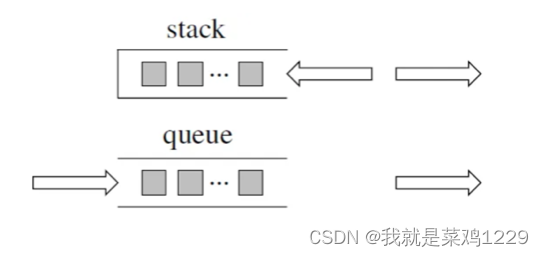
1.栈和队列理论基础
栈和队列的原理大家应该很熟悉了,队列是先进先出,栈是先进后出。
2.用栈实现队列

type MyQueue struct {
head []int
headSize int
store []int
storeSize int
}
func Constructor() MyQueue {
return MyQueue{
head : make([]int,100),
headSize : 0,
store : make([]int,100),
storeSize : 0,
}
}
func (this *MyQueue) Push(x int) {
this.store[this.storeSize] = x
this.storeSize++
}
func (this *MyQueue) Pop() int {
if this.headSize==0{
//需要将store中的数倒过来
for i:=this.storeSize;i>0;{
i--
this.head[this.headSize]=this.store[i]
this.headSize++
}
this.storeSize = 0
}
if this.headSize>0{
this.headSize--
return this.head[this.headSize]
}
return -1
}
func (this *MyQueue) Peek() int {
if this.headSize==0{
//需要将store中的数倒过来
for i:=this.storeSize;i>0;{
i--
this.head[this.headSize]=this.store[i]
this.headSize++
}
this.storeSize = 0
}
if this.headSize>0{
return this.head[this.headSize-1]
}
return -1
}
func (this *MyQueue) Empty() bool {
return this.headSize==0&&this.storeSize==0
}
3.用队列实现栈

type MyStack struct {
store []int
size int
}
func remove(s []int, i int) []int {
s[i] = s[len(s)-1]
return s[:len(s)-1]
}
func Constructor() MyStack {
return MyStack{make([]int,100),0}
}
func (this *MyStack) Push(x int) {
this.store[this.size]=x
this.size++
}
func (this *MyStack) Pop() int {
this.size--
return this.store[this.size]
}
func (this *MyStack) Top() int {
return this.store[this.size-1]
}
func (this *MyStack) Empty() bool {
return this.size==0
}
4.有效的括号

func isValid(s string) bool {
stack := Stack{}
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
println(s[i])
if s[i] == 40 || s[i] == 91 || s[i] == 123 {
stack.Push(int(s[i]))
} else {
char, err := stack.Top()
if err != nil {
return false
}
if char == 40 && s[i] == 41 {
stack.Pop()
continue
}
if char == 91 && s[i] == 93 {
stack.Pop()
continue
}
if char == 123 && s[i] == 125 {
stack.Pop()
continue
}
return false
}
}
if stack.Len() != 0 {
return false
}
return true
}
type Stack []int
func (stack Stack) Len() int {
return len(stack)
}
func (stack Stack) IsEmpty() bool {
return len(stack) == 0
}
func (stack Stack) Cap() int {
return cap(stack)
}
func (stack *Stack) Push(value int) {
*stack = append(*stack, value)
}
func (stack Stack) Top() (int, error) {
if len(stack) == 0 {
return -1, errors.New("Out of index, len is 0")
}
return stack[len(stack)-1], nil
}
func (stack *Stack) Pop() (int, error) {
theStack := *stack
if len(theStack) == 0 {
return -1, errors.New("Out of index, len is 0")
}
value := theStack[len(theStack)-1]
*stack = theStack[:len(theStack)-1]
return value, nil
}
5.删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项

func removeDuplicates(s string) string {
chars := []byte(s)
p1 := 0
for i := 0; i < len(chars); i++ {
if(p1>0 && chars[p1-1]==chars[i]){
p1--
}else{
chars[p1] = chars[i]
p1++
}
}
return string(chars[:p1])
}
6.逆波兰表达式求值

func evalRPN(tokens []string) int {
numIndex := -1
numArr := make([]int,10000)
for _,str := range(tokens){
num, err := strconv.Atoi(str)
if err==nil{
//说明是数字
numIndex++
numArr[numIndex]=num
}else{
//说明是一个+-*/中的一种
num1 := numArr[numIndex]
numIndex--
num2 := numArr[numIndex]
switch str{
case "+":
numArr[numIndex]=num1+num2
case "-":
numArr[numIndex]=num2-num1
case "*":
numArr[numIndex]=num1*num2
case "/":
numArr[numIndex]=num2/num1
}
}
}
return numArr[0]
}
7.滑动窗口最大值

这道题目需要使用单调队列
// 封装单调队列的方式解题
// 那么这个维护元素单调递减的队列就叫做单调队列
// 即单调递减或单调递增的队列
type MyQueue struct {
queue []int
}
func NewMyQueue() *MyQueue {
return &MyQueue{
queue: make([]int, 0),
}
}
func (m *MyQueue) Front() int {
return m.queue[0]
}
func (m *MyQueue) Back() int {
return m.queue[len(m.queue)-1]
}
func (m *MyQueue) Empty() bool {
return len(m.queue) == 0
}
// push(value):如果push的元素value大于入口元素的数值,那么就将队列入口的元素弹出,直到push元素的数值小于等于队列入口元素的数值为止
func (m *MyQueue) Push(val int) {
for !m.Empty() && val > m.Back() {
m.queue = m.queue[:len(m.queue)-1]
}
m.queue = append(m.queue, val)
}
// pop(value):如果窗口移除的元素value等于单调队列的出口元素,那么队列弹出元素,否则不用任何操作
func (m *MyQueue) Pop(val int) {
if !m.Empty() && val == m.Front() {
m.queue = m.queue[1:]
}
}
func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int {
queue := NewMyQueue()
length := len(nums)
res := make([]int, 0)
// 先将前k个元素放入队列
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
queue.Push(nums[i])
}
// 记录前k个元素的最大值
res = append(res, queue.Front())
for i := k; i < length; i++ {
// 滑动窗口移除最前面的元素
queue.Pop(nums[i-k])
// 滑动窗口添加最后面的元素
queue.Push(nums[i])
// 记录最大值
res = append(res, queue.Front())
}
return res
}
8.前K个高频元素

这题目需要实现go中提供的heap的接口。使用大顶堆即可完成任务。
func topKFrequent(nums []int, k int) []int {
items := make(map[int]*Item, 0)
for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {
item, ok := items[nums[i]]
if !ok {
items[nums[i]] = &Item{key: nums[i], value: 1}
} else {
item.value++
}
}
hp := &ItemHeap{}
heap.Init(hp)
for _, value := range items {
heap.Push(hp, *value)
}
res := make([]int, k)
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
item := heap.Pop(hp)
res[i] = item.(Item).key
}
return res
}
//大顶堆
type Item struct {
// 排序的关键词
key int
// value,用来记录出现的次数
value int
}
type ItemHeap []Item
func (h ItemHeap) Len() int {
return len(h)
}
func (h ItemHeap) Swap(i, j int) {
h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i]
}
func (h ItemHeap) Less(i, j int) bool {
return h[i].value > h[j].value
}
// 实现heap.Interface接口定义的额外方法
func (h *ItemHeap) Push(item interface{}) {
*h = append(*h, item.(Item))
}
// 这个方法不是给用户使用的
func (h *ItemHeap) Pop() interface{} {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}