,不同卷积核(形状、大小)对图形的腐蚀、膨胀操作效果不同。
MORPH_RECT(函数返回矩形卷积核)
MORPH_CROSS(函数返回十字形卷积核)
MORPH_ELLIPSE(函数返回椭圆形卷积核)
b 设定卷积核的大小
用 (x, y) 表示,表示卷积核有 x 行 y 列。
c 表示描点的位置,一般 c = 1,表示位于中心。
*/
图像腐蚀
Mat imgErode;
erode(imgDil, imgErode, kernel);
imshow("Image Erode", imgErode);
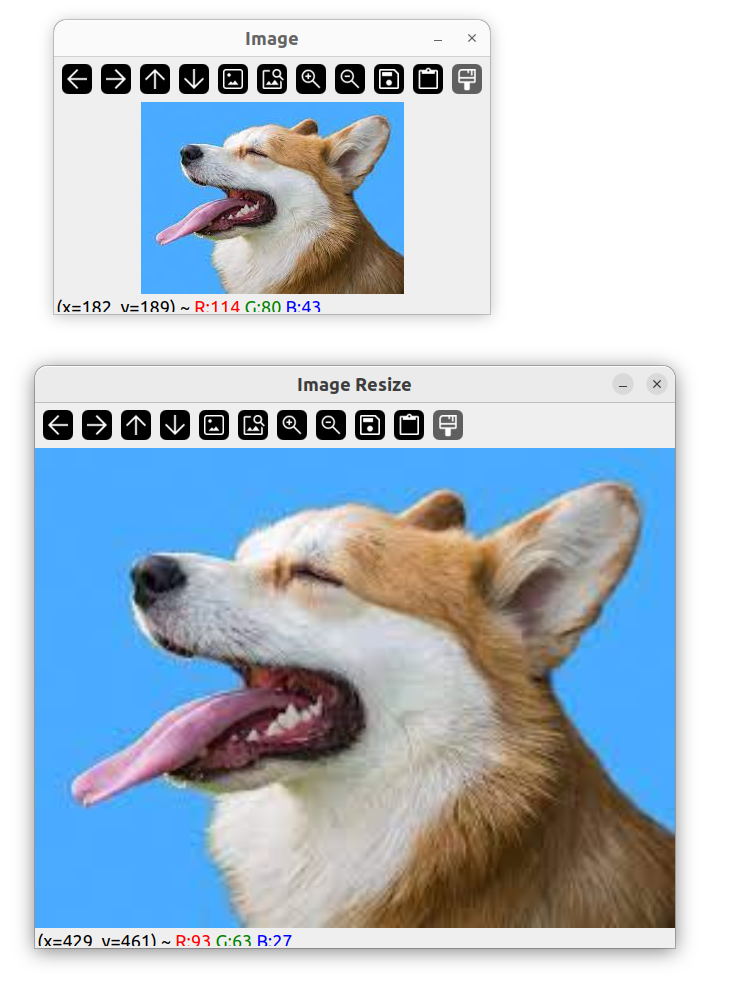
调整图片大小
输出图片的尺寸
cout << img.size() << endl;

对其进行增大
Mat imgResize;
resize(img, imgResize, Size(640, 480));
imshow("Image Resize", imgResize);
如果使用比例进行缩小,缩小到 二分之一
resize(img, imgResize, Size(), 0.5, 0.5);

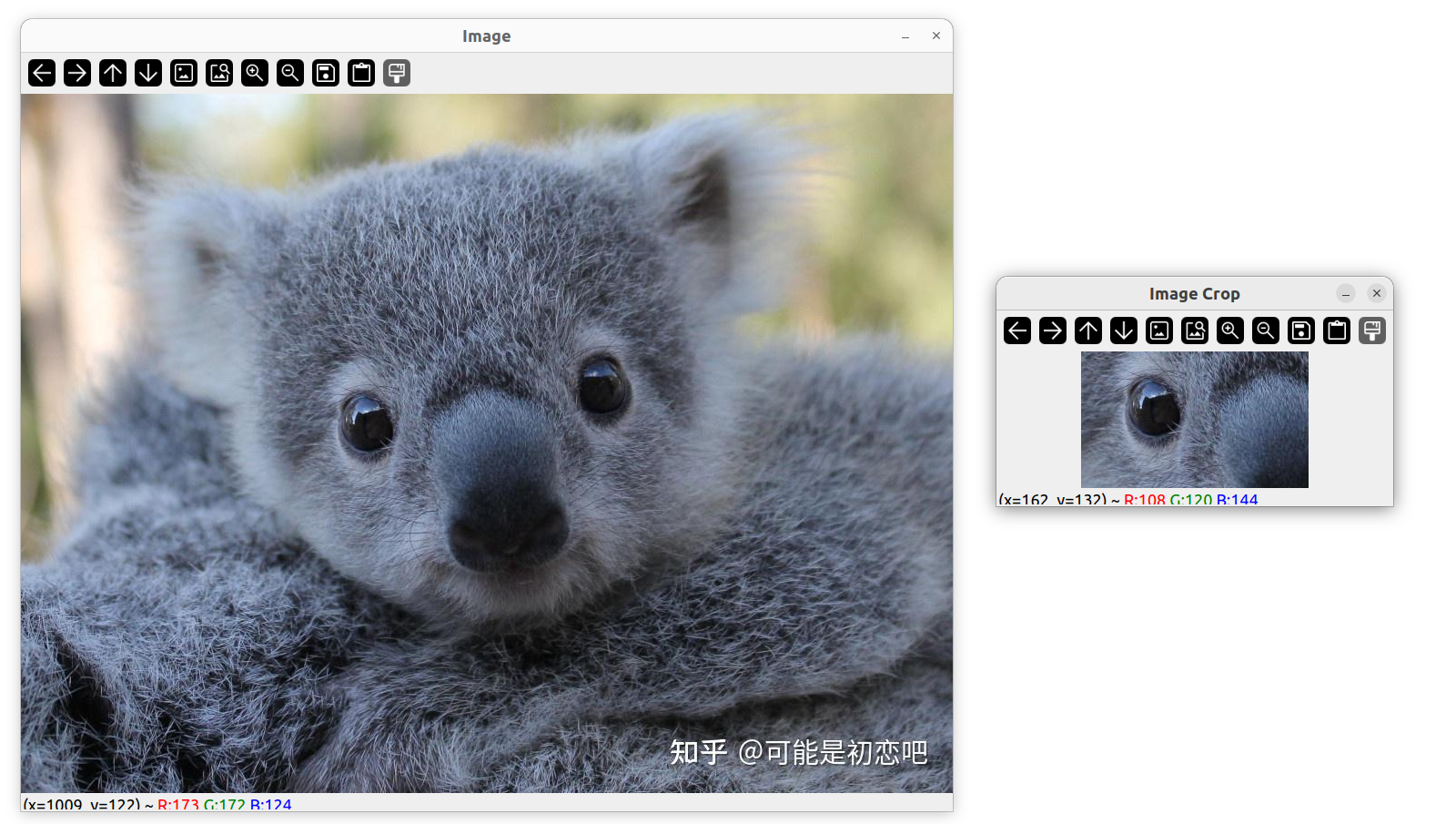
裁剪图片
用 Rect 裁剪一块矩形
Mat imgCrop;
Rect roi(300, 300, 250, 150); // x 坐标 y 坐标 宽度 高度
imgCrop = img(roi);
imshow("Image Crop", imgCrop);
创建图片
创建一张蓝色的图片
Mat img(512, 512, CV_8UC3, Scalar(255, 0, 0));
imshow("Image", img);

绘制图形
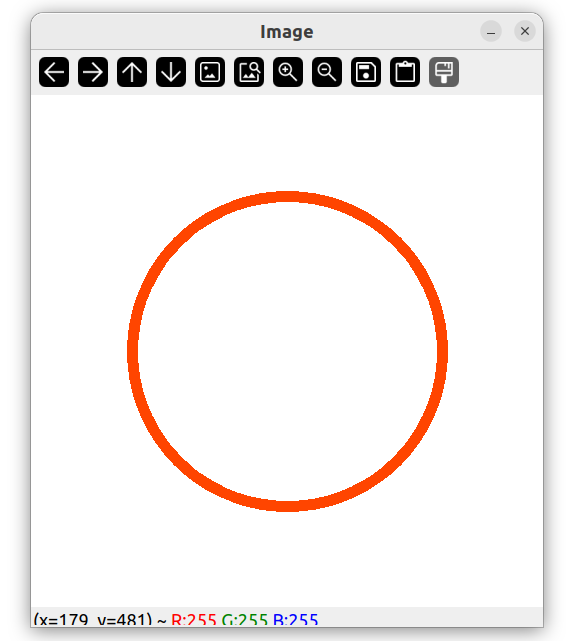
绘制圆圈
// White Image
Mat img(512, 512, CV_8UC3, Scalar(255, 255, 255));
circle(img, Point(256, 256), 155, Scalar(0, 69, 255));
imshow("Image", img);

增加圆圈的厚度
circle(img, Point(256, 256), 155, Scalar(0, 69, 255), 10);
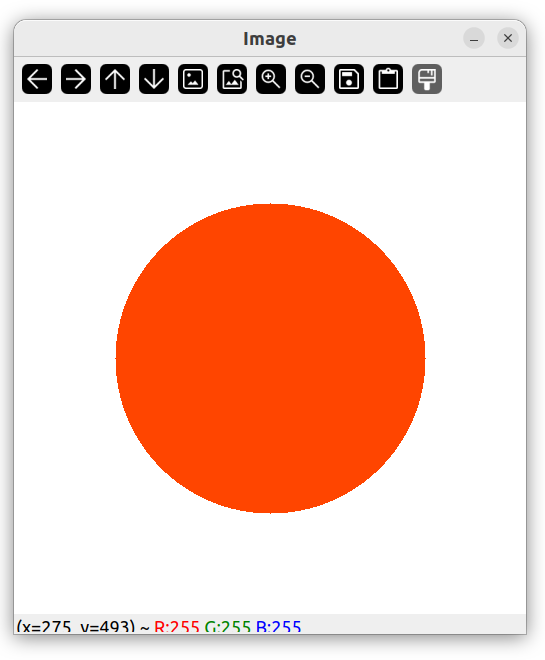
填满圆圈
circle(img, Point(256, 256), 155, Scalar(0, 69, 255), FILLED);
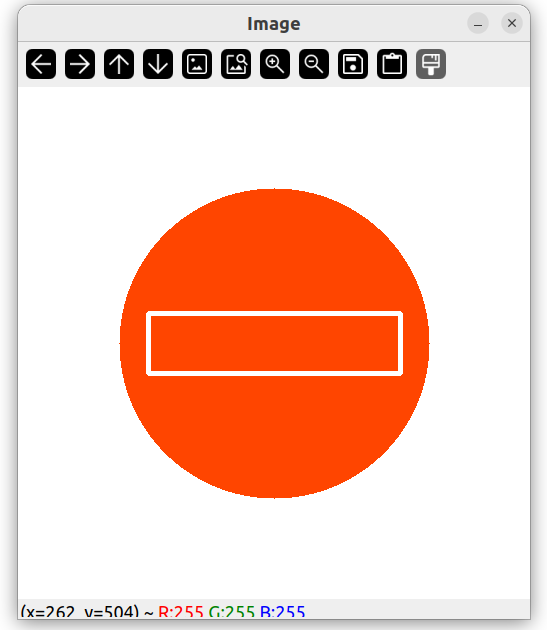
绘制矩形
rectangle(img, Point(130, 226), Point(382, 286), Scalar(255, 255, 255), 3);
// 两个 Point 分别代表矩形左上角坐标和右下角坐标
将矩形填满
rectangle(img, Point(130, 226), Point(382, 286), Scalar(255, 255, 255), FILLED);

绘制一条线
line(img, Point(130, 296), Point(382, 296), Scalar(255, 255, 255), 2);
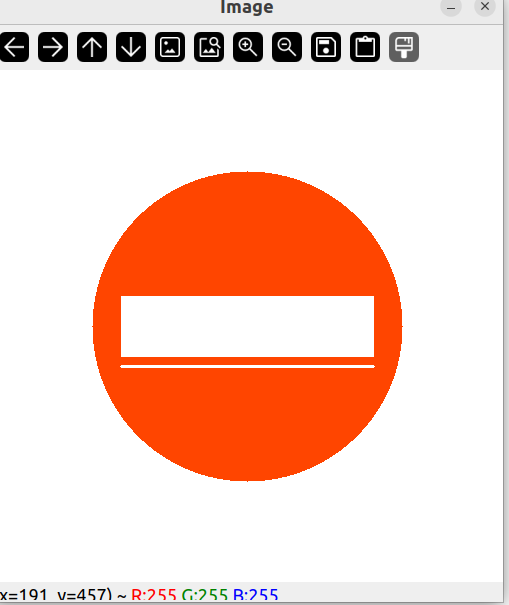
添加文字
putText(img, "Birdy's Workshop", Point(137, 262), FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.75, Scalar(0, 69, 255));

给文字添加厚度
putText(img, "Birdy's Workshop", Point(137, 262), FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.75, Scalar(0, 69, 255), 2);

Warp images
原图像:
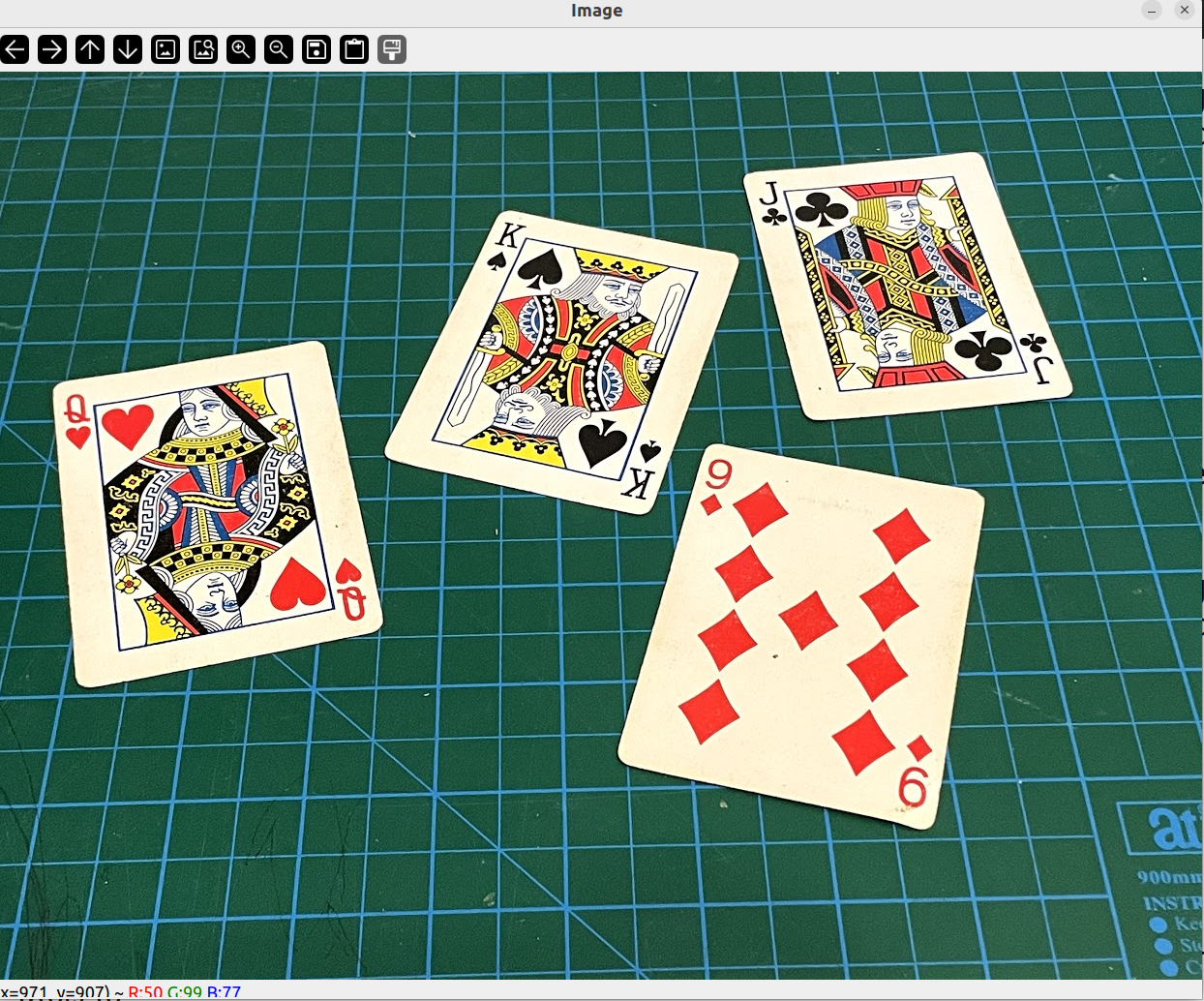
int main()
{
string path = "../image/cards.jpg";
float w = 250, h = 350;
Mat img = imread(path);
Mat matrix, imgWarp;
Point2f src[4] = {{529, 142}, {779, 190}, {405, 395}, {674, 457}};
Point2f dst[4] = {{0.0f, 0.0f}, {w, 0.0f}, {0.0f, h}, {w, h}};
matrix = getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst);
warpPerspective(img, imgWarp, matrix, Point(w, h));
imshow("Image", img);
imshow("Image Warp", imgWarp);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}

圈出选中的四个角
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
circle(img, src[i], 10, Scalar(0, 0, 255), FILLED);
}
imshow("Image", img);
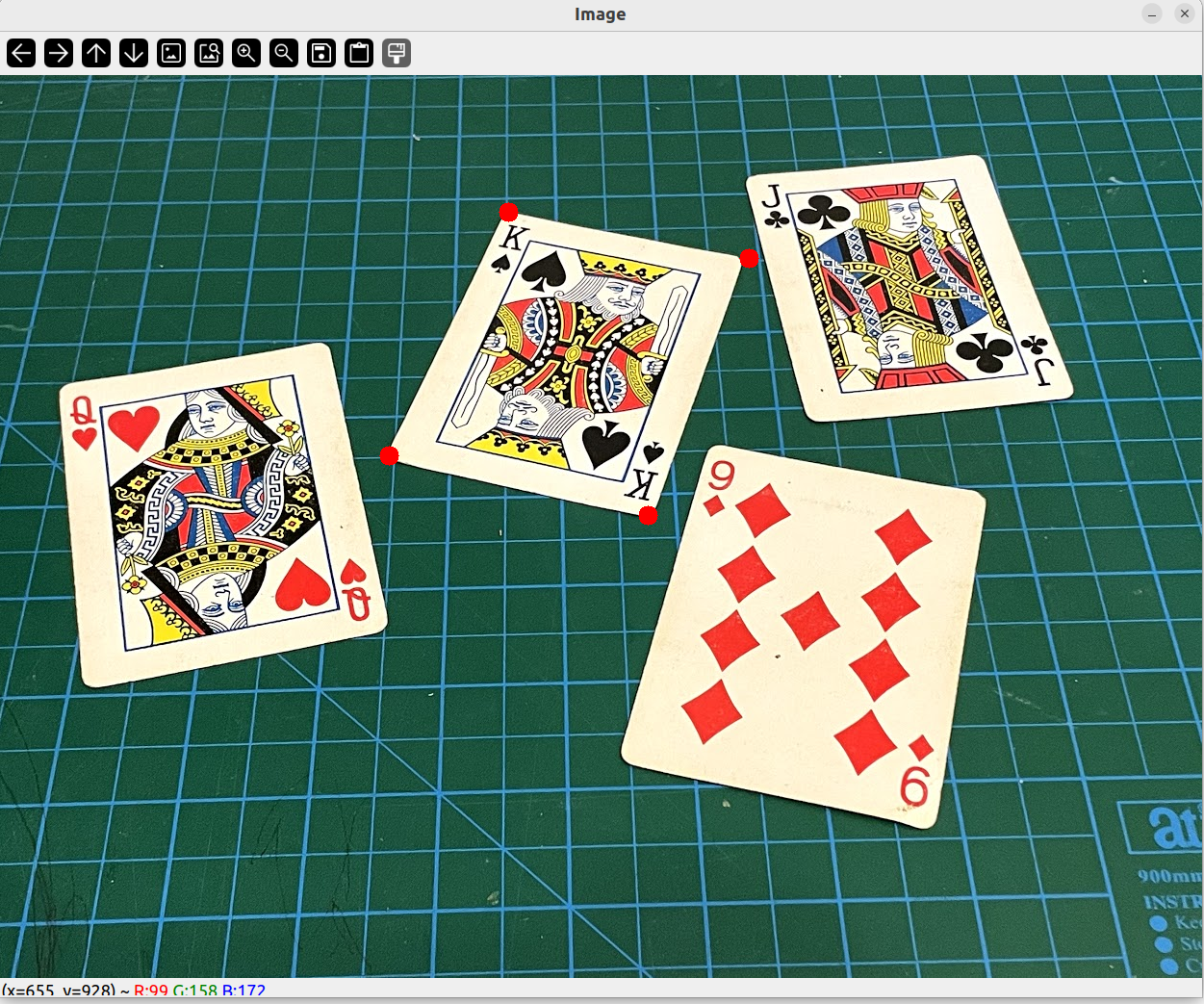
颜色检测
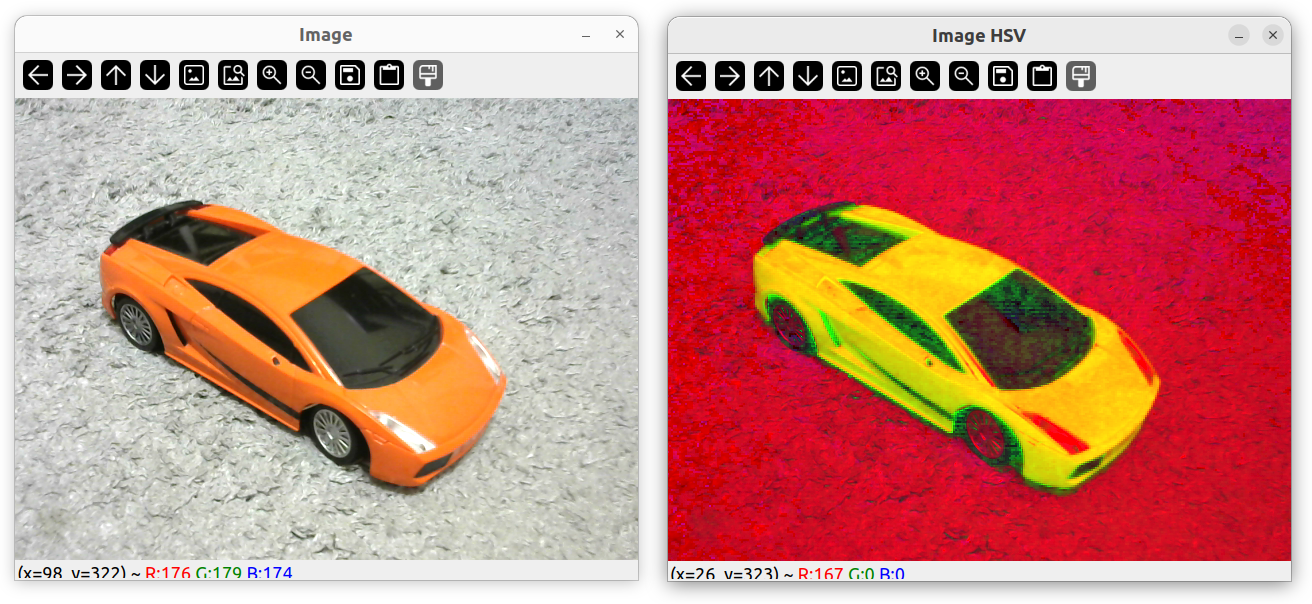
原图像
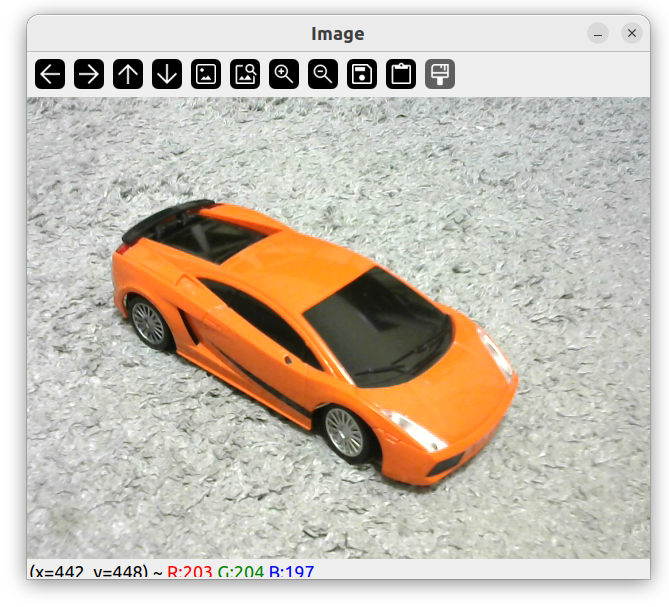
HSV 颜色系统
Hue 色相
Saturation 饱和度
Value 色调、纯度
转换 HSV
将图像转换为 hsv 空间可以更容易识别颜色。
Mat imgHSV;
cvtColor(img, imgHSV, COLOR_BGR2HSV);
imshow("Image HSV", imgHSV);
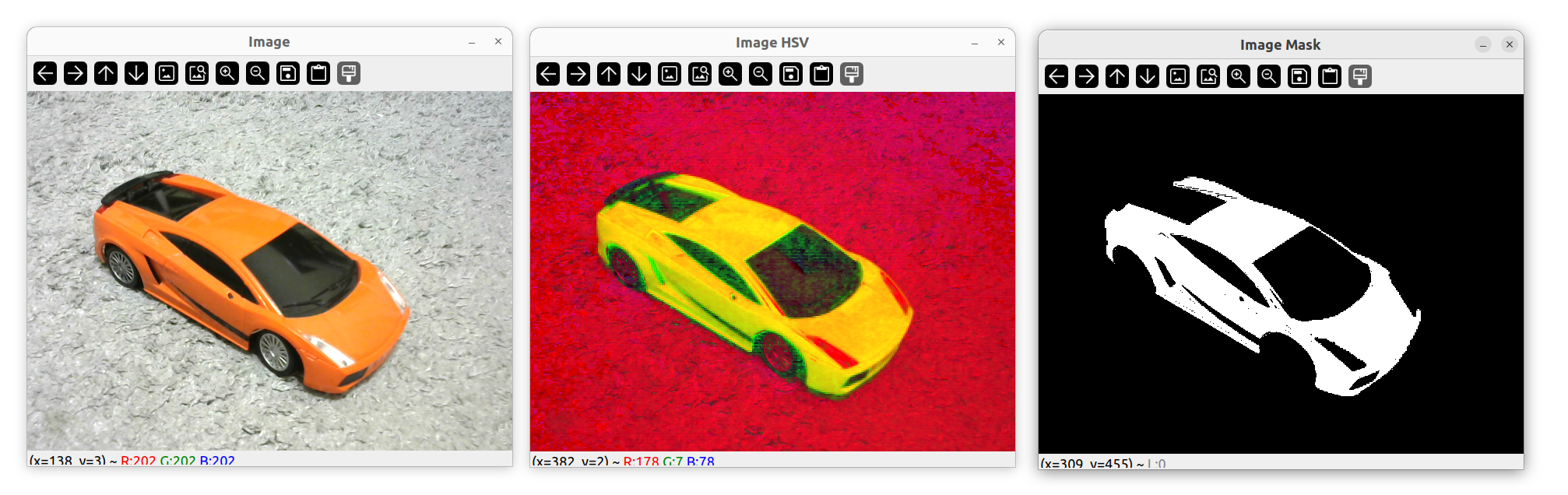
Mask
Mat mask;
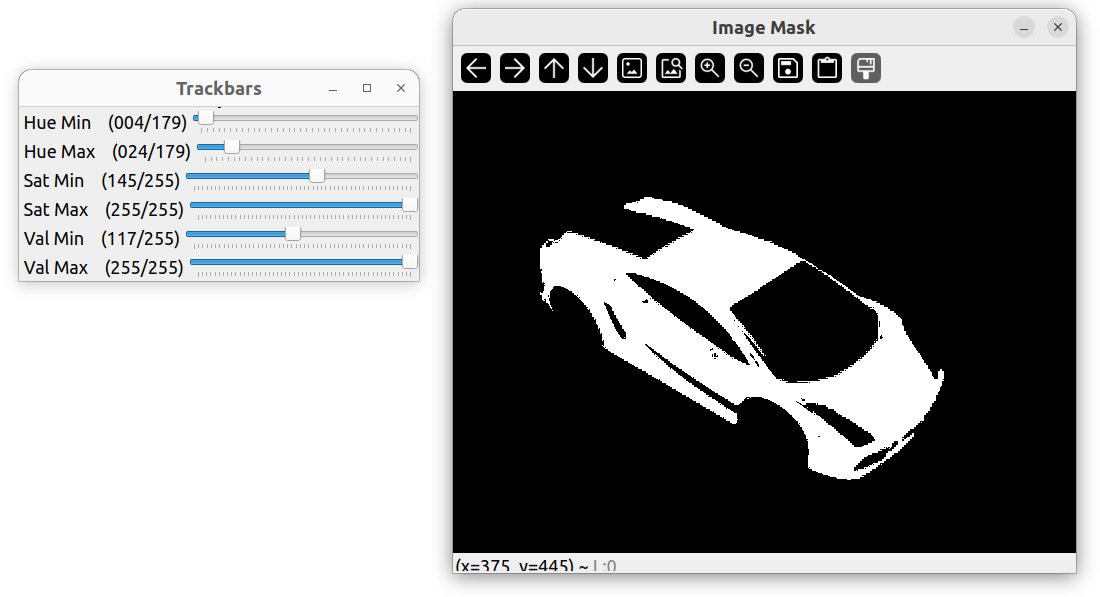
int hmin = 0, smin = 110, vmin = 153;
int hmax = 19, smax= 240, vmax = 255;
Scalar lower(hmin, smin, vmin);
Scalar upper(hmax, smax, vmax);
inRange(imgHSV, lower, upper, mask);
imshow("Image Mask", mask);
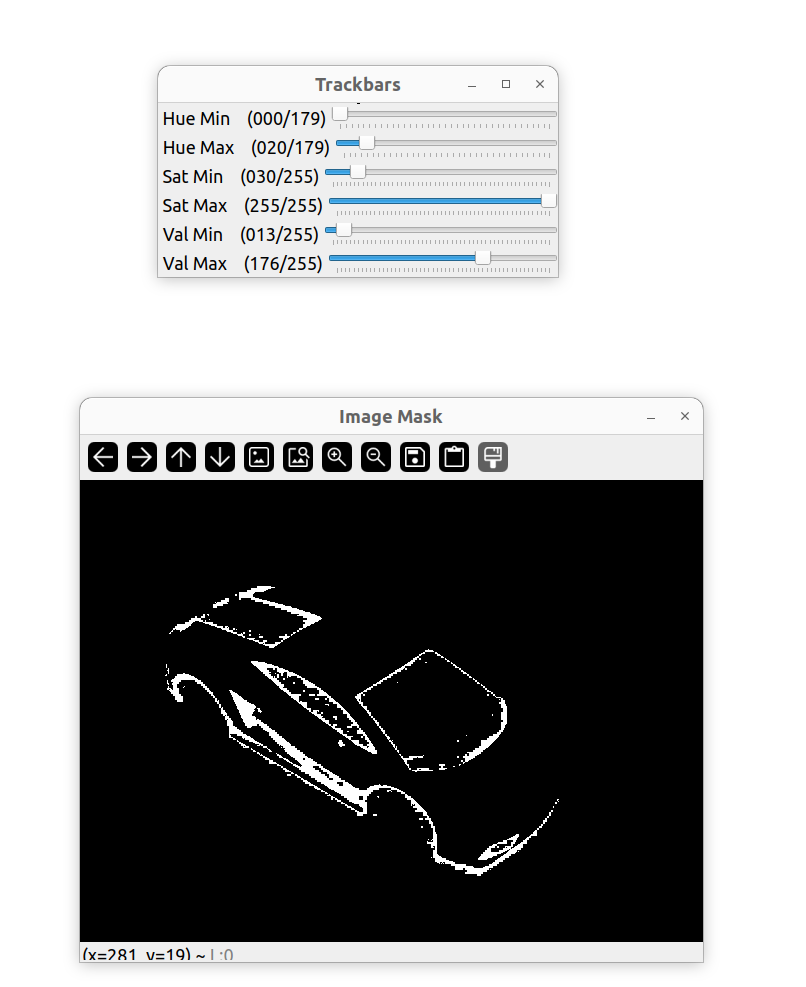
上述代码中的 hmin、smin、vim … 一系列的值如果通过每次手动修改去找到适合的就会非常麻烦。可以通过创建轨道的方式进行动态修改。
int main()
{
string path = "../image/lambo.png";
Mat img = imread(path);
Mat imgHSV, mask;
cvtColor(img, imgHSV, COLOR_BGR2HSV);
int hmin = 0, smin = 110, vmin = 153;
int hmax = 19, smax= 240, vmax = 255;
namedWindow("Trackbars", (640, 200));
createTrackbar("Hue Min", "Trackbars", &hmin, 179);
createTrackbar("Hue Max", "Trackbars", &hmax, 179);
createTrackbar("Sat Min", "Trackbars", &smin, 255);
createTrackbar("Sat Max", "Trackbars", &smax, 255);
createTrackbar("Val Min", "Trackbars", &vmin, 255);
createTrackbar("Val Max", "Trackbars", &vmax, 255);
while(1)
{
Scalar lower(hmin, smin, vmin);
Scalar upper(hmax, smax, vmax);
inRange(imgHSV, lower, upper, mask);
imshow("Image", img);
imshow("Image HSV", imgHSV);
imshow("Image Mask", mask);
waitKey(1);
}
return 0;
}
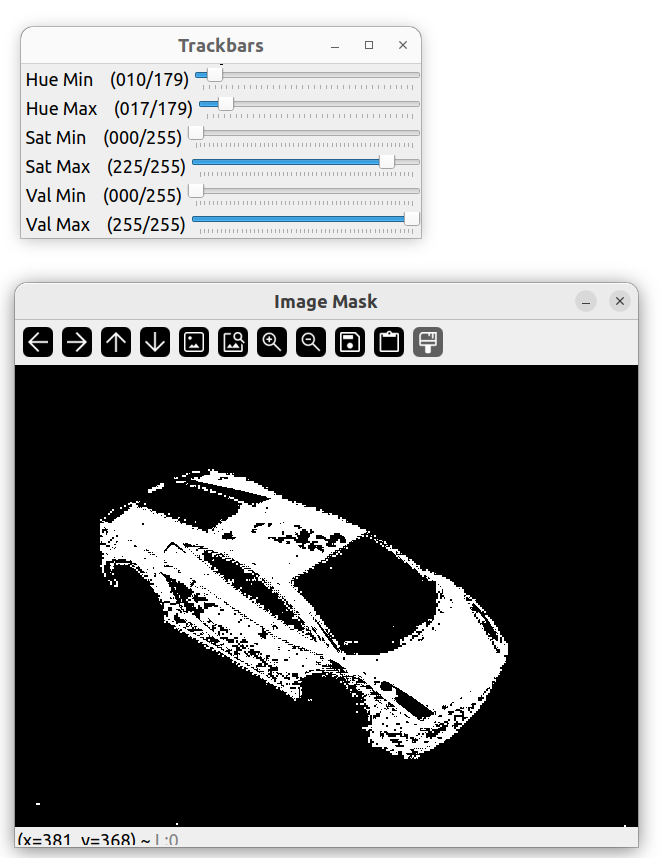
调节之后:
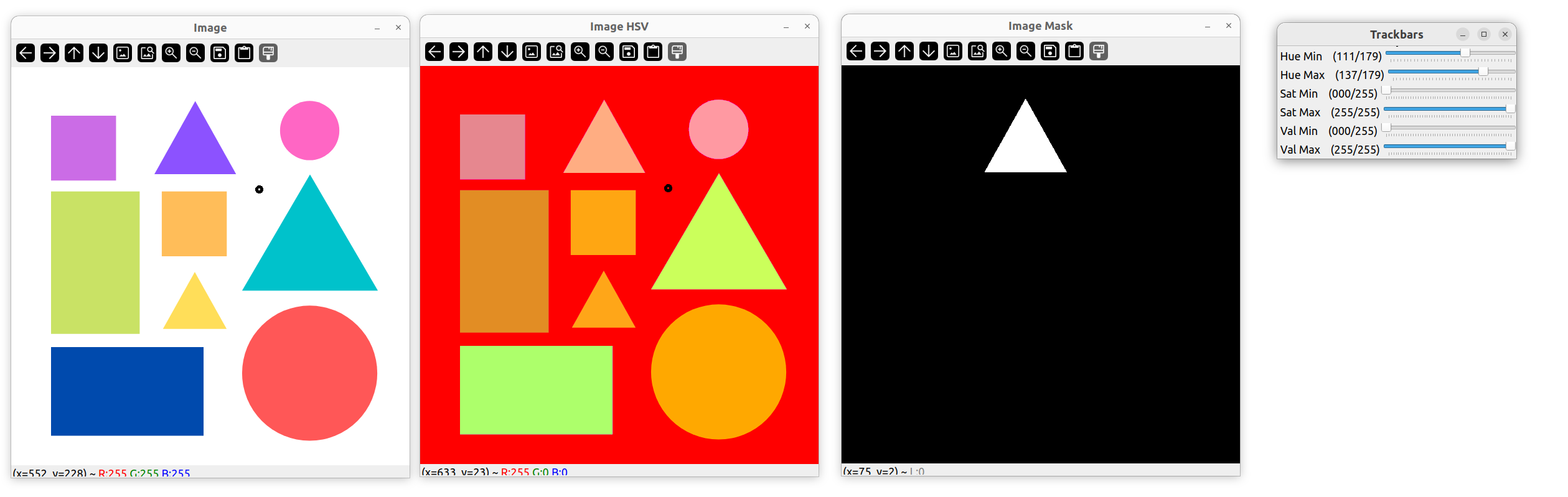
检测不同颜色物体
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string path = "../image/shapes.png";
Mat img = imread(path);
Mat imgHSV, mask;
int hmin = 0, smin = 0, vmin = 0;
int hmax = 179, smax= 255, vmax = 255;
cvtColor(img, imgHSV, COLOR_BGR2HSV);
namedWindow("Trackbars", (640, 200));
createTrackbar("Hue Min", "Trackbars", &hmin, 179);
createTrackbar("Hue Max", "Trackbars", &hmax, 179);
createTrackbar("Sat Min", "Trackbars", &smin, 255);
createTrackbar("Sat Max", "Trackbars", &smax, 255);
createTrackbar("Val Min", "Trackbars", &vmin, 255);
createTrackbar("Val Max", "Trackbars", &vmax, 255);
while(1)
{
Scalar lower(hmin, smin, vmin);
Scalar upper(hmax, smax, vmax);
inRange(imgHSV, lower, upper, mask);
imshow("Image", img);
imshow("Image HSV", imgHSV);
imshow("Image Mask", mask);
waitKey(1);
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
检测轮廓、形状
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string path = "../image/shapes.png";
Mat img = imread(path);
Mat imgGray, imgBlur, imgCanny, imgDil, imgErode;
cvtColor(img, imgGray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
GaussianBlur(imgGray, imgBlur, Size(3, 3), 3, 0);
Canny(imgBlur, imgCanny, 25, 75);
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3));
dilate(imgCanny, imgDil, kernel);
imshow("Image", img);
imshow("Image Gray", imgGray);
imshow("Image Blur", imgBlur);
imshow("Image Canny", imgCanny);
imshow("Image Dil", imgDil);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
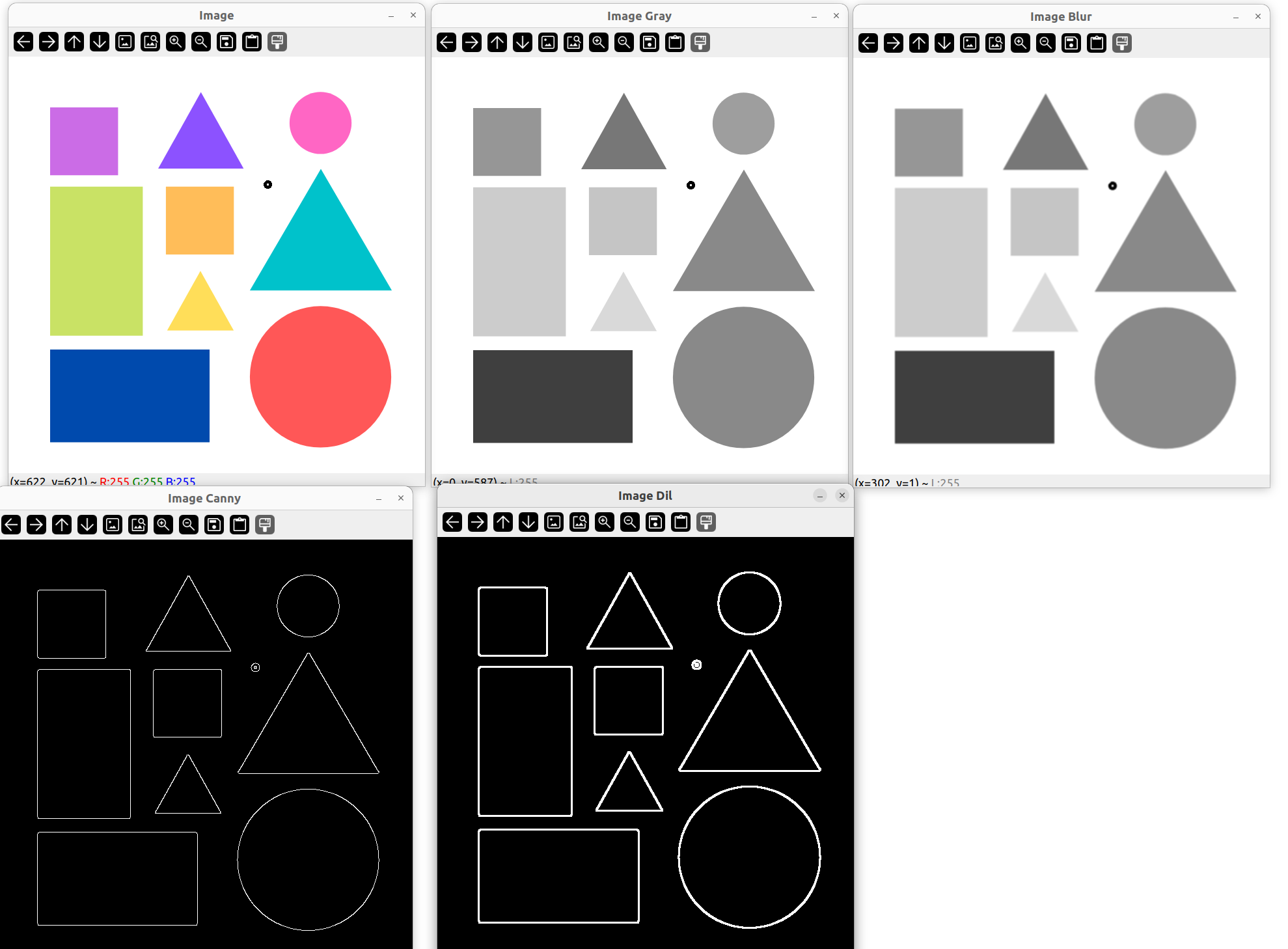
当我们放大 ImgCanny 也就是边缘检测的图像,会发现三角形边有很明显的毛躁和缝隙。
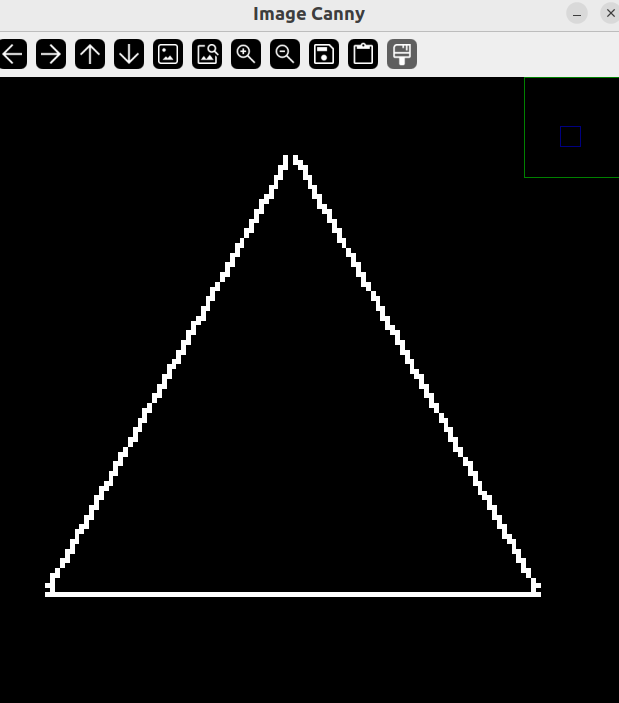
而放大膨胀后的图像,发现这些毛躁和缝隙变少,所以一般用膨胀后的图像来作为边缘检测的图像。
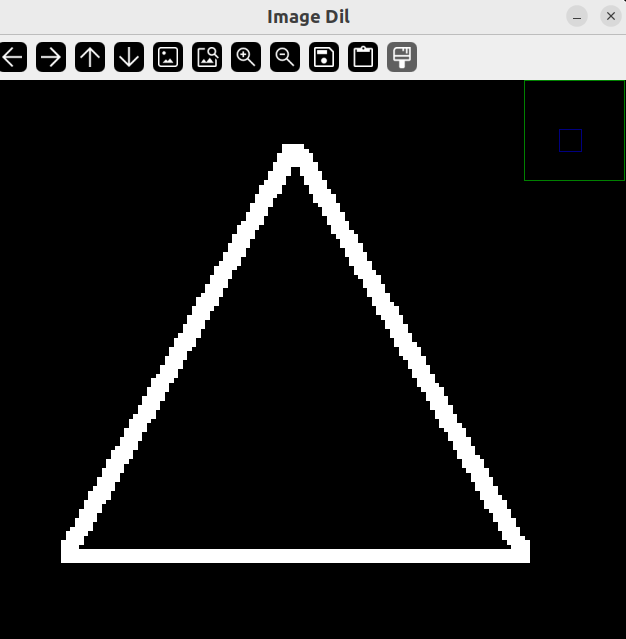
绘制轮廓
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void getContours(Mat imgDil, Mat img)
{
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
findContours(imgDil, contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
drawContours(img, contours, -1, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2);
}
int main()
{
string path = "../image/shapes.png";
Mat img = imread(path);
Mat imgGray, imgBlur, imgCanny, imgDil, imgErode;
// Preprocessing
cvtColor(img, imgGray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
GaussianBlur(imgGray, imgBlur, Size(3, 3), 3, 0);
Canny(imgBlur, imgCanny, 25, 75);
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3));
dilate(imgCanny, imgDil, kernel);
getContours(imgDil, img);
imshow("Image", img);
// imshow("Image Gray", imgGray);
// imshow("Image Blur", imgBlur);
// imshow("Image Canny", imgCanny);
// imshow("Image Dil", imgDil);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
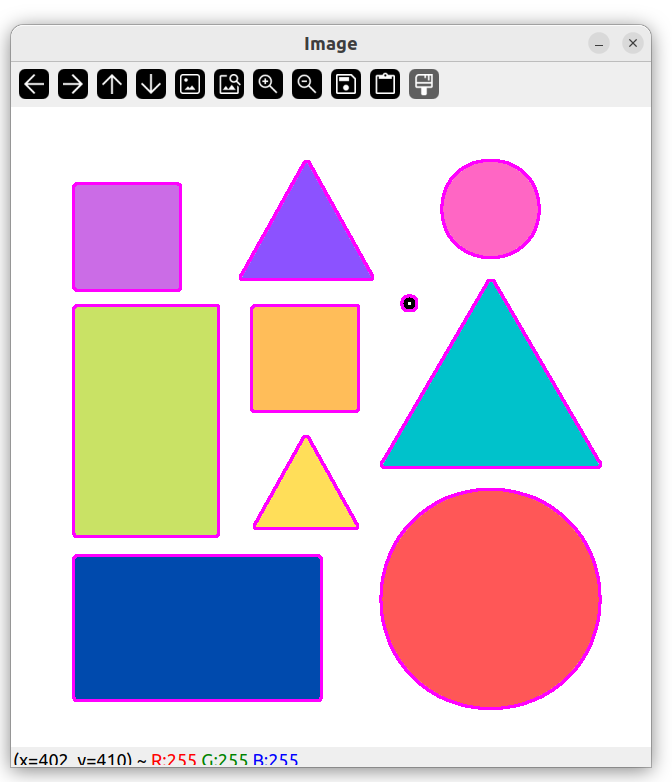
但是我们发现,小噪点也被勾勒了轮廓。
我们想去除这些噪点的轮廓。
打印每个图形面积
for(int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i ++)
{
int area = contourArea(contours[i]);
cout << area << endl;
}
通过输出每个图形的面积,我们发现,噪点面积为 185.

我们可以简单设置如果面积在 1000 以上才回绘制轮廓
void getContours(Mat imgDil, Mat img)
{
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
findContours(imgDil, contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
// drawContours(img, contours, i, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2);
for(int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i ++)
{
int area = contourArea(contours[i]);
cout << area << endl;
if(area > 1000)
{
drawContours(img, contours, i, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2);
}
}
}
可以发现噪点没有被绘制轮廓。
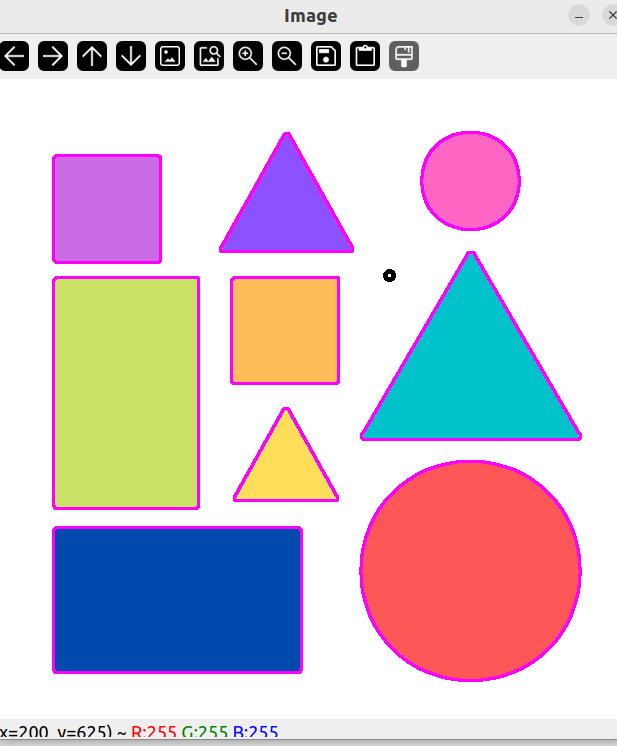
图像轮廓点进行多边形拟合
approxPolyDP 函数主要功能是把一个连续光滑曲线折线化,对图像轮廓点进行多边形拟合。
void getContours(Mat imgDil, Mat img)
{
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
findContours(imgDil, contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
vector<vector<Point>> conPoly(contours.size());
for(int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i ++)
{
int area = contourArea(contours[i]);
cout << area << endl;
if(area > 1000)
{
float peri = arcLength(contours[i], true);
approxPolyDP(contours[i], conPoly[i], 0.02 * peri, true);
drawContours(img, conPoly, i, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2);
cout << conPoly[i].size() << endl;
}
}
}
可以看到它绘制了很多点,然后将它们连接,而不是绘制圆
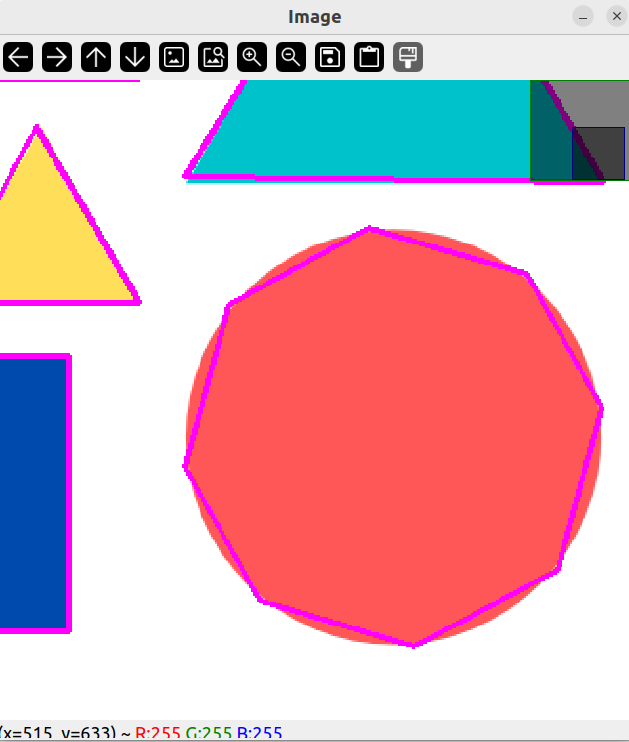
输出每个图形点的个数:

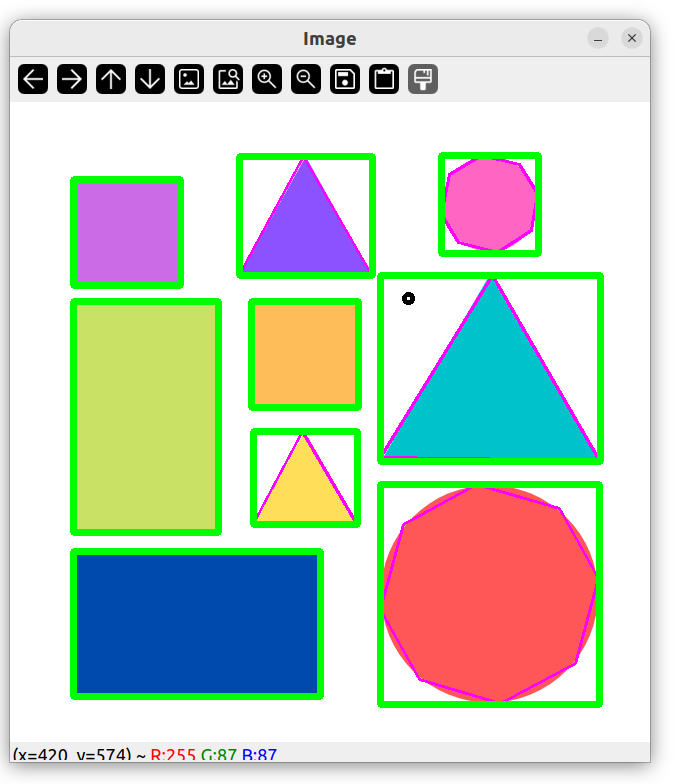
图形边界矩形
void getContours(Mat imgDil, Mat img)
{
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
findContours(imgDil, contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
vector<vector<Point>> conPoly(contours.size());
vector<Rect> boundRect(contours.size());
for(int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i ++)
{
int area = contourArea(contours[i]);
cout << area << endl;
if(area > 1000)
{
float peri = arcLength(contours[i], true);
approxPolyDP(contours[i], conPoly[i], 0.02 * peri, true);
drawContours(img, conPoly, i, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2);
cout << conPoly[i].size() << endl;
boundRect[i] = boundingRect(conPoly[i]);
rectangle(img, boundRect[i].tl(), boundRect[i].br(), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 5);
}
}
}
输出形状名称
void getContours(Mat imgDil, Mat img)
{
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy;
findContours(imgDil, contours, hierarchy, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
vector<vector<Point>> conPoly(contours.size());
vector<Rect> boundRect(contours.size());
for(int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i ++)
{
int area = contourArea(contours[i]);
cout << area << endl;
string objectType;
if(area > 1000)
{
float peri = arcLength(contours[i], true);
approxPolyDP(contours[i], conPoly[i], 0.02 * peri, true);
drawContours(img, conPoly, i, Scalar(255, 0, 255), 2);
cout << conPoly[i].size() << endl;
boundRect[i] = boundingRect(conPoly[i]);
rectangle(img, boundRect[i].tl(), boundRect[i].br(), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 5);
int objCor = (int)conPoly[i].size();
if(objCor == 3) {
objectType = "Tri"; // 如果点数为 3
}
else if(objCor == 4) {
objectType = "Rect"; // 点数为 4
}
else {
objectType = "Circle";
}
putText(img, objectType, {boundRect[i].x, boundRect[i].y - 5}, FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 0.75, Scalar(0, 69, 255)); // 显示文本
}
}
}
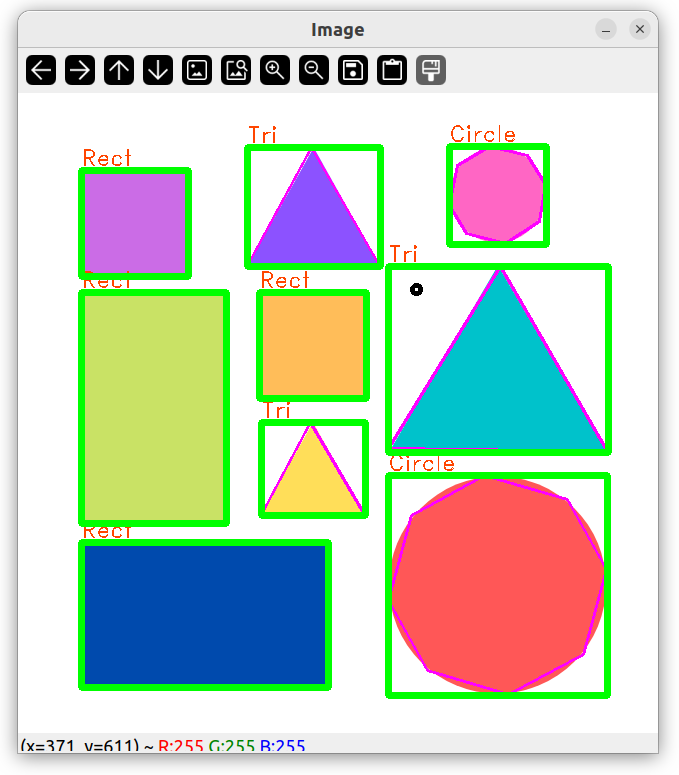
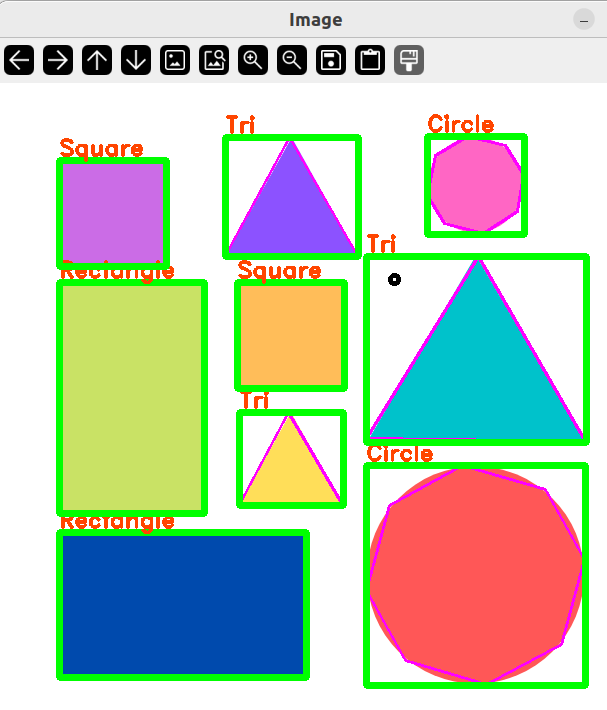
但是上述代码知识简单将长方形和正方形都定义为矩形,那么该如何分辨长方形和正方形呢?
我们用宽高比来判断。
else if(objCor == 4) {
// objectType = "Rect";
float aspRatio = (float)boundRect[i].width / (float)boundRect[i].height;
if(aspRatio > 0.95 && aspRatio < 1.05)
objectType = "Square";
else
objectType = "Rectangle";
}
OPENCV——C++版图像形状简单识别
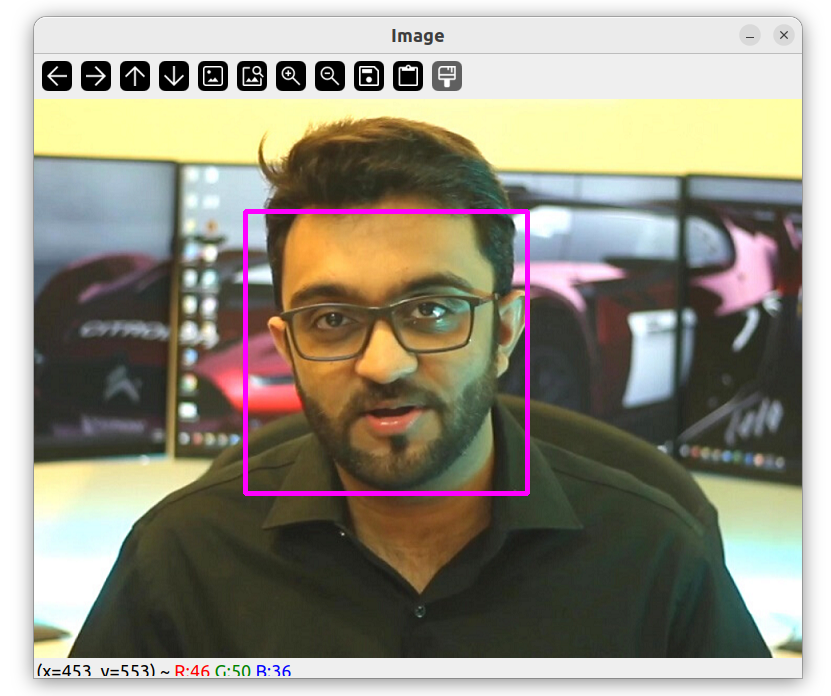
人脸识别
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string path = "../image/test.png";
Mat img = imread(path);
CascadeClassifier faceCascade;
faceCascade.load("../haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml");
if(faceCascade.empty())
puts("None!");
vector<Rect> faces;
faceCascade.detectMultiScale(img, faces, 1.1, 10);
for(int i = 0; i < faces.size(); i ++)
{
rectangle(img, faces[i].tl(), faces[i].br(), Scalar(255, 0, 255), 3);
}
imshow("Image", img);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}