ziplist
redis源码版本:6.0.9。ziplist 的代码均在ziplist.c / ziplist.h文件中。
定义
ziplist总体布局如下:
<zlbytes> <zltail> <zllen> <entry> <entry> ... <entry> <zlend>
zlbytes:uint32_t,记录整个ziplist占用的字节数,包括zlbytes占用的4字节。zltail:uint32_t,记录从ziplist起始位置到最后一个节点的偏移量, 用于支持链表从尾部弹出或反向(从尾到头)遍历链表。zllen:uint16_t,记录节点数量, 如果存在超过 2 16 − 2 2^{16}-2 216−2 个节点, 则这个值设置为 2 16 − 1 2^{16}-1 216−1,这时需要遍历整个ziplist获取真正的节点数量。zlend:uint8_t,一个特殊的标志节点, 等于 255,标志ziplist结尾。其他节点数据不会以255开头。
entry 就是 ziplist 中保存的节点。entry 的格式如下:
<prevlen> <encoding> <entry-data>
- entry-data:该节点元素,即节点存储的数据。
- prevlen:记录前驱节点长度,单位为字节, 该属性长度为1字节或5字节。
- 如果前驱节点长度小于254,则使用1字节存储前驱节点长度。
- 否则,使用5字节,并且第 1 个字节固定为254,剩下4个字节存储前驱节点长度。
- encoding:代表当前节点元素的编码格式, 包含编码类型和节点长度。 一个ziplist中,不同节点元素的编码格式可以不同。编码格式规范如下:
00pppppp(pppppp代表encoding的低 6 位,下同):字符串编码,长度小于或等于 63 ( 2 6 − 1 2^6-1 26−1),长度存放在encoding的低 6 位中。01pppppp:字符串编码, 长度小于或等于16383(24-1),长度存放在encoding的后 6 位和encoding后 1 字节中。10b00000:字符串编码,长度大于 16383 ( 2 14 − 1 2^{14}-1 214−1),长度存放在encoding后 4 字节中。11000000:数值编码, 类型为int16_t,占用 2 字节。11010000:数值编码,类型为int32_t, 占用 4 字节。11100000:数值编码,类型为int64_t,占用 8 字节。11110000:数值编码,使用 3 字节保存一个整数。11111110:数值编码,使用 1 字节保存一个整数。1111xxxx:使用encoding低 4 位存储一个整数, 存储数值范围为 0 ∼ 12 0\sim12 0∼12。该编码下encoding低 4 位的可用范围为 0001 ∼ 1101 0001\sim1101 0001∼1101,encoding低 4 位减 1 为实际存储的值。11111111:255,ziplist结束节点。
注意第 ②、③ 种编码格式,除了 encoding 属性, 还需要额外的空间存储节点元素长度。第 ⑨ 种格式也比较特殊,节点元素直接存放在 encoding属性上。 该编码是针对小数字的优化。这时 entry-data 为空。
字节序
encoding 属性使用多个字节存储节点元素长度, 这种多字节数据存储在计算机内存中或者进行网络传输时的字节顺序称为字节序,字节序有两种类型: 大端字节序和小端字节序。
- 大端字节序: 低字节数据保存在内存高地址位置, 高字节数据保存在内存低地址位置。
- 小端字节序: 低字节数据保存在内存低地址位置, 高字节数据保存在内存高地址位置。
数值 0x44332211 的大端字节序和小端字节序存储方式如下图所示。
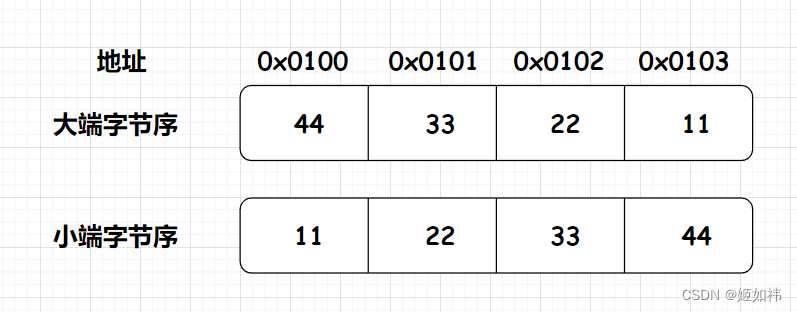
CPU 处理指令通常是按照内存地址增长方向执行的。 使用小端字节序, CPU 可以先读取并处理低位字节,执行计算的借位、 进位操作时效率更高。 大端字节序则更符合人们的读写习惯。
ziplist采取的是小端字节序。
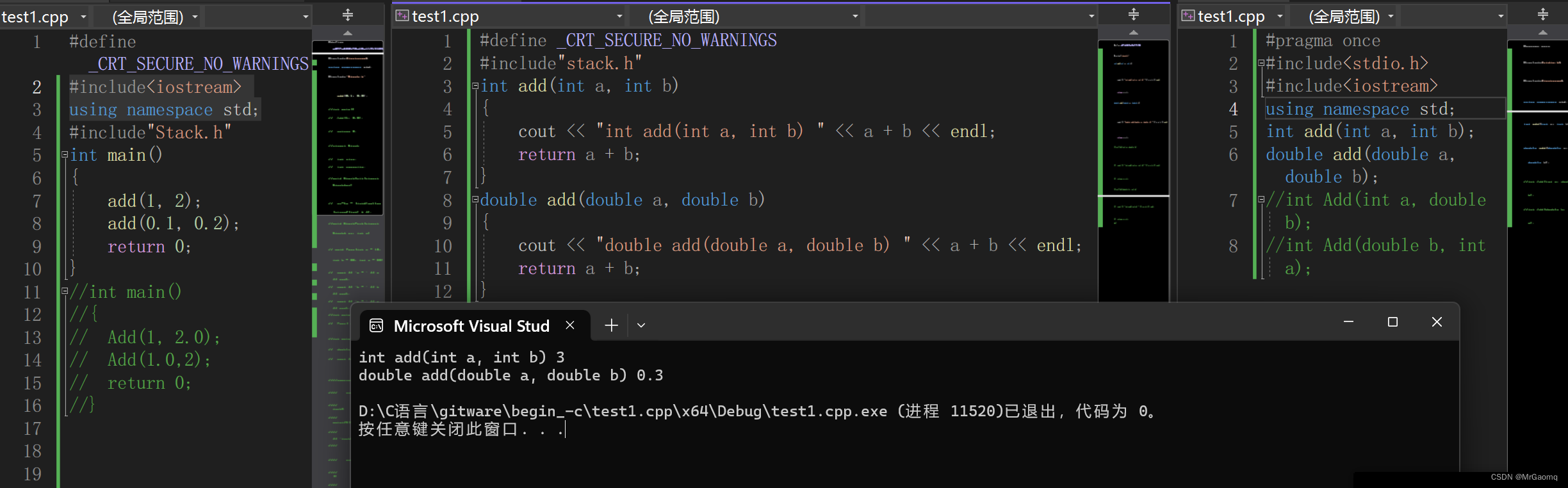
下面是 Redis 提供的一个简单例子:

[0f 00 00 00]:zlbytes为 15,代表整个ziplist占用 15 字节,注意该数值以小端字节序存储。[0c 00 00 00]:zltail为 12,代表从ziplist起始位置到最后 一个节点 ([02 f6]) 的偏移量。[02 00]:zllen为 2,代表ziplist中有 2 个节点。[00 f3]:00 代表前一个节点长度,f3 使用了encoding第 ⑨ 种编码格式,存储数据为encoding低 4 位减 1,即 2。[02 f6]:02 代表前一个节点长度为 2 字节, f5 编码格式同上,存储数据为 5。[ff]:结束标志节点。
ziplist 是 Redis 中比较复杂的数据结构,可以先结合上述属性说明和例子,理解 ziplist 中数据的存放格式。等会儿看了部分源代码之后就比较好理解啦!
ziplistFind
- 参数:
p:指定从ziplist的那个节点开始查找。vstr:待查找元素的内容。vlen:待查找元素的长度。skip:间隔多少个节点才执行一次元素对比操作。
- 返回值:如果找到了目的元素,返回该节点的首地址,如果没有找到目的元素,返回
NULL。
unsigned char *ziplistFind(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *vstr, unsigned int vlen, unsigned int skip) {
int skipcnt = 0;
unsigned char vencoding = 0;
long long vll = 0;
while (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len;
unsigned char *q;
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize); // 获取 prevlen 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 prevlensize 变量中
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len); // 获取 encoding 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 lensize 字段中;获取 ziplist 存储数据的字节数,并将结果保存到 len 中。
q = p + prevlensize + lensize; // 指向 ziplist 存储的数据啦
if (skipcnt == 0) {
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) { // 如果 encoding 是字符串编码
if (len == vlen && memcmp(q, vstr, vlen) == 0) { // 如果找到了目的元素
return p; // 返回节点的首地址
}
} else { // 如果 encoding 不是字符串编码
// 确保对查找元素只进行一次数值编码
if (vencoding == 0) {
// 对查找的元素进行数值编码,如果编码成功将数值保存到 vll,将编码方式保存到 vencoding 修改了 vencoding 确保在查找目的元素的时候只会进行一次数值编码
if (!zipTryEncoding(vstr, vlen, &vll, &vencoding)) {
// 进行数值编码失败了!
vencoding = UCHAR_MAX;
}
// 其实无论是数值编码成功还是失败 vencoding 理论上都不会为 0,但是为了防止程序出问题还是加上了这个断言。再说 release 版本下 assert 根本就没用嘛!
assert(vencoding);
}
/* Compare current entry with specified entry, do it only
* if vencoding != UCHAR_MAX because if there is no encoding
* possible for the field it can't be a valid integer. */
if (vencoding != UCHAR_MAX) {
// 进行数值编码成功了
long long ll = zipLoadInteger(q, encoding); // 根据编码提取数值
if (ll == vll) { // 与参数字符串进行数值编码得到的结果进行对比
return p; // 相等的话,证明找到了,返回节点的首地址
}
}
}
// 重置 skipcnt
skipcnt = skip;
} else {
// skipcnt 不为 0 该节点需要跳过哦!
skipcnt--;
}
p = q + len; // 下一个 ziplist 节点的首地址
}
return NULL;
}
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE
宏功能:获取 prevlen 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 prevlensize 变量中。
ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN:#define ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN 254prevlen字段存储的是前驱节点的长度,单位是字节,该属性长度为 1 字节或 5 字节。- 如果前驱节点长度小于 254,则使用 1 字节存储前驱节点长度。
- 否则使用 5 字节,并且第一个字节固定为 254,剩下 4 字节存储前驱节点的长度。
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize) do { \
if ((ptr)[0] < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) { //前驱节点长度小于 254 \
(prevlensize) = 1; // prevlen 则是 1 字节 \
} else { \
(prevlensize) = 5; // 否则 prevlen 则是 5 字节 \
} \
} while(0)
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH
宏功能:获取 encoding 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 lensize 字段中;获取 ziplist 存储数据的字节数,并将结果保存到 len 中。
-
ptr:指向encoding,即跳过了prevlen字段指向encoding字段。 -
ZIP_STR_06B:#define ZIP_STR_06B (0 << 6)。 -
ZIP_STR_14B:#define ZIP_STR_14B (1 << 6)。 -
ZIP_STR_32B:#define ZIP_STR_32B (2 << 6)。
#define ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(ptr, encoding, lensize, len) do { \
ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING((ptr), (encoding)); // 获取编码方式,将结果保存到 encoding 中 \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) { // 如果是字符串编码 \
if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_06B) { // 如果是字符串的 00pp pppp 编码方式 \
(lensize) = 1; // encoding 字段占 1 个字节,即 encoding 这个字节 \
(len) = (ptr)[0] & 0x3f; // (00pp pppp) & (0011 1111) 获取字符串的长度 \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_14B) { // 如果是字符串的 01pp pppp 编码方式 \
(lensize) = 2; // encoding 字段占 2 个字节:encoding 这个字节+encoding 后 1 字节 \
(len) = (((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1]; // 获取字符串的长度 [1](见注解1) \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_32B) { // 如果是字符串的 1000 0000 编码方式 \
(lensize) = 5; // encoding 字段占 5 个字节:encoding 这个字节+encoding 后 4 字节 \
(len) = ((ptr)[1] << 24) | \
((ptr)[2] << 16) | \
((ptr)[3] << 8) | \
((ptr)[4]); // 获取字符串长度,原理同上一个 if 分支,这里就不再讲了 \
} else { // 无效的字符串编码格式 \
panic("Invalid string encoding 0x%02X", (encoding)); \
} \
} else { // 如果是数值编码 \
(lensize) = 1; // encoding 字段占 1 个字节 \
(len) = zipIntSize(encoding); // 根据 encoding 获取数值编码下存储数值需要的字节数 \
} \
} while(0)
(len) = (((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1];ptr[0]:encoding字段的第一个字节。(ptr)[0] & 0x3f:获取01pp pppp字符串编码下encoding第一个字节的低 6 位。(((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1]:获取到encoding第一字节的低 6 位之后,与encoding的第二字节拼接,最终获取到字符串的长度。
ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING
宏功能:获取编码方式,将结果保存到 encoding 变量中。
-
ZIP_STR_MASK:#define ZIP_STR_MASK 0xc0 -
encoding是字符串编码时,encoding的第一个字节如果小于0xc0那么可以确定是字符串编码。00pppppp(pppppp代表encoding的低6位,下同):字符串编码,长度小于或等于 63 ( 2 6 2^6 26 - 1),长度存放在encoding的低 6 位中。01pppppp:字符串编码,长度小于或等于 16383 ( 2 14 2^{14} 214 - 1),长度存放在encoding的后 6 位和encoding后 1 字节中。10000000:字符串编码,长度大于 16383 ( 2 14 2^{14} 214- 1),长度存放在encoding后 4 字节中。11000000:数值编码,类型为int16_t,占用 2 字节。11010000:数值编码,类型为int32_t,占用 4 字节。11100000:数值编码,类型为int64_t,占用 8 字节。11110000:数值编码,使用 3 字节保存一个整数。11111110:数值编码,使用 1 字节保存 一个整数。1111xxxx:使用encoding低4位存储一个整数, 存储数值范围为 0 ∼ 12 0\sim12 0∼12。该编码下encoding低 4 位的可用范围为 0001 ∼ 1101 0001\sim1101 0001∼1101 ,encoding低 4 位减 1 为实际存储的值。11111111:255,ziplist结束节点。
可以看到即使
encoding编码为字符串时p全部取 1,encoding的首字节还是小于0xc0,因此可以通过encoding首字节的数值大小与0xc0比较来确定编码时字符串还是数值。
#define ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(ptr, encoding) do { \
(encoding) = (ptr[0]); // ptr 指向的就是 encoding \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) (encoding) &= ZIP_STR_MASK; // 获取 encoding 的高 2 位进一步确定编码方式! \
} while(0)
为什么不直接让
encoding &= 0xc0呢?因为后面需要用encoding变量来区分具体是哪一种数值编码。
zipIntSize
函数功能:根据参数 encoding,获取并返回该编码方式下,存储数值需要的字节数。
ZIP_INT_8B:#define ZIP_INT_8B 0xfe。1111 1110数值编码方式。ZIP_INT_16B:#define ZIP_INT_16B (0xc0 | 0<<4)。1100 0000数值编码方式。ZIP_INT_24B:#define ZIP_INT_24B (0xc0 | 3<<4)。1111 0000数值编码方式ZIP_INT_32B:#define ZIP_INT_32B (0xc0 | 1<<4)。1101 0000数值编码方式ZIP_INT_64B:#define ZIP_INT_64B (0xc0 | 2<<4)。1110 0000数值编码方式ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN:#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN 0xf1。1111 xxxx数值编码方式编码数字的最小值。ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX:#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX 0xfd。1111 xxxx数值编码方式编码数字的最大值。
unsigned int zipIntSize(unsigned char encoding) {
switch(encoding) {
case ZIP_INT_8B: return 1; // 1111 1110 数值编码方式,使用 1 个字节保存整数
case ZIP_INT_16B: return 2; // 1100 0000 数值编码方式,使用 2 个字节保存整数
case ZIP_INT_24B: return 3; // 1111 0000 数值编码方式,使用 3 个字节保存整数
case ZIP_INT_32B: return 4; // 1101 0000 数值编码方式,使用 4 个字节保存整数
case ZIP_INT_64B: return 8; // 1110 0000 数值编码方式,使用 8 个字节保存整数
}
// 1111 xxxx 数值编码方式,使用 encoding 存储整数,不需要多余的空间,xxxx 的取值范围是: 0001~1101
// 对应了 ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN 和 ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX,实际存储的整数是 [0000~1100] = [0, 12]
if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX)
return 0; // 直接将整数存储到 encoding 中是对小数字的优化!
panic("Invalid integer encoding 0x%02X", encoding); // 无效的整形编码
return 0;
}
ZIP_IS_STR
宏功能:判断 enc 的编码方式是否是字符串编码!
-
ZIP_STR_MASK:#define ZIP_STR_MASK 0xc0。 -
字符串编码的
encoding最高的两个比特位是:00,01,11中的一个,肯定小于0xc0最高的两个比特位11嘛!并且数值编码的最高两个比特位都是11。
#define ZIP_IS_STR(enc) (((enc) & ZIP_STR_MASK) < ZIP_STR_MASK)
zipTryEncoding
函数功能:传入一个字符串,尝试对其进行数值编码。如果成功,返回 1,并将编码成功的数值保存到 *v,将数值对应的编码方式保存到 *encoding;如果失败,返回 0。
ZIP_INT_8B:#define ZIP_INT_8B 0xfe。1111 1110数值编码方式。ZIP_INT_16B:#define ZIP_INT_16B (0xc0 | 0<<4)。1100 0000数值编码方式。ZIP_INT_24B:#define ZIP_INT_24B (0xc0 | 3<<4)。1111 0000数值编码方式。ZIP_INT_32B:#define ZIP_INT_32B (0xc0 | 1<<4)。1101 0000数值编码方式。ZIP_INT_64B:#define ZIP_INT_64B (0xc0 | 2<<4)。1110 0000数值编码方式。ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN:#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN 0xf1。1111 xxxx数值编码方式编码数字的最小值。ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX:#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX 0xfd。1111 xxxx数值编码方式编码数字的最大值。
int zipTryEncoding(unsigned char *entry, unsigned int entrylen, long long *v, unsigned char *encoding) {
long long value;
if (entrylen >= 32 || entrylen == 0) return 0; // 满足这个条件编码一定会失败的 long long 不可能对 32 个字符的数字进行编码,entyrlen 为 0 一定编码失败
if (string2ll((char*)entry,entrylen,&value)) { // 这个函数讲过啦在字符串的那一节,字符串转 long long
// 如果转化成 long long 成功,根据转换的结果进行判断
if (value >= 0 && value <= 12) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN+value; // 1111 xxxx 数值编码方式
} else if (value >= INT8_MIN && value <= INT8_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_8B; // 1111 1110 数值编码方式。
} else if (value >= INT16_MIN && value <= INT16_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_16B; // 1100 0000 数值编码方式
} else if (value >= INT24_MIN && value <= INT24_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_24B; // 1111 0000 数值编码方式
} else if (value >= INT32_MIN && value <= INT32_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_32B; // 1101 0000 数值编码方式
} else {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_64B; // 1110 0000 数值编码方式
}
*v = value; // 将结果保存到 *v
return 1; // 转换成功
}
return 0; // 如果字符串无法转换为 long long 那么编码成数值就失败啦
}
zipLoadInteger
函数功能:根据 encoding 编码方式,返回 ziplist 节点存储的数值。
- 参数:
p:指向ziplist节点存储数据空间的首字节地址。encoding:数值的编码方式。
int64_t zipLoadInteger(unsigned char *p, unsigned char encoding) {
int16_t i16;
int32_t i32;
int64_t i64, ret = 0;
if (encoding == ZIP_INT_8B) { // 1111 1110 数值编码方式,使用 1 个字节保存整数
ret = ((int8_t*)p)[0]; // 获取存储的数据
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_16B) { // 1100 0000 数值编码方式,使用 2 个字节保存整数
memcpy(&i16,p,sizeof(i16)); // 临时保存转换结果
memrev16ifbe(&i16); // 字节序转换
ret = i16; // 保存字节序转换后的结果
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_32B) { // 1101 0000 数值编码方式,使用 4 个字节保存整数
memcpy(&i32,p,sizeof(i32));
memrev32ifbe(&i32);
ret = i32;
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_24B) { // 1111 0000 数值编码方式,使用 3 个字节保存整数
i32 = 0;
memcpy(((uint8_t*)&i32)+1,p,sizeof(i32)-sizeof(uint8_t));
memrev32ifbe(&i32);
ret = i32>>8; // 转换字节序之后需要 >> 8 位
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_64B) { // 1110 0000 数值编码方式,使用 8 个字节保存整数
memcpy(&i64,p,sizeof(i64));
memrev64ifbe(&i64);
ret = i64;
} else if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX) {
ret = (encoding & ZIP_INT_IMM_MASK)-1; // 1111 xxxx 数值编码方式,规定的 xxxx - 1表示存储的数值
} else {
assert(NULL);
}
return ret; // 返回结果
}
ZIP_INT_IMM_MASK:#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MASK 0x0f
memrev16ifbe
功能:进行字节序的转换,条件编译实现的哈!
#if (BYTE_ORDER == LITTLE_ENDIAN)
#define memrev16ifbe(p) ((void)(0))
#define memrev32ifbe(p) ((void)(0))
#define memrev64ifbe(p) ((void)(0))
#define intrev16ifbe(v) (v)
#define intrev32ifbe(v) (v)
#define intrev64ifbe(v) (v)
#else
#define memrev16ifbe(p) memrev16(p)
#define memrev32ifbe(p) memrev32(p)
#define memrev64ifbe(p) memrev64(p)
#define intrev16ifbe(v) intrev16(v)
#define intrev32ifbe(v) intrev32(v)
#define intrev64ifbe(v) intrev64(v)
#endif
#define memrev16ifbe(p) memrev16(p)
// redis 源码直接一个字节一个字节交换来实现的哈!whatever how much the size is
void memrev16(void *p) {
unsigned char *x = p, t;
t = x[0];
x[0] = x[1];
x[1] = t;
}
// ·······
void memrev64(void *p) {
unsigned char *x = p, t;
t = x[0];
x[0] = x[7];
x[7] = t;
t = x[1];
x[1] = x[6];
x[6] = t;
t = x[2];
x[2] = x[5];
x[5] = t;
t = x[3];
x[3] = x[4];
x[4] = t;
}
ziplistInsert
- 参数:
zl:待插入的ziplist。p: 指向插入位置的后驱节点。s:待插入元素的内容。slen:待插入元素的长度。
unsigned char *ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {
return __ziplistInsert(zl,p,s,slen);
}
__ziplistInsert
-
参数:
-
zl:待插入的ziplist。 -
p: 指向插入位置的后驱节点。 -
s:待插入元素的内容。 -
slen:待插入元素的长度。
-
-
ZIP_END:#define ZIP_END 255。ziplist的结束节点的encoding是 255 哈,ziplist结束节点仅含encoding字段。
unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen; // curlen 整个 ziplist 占用的字节数,ziplist 最开始的四字节存放的就是整个 ziplist 占用的字节数,包括这 4 字节哦!
unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;
size_t offset;
int nextdiff = 0;
unsigned char encoding = 0;
long long value = 123456789; // 源码中的注释说这个注释为了防止编译器报警告
zlentry tail;
// 该代码块就是获取插入位置的前驱节点所占的字节数
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { // 不是尾插
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen); // 获取 p 节点 prevlen 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 prevlensize 变量中,获取前驱节点占用的字节数,并将结果保存到 prevlen 变量中。
} else { // 是尾插
unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl); // 获取 ziplist 尾节点,赋值给 ptail 变量
if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) { // 理论上来说 ptail[0] 不可能等于 ZIP_END 的。
prevlen = zipRawEntryLength(ptail); // 获取 ptail 这个节点的字节数 赋值给 prevlen
// 因为 ziplist 结束节点并没有保存前一个节点的所占的字节数,需要手动计算
}
}
// 尝试对要插入的字符串 s 进行数值编码!
if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) {
// 如果数值编码成功
reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding); // 根据参数 encoding,获取并返回该编码方式下,存储数值需要的字节数。将得到的结果赋值给 reqlen
} else {
// 数值编码失败,reqlen 就是字符串的长度。
reqlen = slen;
}
/* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and
* the length of the payload. */
reqlen += zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL,prevlen); // 参数 1 为 NULL,返回存储前驱节点所占字节数需要的 prevlen 字段的字节数。最后加到 reqlen 上。
reqlen += zipStoreEntryEncoding(NULL,encoding,slen); // 参数 1 为 NULL,返回 encoding 字段所占的字节数。最后加到 reqlen 上。
/* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to
* make sure that the next entry can hold this entry's length in
* its prevlen field. */
int forcelarge = 0;
nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0; // 将后驱节点的 prevlen 字段需要调整的字节数保存到 nextdiff 变量中。
if (nextdiff == -4 && reqlen < 4) { // [2](见注解2)
nextdiff = 0; // 强制修改 nextdiff = 0,使之不要缩容
forcelarge = 1;
}
/* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */
offset = p-zl; // 记录待插入节点的后驱节点相对于 ziplist 首地址的偏移量,因为 realloc 可能会修改ziplist 的首地址。
zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+reqlen+nextdiff); // 开辟新的空间出来哈,包括插入节点的空间,nextdiff 需要调整的空间嘛!该函数会在最后一个字节直接设置 zlend。
p = zl+offset; // 带插入元素的后驱节点的首地址
/* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { // 不是尾插
memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff); // 移动数据,留出空间放新插入的节点,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff 这个 -1 说明没有移动那个 zlend 字段哈!因为在 ziplistResize 函数中已经设置过了嘛
if (forcelarge)
zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p+reqlen,reqlen); // forcelarge 这个名字还是能够理解他的意思的!理论上新插入节点的后驱节点的 prevlen 字段一个字节就够了嘛,但是为了防止缩容情况的出现,被迫让 prevlen 字段占用了 5 字节来存储新插入节点的长度!所以叫 forcelarge,可以理解!
else
zipStorePrevEntryLength(p+reqlen,reqlen); // 给新插入节点的后驱节点的 prevlen 字段赋值
// 更新 ziplist 的 zltail 字段的值
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen);
/* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take
* "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the
* size of prevlen doesn't have an effect on the *tail* offset. */
zipEntry(p+reqlen, &tail); // 构建 zlentry 结构体
if (p[reqlen+tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) { // 如果有多个后驱节点,则还需要加上 nextdiff [1](见注解1)
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff);
}
} else {
// 更新 ziplist 的 zltail 字段的值
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl);
}
/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so
* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */
// 如果 nextdiff 不等于 0 说明需要更新新插入节点的后面节点的 prevlen字段的长度,prevlen 字段存储的值啥的!
if (nextdiff != 0) {
offset = p-zl; // 记录当前节点相对于 ziplist 首地址的偏移量,因为 __ziplistCascadeUpdate 函数可能会修改 zl 指针
zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen);
p = zl+offset; // 重新赋值 p
}
// 插入节点
p += zipStorePrevEntryLength(p,prevlen); // 修改新节点 prevlen 字段的值,并且跳过新节点的 prevlen 字段,指向 encoding 字段。
p += zipStoreEntryEncoding(p,encoding,slen); // 修改新节点 encoding 字段的值,并且跳过新节点的 encoding 字段,指向 entry_data 字段。
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) { // 如果是字符串编码
memcpy(p,s,slen); // 字符串的话, 直接 memcpy 拷贝数据就可以啦!
} else { // 如果是数值编码
zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding);
}
ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1);
return zl;
}
-
如果后驱节点只有一个
nextdiff可以忽略,因为在原偏移量的基础上加上reqlen就是尾节点的指针。但是如果有多个后驱节点,情况就不同啦!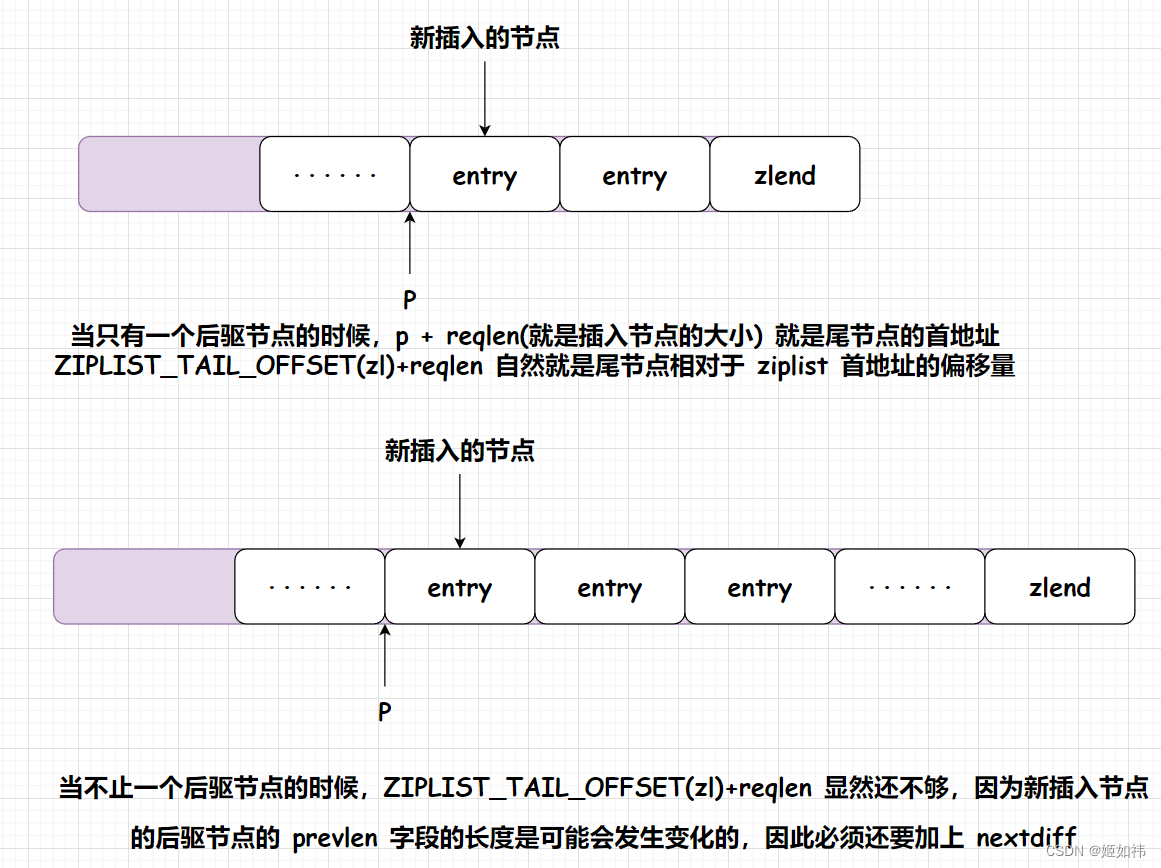
-
如果
reqlen < 4 && nextdiff == -4时,不对nextdiff做调整,那么等会儿调用ziplistResize函数,他的参数curlen+reqlen+nextdiff < curlen,就会进行缩容,导致原ziplist的数据丢失,所以我们需要对nextdiff做调整,防止数据丢失。这只是一方面的原因哈!还有一个原因:出现缩容的情况将
mextdiff强制设置为 0,就可以避免缩容情况下导致的级联更新!所以强制保持后驱节点的prevlen字段保持不变。
intrev32ifbe
- 宏功能:字节序转换,并将转换后的结果返回。相比于
memrev系列函数多了返回值!
#define intrev32ifbe(v) intrev32(v)
uint32_t intrev32(uint32_t v) {
memrev32(&v);
return v;
}
void memrev32(void *p) {
unsigned char *x = p, t;
t = x[0];
x[0] = x[3];
x[3] = t;
t = x[1];
x[1] = x[2];
x[2] = t;
}
ZIPLIST_BYTES
宏功能:将 zl 指针,转换为 uint32_t* 并解引用。 即获取整个 ziplist 占用的字节数。
#define ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) (*((uint32_t*)(zl)))
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN
宏功能:获取 prevlen 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 prevlensize 变量中,获取前驱节点占用的字节数,并将结果保存到 prevlen 变量中。
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(ptr, prevlensize, prevlen) do { \
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize); // 获取 prevlen 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 prevlensize 变量中 \
if ((prevlensize) == 1) { \
(prevlen) = (ptr)[0]; // 将前驱节点的字节数保存到 prevlen 中 \
} else if ((prevlensize) == 5) { \
assert(sizeof((prevlen)) == 4); // debug 模式下的强制检查,确保 prevlen 是 4 字节变量 \
memcpy(&(prevlen), ((char*)(ptr)) + 1, 4); // 当前驱节点的大小大于等于 254,prevlen 字段的第一个字节存储的是 254,第 2-5 四个字节存储的是前驱节点的字节数 \
memrev32ifbe(&prevlen); // 字节序的转换 \
} \
} while(0)
ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL
宏功能:根据 ziplist 的首地址找到 zltail 字段后,解引用获取到最后一个节点的偏移量,并对 zl 字段加上该偏移量,指向 ziplist 的尾节点。ziplist 的首地址向后偏移 4 个字节就是 zltail 字段,该字段是 uint32_t 类型,记录从 ziplit 其实位置到最后一个节点的偏移量。
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl)))
#define ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t))))
zipRawEntryLength
-
函数功能:返回节点 p 占用的字节数。
-
参数:
ziplist尾节点的指针。 -
返回值:整个节点的字节数。
unsigned int zipRawEntryLength(unsigned char *p) {
unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len;
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize); // 获取 prevlen 字段的字节数,将结果保存到 prevlensize 变量中。
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len); // 获取 encoding 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 lensize 字段中;获取 ziplist 存储数据的字节数,并将结果保存到 `len` 中。
return prevlensize + lensize + len; // 返回整个节点的字节数。
}
zipStorePrevEntryLength
-
功能:如果参数 1 为
NULL则返回存储len需要的prevlen字段的字节数;如果参数 1 不为NULL除了返回prevlen字段所占的字节数,还会对参数 1 指向节点的prevlen字段进行赋值。 -
参数:
p:节点首地址。len:节点长度。
-
ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN:#define ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN 254。如果前驱节点长度小于 254,使用 1 字节存储前驱节点长度。如果前驱节点长度大于等于 254,使用 5 字节,第一个字节固定为 254,剩下的 4 字节存储前驱节点的长度。
/* Encode the length of the previous entry and write it to "p". Return the
* number of bytes needed to encode this length if "p" is NULL. */
unsigned int zipStorePrevEntryLength(unsigned char *p, unsigned int len) {
if (p == NULL) { // 如果 p 没有指向一个 ziplist 的节点
return (len < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) ? 1 : sizeof(len)+1; // 返回 prevlen 字段的大小,len < 254 返回 1 否则返回 5 嘛
} else { // 如果 p 指向了一个 ziplist 的节点
if (len < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) { // 如果说节点的长度小于 254
p[0] = len; // 给 prevlen 字段赋值
return 1;
} else { // 如果说节点的长度大于等于 254
return zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p,len); // 也是给 prevlen 字段赋值
}
}
}
zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge
- 功能:参数 2 的长度大于 254 时,调用的这个函数,因此该函数固定返回 5 哈。如果参数 1 为
NULL则返回prevlen字段所占的字节数;如果参数 1 不为NULL除了返回prevlen字段所占的字节数,还会对参数 1 指向节点的prevlen字段进行赋值。 - 参数:
p:节点首地址。len:节点长度。
- 返回值:
prevlen字段所占的字节数,固定为 5。
int zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(unsigned char *p, unsigned int len) {
if (p != NULL) { // 如果 p 不等于 NULL
p[0] = ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN; // 节点长度大于等于 254 prevlen 字段的第一个字节固定是 254 嘛
memcpy(p+1,&len,sizeof(len)); // 剩下的四个字节存储的是实际的长度嘛
memrev32ifbe(p+1); // 转化字节序
}
return 1+sizeof(len); // 返回 prevlen 字段的字节数 + encoding 字段的 1 字节
}
zipStoreEntryEncoding
- 函数功能:如果参数 1 为
NULL则返回encoding字段所占的字节数;如果参数 1 不为NULL,还会对参数 1 指向节点的encoding字段的值进行修改! - 参数:
p:节点首地址。encoding:节点编码。rawlen:待插入元素的长度。
ZIP_STR_06B:#define ZIP_STR_06B (0 << 6)ZIP_STR_14B:#define ZIP_STR_14B (1 << 6)ZIP_STR_32B:#define ZIP_STR_32B (2 << 6)
unsigned int zipStoreEntryEncoding(unsigned char *p, unsigned char encoding, unsigned int rawlen) {
unsigned char len = 1, buf[5]; // len 初始化为 1,encoding 字段最小占一字节
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) { // 判断是否是字符串编码,在 __ziplistInsert 函数中,encoding 字段是被初始化为 0 的嘛,如果数值编码转换失败了,encoding 还是 0 ,那么就是字符串编码啦!高 2 位 00 < 11 嘛
if (rawlen <= 0x3f) { // 00pp pppp 编码,字符串的长度存放在 encoding 的低 6 位
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_06B | rawlen;
} else if (rawlen <= 0x3fff) { // 01pp pppp 编码。字符串的长度存放在 encoding 的低 6 位和 encoding 的后一字节
len += 1; // encoding 字段占 2 字节
if (!p) return len; // if p==NULL 直接就返回 encoding 字段的长度啦
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_14B | ((rawlen >> 8) & 0x3f); // encoding 字段的第一个字节
buf[1] = rawlen & 0xff; // encoding 字段的第二个字节
} else { // 1000 0000 编码,长度存放在 encoding 的后四字节
len += 4; // encoding 字段所占的字节数为 5
if (!p) return len; // if p==NULL 直接就返回 encoding 字段的长度啦
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_32B; // encoding 字段的第一个字节
buf[1] = (rawlen >> 24) & 0xff; // encoding 字段的第一个字节
buf[2] = (rawlen >> 16) & 0xff; // encoding 字段的第二个字节
buf[3] = (rawlen >> 8) & 0xff; // encoding 字段的第三个字节
buf[4] = rawlen & 0xff; // encoding 字段的第四个字节
}
} else { // 数值编码
if (!p) return len; // if p==NULL 直接就返回 encoding 字段的长度啦
buf[0] = encoding; // encoding 字段的第一个字节。
}
// 到这里 p 一定不为 NULL,将 encoding 字段做修改!
memcpy(p,buf,len);
return len; // 返回 encoding 字段所占的字节数
}
zipPrevLenByteDiff
- 功能:传入待插入节点的后驱节点指针,和新插入节点的长度,判断待插入节点的
prevlen字段能否存储新插入节点所占的字节数。 - 参数:
p:指向插入位置的后驱节点。len:待插入节点的长度。
- 返回值:后驱节点的
prevlen字段需要调整多少个字节!- 0:后驱节点的
prevlen字段不需要调整大小。 - -4:后驱节点的
prevlen字段需要减少 4 字节。 - 4:后驱节点的
prevlen字段需要增加 4 字节。
- 0:后驱节点的
int zipPrevLenByteDiff(unsigned char *p, unsigned int len) {
unsigned int prevlensize;
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize); // 解析后驱节点 prevlen 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 prevlensize 变量中
return zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL, len) - prevlensize; // [1](见注解1)
}
zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL, len)参数 1 为NULL返回存储len需要的prevlen字段的字节数。 然后与prevlensize做差,就能知道待插入节点的后驱节点的prevlen字段的字节数能否用来存储新节点所占的字节数。
ziplistResize
- 函数功能:传入
ziplist首地址,重新分配这个ziplist的空间,空间的大小为len。
unsigned char *ziplistResize(unsigned char *zl, unsigned int len) {
zl = zrealloc(zl,len); // realloc 空间
ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) = intrev32ifbe(len); // 更新 zlbytes 字段
zl[len-1] = ZIP_END; // 在 realloc 出来的空间的最后一个字节加上 zlend 字段
return zl;
}
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET
宏功能:返回 ziplist 起始位置到最后一个节点的偏移量。
#define ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t))))
zipEntry
- 函数功能:传入待插入节点的首地址,获取节点相关的数据,用来初始化
zlentry这个结构体。 - 参数:
p:节点首地址。e:传入一个zlentry结构体的地址。
void zipEntry(unsigned char *p, zlentry *e) {
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, e->prevrawlensize, e->prevrawlen); // 获取 prevlen 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 e->prevrawlensize 中,获取前驱节点(新插入节点)占用的字节数,并将结果保存到 e->prevrawlen 中。
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding, e->lensize, e->len); // 获取 encoding 字段的字节数,并将结果保存到 e->lensize 字段中;获取节点 p 存储数据的字节数,并将结果保存到 e->len 中。
e->headersize = e->prevrawlensize + e->lensize; // 计算 headersize 并将结果保存到 e->headersize
e->p = p; // e->p 指向节点的首地址
}
zlentry
/* We use this function to receive information about a ziplist entry.
* Note that this is not how the data is actually encoded, is just what we
* get filled by a function in order to operate more easily. */
// 翻译:我们使用这个结构体来接收有关一个 ziplist 条目的信息。请注意,这并不是数据实际编码的方式,而是我们通过一个结构体填充以便更轻松操作的内容。
typedef struct zlentry {
// prevlen 字段占用的字节数
unsigned int prevrawlensize; /* Bytes used to encode the previous entry len*/
// 前驱节点的字节数
unsigned int prevrawlen; /* Previous entry len. */
// encoding 字段占用的字节数
unsigned int lensize; /* Bytes used to encode this entry type/len.
For example strings have a 1, 2 or 5 bytes
header. Integers always use a single byte.*/
// 存储数据占用的字节数
unsigned int len; /* Bytes used to represent the actual entry.
For strings this is just the string length
while for integers it is 1, 2, 3, 4, 8 or
0 (for 4 bit immediate) depending on the
number range. */
// prevlen 占用的字节数 + encoding 字段占用的字节数
unsigned int headersize; /* prevrawlensize + lensize. */
// 编码方式
unsigned char encoding; /* Set to ZIP_STR_* or ZIP_INT_* depending on
the entry encoding. However for 4 bits
immediate integers this can assume a range
of values and must be range-checked. */
// 节点的首地址
unsigned char *p; /* Pointer to the very start of the entry, that
is, this points to prev-entry-len field. */
} zlentry;
zipSaveInteger
- 函数功能:传入新插入节点存储数据空间的地址,以及数值编码对应的值,对
encoding做判断,将数值插入到该空间。 - 参数:
p:节点存储数据的地址。value:保存的数值。encoding:编码方式。
void zipSaveInteger(unsigned char *p, int64_t value, unsigned char encoding) {
int16_t i16;
int32_t i32;
int64_t i64;
if (encoding == ZIP_INT_8B) {
((int8_t*)p)[0] = (int8_t)value;
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_16B) {
i16 = value;
memcpy(p,&i16,sizeof(i16)); // 拷贝数据
memrev16ifbe(p); // 字节序转换
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_24B) {
i32 = value<<8;
memrev32ifbe(&i32);
memcpy(p,((uint8_t*)&i32)+1,sizeof(i32)-sizeof(uint8_t));
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_32B) {
i32 = value;
memcpy(p,&i32,sizeof(i32));
memrev32ifbe(p);
} else if (encoding == ZIP_INT_64B) {
i64 = value;
memcpy(p,&i64,sizeof(i64));
memrev64ifbe(p);
} else if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX) {
/* Nothing to do, the value is stored in the encoding itself. */
// 这种编码方式,encoding 字段的低 4 字节就已经存储好了数值编码之后的 value 啦,详见 zipTryEncoding 函数。
} else {
assert(NULL);
}
}
ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH
宏功能:修改 ziplist 的 zllen 字段。zllen 字段用来记录 ziplist 的节点数量,类型:uint16_t,如果存在超过
2
16
−
2
2^{16} - 2
216−2 个节点,则这个值设置为
2
16
−
1
2^{16} - 1
216−1,这时需要遍历整个链表来获取正真的节点数量。
#define ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,incr) { \
if (ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) < UINT16_MAX) \
ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) = intrev16ifbe(intrev16ifbe(ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl))+incr); \
}
级联更新
考虑一种极端场景,在 ziplist 的 e2 节点前面插入一个新的节点 ne,元素数据长度为 254,如下图所示:
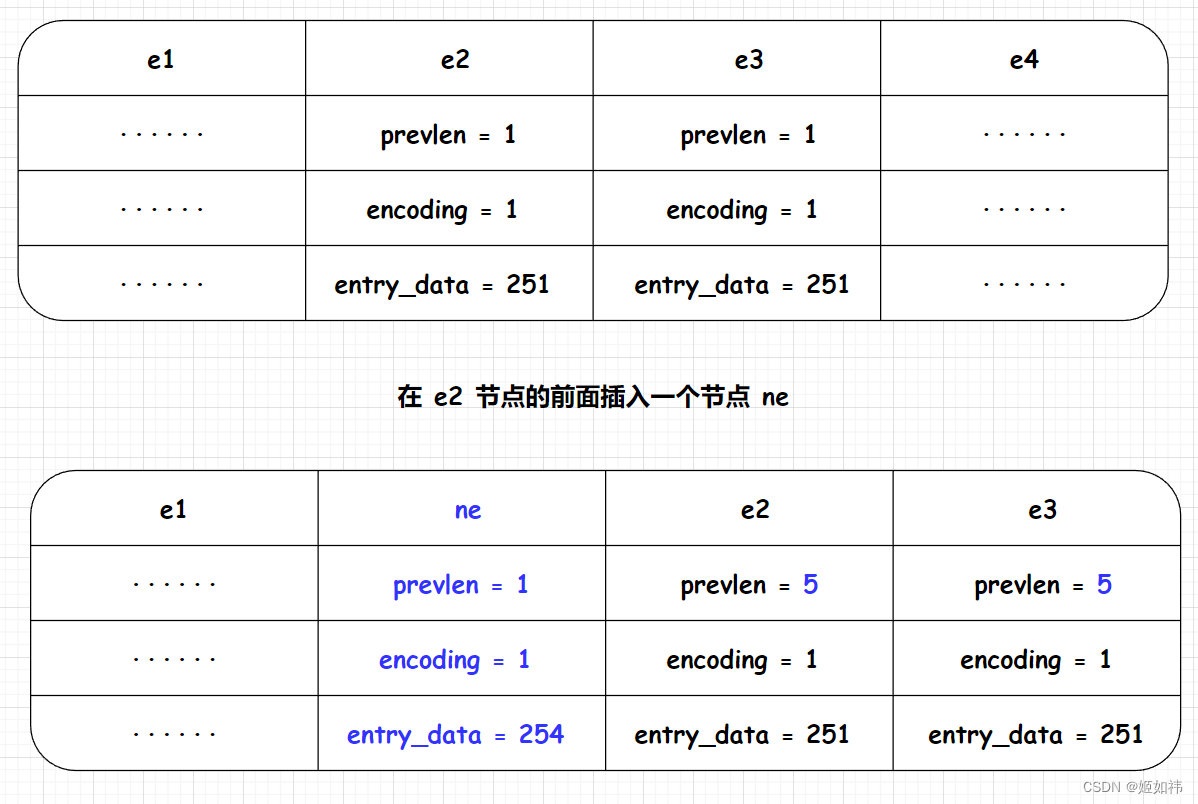
插入节点后 e2 的 prevlen 属性长度需要更新为 5 字节。
注意 e3 的 prevlen,插入前 e2 的长度为 253,所以 e3 的 prevlen 属性长度为 1 字节,插入新节点后,e2 的长度为 257,那么 e3 的prevlen 属性长度也要更新了,这就是级联更新。在极端情况下,e3 的后续节点也要持续更新 prevlen 属性。
在阅读过 __ziplistCascadeUpdate 的代码之后,或者说单凭感觉,我们都足以知道级联更新下的性能是非常糟糕的,而且代码复杂度也高,那么怎么解决这个问题呢?
我们先来看看为什么要使用 prevlen 这个字段?
这是因为反向遍历时,每向前跨过一个节点,都必须知道前面这个节点的长度。
既然这样,我们把每个节点长度都保存一份到节点的最后位置,反向遍历时,直接从前面一个节点的最后位置获取前一个节点的长度不就可以了嘛?而且这样每个节点都是独立的,插入或删除节点都不会有级联更新的现象。基于这种设计,Redis 作者设计另一种结构 listpack。设计 listpack 的目的是取代 ziplist,但是 ziplist 使用范围比较广,替换起来比较复杂,所以目前应用在新增的 Stream 结构中。
__ziplistCascadeUpdate
可以先看看什么是级联更新,看完这个函数可能会比较好理解一点。级联更新
-
函数功能:级联更新节点的
prevlen字段,包括prevlen字段的大小,prevlen字段存储的值哈! -
参数:
zl:ziplist的首地址。p:新插入节点的后驱节点。
unsigned char *__ziplistCascadeUpdate(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p) {
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), rawlen, rawlensize; // ZIPLIST_BYTES 获取整个 ziplist 所占用的字节数
size_t offset, noffset, extra;
unsigned char *np;
zlentry cur, next;
while (p[0] != ZIP_END) { // 遍历整个 ziplist
zipEntry(p, &cur); // 将当前节点的相关信息保存到 cur 这个结构体中,具体的字段可以到这个函数的实现那里去看看
rawlen = cur.headersize + cur.len; // rawlen 就是整个节点占用的字节数
rawlensize = zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL,rawlen); // rawlensize 就是存储当前节点需要的 prevlen 字段的字节数
/* Abort if there is no next entry. */
if (p[rawlen] == ZIP_END) break; // 如果当前节点是 ziplist 的最后一个节点,后面都没有节点了,自然就不需要更新啦!
zipEntry(p+rawlen, &next); // 将下一个节点的相关信息保存到 next 这个结构体中
/* Abort when "prevlen" has not changed. */
if (next.prevrawlen == rawlen) break; // 如果下一个节点 prevlen 字段存储的值和 当前节点所占的字节数相等,说明:当前节点的 prevlen 字段都没有更新,自然就不用往后更新其他节点啦!
if (next.prevrawlensize < rawlensize) { // 存储当前节点需要的 prevlen 字段的字节数大于下一个节点 prevlen 字段的字节数,说明下一个节点需要扩容啦!
offset = p-zl; // 当前节点相对于 ziplist 首地址的偏移量, realloc 可能修改原 zl 嘛,需要记录偏移量
extra = rawlensize-next.prevrawlensize; // 需要在原来的基础上增加多少字节的空间
zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+extra); // 扩容啦!!
p = zl+offset; // 根据偏移量找到当前节点
/* Current pointer and offset for next element. */
np = p+rawlen; // 找到下一个节点的首地址哇!
noffset = np-zl; // 下一个节点相对于 ziplist 首地址的偏移量
// 当下一个节点不是尾节点的时候,我们需要更新 ziplist 的 zltail 字段的值
if ((zl+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))) != np) {
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+extra);
}
// 移动数据
memmove(np+rawlensize,
np+next.prevrawlensize,
curlen-noffset-next.prevrawlensize-1);
zipStorePrevEntryLength(np,rawlen); // 更新下一个节点 prevlen 字段的值
p += rawlen; // 更新当前节点
curlen += extra; // 更新整个 ziplist 的长度
} else { // 下一个节点不需要扩容
if (next.prevrawlensize > rawlensize) {
// 这种情况下,下一个节点的 prevlen 本来需要缩容的!但是,为了不让级联更新继续下去,这个时候强制后驱节点的 prevlen 占用的大小保持不变。
zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p+rawlen,rawlen); // 更新下一个节点的 prevlen 字段存储的值
} else {
zipStorePrevEntryLength(p+rawlen,rawlen); // 更新下一个节点的 prevlen 字段存储的值
}
// 到这里说明级联更新结束啦,因为下一个节点 prevlen 字段足够存储当前节点占用的字节数
break;
}
}
return zl; // 返回 ziplist 的首地址,这是必须的,因为传入的 zl 指针可能会被修改
}
ziplistNew
- 函数功能:创建一个空的
ziplist。 - 返回值:空
ziplist的首地址。 ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE:#define ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE (sizeof(uint32_t)*2+sizeof(uint16_t))。ZIPLIST_END_SIZE:#define ZIPLIST_END_SIZE (sizeof(uint8_t))。
unsigned char *ziplistNew(void) {
unsigned int bytes = ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE+ZIPLIST_END_SIZE; // zlbytes + zltail + zllen + zend
unsigned char *zl = zmalloc(bytes); // 开辟空间
ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) = intrev32ifbe(bytes); // 初始化 zlbytes 字段
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE); // 初始化 zltail 字段
ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) = 0; // 初始化 zlen 字段
zl[bytes-1] = ZIP_END; // 初始化 zend
return zl; // 返回空的 ziplist 啦
}
#define ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) (*((uint16_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t)*2)))
ziplistPush
- 函数功能:在
ziplist头部或者尾部插入一个节点。 - 参数:
zl:ziplist的首地址,表示要在哪一个ziplist中插入节点。s:待插入节点的数据。slen:插入节点的数据的长度。where:头插还是尾插。
- 返回值:
ziplist的首地址。
unsigned char *ziplistPush(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen, int where) {
unsigned char *p;
p = (where == ZIPLIST_HEAD) ? ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl) : ZIPLIST_ENTRY_END(zl);
return __ziplistInsert(zl,p,s,slen); // 插入元素啦
}
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl) ((zl)+ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE)
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl)))
ziplistDelete
- 函数功能:删除给定的节点。
- 参数:
zl:删除的节点属于哪一个ziplist。p:待删除节点的二级指针。
- 返回值:返回删除节点后
ziplist的首地址。
unsigned char *ziplistDelete(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char **p) {
size_t offset = *p-zl; // 要删除的节点相对于 ziplist 首地址的偏移量
zl = __ziplistDelete(zl,*p,1); // 删除节点
/* Store pointer to current element in p, because ziplistDelete will
* do a realloc which might result in a different "zl"-pointer.
* When the delete direction is back to front, we might delete the last
* entry and end up with "p" pointing to ZIP_END, so check this. */
*p = zl+offset;
return zl;
}
__ziplistDelete
- 函数功能:传入
ziplist的首地址,一个节点的地址,向后删除num个节点。 - 参数:
zl:ziplist的首地址。p:节点的首地址。num:要删除的节点数。
unsigned char *__ziplistDelete(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned int num) {
unsigned int i, totlen, deleted = 0;
size_t offset;
int nextdiff = 0;
zlentry first, tail;
zipEntry(p, &first); // 将节点 p 的相关信息保存到 first 结构体中
for (i = 0; p[0] != ZIP_END && i < num; i++) { // 根据 num 找到最后一个可删除节点的首地址,当节点 p 后面的节点数不足 num,就是删除节点 p 之后的所有节点啦!
p += zipRawEntryLength(p); // 依次跳过每个待删除的节点, p 最后指向的应该是最后一个需要删除节点的下一个节点。
deleted++; // 删除的节点数
}
totlen = p-first.p; // 总共需要删除的字节数
if (totlen > 0) { // 有需要删除的节点
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { // 最后一个需要删除节点的下一个节点不是 zlend
/* Storing `prevrawlen` in this entry may increase or decrease the
* number of bytes required compare to the current `prevrawlen`.
* There always is room to store this, because it was previously
* stored by an entry that is now being deleted. */
nextdiff = zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,first.prevrawlen); // 最后一个需要删除节点的下一个节点的 prevlen 字段是否能存储第一个需要删除节点的前驱节点所占的字节数。
/* Note that there is always space when p jumps backward: if
* the new previous entry is large, one of the deleted elements
* had a 5 bytes prevlen header, so there is for sure at least
* 5 bytes free and we need just 4. */
p -= nextdiff; // 适配节点 p 的 prevlen 字段所占的字节数
zipStorePrevEntryLength(p,first.prevrawlen); // 修改节点 p 的 prevlen 字段存储的值
// 更新 ziplist 的 zltail 字段
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))-totlen);
/* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take
* "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the
* size of prevlen doesn't have an effect on the *tail* offset. */
zipEntry(p, &tail); // 将节点 p(需要删除的最后一个节点的下一个节点) 的相关信息保存到 tail 结构体中
if (p[tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) { // 节点 p 之后还有其他的节点,更新 zltail 字段的时候就要加上 nextdiff
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff);
}
// 移动指针 p 之后的所有数据,不包括那个 zlend 哈
memmove(first.p,p,
intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl))-(p-zl)-1);
} else { // 说明节点 p 之后的所有节点都需要删除(包括节点 p)
/* The entire tail was deleted. No need to move memory. */
// 这样的话,我们就不需要移动数据啦,直接修改 zltail 字段就行啦
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe((first.p-zl)-first.prevrawlen);
}
/* Resize and update length */
offset = first.p-zl; // 第一个需要删除节点相对于 ziplist 首地址的偏移量
zl = ziplistResize(zl, intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl))-totlen+nextdiff); // 重新开辟空间,我们已经移动了数据,realloc 符保留所有有效的数据,并且我们放弃了原来空间的继续使用。
ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,-deleted); // 修改 zllen 字段
p = zl+offset; // 让 p 重新指向最后一个需要删除节点的下一个节点
/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so
* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */
if (nextdiff != 0) // nextdiff 不等于 0 进行级联更新
zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p);
}
return zl; // 返回新的 ziplist 的首地址
}
总结
ziplist 每插入一个新节点,需要进行两次内存拷贝操作:
- 为整个链表分配新内存空间,主要是为新节点创建空间。
- 将插入节点所有后驱节点后移,为插入节点腾出空间。
如果链表很长,则每次插入或删除节点时都需要进行大量的内存拷贝,这个性能是无法接受的,为了解决这个问题,我们在下一篇文章中会学到 quicklist。