目录
一,责任链模式
二,特点
四,实现步骤
五,代码
一,责任链模式
责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern)是一种软件设计模式,它属于行为型模式。在这种模式中,一个请求沿着一个由多个处理对象组成的链顺序传递,直到链上的某个处理对象能够处理该请求为止。每个处理对象决定是处理该请求、拒绝它,还是将其传递给链中的下一个处理对象。
二,特点
-
解耦:将请求的发送者和接收者解耦,使得发送者不需要知道谁是请求的处理者,以及链的结构如何。
-
动态性:在运行时,可以动态地改变链的结构,例如增加或删除链中的某些处理对象。
-
避免请求发送者与接收者之间的耦合:请求发送者只需要知道链的头部,而不需要了解链的其余部分。
-
易于扩展:可以根据需要添加新的请求处理对象,而不需要修改现有代码
三,组成部分
- Handler:定义了一个处理请求的接口,通常包含一个指向下一个处理者的引用。
- ConcreteHandler:实现了
Handler接口的具体处理类,决定是否处理请求或将请求传递给下一个处理者。
四,实现步骤
- 定义
Handler接口,包含setNext()方法用于设置链的下一个处理者,以及handleRequest()方法用于处理请求。 - 创建具体的处理者类,实现
Handler接口,并在handleRequest()方法中实现具体的请求处理逻辑。 - 将处理者对象通过
setNext()方法连接起来,形成一条处理链。 - 发送请求,从链的开始传递,直到被处理或传递到链的末尾。
五,代码
1.创建抽象的记录器类。
public abstract class AbstractLogger {
public static int INFO = 1;
public static int DEBUG = 2;
public static int ERROR = 3;
protected int level;
//下一个元素
AbstractLogger nextLogger;
protected void nextLogger(AbstractLogger nextLogger) {
this.nextLogger = nextLogger;
}
public void logMessage(int level, String message) {
if (this.level <= level) {//如果小于传入的,那么打印出来
write(message);
}
if (nextLogger != null) {
nextLogger.logMessage(level, message);//下一个
}
}
abstract protected void write(String message);
}2.创建扩展了该记录器类的实体类。
public class ConsoleLogger extends AbstractLogger{//控制台日志
public ConsoleLogger(int level){
this.level = level;
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("Standard Console::logger" + message);
}
}public class ErrorLogger extends AbstractLogger{
public ErrorLogger(int level){
this.level = level;
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("Error Console::logger" + message);
}
}public class FileLogger extends AbstractLogger{
public FileLogger(int level){
this.level = level;
}
@Override
protected void write(String message) {
System.out.println("File Console::logger" + message);
}
}3.创建不同类型的记录器。赋予它们不同的错误级别,并在每个记录器中设置下一个记录器。每个记录器中的下一个记录器代表的是链的一部分。
public class ChainPatternDemo {
public static AbstractLogger getChains(){
AbstractLogger error = new ErrorLogger(AbstractLogger.ERROR);//3
AbstractLogger file = new FileLogger(AbstractLogger.DEBUG);//2
AbstractLogger console = new ConsoleLogger(AbstractLogger.INFO);//1
error.nextLogger(file);
file.nextLogger(console);
return error;//3
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractLogger chains = getChains();
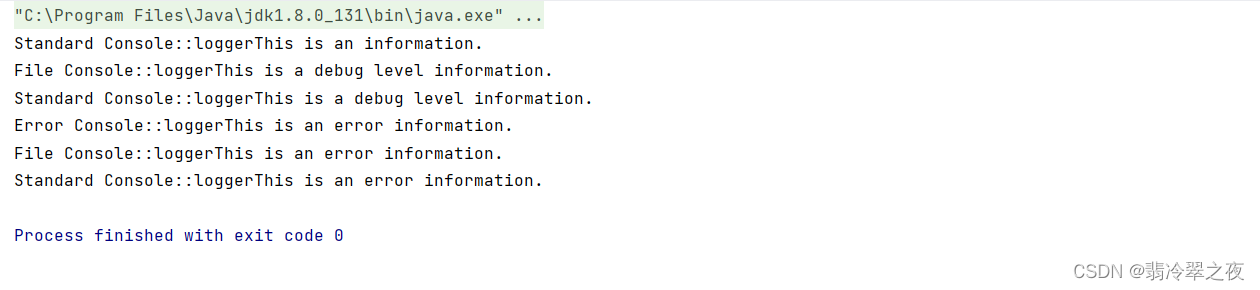
chains.logMessage(AbstractLogger.INFO,"This is an information.");//1
chains.logMessage(AbstractLogger.DEBUG,"This is a debug level information.");//2
chains.logMessage(AbstractLogger.ERROR,"This is an error information.");//3
}
}4.输出