141. 环形链表
判断链表是否有环:如果链表中存在环,则在链表上不断前进的指针会一直在环里绕圈子,且不能知道链表是否有环。使用快慢指针,当链表中存在环时,两个指针最终会在环中相遇。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};142. 环形链表 II
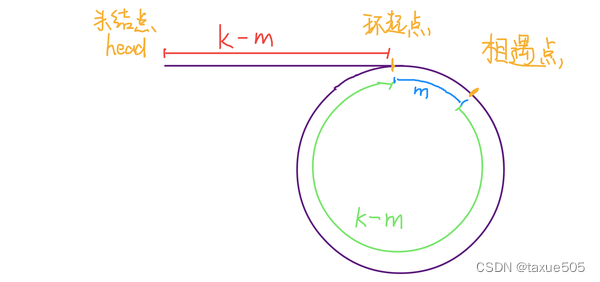
判断链表中环的起点:当我们判断出链表中存在环,并且知道了两个指针相遇的节点,我们可以让其中任一个指针指向头节点,然后让它俩以相同速度前进,再次相遇时所在的节点位置就是环开始的位置。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (true) {
// 如果没有环,直接返回
if (fast == NULL || fast->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) {
break;
}
}
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};876. 链表的中间结点
快指针一次前进两步,慢指针一次前进一步,当快指针到达链表尽头时,慢指针就处于链表的中间位置。
- 当链表的长度是奇数时,slow 恰巧停在中点位置;
- 如果长度是偶数,slow 最终的位置是中间偏右
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* middleNode(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
};19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
先让其中一个指针向前走k步,接着两个指针以同样的速度一起向前进,直到前面的指针走到尽头了,则后面的指针即为倒数第k个元素。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* findNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* pre = findNthFromEnd(dummy, n + 1);
pre->next = pre->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};674. 最长连续递增序列
思路分析:
题目要求我们找的子序列是 连续 的,并且子序列里的元素要求 严格单调递增。在遍历的时候,从第 2 个元素开始;
- 如果当前遍历到的元素比它左边的那一个元素要严格大,「连续递增」的长度就加 1;
- 否则「连续递增」的起始位置就需要重新开始计算。
class Solution {
public:
int findLengthOfLCIS(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
int left = 0, right = 0;
int res = 0;
while (right < len) {
if (right > 0 && nums[right-1] >= nums[right]) {
left = right;
}
right++;
res = max(res, right - left);
}
return res;
}
};26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
while (right < nums.size()) {
if (nums[right] > nums[left]) {
left++;
nums[left] = nums[right];
}
right++;
}
return left + 1;
}
};80. 删除有序数组中的重复项 II
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicatesK(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int len = nums.size();
if (len <= k) {
return len;
}
int slow = k;
for (int fast = k; fast < len; ++fast) {
if (nums[fast] != nums[slow - k]) {
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
slow++;
}
}
return slow;
}
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
return removeDuplicatesK(nums, 2);
}
};283. 移动零
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int left = 0,right = 0;
while (right < nums.size()) {
if (nums[right] != val) {
nums[left] = nums[right];
left++;
}
right++;
}
return left;
}
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
int index = removeElement(nums, 0);
for (; index < nums.size(); ++index) nums[index] = 0;
}
};


![[HNOI2003]激光炸弹](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/4b9f37466d494471bfd12a444a93d721.png)