1. 为什么要学习string类
1.1 C语言中的字符串
2. 标准库中的string类
2.1 string类的了解
1. 字符串是表示字符序列的类2. 标准的字符串类提供了对此类对象的支持,其接口类似于标准字符容器的接口,但添加了专门用于操作单字节字符字符串的设计特性。3. string类是使用char(即作为它的字符类型,使用它的默认char_traits和分配器类型(关于模板的更多信息,请参阅basic_string)。4. string类是basic_string模板类的一个实例,它使用char来实例化basic_string模板类,并用char_traits和allocator作为basic_string的默认参数(根于更多的模板信息请参考basic_string)。5. 注意,这个类独立于所使用的编码来处理字节:如果用来处理多字节或变长字符(如UTF-8)的序列,这个类的所有成员(如长度或大小)以及它的迭代器,将仍然按照字节(而不是实际编码的字符)来操作。
2.2 string类的常用接口说明
我们看string类的文档可以发现
有以下几种接口:



内容选自:string::string - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com)
2.2.1 string() ---- 无参构造函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cout << s <<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2.2.2 string (const string& str)-----复制构造函数
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
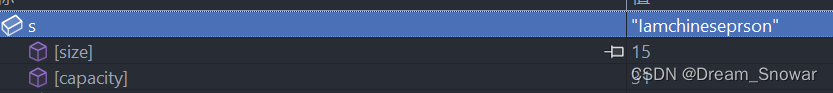
string s("Iamchineseprson");
string s1(s);
cout << s << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:



2.2.3 string(const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos);----复制从字符位置 pos 开始并跨越 len 字符的 str 部分(如果任一 str 太短或 len 为 string::npos,则复制 str 的末尾)
代码示例:

运行结果:

2.2.4 string(const char*)---- 用char*构造函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Iamchineseperson");
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
2.3 string对象的容量操作
2.3.1size函数
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Iamchineseprson");
cout << s.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:


2.3.2 length函数
返回字符串有效字符长度 size() 与 length() 方法底层实现原理完全相同, 引入 size() 的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一致, 一般情况下基本都是用 size()。
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Iamchineseprson");
cout << s.length() << endl;
return 0;
}


2.3.3 capacity函数
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Iamchineseprson");
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:


2.3.4 empty函数
检测字符串释放为空串,是返回true,否则返回false
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("Iamchineseprson");
string s2;
cout << s1.empty() << endl;
cout << s2.empty() << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:

2.3.5 clear函数
clear()清空有效字符
clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Iamchineseprson");
cout << s.length() << endl;
s.clear();
cout << s.length() << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:



2.3.6 reserve函数
作用:为字符串预留空间
写法:reserve(size_t res_arg=0):
特点:为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量小。
代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Iamchineseprson");
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.reserve(30);
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:


2.3.7 resize函数
resize(size_t n) 与 resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字符个数增多时:resize(n)用 '\0' 来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。
注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Iamchineseprson");
cout << s << endl;
s.resize(30,'L');
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:

2.4 string对象的访问及遍历接口
//迭代器
string::iterator being();//返回第一个位置的迭代器
string::iterator end();//返回结束位置下一个位置的迭代器
reverse_iterator rbeign();//返回结束位置的迭代器
reverse_iterator rend();//返回开始的前一个位置的迭代器
//at访问位置的值
char& at (size_t pos); //返回pos位置的值
const char& at (size_t pos) const; //返回const修饰的pos位置的位置的值
//重载 []
char& operator[] (size_t pos);
const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const;
2.4.1 operator[]
作用:返回pos位置的字符,const string对象调用
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Iamchineseprson");
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
printf("[%d] : %c\n", i, s[i]);
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:

2.4.2 迭代器 begin 、end
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Iamchineseprson");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it < s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:

2.4.3 迭代器 rbegin 、rend
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("iamchineseprson");
string::reverse_iterator it = s.rbegin();
while (it != s.rend())
{
cout << *it << ' ';
it++;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2.4.4 at
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("iamchineseprson");
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
cout << s.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2.4.5 范围for
这里是遍历,自然我们也能用前面学习的范围for
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("iamchineseperson");
for (const char ch : s)
{
cout << ch << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

但这里ch的类型是char,我们可能吃不准,所以,很多时候我们都会选择用auto类型
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("iamchineseperson");
for (auto ch : s)
{
cout << ch << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2.5 string的增删查改
1.增
1.连接
(1)函数原型:
//重载 +=
string& operator+= (const string& str); //在结尾处连接字符串str
string& operator+= (const char* s); //在结尾处连接字符串s
string& operator+= (char c); //在结尾处连接字符c
//append 在字符串结尾连接
string& append (const string& str); //在结尾处连接字符串str
string& append (const char* s); //在结尾处连接字符串s
//连接从迭代器first 到 last 这个区间到结尾 左闭右开
template <class InputIterator>
string& append (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("iamchineseperson");
s += '1';
cout << s << endl;
s += "666666";
cout << s << endl;
string ss("2333");
s += ss;
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2.尾插
push_back 函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("iamchineseprson");
s.push_back('1');
cout << s << endl;
s.push_back('2');
cout << s << endl;
s.push_back('3');
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

3.append函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("iamchineseperson");
// 追加n个字符
s.append(1, '1');
cout << s << endl;
// 追加一个字符串
s.append("12345");
cout << s << endl;
// 追加一个字符串的前n个
s.append("12345678", 3);
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

4.insert 函数
string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str);
//insert函数能够在字符串任意位置插入一个string容器内的字符串
string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen);
//insert函数能够在字符串任意位置插入一个string对象内的字符串的一段字符串
string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s);
//insert函数能够在字符串一段字符串
string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s, size_t n);
//insert 函数还能够在字符串任意位置插入字符串的前 n 个
string& insert (size_t pos, size_t n, char c);
//insert 函数还能够在字符串任意位置插入n个字符
//插入
int main()
{
string s1("iamchineseperson");
string s2("hello");
//在pos位置插入string
s1.insert(0, s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
//在pos位置插入char*
s1.insert(0, "hehe");
cout << s1 << endl;
// 在最后插入string的一部分
s1.insert(s1.size(), s2, 0, 2);
cout << s1 << endl;
// 在第一个位置插入string
s1.insert(0, "sadasdxzczasd");
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
至于其他情况这里我就不多展示了。
2.删
//清空
clear()
//尾删
pop_back();
//erase 删除
//删除从pos位置开始删除len个
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
//删除迭代器p位置
iterator erase (iterator p);
//删除迭代器区间左闭右开
iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last);
1. erase 函数
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);erase 函数能够删除第 n 个位置后面长度为 len 的字符串
如果没有传 len 或是 第 n 个位置后面的字符数小于 len ,则n后面的字符全部删除
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("iamaperson");
s.erase(3, 2);
cout << s << endl;
s.erase(1);
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果:

2.尾删
pop_back()
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str ("hello world!");
str.pop_back();
std::cout << str << '\n';
return 0;
}运行结果:

3.clear()
// string::clear
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
char c;
std::string str;
std::cout << "Please type some lines of text. Enter a dot (.) to finish:\n";
do {
c = std::cin.get();
str += c;
if (c=='\n')
{
std::cout << str;
str.clear();
}
} while (c!='.');
return 0;
}该程序重复用户引入的每一行,直到一行包含一个点 ('.')。每个换行符 ('\n') 都会触发行的重复和当前字符串内容的清除。
这里我就不运行了
3.查
//find从pos位置向后查找 找到返回下标位置,找不到返回npos
//查找字符串str
size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
//查找字符串s
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//查找字符c
size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
//rfind 从pos位置向前找 找到返回下标位置,找不到返回npos
size_t rfind (const string& str, size_t pos = npos) const;
size_t rfind (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
size_t rfind (char c, size_t pos = npos) const;
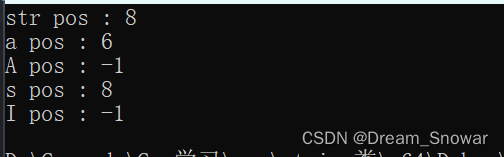
1.find()
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
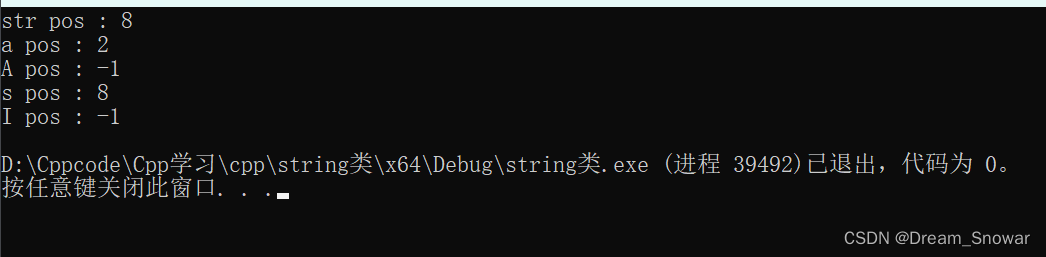
int main()
{
string s("i am a studentt");
string str("student");
// 查找 str --> 找得到
int pos = s.find(str, 0);
cout << "str pos : " << pos << endl;
// 查找字符串 --> 找得到
pos = s.find("a", 0);
cout << "a pos : " << pos << endl;
// 查找字符串 --> 找不到
pos = s.find("A", 0);
cout << "A pos : " << pos << endl;
// 查找字符 --> 找得到
pos = s.find('s', 0);
cout << "s pos : " << pos << endl;
// 查找字符 --> 找不到
pos = s.find('I', 0);
cout << "I pos : " << pos << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2.rfind()
//rfind 从pos位置向前找 找到返回下标位置,找不到返回npos
size_t rfind (const string& str, size_t pos = npos) const;
size_t rfind (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
size_t rfind (char c, size_t pos = npos) const;#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("i am a studentt");
string str("student");
// 查找 str --> 找得到
int pos = s.rfind(str);
cout << "str pos : " << pos << endl;
// 查找字符串 --> 找得到
pos = s.rfind("a");
cout << "a pos : " << pos << endl;
// 查找字符串 --> 找不到
pos = s.rfind("a", 0);
cout << "A pos : " << pos << endl;
// 查找字符 --> 找得到
pos = s.rfind('s',8);
cout << "s pos : " << pos << endl;
// 查找字符 --> 找不到
pos = s.rfind('s', 5);
cout << "I pos : " << pos << endl;
return 0;
}
4.改
//assign 全部替换
//用字符串str替换原来的内容
string& assign (const string& str);
//用字符串s替换原来的内容
string& assign (const char* s);
//迭代器first到迭代器last这个区间替换原来的内容 左闭右开
template <class InputIterator>
string& assign (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
//replace替换一部分
//将pos到len位置替换成str
string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str);
//将迭代器i1到i2替换成str
string& replace (iterator i1, iterator i2, const string& str);
//将pos到len位置替换成s
string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s);
//将迭代器i1到i2替换成s 左闭右开
string& replace (iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s);
1.assign()
int main()
{
string s1("i am a studentt");
string s2("student");
//修改stirng
s1.assign(s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
//修改char *
s1.assign("he");
cout << s1 << endl;
//迭代器
s1.assign(s2.begin(), s2.end());
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2.replace()
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("i am a student");
string s2("person");
//将pos到len位置替换string
s1.replace(8, 15, s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
//将pos到len位置替换char*
s1.replace(0, 0, "asdsd");
cout << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

2.6 一些小东西的介绍
1. npos
npos的值通常是一个很大的正数,等于-1(当作为无符号数解释时或等于string::size_type的最大可能值。
2.c_str 函数
作用:返回C格式字符串
C++中,
printf是一个C语言函数,它不支持直接打印std::string类型的内容。这是因为printf是一个可变参数函数,而std::string不是基本数据类型,因此需要转换为C风格字符串才能由printf输出。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("Hello world");
printf("%s\n", s);
printf("%s\n", s.c_str());
return 0;
}
运行结果:

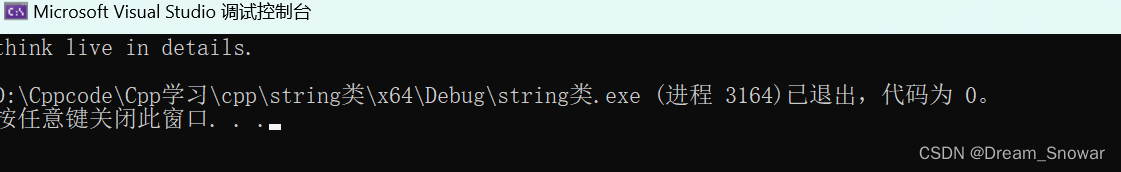
3.substr()
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;在字符串中从第pos个位置开始截取len个字符返回
// string::substr
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str="We think in generalities, but we live in details.";
// (quoting Alfred N. Whitehead)
std::string str2 = str.substr (3,5); // "think"
std::size_t pos = str.find("live"); // position of "live" in str
std::string str3 = str.substr (pos); // get from "live" to the end
std::cout << str2 << ' ' << str3 << '\n';
return 0;
}