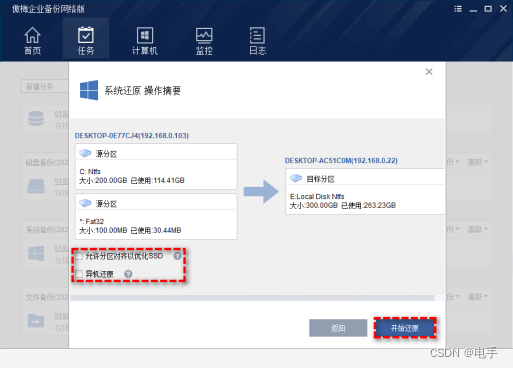
一、分析
栈的特点是先出再入,而队列的特点为先入先出,所以我们创造两个栈,一个用来存放数据,一个用来实现其它功能此时栈顶为队尾;当要找队头数据时将前n-1个数据移入到另一个栈中,此时剩余那个数据为队头数据:(注意转换一次后顺序颠倒,需要再转化一次)
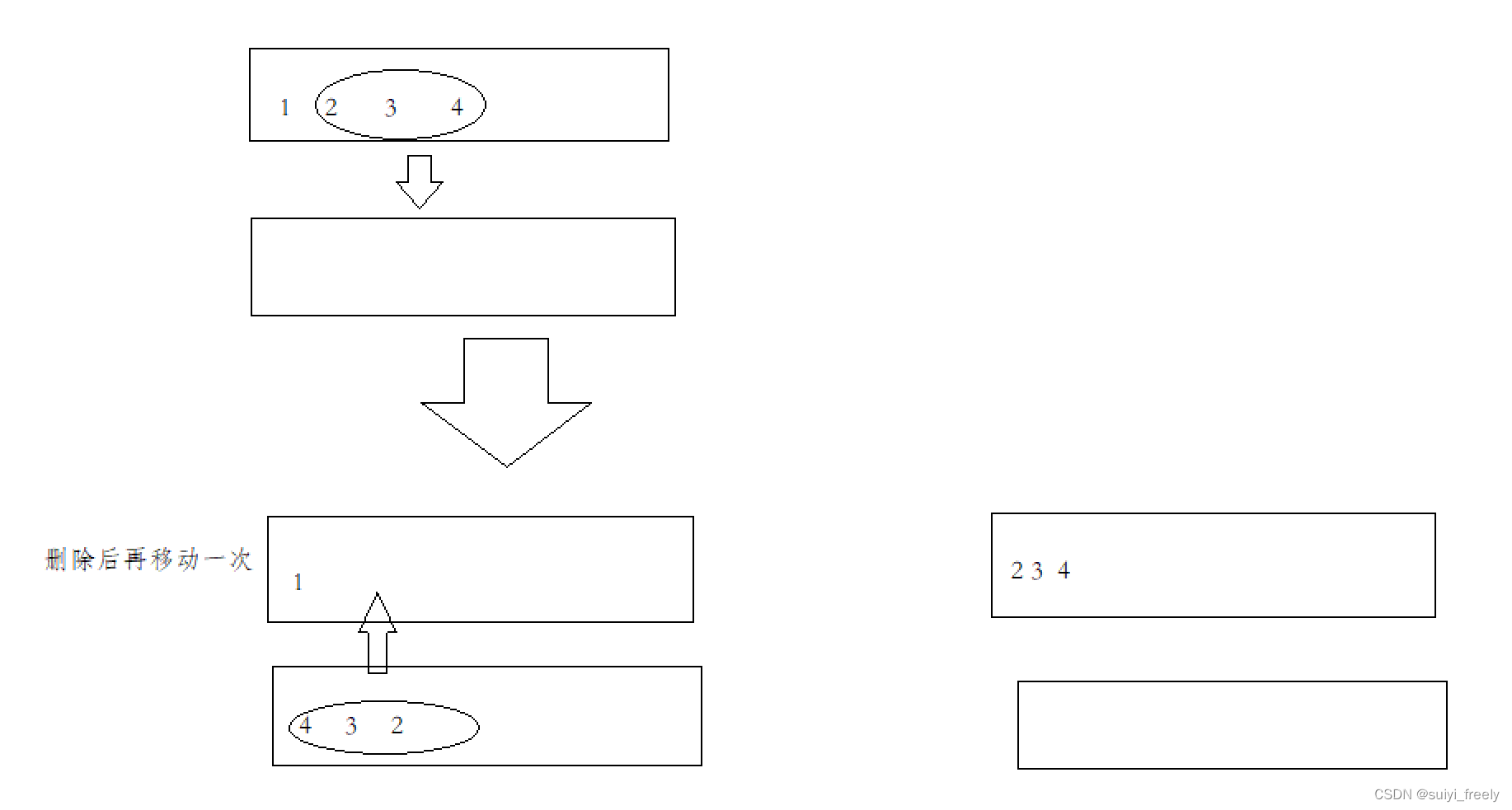

关于这个函数的书写,本人想了一种投机的小技巧,我们将实际数据通过局部变量铐过来,这样我们再访问队头数据时就不会对实际顺序有影响。(但是时间复杂度为O(N))其他办法确实没有想到,请见谅
二、实现
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
// 初始化和销毁
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
// 入栈 出栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
// 取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
// 判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
// 获取数据个数
int STSize(ST* pst);
// 初始化和销毁
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
// top指向栈顶数据的下一个位置
pst->top = 0;
// top指向栈顶数据
//pst->top = -1;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
// 入栈 出栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
// 扩容
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
// 20:08继续
// 取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
// 判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
// 获取数据个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
typedef struct {
ST p1;
ST p2;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* mq =(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&mq->p1);
STInit(&mq->p2);
return mq;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
if(!STEmpty(&obj->p1))
{
STPush(&obj->p1,x);
}
else
{
STPush(&obj->p1,x);
}
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{
ST* tmp=&obj->p1;//假设法
ST* ntmp=&obj->p2;
if(!STEmpty(&obj->p1))
{
tmp=&obj->p2;
ntmp=&obj->p1;
}
while(STSize(ntmp)>1)
{
STPush(tmp,STTop(ntmp));
STPop(ntmp);
}
int top=STTop(ntmp);
STPop(ntmp);
while(STSize(tmp))//将顺序转换过来
{
STPush(ntmp,STTop(tmp));
STPop(tmp);
}
return top;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
ST tmp=obj->p1;//通过创建局部变量来访问数据不影响实际数据
ST ntmp=obj->p2;
if(!STEmpty(&obj->p1))
{
tmp=obj->p2;
ntmp=obj->p1;
}
while(STSize(&ntmp)>1)
{
STPush(&tmp,STTop(&ntmp));
STPop(&ntmp);
}
int top=STTop(&ntmp);
return top;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&obj->p1)&&STEmpty(&obj->p2);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestroy(&obj->p1);
STDestroy(&obj->p2);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/