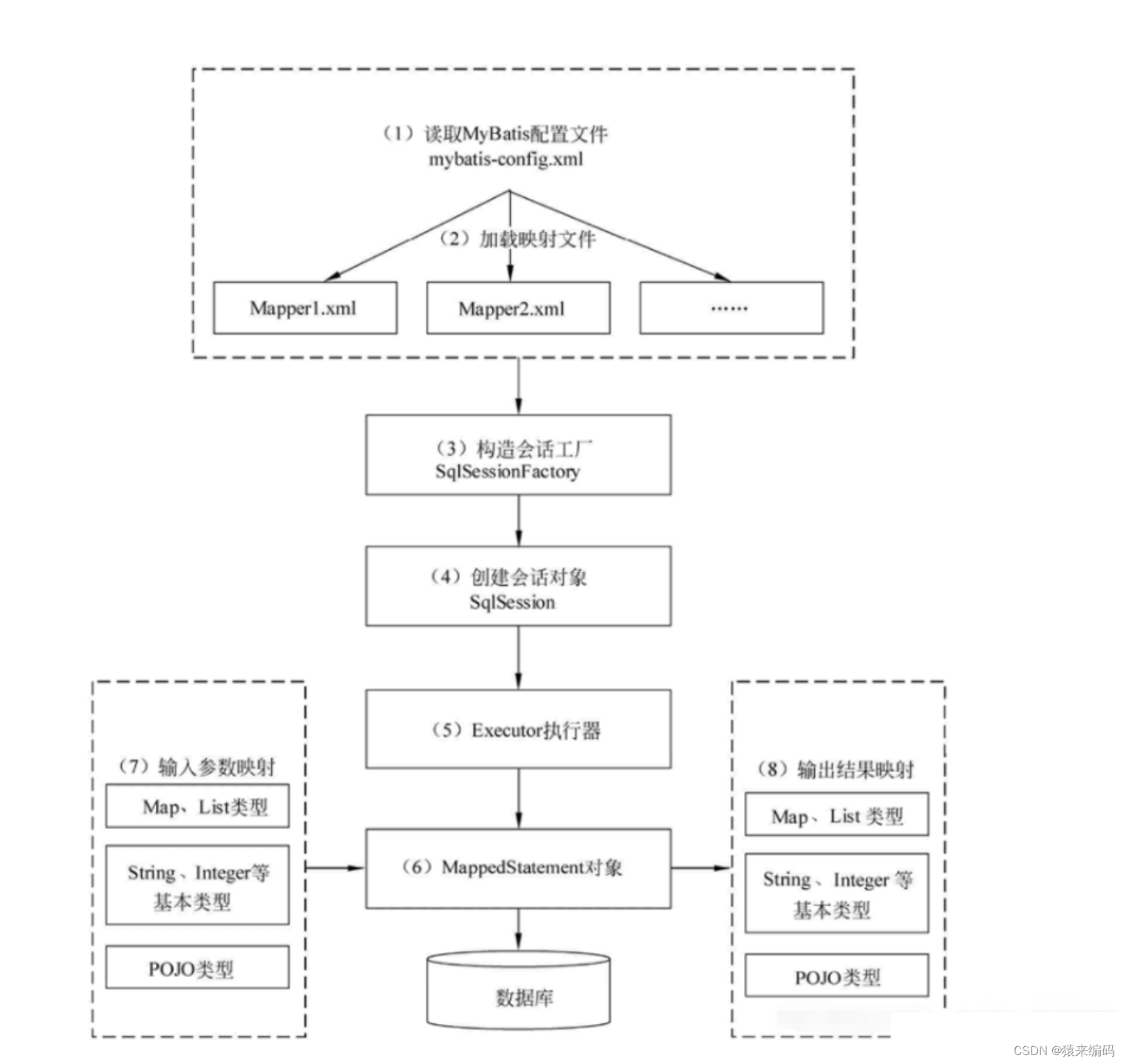
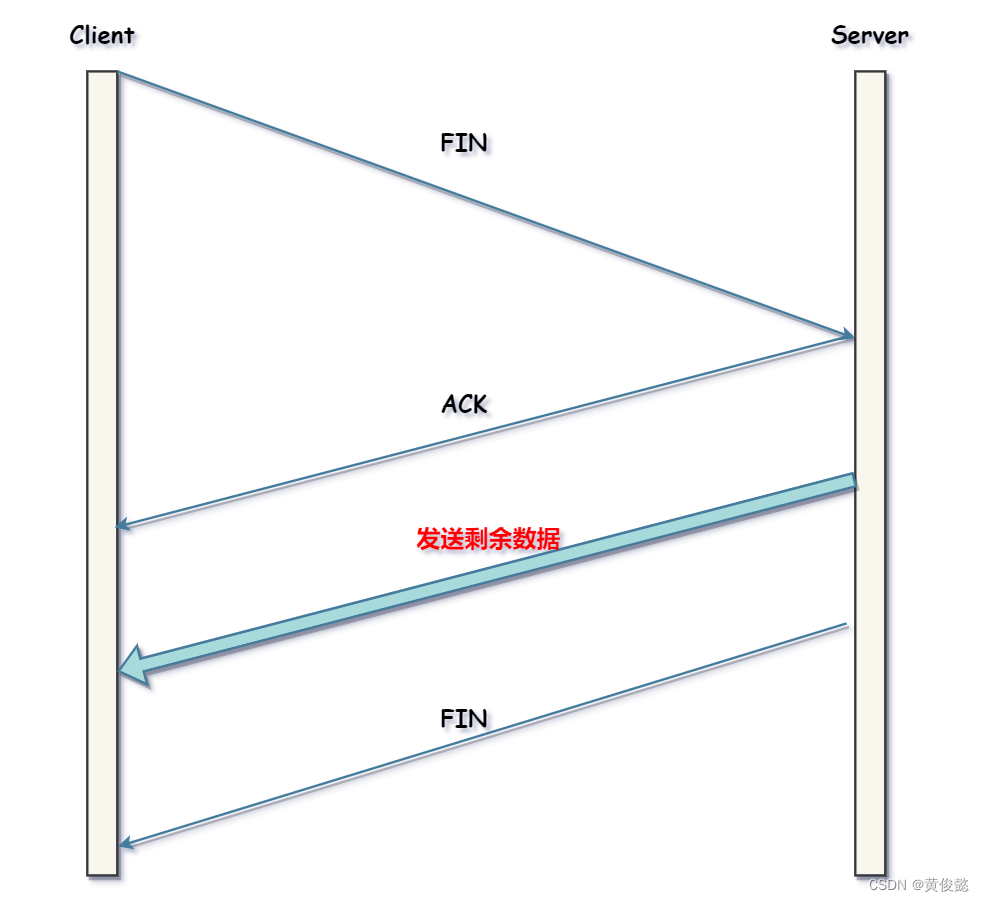
1.简介
BeautifulSoup是一个用于解析 HTML 和 XML 文档的 Python 库。它提供了一种灵活且方便的方式来导航、搜索和修改树结构或标记文档。这个库非常适合网页抓取和数据提取任务,因为它允许你以非常直观的方式查询和操作文档内容。
2.安装 Beautiful Soup
终端输入:pip install beautifulsoup4
3.四个关键对象-覆盖了HTML或XML的所有内容
Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是Python对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种:
Tag,NavigableString,BeautifulSoup,Comment.
3.1 BeatifulSoup对象
BeautifulSoup 对象在 BeautifulSoup 库中是一个特殊的对象,它代表了一个被解析的 HTML 或 XML 文档的整体内容。
我们可以使用BeautifulSoup方法实例化一个BeatifulSoup对象,接下来查看此对象的类型
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
#这里,html_doc是你想要解析的HTML文档字符串,'html.parser'是解析器,它告诉BeautifulSoup使用Python的标准库来解析文档。
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'html.parser')
print(type(soup))
3.2 tag对象
tag对象与XML或HTML原生文档中的tag相同,我们可以使用BeautifulSoup对象来获取到tag对象。
通过tag对象获取属性值,方式:标签名['属性名'],示例如下:
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'html.parser')
tag=soup.p#获取tag对象,当有多个同名标签,这种获取方式只会获取第一个
print(type(tag))
print(tag['class'])#获取指定属性值
当然属性值可能会有多个,HTML 4定义了一系列可以包含多个值的属性.在HTML5中移除了一些,却增加更多.最常见的多值的属性是 class (一个tag可以有多个CSS的class). 还有一些属性 rel , rev , accept-charset , headers , accesskey . 在Beautiful Soup中多值属性的返回类型是list,如果某个属性看起来好像有多个值,但在任何版本的HTML定义中都没有被定义为多值属性,那么Beautiful Soup会将这个属性作为字符串返回,实例如下:
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title test" id="title test"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'html.parser')
tag=soup.p#获取tag对象
print(tag['class'])#获取指定属性值
print(tag['id'])
3.3 NavigableString对象
NavigableString 是 BeautifulSoup 库中的一个类,用于表示 HTML 或 XML 文档中的纯文本字符串,我们可以使用此对象获取标签中的值,获取方式为tag.string获取NavigableString对象,示例如下:
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title test" id="title test"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'html.parser')
tag=soup.p#获取tag对象
print(tag.string,type(tag.string))![]()
3.4 Comment对象
对象是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象,他可用来表示注释内容
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title test" id="title test"><!--<b>The Dormouse's story</b>--></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'html.parser')
tag=soup.p#获取tag对象
print(tag.string,type(tag.string))![]()
Beautiful Soup中定义的其它类型都可能会出现在XML的文档中:
CData,ProcessingInstruction,Declaration,Doctype.与Comment对象类似,这些类都是NavigableString的子类,只是添加了一些额外的方法的字符串独享。
4.搜索文档树
搜索文档实际上是通过过滤器来实现的,这种过滤器类似于条件查询,过滤器可以被用在tag的name中,节点的属性中,字符串中或他们的混合中。
4.1 find_all方法
find_all方法法搜索当前tag的所有tag子节点,并判断是否符合过滤器的条件,当查询结果有多项时返回list列表。这是方法中的参数,下列是对这些参数的使用:
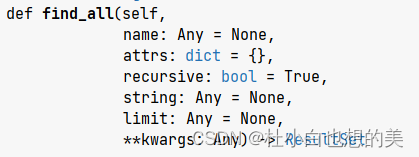
按属性查找
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>网站标题</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>第一个段落</b></p>
<p class="story">第二个段落。</p>
<p class="story">第三个段落。</p>
<p class="title"><b>第四个段落</b></p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser')
# 查找所有 class 属性为 "title" 的标签
title_tags = soup.find_all(attrs={"class": "title"})
for tag in title_tags:
print(tag)
按CSS选择器查找
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>网站标题</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>第一个段落</b></p>
<p class="story">第二个段落。</p>
<p class="story">第三个段落。</p>
<p class="title"><b>第四个段落</b></p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser')
# 使用 CSS 类选择器查找
title_tags = soup.find_all(class_="title")
for tag in title_tags:
print(tag)
# 使用 CSS 属性选择器查找
tags_with_href = soup.find_all(attrs={"href": True})
for tag in tags_with_href:
print(tag)
按文本内容查找
你可以通过 string 参数来根据标签中的文本内容查找元素。
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>网站标题</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>第一个段落</b></p>
<p class="story">第二个段落。</p>
<p class="story">第三个段落。</p>
<p class="title"><b>第四个段落</b></p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser')
# 查找包含特定文本的 <p> 标签
p_tags_with_text = soup.find_all('p', string="第二个段落。")
for tag in p_tags_with_text:
print(tag)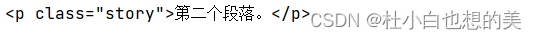
使用正则表达式查找
你还可以使用正则表达式来匹配标签中的文本内容。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>网站标题</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>第一个段落</b></p>
<p class="story">第2个段落。</p>
<p class="story">第三个段落。</p>
<p class="title"><b>第四个段落</b></p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser')
p_tags_with_numbers = soup.find_all('p', string=re.compile(r'\d'))#\d表示匹配到任意数字,r表示普通字符串
for tag in p_tags_with_numbers:
print(tag)
限制返回结果数量
你可以使用 limit 参数来限制 find_all 方法返回的结果数量。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>网站标题</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>第一个段落</b></p>
<p class="story">第2个段落。</p>
<p class="story">第三个段落。</p>
<p class="title"><b>第四个段落</b></p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser')
# 只查找前两个 <p> 标签
first_two_p_tags = soup.find_all('p', limit=2)
for tag in first_two_p_tags:
print(tag)4.2 find方法
find方法与find_all方法使用方式基本一致,但是他只会匹配到第一项。
4.结尾
BeautifulSoup是解析爬取数据的利器,但是往往我们在采集数据时会遇到许多的问题,比如说ip封禁,明显是网站进行了反爬处理:限制IP请求频率。这个时候,代理ip解决这类问题就十分有效。这里推荐一款最近发现的代理商家:协采云IP池。