文章目录
- [A - The bottom of the ninth](https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc351/tasks/abc351_a)
- [B - Spot the Difference ](https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc351/tasks/abc351_b)
- [D - Grid and Magnet](https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc351/tasks/abc351_d)
- E
Note:省略模板代码,模版代码在末尾
A - The bottom of the ninth
题目:
给两个序列A和B,求B总和比A总和大时需要加上的最小值
思路:
答案=A总和-B总和+1
static void solve() throws IOException {
int[] a = pIntArray(0);
int[] b =pIntArray(0);
int acnt = 0, bcnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
acnt += a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i ++) {
bcnt += b[i];
}
out.println(acnt - bcnt + 1);
}
B - Spot the Difference
题目:
给两个仅包含小写字母的NxN矩阵,找出唯一不同字母的下标对
思路:
模拟
static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = pInt(in.readLine());
String[] a = new String[n], b = new String[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = in.readLine();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
b[i] = in.readLine();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (a[i].charAt(j) != b[i].charAt(j)) {
out.println(i + 1 + " " + (j + 1) );
return;
}
}
}
}
C - Merge the balls
题目:
给一个空序列和N个球,第i个球的大小为
2
A
i
2^{A_i}
2Ai;执行N次操作,在第i次操作时将第i个球加入到序列的最右边,然后重复以下步骤:当序列有两个及以上的球且最右边的两个球大小相同时,移去这两个球,并加入一个球,其大小为移除的球大小的总和,直到不能执行该步骤为止;
求执行完N次操作后序列还有多少个球
思路:
模拟
static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = pInt(in.readLine());
long[] balls = pLongArray(1);
long[] t = new long[n + 1];
int hh = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
t[++ hh] = balls[i];
while (hh > 1 && t[hh] == t[hh - 1]) {
t[hh - 1] += 1;
hh -= 1;
}
}
out.println(hh);
}
D - Grid and Magnet
题目:
一个HxW的矩阵,某些格子里面会有磁铁,用 # 表示,其余格子为空,用. 表示;
如果在一个有磁铁的格子旁边,则无法继续移动;
问在这个矩阵里面的某个点出发能够移动的最大单元格数量;
思路:
实际上是求最大的连通块的格子数量,但连通块中边缘是一些磁铁,那么可以标记一下磁铁旁边的空单元格,当走到该种单元格时无法继续移动;
剩下的只需要用 BFS 来求连通块的大小即可;
static final int EMPTY = 0;
static final int MAGNET = 1;
static final int STICK = 2;
static final int[] d = new int[] {0, -1, 0, 1, 0};
static int bfs(int h, int w, int sx, int sy, int[][] vis) {
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[] {sx, sy});
final int CURRENT_VISITED = 1010 * (sx + 1) + sy;
vis[sx][sy] = CURRENT_VISITED;
int ans = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] u = q.poll();
int x = u[0], y = u[1];
ans ++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++) {
int dx = x + d[i], dy = y + d[i + 1];
if (dx < 0 || dx >= h || dy < 0 || dy >= w || vis[dx][dy] == MAGNET || vis[dx][dy] == CURRENT_VISITED) continue;
if (vis[dx][dy] == EMPTY) {
q.offer(new int[] {dx, dy});
vis[dx][dy] = CURRENT_VISITED;
} else if (vis[dx][dy] != MAGNET && vis[dx][dy] != CURRENT_VISITED) {
ans ++;
vis[dx][dy] = CURRENT_VISITED;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
static void solve() throws IOException {
String[] ins = pStringArray();
int h = pInt(ins[0]), w = pInt(ins[1]);
char[][] map = new char[h][w];
int[][] vis = new int[h][w];
for (int i = 0; i < h; i ++) {
char[] t = in.readLine().toCharArray();
System.arraycopy(t, 0, map[i], 0, w);
for (int j = 0; j < w; j ++) {
if (map[i][j] == '#') {
vis[i][j] = MAGNET;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int dx = i + d[k], dy = j + d[k + 1];
if (dx < 0 || dx >= h || dy < 0 || dy >= w) continue;
if (vis[dx][dy] == EMPTY) {
vis[dx][dy] = STICK;
}
}
}
}
}
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < h; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < w; j ++) {
if (vis[i][j] == EMPTY) {
ans = Math.max(ans, bfs(h, w, i, j, vis));
}
}
}
out.println(ans);
}
E
题目:
在二维坐标平面上有 N 个点,兔子只能走对角线,计算AB两个点之间的距离
d
i
s
t
(
P
A
,
P
B
)
dist(P_A, P_B)
dist(PA,PB) 为:兔子从A点开始走对角线,到达B点的最小次数;求
∑
i
=
1
N
−
1
∑
j
=
i
+
1
N
d
i
s
t
(
P
i
,
P
j
)
\sum^{N-1}_{i=1}\sum^{N}_{j=i + 1} dist(P_i, P_j)
∑i=1N−1∑j=i+1Ndist(Pi,Pj)
思路:
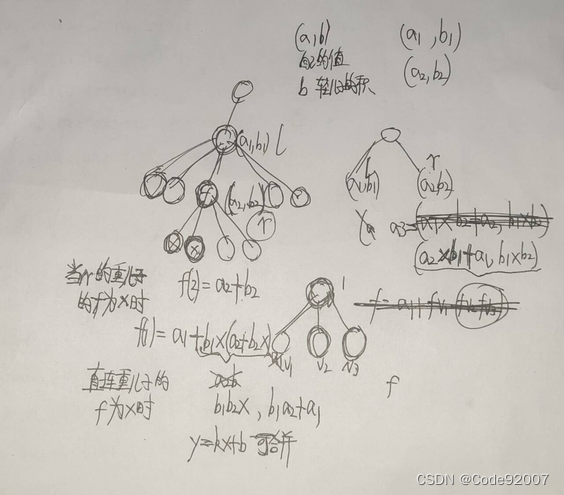
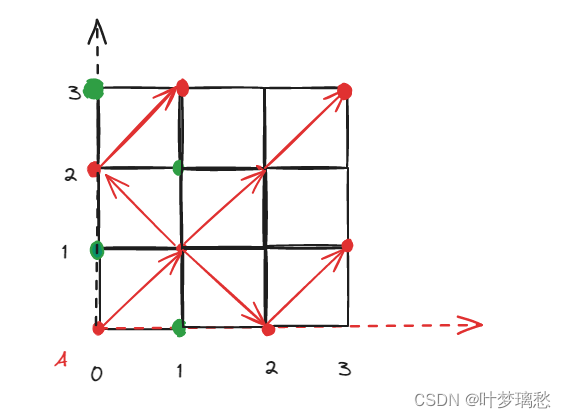
找规律,如下图,兔子从A点开始走,那么红色路线上的点都是可以到达的,注意到,可达点的坐标
(
x
,
y
)
(x,y)
(x,y) 相加之后与起点A的坐标相加后模2同余,那么可以对此进行分类;
如何进行计算距离呢?
将二维坐标平面旋转45度(坐标可以变换为:
x
′
=
x
+
y
,
y
′
=
x
−
y
x'=x+y, y'=x-y
x′=x+y,y′=x−y),兔子从走对角线就变成了上下左右走,两个点的距离就变成了水平方向和竖直方向上的距离了;
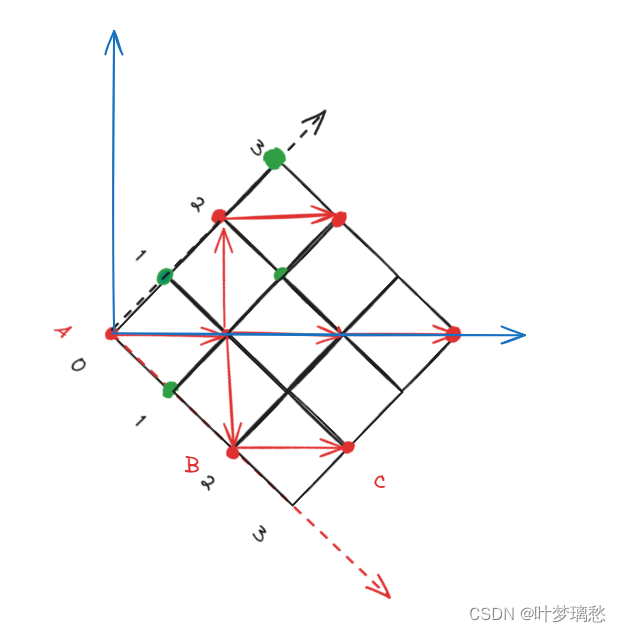
题目数据量是2e5,不可能两重循环来计算两个点的距离,这样会超时;
我们可以将x轴和y轴分开来计算:比如上面的A、B、C点
- 先计算x轴的,A到B的距离为1,B到C的距离为1,因为C点在A点的右边,那么A到C的距离为1+1=2
- 计算y轴的,A到B的距离为1
总的值就是3
需要注意的是,需要对转换后的x轴和y轴坐标排序,保证可以根据前面计算的距离来推出当前的距离(比如上面的A到C点)
static void solve() throws IOException {
int n = pInt(in.readLine());
List<Integer>[] px = new ArrayList[2];
List<Integer>[] py = new ArrayList[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i ++) {
px[i] = new ArrayList<>();
py[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i =0 ; i < n; i ++) {
String[] ins = pStringArray();
int x = pInt(ins[0]), y = pInt(ins[1]);
int t = Math.abs(x + y) % 2;
// 根据取模的结果分别拆分x轴和y轴
px[t].add( x - y);
py[t].add(x + y);
}
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i ++) {
// 排序,保证坐标小的在前面
px[i].sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a));
py[i].sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a));
int size = px[i].size();
long sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < size; j ++) {
// 当前点到前面其他点位置的距离
ans += (long) j * (px[i].get(j) + py[i].get(j)) - sum1 - sum2;
sum1 += px[i].get(j);
sum2 += py[i].get(j);
}
}
// 要求的值是 0->N-1, i+1->N-1 所以除以2
out.println(ans / 2);
}
模版代码:
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Example {
static void solve() throws IOException {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int t = 1;
// t = Integer.parseInt(in.readLine());
while (t -- > 0) {
solve();
}
in.close();
out.flush();
out.close();
}
private static InputStream is = System.in;
static {
try {
is = Files.newInputStream(Paths.get("F:\\Notes\\Algorithm\\Problems\\java\\java\\src\\main\\java\\input.txt"));
} catch (Exception e) {
is = System.in;
}
}
private static final BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
private static final PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(System.out);
private static int pInt(String s) {
return Integer.parseInt(s);
}
private static long pLong(String s) {
return Long.parseLong(s);
}
private static String[] pStringArray() throws IOException {
return in.readLine().split(" ");
}
private static int[] pIntArray(int start) throws IOException {
String[] s = pStringArray();
int[] arr = new int[start + s.length];
for (int i = start, j = 0; i < arr.length; i++, j ++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(s[j]);
}
return arr;
}
private static long[] pLongArray(int start) throws IOException {
String[] s = pStringArray();
long[] arr = new long[start + s.length];
for (int i = start, j = 0; i < arr.length; i++, j ++) {
arr[i] = Long.parseLong(s[j]);
}
return arr;
}
}