前言
前段时间在做一个导出的功能,本以为是平平无奇的一个功能。就用公司内部的一个导出工具类三下五除二就写完了,做法是直接查全量数据,然后直接往Excel里写。一开始没多少数据也没什么问题,但是当数据量逐渐多了起来后,达到一万多条,导出的时候就会报OOM。然后我就换成了阿里开源的EasyExcel,但是导出的时候也不太稳定,偶尔也会OOM。所以应该是数据量太大了,在写入的时候把内存占满了。然后我就放弃了查全量数据一次性写入Excel的做法,采用分页查询,分批次写入Excel的方式,果然不会出现OOM了。
虽然这种方式不会出现OOM,但是每次导出都写一遍重复的代码着实有点麻烦,所以结合自己平时的使用场景,封装了一个EasyExcel的导出工具类,这样只要在分页查询的基础上写少量的代码,就可以实现分批次写入Excel,简化代码的编写并且解决OOM的问题。
实现
@Slf4j
public abstract class EasyExcelExport<T, S> {
/**
* EasyExcel导出Excel表格,每个sheet默认最大10万条数据
*
* @param fileName excel文件前缀名
* @param sheetName 表页名
*/
public void easyExcelBatchExport(String fileName, String sheetName, HttpServletResponse response) {
this.easyExcelBatchExport(fileName, sheetName, 100000, response);
}
/**
* 分批次导出excel数据
*
* @param fileName excel文件前缀名
* @param sheetSize 每个sheet的数据量,默认10万,excel有限制不能大于1048576
* @param sheetName 表页名
*/
public void easyExcelBatchExport(String fileName, String sheetName, Integer sheetSize, HttpServletResponse response) {
fileName = fileName + LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMddHHmmss")) + ".xlsx";
int currentSheet = 1; // 当前处于第几个sheet
int totalLine = 0; // 总共写入的条数
int currentBatch = 1; // 当前写入excel的批次(第几页)
int lineNum = 1; // 行号,当前写入的是第几条数据
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 告诉浏览器用什么软件可以打开此文件
response.setHeader("content-Type", "application/vnd.ms-excel");
// 下载文件的默认名称
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "utf-8"));
ExcelWriter excelWriter = EasyExcel.write(response.getOutputStream(), (Class<T>) ((ParameterizedType) getClass().getGenericSuperclass()).getActualTypeArguments()[0]).build();
WriteSheet sheet = EasyExcel.writerSheet(sheetName).build();
while (true) {
// 获取数据,然后currentBatch+1,下次调用就会获取新的数据
List<S> sourceDataList = getData(currentBatch);
currentBatch++;
List<T> exportEntityList = new ArrayList<>();
if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(sourceDataList)) {
totalLine += sourceDataList.size();
log.info("EasyExcel开始写入第{}批数据,当前批次数据大小为{}", currentBatch - 1, sourceDataList.size());
for (S sourceData : sourceDataList) {
exportEntityList.add(convertSourceData2ExportEntity(sourceData, lineNum));
lineNum++;
// 当前sheet数据已经到达最大值,将当前数据全写入当前sheet,下一条数据就会写入新sheet
if (lineNum > sheetSize) {
excelWriter.write(exportEntityList, sheet);
exportEntityList.clear();
lineNum = 1;
currentSheet++;
sheet = EasyExcel.writerSheet(sheetName + currentSheet).build();
}
}
// 写入excel
excelWriter.write(exportEntityList, sheet);
} else {
// 未获取到数据,结束
break;
}
}
excelWriter.finish();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("EasyExcel导出异常", e);
}
log.info("EasyExcel导出数据结束,总数据量为{},耗时{}ms", totalLine, (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
}
/**
* 不分批次导出excel。一次性获取所有数据写入excel,确定数据量不大时可以使用该方法,数据量过大时使用分批次导出,否则会OOM
*
* @param fileName excel文件前缀名
* @param sheetName 表页名
*/
public void easyExcelExport(String fileName, String sheetName, HttpServletResponse response) {
fileName = fileName + LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMddHHmmss")) + ".xlsx";
int totalLine = 0; // 总共写入的条数
int lineNum = 1; // 行号,当前写入的是第几条数据
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 告诉浏览器用什么软件可以打开此文件
response.setHeader("content-Type", "application/vnd.ms-excel");
// 下载文件的默认名称
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "utf-8"));
List<S> sourceDataList = getData(1);
List<T> exportEntityList = new ArrayList<>();
if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(sourceDataList)) {
totalLine += sourceDataList.size();
log.info("EasyExcel开始写入数据,数据大小为{}", sourceDataList.size());
for (S sourceData : sourceDataList) {
exportEntityList.add(convertSourceData2ExportEntity(sourceData, lineNum));
lineNum++;
}
}
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 告诉浏览器用什么软件可以打开此文件
response.setHeader("content-Type", "application/vnd.ms-excel");
// 下载文件的默认名称
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "utf-8"));
EasyExcel.write(response.getOutputStream(), (Class<T>) ((ParameterizedType) getClass().getGenericSuperclass()).getActualTypeArguments()[0]).sheet(sheetName).doWrite(exportEntityList);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("EasyExcel导出异常", e);
}
log.info("EasyExcel导出数据结束,总数据量为{},耗时{}ms", totalLine, (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
}
/**
* 将原数据对象转换为需要导出的目标对象
*
* @param sourceData 原对象
* @param lineNum 行号
*/
public abstract T convertSourceData2ExportEntity(S sourceData, Integer lineNum);
/**
* 获取原始数据,通过currentBatch参数分页获取数据。
*
* @param currentBatch 获取第几批(页)数据,通过该参数分页查询,每次调用自动递增。不分批次导出时可以忽略该参数
*/
public abstract List<S> getData(int currentBatch);
}
首先,这是EasyExcelExport是一个抽象类,指定了泛型 T 和 S,T是target目标类,也就是导出时对应的类,S是source原对象所对应的类。
EasyExcelExport里还有两个抽象方法,getData() 和 convertSourceData2ExportEntity() 。这两个方法是需要在平时使用时自己去实现的,getData是数据查询的方法,可以在这里面去实现分页查询的逻辑,currentBatch参数是用来控制分页查询页码的,从1开始,会自动递增。如果确定数据量不大不需要分批次导出的话,那么getData()里只需要进行普通的查询即可,忽略currentBatch参数不用分页查询。还有一个方法是convertSourceData2ExportEntity(),这个是用来将对象S转为对象T的方法,因为从数据库查询或者是从其他地方获取到的对象类型可能是S,而导出时需要的对象类型是T,所以通过该方法进行对象转换。
最核心的是 easyExcelBatchExport() 方法,里面有一个while循环,while循环里首先会去调用getData()方法获取数据,然后将currentBatch加1便于下次获取数据,接下来有个for循环去进行对象的转换并添加到exportEntityList集合中,这个集合中装的是最终写到Excel里的对象。当转换完成后就将当前批次的数据写入Excel中,然后进行下一次循环,当getData()方法未获取到数据时,就结束循环。
同时支持指定每个sheet页的最大行数。在对对象进行转换时有一个判断,当前sheet页的数据是否到达指定值,到达后,直接写入excel,然后新建一个sheet页,这样新的数据就会写入新的sheet页。
使用
那么如何使用这个工具类呢。很简单,只要new出EasyExcelExport的对象,然后实现一下 convertSourceData2ExportEntity() 方法和 getData() 方法即可,然后再根据需要去调用不同的导出方法即可。导出方法有指定和不指定sheet数据页大小的分批写入方法 easyExcelBatchExport() 和不分批次直接一次性写入的 easyExcelExport() 方法。
下面通过一个小案例展示一下。假设现在有个导出用户列表的需求,数据库User表对应的是UserPO类:
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class UserPO {
private Long id;
/**
* 用户编号
*/
private String code;
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 手机号码
*/
private String phone;
/**
* 性别。1-男,2-女
*/
private Integer sex;
}
导出对应的类是UserExportEntity:
@Data
public class UserExportEntity {
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 0, value = "序号")
private Integer line;
@ColumnWidth(35)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 1, value = "用户编号")
private String code;
@ColumnWidth(35)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 2, value = "姓名")
private String name;
@ColumnWidth(35)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 3, value = "手机号码")
private String phone;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 4, value = "性别")
private String sexStr;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 5, value = "fieldA")
private String fieldA;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 6, value = "fieldB")
private String fieldB;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 7, value = "fieldC")
private String fieldC;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 8, value = "fieldD")
private String fieldD;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 9, value = "fieldE")
private String fieldE;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 10, value = "fieldF")
private String fieldF;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 11, value = "fieldG")
private String fieldG;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 12, value = "fieldH")
private String fieldH;
@ColumnWidth(10)
@ContentStyle(horizontalAlignment = HorizontalAlignmentEnum.CENTER, verticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentEnum.CENTER)
@ExcelProperty(index = 13, value = "fieldI")
private String fieldI;
}
先测试一下不分批次导出,导出123456条数据。
@GetMapping("/testExport")
public void testExport(HttpServletResponse response) {
new EasyExcelExport<UserExportEntity, UserPO>() {
@Override
public UserExportEntity convertSourceData2ExportEntity(UserPO sourceData, Integer lineNum) {
UserExportEntity entity = new UserExportEntity();
entity.setLine(lineNum);
entity.setCode(sourceData.getCode());
entity.setName(sourceData.getName());
entity.setPhone(sourceData.getPhone());
entity.setSexStr(Objects.equals(sourceData.getSex(), 1) ? "男" : Objects.equals(sourceData.getSex(), 2) ? "女" : StrUtil.EMPTY);
return entity;
}
@Override
public List<UserPO> getData(int currentBatch) {
List<UserPO> userPOList = new ArrayList<>();
// 模拟查询数据库,假设每次查询会查出123456条数据
for (int i = 0; i < 123456; i++) {
userPOList.add(UserPO.builder()
.code("USER_" + RandomUtil.randomString("1234567890", 6))
.name(RandomUtil.randomString("qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm", 10))
.phone("138" + RandomUtil.randomString("1234567890", 8))
.sex(RandomUtil.randomInt(1, 3))
.build());
}
log.info("userPOList-->{}", JSONUtil.toJsonStr(userPOList));
return userPOList;
}
}.easyExcelExport("测试不分批次导出", "测试不分批次导出", response);
}
为了更清晰地看到效果,我将内存大小限制为128M。
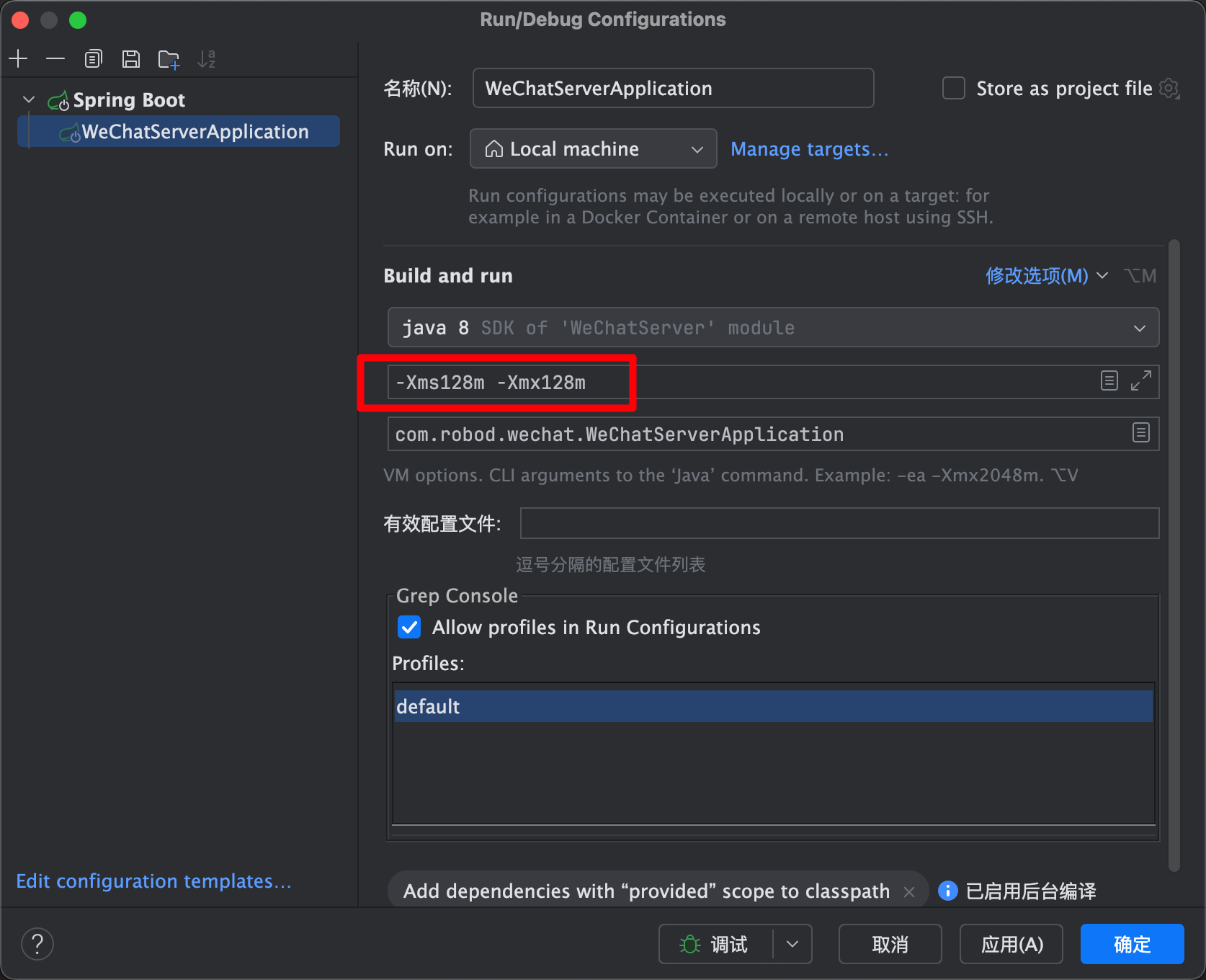
调用一下测试接口,可以看到,导出十几万条数据时发生了OOM。

再来看看分批次导出的效果,模拟一下分页查询,假设有200页数据,每页8888条,一共是170多万条数据。
@GetMapping("/testBatchExport")
public void testBatchExport(HttpServletResponse response) {
new EasyExcelExport<UserExportEntity, UserPO>() {
@Override
public UserExportEntity convertSourceData2ExportEntity(UserPO sourceData, Integer lineNum) {
UserExportEntity entity = new UserExportEntity();
entity.setLine(lineNum);
entity.setCode(sourceData.getCode());
entity.setName(sourceData.getName());
entity.setPhone(sourceData.getPhone());
entity.setSexStr(Objects.equals(sourceData.getSex(), 1) ? "男" : Objects.equals(sourceData.getSex(), 2) ? "女" : StrUtil.EMPTY);
return entity;
}
@Override
public List<UserPO> getData(int currentBatch) {
// 模拟分页查询,假设数据库中有200页数据
if (currentBatch <= 200) {
List<UserPO> userPOList = new ArrayList<>();
// 模拟查询数据库,假设每次查询会查出8888条数据
for (int i = 0; i < 8888; i++) {
userPOList.add(UserPO.builder()
.code("USER_" + RandomUtil.randomString("1234567890", 6))
.name(RandomUtil.randomString("qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm", 10))
.phone("138" + RandomUtil.randomString("1234567890", 8))
.sex(RandomUtil.randomInt(1, 3))
.build());
}
return userPOList;
} else {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}
}.easyExcelBatchExport("测试分批次导出", "测试分批次导出", response);
}

通过分批次写入Excel的方式,成功导出了170多万条数据,相较于不分批次导出,效果显而易见。而且通过调用工具类的方式,进一步简化了导出时代码的编写。
OK!本次的分享就到这里!
如果您觉得文章还不错,请给我来个
点赞,收藏,关注
学习更多编程知识,微信扫描下方二维码关注公众号『 R o b o d 』:







![[嵌入式系统-58]:RT-Thread-内核:线程间通信,邮箱mailbox、消息队列MsgQueue、信号Signal](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/e58b0ede5e20ae25113dffc7cab94fb3.png)