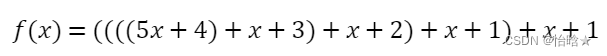目录
A - Programming Contest
B - Base Station Construction
C - Trading
D - New Houses
E - New but Nostalgic Problem
I - Path Planning
K - Peg Solitaire
A - Programming Contest
签到题:直接模拟
直接按照题目意思模拟即可,为了好去重,我们使用set即可
void solve(){
int l,r; cin>>l>>n;
set<int> s;
while(n--){
int x; cin>>x;
s.insert(x);
}
cin>>r;
int ans = 0;
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) ans += !s.count(i);
cout << ans << endl;
return ;
}
B - Base Station Construction
银牌题:优先队列优化dp
我们可以读懂题目也就是说对于一个区间[l,r]而言我们一定要选一个,可以知道r+1从l转移过来肯定是最优的,由此我们可以对于每一个点维护最优的前一个点的转移,同时注意到后缀一定是满足前缀的要求的所以pre[r+1]=max(pre[r+1],l)同时再用前缀最大值处理一下,我们定义在第i个点建立电站同时满足前面的每一个区间的同时的最优解为,转移方程为
,为前缀的点同时随着i的增大j一定是同时增大的变化,所以可以考虑使用优先队列维护dp即可,同时注意怎么判断最后答案是上面,我们可以++n这样满足答案就是
void solve(){
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n+5),pre(n+5),q(n+5);
vector<LL> dp(n+5);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
n++;
cin>>m;
while(m--){
int l,r; cin>>l>>r;
pre[r+1]=max(pre[r+1],l);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) pre[i]=max(pre[i-1],pre[i]);
int hh=0,tt=0;
q[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
while(hh<=tt and q[hh]<pre[i]) hh++;
dp[i] = dp[q[hh]] + a[i];
while(hh<=tt and dp[q[tt]]>=dp[i]) tt--;
q[++tt]=i;
}
cout << dp[n] << endl;
return ;
}C - Trading
签到题:贪心
我们可以有个明显的结论就是从价格最便宜的买入,在贵的卖出就行了,进一步贪心我肯定是买最多的同时卖了最优,所以就是买一半卖一半即可
void solve(){
cin>>n;
LL sum = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int a,b; cin>>a>>b;
w[i]={a,b};
sum += b;
}
sort(w+1,w+1+n);
LL buy = 0,cnt = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
auto [a,b]=w[i];
int now = min(sum/2-cnt,b);
buy += (LL)a*now;
cnt += now;
}
LL use = 0,num = 0;
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--){
auto [a,b]=w[i];
int now = min(sum/2-num,b);
use += (LL)a*now;
num += now;
}
LL ans = use - buy;
cout << ans << endl;
return ;
}D - New Houses
签到题:贪心
设有邻居贡献为x,无为y
我们有个明显的结论就是如果你是有邻居优就让你有邻居,否则让你没邻居,我们一开始可以所有人挤在一起,放置在前i个位置,,(特判n==1)接着按照没有邻居贡献大的来排序,可以注意到多了几个位置就可以有多少人是可以没有邻居的同时贡献要大于有邻居的时候才考虑,贡献为y-x,同时注意到如果说后面排了n-1个人的时候前面最开始就没有邻居了,就需要特判到底是合在一起还是分开贡献最优即可
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m;
LL ans = 0;
// 一开始所有人都挤在一起
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int x,y; cin>>x>>y;
a[i]={x,y};
ans += x;
}
if(n==1){
cout << a[1].second << endl;
return ;
}
sort(a+1,a+1+n,[](PII a,PII b){return a.second-a.first>b.second-b.first;});
int pos = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=m-n and a[i].second-a[i].first>=0 and i<=n;i++){
auto [x,y]=a[i];
ans += y-x;
pos = i;
}
if(pos==n-1){// 由于前面挤在一起的只有一个人 考虑合在一起或者是分开
ans = max(ans+a[n-1].first-a[n-1].second,ans-a[n].first+a[n].second);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return ;
}E - New but Nostalgic Problem
银牌-金牌题:trie树+dfs贪心
我们选出m个使得结果最小我们可以发现要维护的是最长公共前缀,那么我们考虑字符的存储可以考虑使用trie树,我们有一个贪心的想法,我一定是从aaa...abc....这样的结果来看是不是满足数量最优的,如果说对于当前已经选了“abc"下一个是选择d组合为abcd,那么满足是abcd的前缀起码要选择两个,同时前面的abc[a-c]肯定是都得加上因为如果这前面有更优解肯定跑到前面去了,同时对于[e-z]每一个分支最多选择一个,因为如果选择多了当前结果就不是abcd了,同时我们可以发现这样也就是遍历了每一个字符串而已,所以时间是符合要求,接下来就是用实现即可
int tr[N][26],sum[N],ed[N];
string s,ans;
bool ok;
void insert(){
int p = 0;
for(auto&v:s){
int x=v-'a';
if(!tr[p][x]) tr[p][x]=++idx;
p = tr[p][x];
sum[p]++;
}
ed[p]++;
}
void used(){
for(int i=0;i<=idx;i++){
for(int j=0;j<26;j++) tr[i][j]=0;
sum[i]=ed[i]=0;
}
ok = false;
idx = 0;
ans.clear();
}
void dfs(int u,int last){
if(ok) return ;
int s = 0;
//ab 之后 aba abb abc abd ...
//得到的答案是ab
int now = last + ed[u];
for(auto v : tr[u]) s += min(1,v); // 表示对于当前分支接着都取不一样
if(now + s>=m){
cout << (u ? ans : "EMPTY") << endl;
ok = true;
return ;
}
int pre = 0;
for(int i=0;i<26;i++){
if(!tr[u][i]) continue;
// 表示需要加一个分支去走
ans.push_back(i+'a');
dfs(tr[u][i],now+pre+s-1); // 表示在s取过了
ans.pop_back();
pre += sum[tr[u][i]]-1; // 表示这个字母在s取过了
}
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>s;
insert();
}
dfs(0,0);
used();
return ;
}
F - Traveling in Cells
金牌题:二分+动态开点线段树+树装数组
我们有个明显的想法就是对于操作3二分找到最远左右边界即可,但是对于左右边界如果判断是不是符合集合的值难以解决,我们可以注意到 颜色的数量过多,同时还得支持颜色的修改,我们考虑使用动态开点线段树来维护,对于每一个点开出的线段树的用到的节点数量只有(n+m)logn个,我们使用这个数据结构可以维护要求,同时对于查询左右区间的贡献已经修改值都可以通过树装数组来维护,核心还是考察了动态开点线段树
int t,n,m,k,idx;
struct code{
int l,r;
int val;
}tr[N*40];
int c[N],v[N],s[M];
int rc[N];
LL vc[N];
void update(int p){
tr[p].val = tr[tr[p].l].val + tr[tr[p].r].val;
}
void change(int &p,int l,int r,int x,int val){
if(!p) p = ++ idx;
if(l==r){
tr[p].val+=val;
return ;
}
int mid = l+r>>1;
if(x<=mid) change(tr[p].l,l,mid,x,val);
else change(tr[p].r,mid+1,r,x,val);
update(p);
}
int query(int p,int l,int r,int L,int R){
if(!p) return 0;
if(L <= l and r <= R) return tr[p].val;
int mid = l+r>>1;
int res = 0;
if(L<=mid) res += query(tr[p].l,l,mid,L,R);
if(R>mid) res += query(tr[p].r,mid+1,r,L,R);
return res;
}
void add(int k,int x){
for(int i=k;i<=n;i+=lowbit(i)) vc[i] += x;
}
LL ask(int k){
LL res = 0;
for(int i=k;i;i-=lowbit(i)) res += vc[i];
return res;
}
bool check(int l,int r){
int cnt = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
cnt += query(rc[s[i]],1,n,l,r);
return cnt == r-l+1;
}
void clear(){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) rc[i]=vc[i]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=idx;i++) tr[i].l=tr[i].r=tr[i].val=0;
idx = 0;
}
void solve(){
clear();
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>c[i];
change(rc[c[i]],1,n,i,1);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>v[i];
add(i,v[i]);
}
while(m--){
int op,p,x;
cin>>op;
if(op==1){
cin>>p>>x;
change(rc[c[p]],1,n,p,-1);
change(rc[x],1,n,p,1);
c[p]=x;
}
else if(op==2){
cin>>p>>x;
add(p,x-v[p]);
v[p]=x;
}
else{
int pos;
cin>>pos>>k;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++) cin>>s[i];
LL ans = 0;
int posl = pos,posr = pos;
int l = 1, r = pos;
while(l<r){
int mid = l+r>>1;
if(check(mid,pos)) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
posl = l;
l = pos,r = n;
while(l<r){
int mid=l+r+1>>1;
if(check(pos,mid)) l=mid;
else r=mid-1;
}
posr = r;
cout << ask(posr)-ask(posl-1) << endl;
}
}
return ;
}
I - Path Planning
铜牌题:mex + 二分
我们可以注意到题目要求路径上的mex最大,如果x是可以的那么[1-x]一定是可以的,同时如果x不可以那么[x,..]一定是不可以的,所以具有二分性质,现在核心就是二分,我们可以发现路径一定是右下的走法,也就是满足要求的j一定不会比上面满足要求的j要小否则就是往回走了,由此我们可以得到二分的写法
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m;
vector<vector<int>> s(n+5,vector<int>(m+5));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
cin>>s[i][j];
auto check = [&](int x){
int last = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
if(s[i][j]<x){
if(j<last) return false;
last = max(last,j);
}
return true;
};
int l=1,r=n*m;
while(l<r){
int mid=l+r+1>>1;
if(check(mid)) l=mid;
else r=mid-1;
}
cout << l << endl;
return ;
}K - Peg Solitaire
签到-铜牌题:dfs暴力
可以注意到数据范围是很小的所以我们可以考虑直接暴力因为分支很少dfs的不会很多
按照题目意思模拟暴力即可
int ans;
int dx[]={-1,1,0,0},dy[]={0,0,1,-1};
void dfs(int cnt){
ans = min(ans,cnt);
if(ans==1) return ;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
if(s[i][j]){
for(int u=0;u<4;u++){
int a=i+dx[u],b=j+dy[u];
int na=i+2*dx[u],nb=j+2*dy[u];
if(1<=na and na<=n and 1<=nb and nb<=m
and s[a][b] and !s[na][nb]){
s[a][b]=s[i][j]=false;
s[na][nb]=true;
dfs(cnt-1);
s[a][b]=s[i][j]=true;
s[na][nb]=false;
}
}
}
}
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m>>k;
ans = k;
memset(s,0,sizeof s);
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
int x,y; cin>>x>>y;
s[x][y]=true;
}
dfs(k);
cout << ans << endl;
return ;
}
![正点原子[第二期]Linux之ARM(MX6U)裸机篇学习笔记-9.1-LED灯(模仿STM32驱动开发实验)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7ec638eebccc46c0b66e3859f0454c1a.png)