1、EPollPoller.h

EPollPoller的主要实现:作为poller的派生类,把基类给派生类保留的这些纯虚函数的接口实现出来。
override表示在派生类里面,这些方法是覆盖方法。必须由编译器来保证在基类里面一定有这些函数的接口的声明。在派生类要重写他们。
给EPollPoller的析构函数写override,就是让编译器给你检查基类的析构一定是虚函数。
底层是vector,放EventList,可以动态地扩容。
成员变量的epollfd要通过epoll_create来创建,映射的就是epoll底层的文件系统
#pragma once
#include "Timestamp.h"
#include "Poller.h"
#include <vector>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
/**
* epoll的使用
* epoll_create
* epoll_ctl add/mod/del
* epoll_wait
*/
class EPollPoller:public Poller
{
public:
EPollPoller(EventLoop* loop);//epoll_create
~EPollPoller()override;
//重写基类Poller的抽象方法
Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs,ChannelList* activeChannels)override;//epoll_wait
void updateChannel(Channel* channel)override;//epoll_ctl
void removeChannel(Channel* channel)override;//epoll_ctl
private:
static const int kInitEventListSize=16;//给vector<epoll_event>初始化的长度
using EventList=std::vector<epoll_event>;
//填写活跃的连接
void fillActiveChannels(int numEvents,ChannelList* activeChannels)const;
//更新channel通道
void update(int operation,Channel* channel);
int epollfd_;
EventList events_;
};2、EPollPoller.cc
epoll_wait:第2个参数epoll_event 是最终发生事件的fd,返回值是发生事件fd的数量。
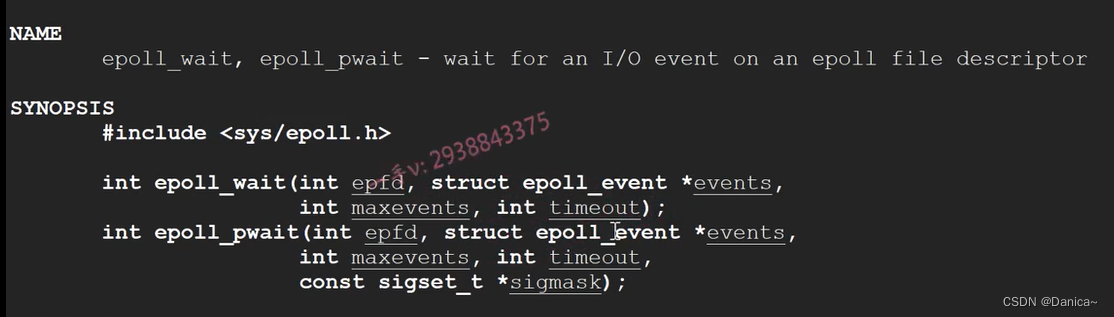
epoll_create的参数size在Liunx内核2.6.8以后没有意义了,但是必须是大于0的数

epoll_create1,flags=0时和epoll_create一样,提供了行为选项EPOLL_CLOEXEC


当我们去使用epoll_create1的时候,创建的epollfd,然后在当前线程里面再去fork创建一个子进程,然后用exec替换子进程的时候,在子进程里面就把父进程设置成标志的fd,资源就都给关闭了。

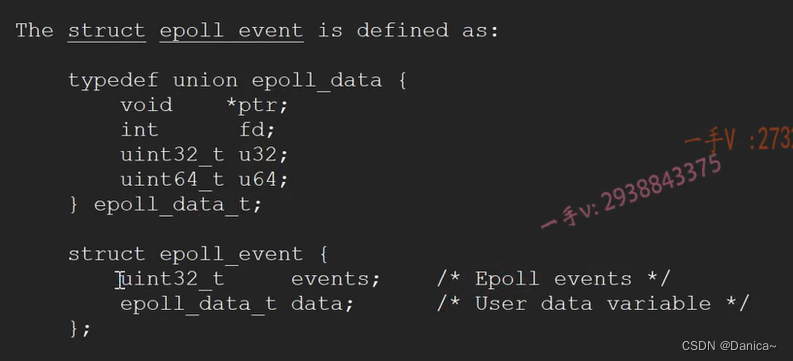
结构体的fd就是epoll要监听的事件,ptr指向fd对应的channel,channel包含fd以及感兴趣的事件
#include "EPollPoller.h"
#include "Logger.h"
#include "Channel.h"
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
// channel还没有被添加到Poller中
const int kNew = -1; // channel的成员index_=-1
// channel已经添加到Poller中
const int kAdded = 1;
// channel从Poller中删除
const int kDeleted = 2;
EPollPoller::EPollPoller(EventLoop *loop)
: Poller(loop), epollfd_(::epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC)), events_(kInitEventListSize) // vector<epoll_event> 默认大小16
{
if (epollfd_ < 0)
{
LOG_FATAL("epoll_create error:%d \n", errno);
}
}
EPollPoller::~EPollPoller()
{
::close(epollfd_);
}
//epoll_wait
//eventloop会创建一个channellist,并把创建好的channellist的地址传给poll
//poll通过epoll_wait监听到哪些fd发生了事件,把真真正正发生事件的channel通过形参发送到eventloop提供的实参里面
Timestamp EPollPoller::poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels)
{
// 实际上应该用LOG_DEBUG输出日志更为合理,可以设置开启或者不开启 因为LOG_INFO是每次都要输出的,会影响epoll的效率
LOG_INFO("func=%s => fd total count:%lu\n", __FUNCTION__, channels_.size());
//events_.begin()返回首元素的迭代器(数组),也就是首元素的地址,是面向对象的,要解引用,就是首元素的值,然后取地址
//就是vector底层数组的起始地址 static_cast类型安全的转换 timeoutMs超时时间
int numEvents = ::epoll_wait(epollfd_, &*events_.begin(), static_cast<int>(events_.size()), timeoutMs);
//全局的变量errno,库里的,poll可能在多个线程eventloop被调用 ,所以用局部变量存起来
int saveErrno = errno; // 在loop开始时,保存当前loop的errno,防止中间操作发生错误对全局的errno进行改写,那在日志打印的时候就获取不到当前loop的errno了
Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());
if (numEvents > 0)//表示有已经发生相应事件的个数
{
LOG_INFO("%d events happened \n", numEvents);
fillActiveChannels(numEvents, activeChannels);
// 如果返回的numEvents和实际vector中的events的长度是一样的,说明这一轮监听的所有的event都发生事件了,就要进行扩容了
if (numEvents == events_.size())
{
events_.resize(events_.size() * 2);
}
}
else if (numEvents == 0) // 没有事件发生,超时
{
LOG_DEBUG("%s timeout!\n", __FUNCTION__);
}
else // 发生错误
{
if (saveErrno != EINTR) // EINTR=>外部中断,不等于外部的中断 ,是由其他错误类型引起的
{
errno = saveErrno; //适配 ,把errno重置成当前loop之前发生的错误的值
LOG_ERROR("EPollPoller::poll() err!");
}
}
return now;
}
// channel update remove=>EventLoop updateChannel removeChannel=>Poller updateChannel removeChannel
/**
* EventLoop => poller.poll
* ChannelList Poller
* ChannelMap <fd,Channel*> (保存的是向poller注册过的channel) epollfd
*/
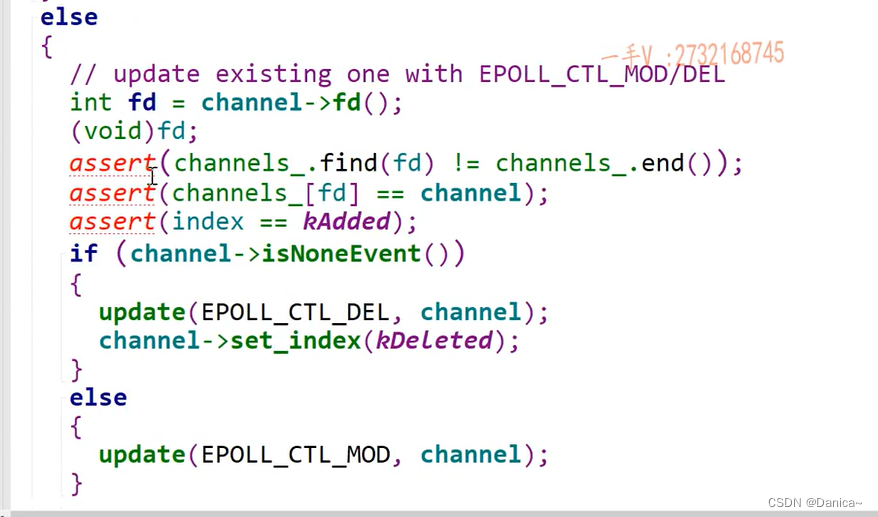
void EPollPoller::updateChannel(Channel *channel)
{
const int index = channel->index();
LOG_INFO("func=%s=> fd=%d events=%d index=%d \n", __FUNCTION__, channel->fd(), channel->events(), index);
if (index == kNew || index == kDeleted)//未添加或者已删除
{
if (index == kNew)//未添加,键值对写入map中
{
int fd = channel->fd();
channels_[fd] = channel;
}
channel->set_index(kAdded);
update(EPOLL_CTL_ADD, channel);//相当于调用epoll_ctl,添加1个channel到epoll中
}
else // channel已经在poller上注册过了
{
int fd = channel->fd();
if (channel->isNoneEvent()) // channel对任何事件都不感兴趣,不需要poller帮忙监听了
{
update(EPOLL_CTL_DEL, channel);//删除已注册的channel的感兴趣的事件
channel->set_index(kDeleted);
}
else
{
update(EPOLL_CTL_MOD, channel);
}
}
}
// 从poller中删除channel
void EPollPoller::removeChannel(Channel *channel)
{
int fd = channel->fd();
channels_.erase(fd);
LOG_INFO("func=%s => fd=%d\n", __FUNCTION__, fd);
int index = channel->index();
if (index == kAdded)//如果已注册过
{
update(EPOLL_CTL_DEL, channel);//通过epoll_ctl 删掉
}
channel->set_index(kNew);//设置成未添加的状态
}
// 填写活跃的连接
void EPollPoller::fillActiveChannels(int numEvents, ChannelList *activeChannels) const
{
for(int i=0;i<numEvents;i++)
{
Channel* channel=static_cast<Channel*>(events_[i].data.ptr);
channel->set_revents(events_[i].events);
activeChannels->push_back(channel);//EventLoop就拿到了它的poller给它返回的所有发生事件的channel列表了
//至于EventLoop拿到这些channel干什么事情,我们看 EventLoop的代码
}
}
// 更新channel通道 epoll_ctl add/mod/del
void EPollPoller::update(int operation, Channel *channel)
{
epoll_event event;
memset(&event, 0, sizeof event);
int fd = channel->fd();
event.events = channel->events();//返回的就是fd所感兴趣的事件
event.data.fd = fd;
event.data.ptr = channel;//绑定的参数
if (::epoll_ctl(epollfd_, operation, fd, &event) < 0)//把fd相关事件更改
{
if (operation == EPOLL_CTL_DEL)
{
LOG_ERROR("epoll_ctl del error:%d\n", errno);
}
else
{
LOG_FATAL("epoll_ctl add/mod error:%d\n", errno); // add/mod如果失败了,是无法挽回的,所以LOG_FATAL会自动exit
}
}
}channel要把自己注册到poller上,但channel无法与poller直接通信,channel调用的是EventLoop的updatechannel和removechannel,EventLoop的updatechannel和removechannel最终还是调用的EPollPoller,做的相当于是epoll_ctl,最后进行epoll_wait就是EPollPoller中的poll函数,使用vector数组存放发生的事件,如果返回值numEvents和vector数组长度一样,说明可能还有更多的事件没有处理,需要扩容,下一轮再来处理,因为muduo库采用的是LT模式,没有处理的事件会不断上报。
![[蓝桥杯2024]-PWN:ezheap解析(堆glibc2.31,glibc2.31下的double free)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/024fd81f6b5349b3a54d001c5aab31e8.png)